Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Organizational Behavior: Stephen P. Robbins
Hochgeladen von
alex5566Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Organizational Behavior: Stephen P. Robbins
Hochgeladen von
alex5566Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR
S T E P H E N P. R O B B I N S
WWW.PRENHALL.COM/ROBBINS T E N T H E D I T I O N
2003 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
PowerPoint Presentation by Charlie Cook
OBJECTIVES LEARNING
AFTER STUDYING THIS CHAPTER, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
1. Define the key biographical characteristics.
2. Identify two types of ability. 3. Shape the behavior of others. 4. Distinguish between the four schedules of reinforcement. 5. Clarify the role of punishment in learning. 6. Practice self-management 7. Exhibit effective discipline skills.
2003 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
22
Biographical Characteristics
2003 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
23
Ability
2003 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
24
Dimensions of Intellectual Ability
Number aptitude Verbal comprehension Perceptual speed Inductive reasoning Deductive reasoning Spatial visualization Memory
EXHIBIT 2003 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
2-1
25
Physical Ability
2003 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
26
Nine Physical Abilities
Strength Factors
Dynamic strength Trunk strength Static strength Explosive strength
Flexibility Factors
Extent flexibility Dynamic flexibility
Other Factors
Body coordination Balance Stamina
EXHIBIT 2003 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
2-2
27
The Ability-Job Fit
Employees Abilities
Ability-Job Fit
Jobs Ability Requirements
2003 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
28
Learning
Learning Involves change Is relatively permanent Is acquired through experience
2003 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
29
Theories of Learning
Key Concepts Unconditioned stimulus
Unconditioned response
Conditioned response
2003 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 210
Theories of Learning (contd)
Key Concepts Reflexive (unlearned) behavior
Conditioned (learned) behavior
Reinforcement
2003 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 211
Theories of Learning (contd)
Key Concepts
Attention processes Retention processes
Motor reproduction processes
Reinforcement processes
2003 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 212
Theories of Learning (contd)
Key Concepts Reinforcement is required to change behavior. Some rewards are more effective than others. The timing of reinforcement affects learning speed and permanence.
2003 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 213
Schedules of Reinforcement
2003 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
214
Schedules of Reinforcement (contd)
2003 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
215
Schedules of Reinforcement
Fixed-ratio
EXHIBIT 2003 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
2-4
216
Intermittent Schedules of Reinforcement
EXHIBIT 2003 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
2-5a
217
Intermittent Schedules of Reinforcement (contd)
EXHIBIT 2003 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
2-5b
218
Behavior Modification
Problem-solving Model Identify critical behaviors Develop baseline data Identify behavioral consequences Apply intervention Evaluate performance improvement
2003 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved. 219
OB MOD Organizational Applications
Well Pay versus Sick Pay
Reduce absenteeism by rewarding attendance, not absence.
Employee Discipline
The use of punishment can be counter-productive.
Developing Training Programs
OB MOD methods improve training effectiveness.
Self-management
Reduces the need for external management control.
2003 Prentice Hall Inc. All rights reserved.
220
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Assessment of Executive Functions WorkshopDokument70 SeitenAssessment of Executive Functions Workshopdreams299100% (1)
- Robbins9 ppt02Dokument23 SeitenRobbins9 ppt02Sidra KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership and Trust: Powerpoint Presentation by Charlie Cook All Rights ReservedDokument33 SeitenLeadership and Trust: Powerpoint Presentation by Charlie Cook All Rights ReservedKarel A. HilversumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Booklet OECD Transfer Pricing Guidelines 2017Dokument24 SeitenBooklet OECD Transfer Pricing Guidelines 2017Tommy StevenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of Executive Functions in Service Fall 2011 PDFDokument70 SeitenAssessment of Executive Functions in Service Fall 2011 PDFRachel100% (1)
- Outcome-Based Experiential Learning: Let's Talk About, Design For, and Inform Teaching, Learning, and Career DevelopmentVon EverandOutcome-Based Experiential Learning: Let's Talk About, Design For, and Inform Teaching, Learning, and Career DevelopmentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drama Lesson PlanDokument4 SeitenDrama Lesson Planapi-393598576Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Rubric For Powerpoint Presentations Beginning Developing Accomplish Ed Exemplary PointsDokument4 SeitenAssessment Rubric For Powerpoint Presentations Beginning Developing Accomplish Ed Exemplary PointsyatzirigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Workbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesVon EverandWorkbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- Vedantu Chemistry Mock Test Paper 1 PDFDokument10 SeitenVedantu Chemistry Mock Test Paper 1 PDFSannidhya RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Change Management Process for Information TechnologyVon EverandChange Management Process for Information TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robbins CH 171 - ch01Dokument32 SeitenRobbins CH 171 - ch01Mohammad Nazmul Islam100% (1)
- Summary Essay of "Professional Writing"Dokument2 SeitenSummary Essay of "Professional Writing"dope arnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan on "The StrangerDokument3 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan on "The StrangerNhelia Mae Ebo Abaquita100% (1)
- Ecole Ducasse - 2020 2021 PricingDokument4 SeitenEcole Ducasse - 2020 2021 PricingminkhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accelerating Complex Problem-Solving Skills: Problem-Centered Training Design MethodsVon EverandAccelerating Complex Problem-Solving Skills: Problem-Centered Training Design MethodsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guthrie A History of Greek Philosophy AristotleDokument488 SeitenGuthrie A History of Greek Philosophy AristotleLuiz Henrique Lopes100% (2)
- Foundations of Individual BehaviorDokument20 SeitenFoundations of Individual Behaviorsuman_94103Noch keine Bewertungen
- Foundations of Individual BehaviorDokument14 SeitenFoundations of Individual BehaviorNiraj SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organizational Behavior: Stephen P. RobbinsDokument20 SeitenOrganizational Behavior: Stephen P. RobbinsVarshik FlashNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 01Dokument32 SeitenCH 01Saad SohailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2-HBODokument22 SeitenChapter 2-HBOAccounting LayfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Individual BehaviorDokument22 SeitenIndividual Behaviorsankara subramaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organizational Behav Ior: Eleventh Editi OnDokument23 SeitenOrganizational Behav Ior: Eleventh Editi OnDhananjay SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap-2 Foundation of Individual Behavior 2Dokument22 SeitenChap-2 Foundation of Individual Behavior 2Shovon AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter One: What Is Organizational BehaviorDokument56 SeitenChapter One: What Is Organizational BehaviorsahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Perception & Individual Decision MakingDokument26 SeitenChapter 5 Perception & Individual Decision MakingArifTapoosiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organizational Behavior: Stephen P. RobbinsDokument26 SeitenOrganizational Behavior: Stephen P. RobbinsKhaled Hasan KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch02 ClassDokument22 Seitench02 ClassJohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundations of Individual Behavior: © 2007 Prentice Hall Inc. All Rights ReservedDokument22 SeitenFoundations of Individual Behavior: © 2007 Prentice Hall Inc. All Rights ReservedAnonymous yy8In96j0rNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organizational Behavior: Stephen P. RobbinsDokument34 SeitenOrganizational Behavior: Stephen P. RobbinsHero CourseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robbins Ob14 PPT 02Dokument19 SeitenRobbins Ob14 PPT 02Rizal Pandu NugrohoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter+No +2Dokument19 SeitenChapter+No +2Zain MushtaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Yesterday and TodayDokument26 SeitenManagement Yesterday and Todaymochammad fadliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument34 SeitenChapter 2Augustus J SanyangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Yesterday and Today: Stephen P. Robbins Mary CoulterDokument35 SeitenManagement Yesterday and Today: Stephen P. Robbins Mary CoulterallanrnmanalotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundations of Individual BehaviorDokument31 SeitenFoundations of Individual BehaviorMuneeb SikanderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Robbins PPT13Dokument28 SeitenManagement Robbins PPT13Mehfuz KhaledNoch keine Bewertungen
- Individual DifferencesDokument51 SeitenIndividual DifferencesTri AstutiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Yesterday and Today: Stephen P. Robbins Mary CoulterDokument32 SeitenManagement Yesterday and Today: Stephen P. Robbins Mary CoulterSyarif HidayatullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organizational Behavior: Stephen P. RobbinsDokument22 SeitenOrganizational Behavior: Stephen P. RobbinsChanduChandranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management History: The First Pyramid Was The Step Pyramid at Saqqara, Built For King Zoser in 2750 BCDokument36 SeitenManagement History: The First Pyramid Was The Step Pyramid at Saqqara, Built For King Zoser in 2750 BCNurul An Nisa SilmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organizational Behavior: Chapter 2: Foundations of Individual BehaviorDokument12 SeitenOrganizational Behavior: Chapter 2: Foundations of Individual BehaviorHira Mustafa ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1: What Is Organizational BehaviorDokument19 SeitenTopic 1: What Is Organizational BehaviorShubham NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organizational Behavior: Robbins & JudgeDokument20 SeitenOrganizational Behavior: Robbins & JudgedjlakshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organizational Behavior: Stephen P. RobbinsDokument26 SeitenOrganizational Behavior: Stephen P. RobbinsDe LuicferrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robbins PPT02Dokument34 SeitenRobbins PPT02DikshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organizational Behav Ior: Eleventh Editi OnDokument37 SeitenOrganizational Behav Ior: Eleventh Editi OnWasim JamaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ob 02Dokument19 SeitenOb 02Junaid MalicNoch keine Bewertungen
- LearningDokument20 SeitenLearningSushreeta PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIDTERMrobbins PPT02Dokument17 SeitenMIDTERMrobbins PPT02Cybelle TradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robbins ManagementDokument30 SeitenRobbins ManagementImD3v1LNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management CH02Dokument32 SeitenManagement CH02aiesh.javNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organizational Culture and Environment Theconstraints Managementbyrobbinscoulter9e 130131131212 Phpapp02Dokument32 SeitenOrganizational Culture and Environment Theconstraints Managementbyrobbinscoulter9e 130131131212 Phpapp02gondalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 Edition: Steven P. Robbins Mary CoulterDokument43 Seiten8 Edition: Steven P. Robbins Mary CoulterTeddy León ZegarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Management: Managing Change, Stress, and InnovationDokument30 SeitenFundamentals of Management: Managing Change, Stress, and InnovationHappy_man_KSANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapt 11 Leadership and TrustDokument33 SeitenChapt 11 Leadership and TrustAbu UmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundations of Individual Behavior and LearningDokument20 SeitenFoundations of Individual Behavior and LearningPasula VaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 What Is Organizational BehaviorDokument21 SeitenChapter 1 What Is Organizational Behavioriqbal febriyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bab 2 Sejarah Perkembangan Manajemen INDODokument29 SeitenBab 2 Sejarah Perkembangan Manajemen INDOWinni BakkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stu RC8 e CH 02Dokument24 SeitenStu RC8 e CH 02Moeen AnwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pom Paper Wa QasDokument44 SeitenPom Paper Wa QasM Hamza SultanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organizational Behavior: Stephen P. RobbinsDokument24 SeitenOrganizational Behavior: Stephen P. RobbinsDe LuicferrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diversity in Organizations: Robbins and JudgeDokument22 SeitenDiversity in Organizations: Robbins and JudgeNIKHILESHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thill Ebc10 Inppt 02Dokument45 SeitenThill Ebc10 Inppt 02amilee_nsuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accelerated Proficiency for Accelerated Times: A Review of Key Concepts and Methods to Speed Up PerformanceVon EverandAccelerated Proficiency for Accelerated Times: A Review of Key Concepts and Methods to Speed Up PerformanceNoch keine Bewertungen
- LanguageDokument1 SeiteLanguagealex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Refers To The ProcessDokument1 SeiteRefers To The Processalex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Responsible To All Projects Under The Group and To Ensure The Profitability of The GroupDokument1 SeiteResponsible To All Projects Under The Group and To Ensure The Profitability of The Groupalex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- To Procure New Cost Tracking SystemDokument1 SeiteTo Procure New Cost Tracking Systemalex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Oversight Agencies and Tax CollectionDokument1 SeiteOversight Agencies and Tax Collectionalex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case StudyDokument1 SeiteCase Studyalex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Improving Project Reporting for GrowthDokument1 SeiteImproving Project Reporting for Growthalex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mary's bonus at risk due to cost overrunsDokument1 SeiteMary's bonus at risk due to cost overrunsalex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 3 AaDokument1 SeiteAssignment 3 Aaalex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test 4Dokument1 SeiteTest 4alex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- He Worked at A Company and A Consultancy Firm For Five Years Before Joining USMDokument1 SeiteHe Worked at A Company and A Consultancy Firm For Five Years Before Joining USMalex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analyzing and ReportingDokument1 SeiteAnalyzing and Reportingalex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ratio 2Dokument1 SeiteRatio 2alex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study 2Dokument1 SeiteCase Study 2alex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test 2Dokument1 SeiteTest 2alex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test 1Dokument1 SeiteTest 1alex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- P8 ImportantDokument1 SeiteP8 Importantalex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Refers To The ProcessDokument1 SeiteRefers To The Processalex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- P5 ImportantDokument1 SeiteP5 Importantalex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- P6 ImportantDokument1 SeiteP6 Importantalex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Systematic and ComprehensiveDokument1 SeiteSystematic and Comprehensivealex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Transactions PertainingDokument1 SeiteFinancial Transactions Pertainingalex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- AccountingDokument1 SeiteAccountingalex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- P4 ImportantDokument1 SeiteP4 Importantalex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- P2 Is Evry ImportantDokument1 SeiteP2 Is Evry Importantalex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- P3 Every ImportantDokument1 SeiteP3 Every Importantalex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- P1 Is Evry ImportantDokument1 SeiteP1 Is Evry Importantalex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- CDDokument1 SeiteCDalex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Professional EthicsDokument1 SeiteProfessional Ethicsalex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- CagneyDokument1 SeiteCagneyalex5566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Director Human Resources Management in Northern VA Resume Jessica ErnstDokument3 SeitenDirector Human Resources Management in Northern VA Resume Jessica ErnstJessicaErnst1Noch keine Bewertungen
- MOOC 4 Negotiation GameDokument1 SeiteMOOC 4 Negotiation GameRoberto MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factors Affecting The Deterioration of Educational System in The PhilippinesDokument6 SeitenFactors Affecting The Deterioration of Educational System in The PhilippinesJim Dandy Capaz100% (11)
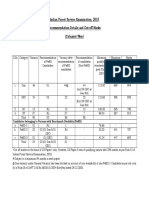
- Indian Forest Service Exam Cut-Off Marks 2018Dokument1 SeiteIndian Forest Service Exam Cut-Off Marks 2018surajcool999Noch keine Bewertungen
- De DP 16 19 Colonial School District vs. StudentDokument7 SeitenDe DP 16 19 Colonial School District vs. StudentKevinOhlandtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Web Systems Subject OutlineDokument11 SeitenWeb Systems Subject OutlineJoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Speaking Section Question 3Dokument14 SeitenIntegrated Speaking Section Question 3manojNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nature of Performance-Based AssessmentDokument3 SeitenNature of Performance-Based AssessmentDarel GarzNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV Nitin GuptaDokument2 SeitenCV Nitin GuptaNitin GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NAVMC 3500.89B Ammunition Technician Officer T-R ManualDokument48 SeitenNAVMC 3500.89B Ammunition Technician Officer T-R ManualtaylorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd Quarter ToolkitDokument10 Seiten3rd Quarter ToolkitDimple BolotaoloNoch keine Bewertungen
- KEMFSED Scholarship Application FormsDokument8 SeitenKEMFSED Scholarship Application Formsvincentzuma005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Reasoning Strategies in PTDokument19 SeitenClinical Reasoning Strategies in PTamitesh_mpthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class SizeDokument6 SeitenClass Sizeapi-305853483Noch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument417 SeitenPDFVelya GalyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReflectionDokument8 SeitenReflectionapi-260964883Noch keine Bewertungen
- Click To Download IELTS Application FormDokument2 SeitenClick To Download IELTS Application Formapi-3712408Noch keine Bewertungen
- Venn DiagramDokument2 SeitenVenn Diagramapi-255836042Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lac Understanding ResponsesDokument20 SeitenLac Understanding ResponsesSheila Jane Dela Pena-LasalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jms School Fee 2022-2023Dokument1 SeiteJms School Fee 2022-2023Dhiya UlhaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Students' creative writing and language skills benefit more from reading books than online newspapersDokument36 SeitenStudents' creative writing and language skills benefit more from reading books than online newspapersTrần NgọcNoch keine Bewertungen