Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Prepare
Hochgeladen von
anwarjaved0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
65 Ansichten30 Seitenits good for ur knowledge
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenits good for ur knowledge
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
65 Ansichten30 SeitenPrepare
Hochgeladen von
anwarjavedits good for ur knowledge
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 30
Prepare a Patient for
General Anesthesia
081-833-4522
INSTRUCTOR
SFC HILL
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
OBJECTIVE
As a Special Forces Medic,
prepare a patient for general
parenteral anesthesia, in
accordance with JSOMTC student
manual of anesthesia.
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
REASON
• As a Special Forces Medic preparation
of the patient and yourself will be a
critical task in the successful
performance of general parenteral
anesthesia
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
PROCEDURES
• The Preanesthetic Visit
• Prep for general parenteral anesthesia
• Emergency prep for general parenteral
anesthesia
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
The Preanesthetic Visit
• The preanesthetic visit is conducted
so the anesthetist can meet with the
patient for the purpose of identifying
any possible complications prior to
the anesthetic procedure and
alleviating the patients possible
anxiety or fear of anesthesia/surgery
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
Preanesthetic Visit
• Should take place at least 24
hours prior to the scheduled
procedure
• If possible, it should be
conducted prior to emergency
administration of anesthesia
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
Preanesthetic Visit
• What are some possible
problems or complication that
can be identified prior to the
administration of anesthesia?
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
Preanesthetic Visit
• Tracheal Intubation Problems
• Allergies
• Drug interactions
• Previous Exposure to Anesthesia
• Concurrent Illnesses
• Classification of Physical Status
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
Tracheal Intubation
Problems
• Short Thick Neck
• Disease of Pharynx or Larynx
• Tracheal Deviation
• Small Mouth
• Stiff Temporomandibular Joint
• Prominent Upper Incisors
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
Tracheal Intubation
Problems
• Chipped or Cracked Enamel
• Caries
• Loose Teeth
• Dentures, Crowns
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
Allergies
• All Pharmacological Agents are potential
allergens
• Emergency drugs for anaphylactic
shock must be on hand prior to
administration of any drug
• Take detailed History to differentiate
between side effects and allergic
reaction
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
DRUG INTERACTIONS
• Note present drug therapy
• Research any present drug therapies
verses the anesthetic therapy plan for
this procedure
• Many drugs will not interact well with
anesthetic agents
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
Previous Exposure to
Anesthesia
• Repeat use of certain anesthetic agents may cause
hepatic damage or stress
• Take a detailed History of previous use of anesthesia
• Agents that caused problems in the past should not
be repeated
• Take a detailed History of any previous difficulties
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
Concurrent Illnesses
• Common Cold
• Liver Disease
• Diabetes Mellitus
• Anemia
• COPD
• Heart Disease
• Essential Hypertension
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
Classification of Physical
Illnesses
• Class I- fit and healthy
• Class II- Mild systemic illness
• Class III- Severe systemic illness that is not
incapacitating
• Class IV- Incapacitating, systemic, life
threatening illness
• Class V- Expectant, with or without surgery
• “E”- Emergency
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
Record information
• Record all the information from the
preanesthetic visit into the
preanesthetic summary of the patient’s
SF 517
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
Patient Instructions
• Review the upcoming
procedure with the patient
• Ensure the patient
understands his/her
responsibilities prior to the
planned procedure
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
Prep for general parenteral
anesthesia
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
Review and Prep
• Review the patients SF517
• Prepare the anesthetist cart and
all equipment to be utilized
during the procedure to include
back-up and emergency
equipment
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
Receive the patient
• Identify patient and reconfirm type and
location of procedure
• Converse with the patient to establish his or
her mental status
• Establish the patients compliance with his or
her preanesthetic orders
• Review the procedure once again with the
patient
• Calm and reassure the patient
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
Prepare the patient
• Establish baseline set of vitals for the
patient
• Establish the patient on 2 liters a
minute, humidified oxygen
• Establish patient on monitors
• Establish IV access, Normal Saline,
TKO
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
Administer Premedication
• Administer antisialagogue (Atropine, .
4-.6mg deep IM 45 minutes prior to
induction)
• Administer sedative (Promethazine, 25-
50mg PO 30 minutes prior to induction)
• Continue to monitor the patients vitals
every 15 minutes until induction
• Move the patient to the OR
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
Emergency prep for general
parenteral anesthesia
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
Receive the patient
• Identify the patient and attempt to obtain a
brief but thorough history
• Work with the surgical team to establish the
patients condition (A-B-C) and level of
consciousness
• Perform life saving measures
• If the patient is conscious and orientated X 3,
converse with the patient to establish his or
her mental status
• If the patient is conscious and orientated X 3,
attempt to calm and reassure the patient
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
Prepare the patient
• Obtain vitals of the patient
• Establish and maintain the patients
airway
• Establish the patient on 6 - 15 liters a
minute, humidified oxygen
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
Prepare the patient
• Draw blood for grouping and cross-
matching
• Establish large bore IV access and
prepare for fluid resuscitation and
possible transfusion
• Establish patient on monitors
• Establish nasogastric tube
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
Administer Premedication
• Administer antisialagogue (Atropine, .
4-.6mg deep IM)
• Administer sedative (Promethazine, 25-
50mg slow IV)
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
Prepare for induction
• Prepare for induction of anesthesia
• Emergency patients should be stabilized prior
to induction of anesthesia whenever possible.
• With the unstable patient, induction should
proceed when only the immediate surgical
intervention will save the patients life
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
SUMMARY OF
PROCEDURES
• The Preanesthetic Visit
• Prep for general parenteral anesthesia
• Emergency prep for general parenteral
anesthesia
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
RESTATED
OBJECTIVE
As a Special Forces Medic,
prepare a patient for general
parenteral anesthesia, in
accordance with JSOMTC student
manual of anesthesia.
Joint Special Operations Medical Training Center
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- English For Medical Students CoursebookDokument117 SeitenEnglish For Medical Students CoursebookNevfel100% (10)
- FNCP HyperacidityDokument2 SeitenFNCP HyperacidityJeriel DelavinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spa Kaki Diabetik Efektif Memperbaiki Sensasi Kaki Pada DiabetesiDokument8 SeitenSpa Kaki Diabetik Efektif Memperbaiki Sensasi Kaki Pada DiabetesiDETA INDRAYANTINoch keine Bewertungen
- Forxiga Presentation Kaltim - Prof AgungDokument36 SeitenForxiga Presentation Kaltim - Prof AgungSanrio NeuroNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV Roxana Bucur OncoDokument3 SeitenCV Roxana Bucur OncoOctavian PopoviciNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instant Download Macroeconomics 4th Edition Hubbard Test Bank PDF Full ChapterDokument32 SeitenInstant Download Macroeconomics 4th Edition Hubbard Test Bank PDF Full ChapterHowardZunigaxgqt100% (5)
- Babesia Species: - Order: Piroplasmida - Family: Babesiidae - Medically Important SpeciesDokument7 SeitenBabesia Species: - Order: Piroplasmida - Family: Babesiidae - Medically Important SpeciesMegbaru100% (1)
- 3, Prof. Brendon Kearney - Health Technology AssessmentDokument19 Seiten3, Prof. Brendon Kearney - Health Technology Assessmentave mariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cristal TrialDokument9 SeitenCristal TrialJorge Barrios FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- HUNNER LESION DIAGNOSISDokument4 SeitenHUNNER LESION DIAGNOSISVasishta NadellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Growth Hormone DeficiencyDokument11 SeitenGrowth Hormone DeficiencyIgor VasićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steps of Repertorization - 5e097dab9ad98Dokument18 SeitenSteps of Repertorization - 5e097dab9ad98Sowjanya JyothsnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Idiophatic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) in PregnancyDokument27 SeitenIdiophatic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) in PregnancyAdietya Bima PrakasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antianginal Drugs: Claro M. Isidro M.DDokument34 SeitenAntianginal Drugs: Claro M. Isidro M.DNikki ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study 12Dokument4 SeitenDrug Study 12Nathalie kate petallarNoch keine Bewertungen
- NHSN Manual OverviewDokument445 SeitenNHSN Manual OverviewDayana RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
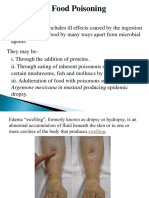
- Food Poisoning and IntoxicationsDokument26 SeitenFood Poisoning and IntoxicationslakshmijayasriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature ReviewDokument3 SeitenLiterature Reviewapi-509948413Noch keine Bewertungen
- CDM CasesDokument24 SeitenCDM CasesmalcomxNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 - Cellular Adaptations - SimpleMed - Learning Medicine, SimplifiedDokument7 Seiten05 - Cellular Adaptations - SimpleMed - Learning Medicine, SimplifiedRachel ManaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crossfit Gym Membership Contract and Receipt TemplateDokument6 SeitenCrossfit Gym Membership Contract and Receipt Templatemohit jNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internship Manual 20-21 PDFDokument19 SeitenInternship Manual 20-21 PDFMsalik1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ikon New CatelogueDokument32 SeitenIkon New CatelogueShlokeasundNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLAVUS - An Overview and Case StudyDokument3 SeitenCLAVUS - An Overview and Case StudyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 60 Most Common DrugsDokument1 Seite60 Most Common DrugsNikkaLim100% (1)
- Airway AssessmentDokument58 SeitenAirway AssessmentSanjit Singh100% (3)
- Psychiatric Nursing Practice Test 5Dokument8 SeitenPsychiatric Nursing Practice Test 5Filipino Nurses Central100% (1)
- Dr. M.S. Shamol Fcps (Medicine) : C O T S N I P A T I O NDokument20 SeitenDr. M.S. Shamol Fcps (Medicine) : C O T S N I P A T I O NiwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medication AdministrationDokument14 SeitenMedication AdministrationLiel TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Sugar Levels Blood Glucose Charts For Children and AdultsDokument1 SeiteBlood Sugar Levels Blood Glucose Charts For Children and Adultsyvess leyv ignacioNoch keine Bewertungen