Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
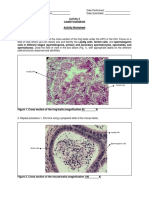
Micromanipulation techniques
Hochgeladen von
Sai SridharOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Micromanipulation techniques
Hochgeladen von
Sai SridharCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Micromanipulation
MICROMANIPULATION Birth of the first baby achieved through conception outside the human body 1978 Embryos can be manipulated for cell biopsy to determine their genetic status. It is the technique whereby sperm, eggs and embryos can be handled on an inverted microscope stage, performing minute procedures at the microscope stage, performing minute procedures at the microscopic level via joystick that hydraulically operate glass micro tools
Male infertility Intracytopasmic Sperm Injection ot ICSI Sperm of any quality and from any level of the male reproductive tract may be used with the only criterian for that the spermis alive even it is non motile. Dead sperm may be able to fertilize , however the DNA from such sperm is too degenerate to form a viable embryo Immature sperm from the testicle or the epididymis can be retrieved for use with ICSI for men who possess no sperm in the ejaculated semen (azoospermia) Azoospermia is due to obstruction in the tract. Necrozoospermia do not survive to the point of ejaculation To overcome this testicular biopsy can be done for a ready source of freshly produced viable sperm.
ICSI for non male factor infertility To over come the problem cytogenetic screening prformed. The use of ICSI is now routinely applied to a range of clinical situations wherever there is a possiblilty that conventional in vitro fertilization may be suppressed or not occur. Such situations include the following Idiopathic or unexplained fertility Hyper responsive ovarian stimulation cases where egg quality may be reduced Post thaw sperm samples that survive poorly, post thaw egg insemination, Generation of pre implantation genetic screening where embryos clean from extraneous contaminating sperm is needed The conventional problem in fertilization can be overcome by ICSI
Assisted hatching Problems faced by the embryo during implantation -unable to breal free from the surrounding Jelly coat called Zona pelucida This glycoprotein coat acts to protect the egg and to regulate normal fertilization And further continues to protect the embryo until blastocyst stage. During blastocyst stage the embryp fills itself up with fluid like a water filled balloon pumping itself larger and larger until it rupture and hatches from the zona pelucida and implants itself in the endometrium. Due to various reason the Zona pelucida will be thicker and cannot implant, such cases will be assisted by micromanipulation technique A hole is made on the Zona pelucida layer prior to transfer This can be done by mechanical, chemically laser. `
Embryo biopsy Can be done for both eggs and the sperm for pre implantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) and enables both the unfertilized egg by removing the first polar body. In fertilized multi cellular stage (6 to 12 cell stage) or from the trophoectoderm of the blastocyst. To identify any mutations or cross chromosomal errors. Micro insemination Procedure that can be used to increase the chance of fertilization and embry transfer (IV-ET) who may have reduced chance of fertilization through standard egg insemination procedures Active sperms are made to retain in the culture menium.After exposing the mature eggs to an enzyme that removes the cumulus cells which surrounds the cells. Each egg is placed under a microscope and held in place by gentle vaccum with a small glass tube called micropipette. A single sperm is drawn into the hollow glass needle along with small amount of the nutrient liquid medium. The needle is then passed through the Zona pelucida and the cell membrane to inject the sperm into the center of the egg After 18 -18 hrs after ICSI. The eggs are examined for two distinct proneuclei Risks and benefits
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- USMLE - BRS Pathology - Flash CardsDokument37 SeitenUSMLE - BRS Pathology - Flash CardsJake ChuengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of Frog HistologyDokument6 SeitenParts of Frog HistologyVanessa RebancosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radio Immuno As SayDokument3 SeitenRadio Immuno As SaySai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) : and ApplicationDokument38 SeitenAssisted Reproductive Technology (ART) : and ApplicationPraluki HerliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- In VitrofertilizationDokument29 SeitenIn VitrofertilizationRad RYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies OverviewDokument35 SeitenAssisted Reproductive Technologies OverviewPraluki HerliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 - Fertilization Cleavage Implantation-Dr - GosaiDokument41 Seiten5 - Fertilization Cleavage Implantation-Dr - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assisted Reproductive Technology by Rosemary C. AgboDokument19 SeitenAssisted Reproductive Technology by Rosemary C. AgboRosemaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- In-Vitro Fertilisation: Shruti Samal ROLL NUMBER - 1120096 B.Sc. Life Science Second SemesterDokument20 SeitenIn-Vitro Fertilisation: Shruti Samal ROLL NUMBER - 1120096 B.Sc. Life Science Second SemesterSHRUTI SAMALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assisted Reproductive TechnologyDokument14 SeitenAssisted Reproductive Technologyarchana jainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter:4 Reproductive Health: Assisted Reproductive Technology (Art)Dokument11 SeitenChapter:4 Reproductive Health: Assisted Reproductive Technology (Art)Nikhil BijuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assisted Reproductive TechnologyDokument12 SeitenAssisted Reproductive Technologyvpnayak777Noch keine Bewertungen
- Artificial ReproductionDokument9 SeitenArtificial ReproductionSagar HanamasagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ivf Techniques PresentationDokument7 SeitenIvf Techniques Presentationjoshuasommy3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assisted Reproductive TechnologyDokument16 SeitenAssisted Reproductive TechnologyAnanda SadhukhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- In Vitro FertilizationDokument34 SeitenIn Vitro FertilizationShally May Estrella OrozcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FertilizationDokument108 SeitenFertilizationDauda RukaiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micromanipulation of Human Gamates and EmbryoDokument11 SeitenMicromanipulation of Human Gamates and EmbryosumanavijitNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICSIDokument31 SeitenICSIHossam ElsakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) : Doaa HegabDokument23 SeitenAssisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) : Doaa HegabLinguum100% (1)
- Assited Reproductive TechnologyDokument40 SeitenAssited Reproductive TechnologySanthosh.S.UNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ivf ENTER - Final FinalDokument15 SeitenIvf ENTER - Final FinalsumanavijitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproductive HealthDokument6 SeitenReproductive HealthAdesh BhullarNoch keine Bewertungen
- IVF at Genesis Fertility Center, KalyanDokument4 SeitenIVF at Genesis Fertility Center, KalyanMayuri SwamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Paper Apa FormatDokument19 SeitenResearch Paper Apa FormatIvonne SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASSISTED REPRODUCTIVE TECHNOLOGY EXPLAINEDDokument34 SeitenASSISTED REPRODUCTIVE TECHNOLOGY EXPLAINEDBhawna JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RECENT ADVANCEMENTS IN INFERTILITY TECHNIQUESDokument111 SeitenRECENT ADVANCEMENTS IN INFERTILITY TECHNIQUESsanthanalakshmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assisted Reproductive TechnologyDokument16 SeitenAssisted Reproductive TechnologyQilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IVF Basic Principles SourceDokument3 SeitenIVF Basic Principles SourcereadtometooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ivf Clinic at AurangabadDokument7 SeitenIvf Clinic at AurangabadSanjay PagareNoch keine Bewertungen
- 771 Topic6-Fertilization%2Ccapacitation%2CimplantationDokument22 Seiten771 Topic6-Fertilization%2Ccapacitation%2CimplantationGowtham G DineshNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAQDokument14 SeitenSAQShilpa DuttaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infertility, ART, and The Reproductive SystemDokument5 SeitenInfertility, ART, and The Reproductive Systemsomeone4630Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1. 1st&2nd weekDokument38 Seiten1. 1st&2nd weekJeniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assisted Fertilization Techniques ExplainedDokument180 SeitenAssisted Fertilization Techniques ExplainedPaul Kevin Mendoza67% (3)
- In Vitro FertilizationDokument21 SeitenIn Vitro FertilizationRahul shyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embryo Transfer TechnologyDokument49 SeitenEmbryo Transfer TechnologyshubhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assisted Reproductive TechnologyDokument21 SeitenAssisted Reproductive TechnologySurya SetiawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assisted Reproductive TechnologiesDokument19 SeitenAssisted Reproductive TechnologiesGURU ROHIIT KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selecting Male Or Female Child Here's How It Works - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Andrew Huberman: A Guide To Gender SelectionVon EverandSelecting Male Or Female Child Here's How It Works - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Andrew Huberman: A Guide To Gender SelectionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embryo Transfer TechnologyDokument55 SeitenEmbryo Transfer TechnologyShubham AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 FertilizationDokument37 Seiten3 FertilizationIRENE SEBASTIANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assisted ReproductionDokument22 SeitenAssisted ReproductionAbong Che InnocentNoch keine Bewertungen
- IVF Embryology 5Dokument29 SeitenIVF Embryology 5alhader libraryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Dr. Seng Shay WayDokument8 SeitenBest Dr. Seng Shay Wayhar shishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why and When Do You Need To Go For IVF?Dokument2 SeitenWhy and When Do You Need To Go For IVF?gbrclinicNoch keine Bewertungen
- In Vitro FertilizationDokument3 SeitenIn Vitro Fertilizationeliz03Noch keine Bewertungen
- EMBRYOLOGY Lab Procedures: Step 1: Evaluation of Female InfertilityDokument8 SeitenEMBRYOLOGY Lab Procedures: Step 1: Evaluation of Female InfertilitySaloni KhannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- in Vitro GrowthDokument23 Seitenin Vitro GrowthYến NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Tube Baby 1Dokument16 SeitenTest Tube Baby 1nitesh.th15005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Embryo TransferDokument47 SeitenEmbryo TransferArchael De GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12 Investigatory Project....Dokument8 SeitenClass 12 Investigatory Project....shivshankardahayat80Noch keine Bewertungen
- Artificial Insemination BY R. Mohana KrishnanDokument45 SeitenArtificial Insemination BY R. Mohana KrishnanMohan KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Female InfertilityDokument33 SeitenFemale InfertilityKiprotich Titus NgetichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate: Abhishek GautamDokument12 SeitenCertificate: Abhishek GautamANIL KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Family Having Difficulty Conceiving A ChildDokument10 Seiten4 Family Having Difficulty Conceiving A ChildDrex CuritanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st 02nd WeekDokument44 Seiten1st 02nd WeekMajd HusseinNoch keine Bewertungen
- In Vitro FertilisationDokument5 SeitenIn Vitro FertilisationVikram VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiologyDokument17 SeitenBiologyharveylenseena2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- ARTDokument36 SeitenARTTtyyfff Fyyu89-Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Investigatory Project Class 12 - EditedDokument17 SeitenBiology Investigatory Project Class 12 - Editedharveylenseena2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- EmbryologyDokument60 SeitenEmbryologyDaniella AwurumibeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abnormal Fertilization in ARTDokument33 SeitenAbnormal Fertilization in ARTAl Mamun100% (1)
- Consumer Buyer BehaviorDokument29 SeitenConsumer Buyer BehaviorSai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Video Conferencing TechnologyDokument31 SeitenVideo Conferencing TechnologySai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental ScienceDokument12 SeitenEnvironmental ScienceSai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gamete and Fertilization BiologyDokument12 SeitenGamete and Fertilization BiologySai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- VDRL TestDokument3 SeitenVDRL TestSai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grif IthDokument9 SeitenGrif IthSai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of AnimalsDokument23 SeitenClassification of AnimalsSai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer AttitudeDokument13 SeitenConsumer AttitudeSai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConciliationDokument22 SeitenConciliationSai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- As A Man ThinkethDokument28 SeitenAs A Man ThinkethSai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Education in Conservation of BiodiversityDokument18 SeitenRole of Education in Conservation of BiodiversitySai Sridhar100% (1)
- Introduction To BiotechnologyDokument49 SeitenIntroduction To BiotechnologyTanvi Jain100% (2)
- Bio ChemDokument3 SeitenBio Chemsujithas0% (1)
- Widal TestDokument3 SeitenWidal TestSai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water BathDokument5 SeitenWater BathSai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of CarcinogensDokument33 SeitenTypes of CarcinogensSai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visible Spectro Photo Me TryDokument2 SeitenVisible Spectro Photo Me TrySai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selective, Differential, Enriched MediaDokument5 SeitenSelective, Differential, Enriched MediaSai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple, Differential Staining and MotilityDokument8 SeitenSimple, Differential Staining and MotilitySai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit II - Fatty LiverDokument2 SeitenUnit II - Fatty LiverSai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit IIIDokument31 SeitenUnit IIISai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- UMLSDokument4 SeitenUMLSSai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDS - PageDokument5 SeitenSDS - PageSai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- RadioactivityDokument2 SeitenRadioactivitySai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preparation of Molar SolutionDokument1 SeitePreparation of Molar SolutionSai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper Chromatography: Separating Mixtures Using Capillary ActionDokument4 SeitenPaper Chromatography: Separating Mixtures Using Capillary ActionSai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scientific Technique Molecular Biology Amplify DNA DNA Sequence Kary MullisDokument4 SeitenScientific Technique Molecular Biology Amplify DNA DNA Sequence Kary MullisSai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nucleic Acid HybridizationDokument2 SeitenNucleic Acid HybridizationSai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2. Physical SelfDokument7 SeitenChapter 2. Physical SelfJaya CajalneNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOTECHNOLOGY MODULE 2 ApplicationsofBiotechnologyinAgricultureanditsImportance V2 1Dokument20 SeitenBIOTECHNOLOGY MODULE 2 ApplicationsofBiotechnologyinAgricultureanditsImportance V2 1Francis Ashley TeañoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers & Solutions: For For For For For NEET (UG) - 2017Dokument31 SeitenAnswers & Solutions: For For For For For NEET (UG) - 2017Siva Kumar100% (3)
- Scheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 5, 2012Dokument46 SeitenScheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 5, 2012sitnorsyahidah100% (2)
- Biology Organisms and Adaptations Media Update Enhanced Edition 1st Edition Noyd Solutions Manual DownloadDokument22 SeitenBiology Organisms and Adaptations Media Update Enhanced Edition 1st Edition Noyd Solutions Manual DownloadKaren Zavala100% (30)
- Demo Lesson Female Repro 19-20Dokument4 SeitenDemo Lesson Female Repro 19-20Rhandy Buenecille100% (1)
- When Does Human Life Begin PDFDokument18 SeitenWhen Does Human Life Begin PDFApple Obias100% (1)
- New Gcse: Foundation Tier Biology 1Dokument15 SeitenNew Gcse: Foundation Tier Biology 1dao5264Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Regent 2001Dokument28 SeitenBio Regent 2001Hana Nur HidayatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10Dokument11 SeitenHow Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10Pranay Kumar60% (5)
- Practice Exam 1 - 2015 BOT 101Dokument12 SeitenPractice Exam 1 - 2015 BOT 101Daniel GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- SQP Science Vii Kvs Ro LkoDokument25 SeitenSQP Science Vii Kvs Ro Lkotharishr@gmail.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 FY11 Biology Detailed SolutionDokument31 Seiten2016 FY11 Biology Detailed SolutionPeter MayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 8 Science EnglishMediumDokument242 SeitenClass 8 Science EnglishMediumjatinry33% (3)
- How Do Organisms Reproduce Chapter 8Dokument8 SeitenHow Do Organisms Reproduce Chapter 8Rajveer ShekhawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- DK Olukoya - Prayer Passport-2Dokument292 SeitenDK Olukoya - Prayer Passport-2Franck100% (1)
- Class 10 Important DiagramsDokument20 SeitenClass 10 Important DiagramsRick RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE ExerciseDokument10 SeitenHOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE ExerciseShreyansh DugarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9700 s03 QP 6 PDFDokument28 Seiten9700 s03 QP 6 PDFIG UnionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Notes For Grade Week 9-10 For Grade 12Dokument25 SeitenBiology Notes For Grade Week 9-10 For Grade 12Adeola YusufNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIDTERMDokument6 SeitenMIDTERMElliey Diane ApelacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life Sciences Reproduction in Vertebrates 22 February 2024Dokument24 SeitenLife Sciences Reproduction in Vertebrates 22 February 2024finnhyacinthNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 3 2 1 3Dokument15 Seiten1 3 2 1 3Himanshu GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine Assisted Reproductive Technologies Act (Proposed Version by Emir Mendoza)Dokument5 SeitenPhilippine Assisted Reproductive Technologies Act (Proposed Version by Emir Mendoza)Emir MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/22Dokument16 SeitenCambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/22shabanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument9 SeitenChapter 1Anirudh CNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diet and Effort To Have OffspringDokument1 SeiteDiet and Effort To Have OffspringKlinik Assalam SidrapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aboriginal Spirituality and the DreamingDokument11 SeitenAboriginal Spirituality and the DreamingEugene YambaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frog Reproductive SystemDokument13 SeitenFrog Reproductive Systemkaiden.g.lambertNoch keine Bewertungen