Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chapter 2
Hochgeladen von
Ali YahyaOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 2
Hochgeladen von
Ali YahyaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
EDU 3106 CULTURE AND LEARNING
Understanding the identity of a nation is important in the process of strengthening and enhancing the relationship between various ethnic groups in a society. Misunderstandings about the identity of the nation would create prejudice, stereotypes and ethnocentric that would eventually cause social discrimination.
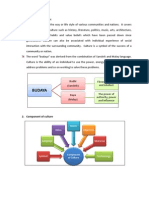
Social integration is a process of uniting various groups through joint identity by eliminating the communitys differences and identity. Integration will occur when the members of a society are able to accept its other members without regarding their identity and origin.
Integration also involves assimilation.
Assimilation is the process when the minority group loses their identity and are absorbed by the dominant group in terms of culture and social.
Cultural
Two types of assimilation
Structural
Cultural assimilation is the process by which the minority group learns the cultural characteristics of the local community to be applied in their daily life.
Example: dressing style, language and customs
Structural assimilation is the process where minority groups successfully join the principal institutions and social activities in the dominant community. Integration also involves acculturation which is a process where changes and borrowing of cultural elements occur.
Example: using same language so that the social interaction would not be affected by the differences between the groups.
Integration might also include amalgamation which is the process of uniting biologically different ethnic groups. In this process, all cultural entities of various groups are mixed through intermarriage which creates a new race. This can only happen if the dominant groups allow and encourage the minority groups to do so. Minority groups cannot be forced.
Generally, Nation is a group of people who are considered to have a common identity, same language, religion, ideology and culture. Considered to have the same origin and descent. Each race has its own identity
Example: Malays with their Malay culture, Chinese with their Chinese culture and Indians with their Indian culture.
A tool or a manifestation of culture used by humans to communicate or contact each other, in terms of writing, orally, or motion (sign language) in order to convey their desire to others Enable humans to adapt themselves to the customs, behaviours and societal rules Easier to get used with all kinds of people
Has a number of functions that can be divided into general functions and specific functions. General Functions
Tool to communicate Tool to make integration To make social adaptation
Specific Functions
To engage in day-to-day interactions Create art (literature) To learn the old manuscripts Exploit knowledge and technology
The symbols in the language of a society might be identical but usually are different. Important factor in fostering unity among the various races in Malaysia.
In Malaysia, Malay language is the official language. Article 152 of the Malaysian Constitution provides Malay language as the national language and the official language of Malaysia. Malay language became a tool of unity among Malaysians who are of various races and cultures.
Social structure is the arrangement of the basic social elements of a society, such as the group, social class, values and social norms, and social institutions.
There are two ways to analyse social structure a) Descent/caste, education level, wealth and age. This division is named social stratification (different levels).
In Malaysian context, social structure can be seen more on the level of education, wealth and age.
b) Ethnicity, race, class/group, family type, religion and so on. This distribution is named social difference (The difference of functions and custom).
Status is the important element in social stratification.
Status is the position of a person or group in the social structure of a society or a particular pattern of social relations.
Status is obtained in three ways. a) Acquired since birth (ascribed status) b) Is given for the services (assigned status) c) For the performances and cause (achieved status)
Custom is the rules, law, norms that are upheld by the community groups. In old Malay language, custom refers to the legal or customary law which include social, political, economic and even ocean law. Rules that have been practiced for generations in a community until it has become a customary law or rule that has to be obeyed.
A common way that is inherited in a society. Custom includes all aspects beginning from birth, marriage until death. A common way of life practiced by a particular community that illustrates the communitys cultural pattern.
The customs of the society in Malaysia are based on the following community: Malay customs Chinese customs Indians customs Customs of the ethnic communities in Sabah Customs of the ethnics communities in Sarawak Customs of the aborigines
a) b) c) d) e) f)
1) 2) 3) 4)
5)
6)
Malay communitys customs Chinese communitys customs Indian communitys customs Iban communitys customs Kadazan communitys customs Aborigines customs
Comprise three big groups
Negrito Senoi Original Malay (Proto Malay/ Melayu Proto)
Gender role differences that arise based on social and cultural characteristics can be changed through learning process or education. Example, women work in the house (do housework) while men work outside house.
Belief means accepting the truth about something. Normally when a person believes something, they will have a feeling of sure or surety towards it.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cultural ChangesDokument18 SeitenCultural ChangesRoy De GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CultureDokument108 SeitenCultureReshantini Rajendran100% (1)
- Characteristics of Society and CultureDokument113 SeitenCharacteristics of Society and CultureSamantha HinesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obj 3 Complete NotesDokument7 SeitenObj 3 Complete NotesVishesh MattaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition of CultureDokument4 SeitenDefinition of Cultureapril18loveNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDU 3106 Topic 2: Awareness of Socio-Cultural Aspects of Ethnic GroupsDokument14 SeitenEDU 3106 Topic 2: Awareness of Socio-Cultural Aspects of Ethnic GroupsIkhwan Firdausi SazaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Culture and Ethnic Groups in Malaysia: Jabatan Ilmu PendidikanDokument26 SeitenCulture and Ethnic Groups in Malaysia: Jabatan Ilmu PendidikanAstroRia2Noch keine Bewertungen
- UCSP Week 1 6Dokument44 SeitenUCSP Week 1 6Eunice GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 CCDokument25 SeitenUnit 1 CCGunveen AbrolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ucsp 082923Dokument36 SeitenUcsp 082923Clarence AlolodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conceptualization and TermsDokument24 SeitenConceptualization and Termsmrcornis18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Language and CultureDokument48 SeitenLanguage and CultureAli Raza BokhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linguistic Communities and Social IdentitiesDokument40 SeitenLinguistic Communities and Social IdentitiesPRINCESS KAYE ANGEL MAMALONoch keine Bewertungen
- 103 CieDokument41 Seiten103 CieShashi KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trabajo Final de CulturaanglofonaDokument22 SeitenTrabajo Final de Culturaanglofonajose limaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multi ECCE - Chapter 1Dokument21 SeitenMulti ECCE - Chapter 1Eskindir JembereNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.social Concept Related To CultureDokument19 Seiten2.social Concept Related To Cultureaimenyamin3868Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1.understanding Culture Society and PoliticsDokument7 SeitenLesson 1.understanding Culture Society and Politicselie lucidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cultural ChangesDokument5 SeitenCultural ChangesNaomi YsabelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q1. W3. Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDokument9 SeitenQ1. W3. Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsNatsumiGraceNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDUDokument408 SeitenEDUWahidahHusainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cultural Transmission in SchoolsDokument5 SeitenCultural Transmission in SchoolsNurhashimah Za'ba50% (2)
- Culture: Do Non-Humans Have A Culture?Dokument5 SeitenCulture: Do Non-Humans Have A Culture?arslan shahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes L2Dokument6 SeitenLecture Notes L2劉瑜Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4 Culture and IdentitiesDokument6 SeitenLesson 4 Culture and IdentitiesDan FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Cultural DiversityDokument12 SeitenChapter 1 Introduction To Cultural Diversitynur atikah67% (3)
- XI Chapter 4Dokument4 SeitenXI Chapter 4Moumita Banerjee MukherjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identity and Social FormationDokument9 SeitenIdentity and Social Formationqzvcxmh9k9Noch keine Bewertungen
- LC 2 Mod 2 Concept Aspect and Changes in Culture SocietyDokument7 SeitenLC 2 Mod 2 Concept Aspect and Changes in Culture SocietyLilie GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social Relations On Multicultural Society in The Context of Social Change: Indonesian PerspectiveDokument20 SeitenSocial Relations On Multicultural Society in The Context of Social Change: Indonesian PerspectivearisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cultural UniformityDokument6 SeitenCultural Uniformitytetarwal67% (6)
- IBTDokument10 SeitenIBTNecy AlbuenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Culture and Learning (EDU 3106) Chapter 1: Culture and Diversity Groups in MalaysiaDokument35 SeitenCulture and Learning (EDU 3106) Chapter 1: Culture and Diversity Groups in MalaysiaClarie LohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sociology 2Dokument6 SeitenSociology 2WasifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material For Teaching in Mult SettingDokument50 SeitenMaterial For Teaching in Mult SettingMustefa mohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 Characteristics of CultureDokument31 SeitenUnit 3 Characteristics of Cultureshort talk tvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social Institutions of Indian SocietyDokument4 SeitenSocial Institutions of Indian SocietyChris DsouzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social Stratification: Class, Race, Ethnicity, Gender, and SexDokument5 SeitenSocial Stratification: Class, Race, Ethnicity, Gender, and SexAndrea Hana DevezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-CultureDokument35 Seiten3-CultureUsmanChaudhryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ucsp ReportDokument4 SeitenUcsp ReportMaxine AlipioNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Characteristics of CultureDokument3 SeitenThe Characteristics of CultureMohammed Omar GhaffourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Culture The Meaning of CultureDokument7 SeitenCulture The Meaning of Culturef abbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final NotesDokument17 SeitenFinal NotesMylene MangabangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intercultural CommunicationDokument11 SeitenIntercultural CommunicationMia SamNoch keine Bewertungen
- PelajaranDokument4 SeitenPelajaranYusra AinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9: The Characteristics of CultureDokument4 SeitenChapter 9: The Characteristics of CultureSajid Mehdi100% (1)
- CultureDokument2 SeitenCultureArchie PolicarpioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cultural Changes: Jube-Lee C. TungpalanDokument30 SeitenCultural Changes: Jube-Lee C. TungpalanJubelee TungpalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Society and CultureDokument22 SeitenSociety and CultureTasneem SaifeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Socio-Cultural & Demographic EnvironmentDokument52 SeitenSocio-Cultural & Demographic EnvironmentNihalNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Assignment: Society, Culture: Does Culture Matter?Dokument6 SeitenEnglish Assignment: Society, Culture: Does Culture Matter?bala1307Noch keine Bewertungen
- 15 - Unit 1 Lesson 7Dokument14 Seiten15 - Unit 1 Lesson 7Donna May B. ReforsadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Features of Indian Society 1Dokument21 SeitenFeatures of Indian Society 1Jojo NutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Media and Society Assignment 1Dokument8 SeitenMedia and Society Assignment 1MenduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 4 Q2 Ucsp New Template HANDOUTDokument5 SeitenWeek 4 Q2 Ucsp New Template HANDOUTJIYAN BERACISNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDU 3053E: Awareness of Socio-Cultural DiversityDokument13 SeitenEDU 3053E: Awareness of Socio-Cultural DiversityHawa ZainoddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ucsp Online Module 2Dokument5 SeitenUcsp Online Module 2elie lucido100% (1)
- Assignment 5 June 21 Nur MaykasariDokument3 SeitenAssignment 5 June 21 Nur MaykasariNur MaykasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Date: Class:: Feeds OnDokument3 SeitenName: Date: Class:: Feeds OnAli YahyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading Passage: A Visit To A FarmDokument1 SeiteReading Passage: A Visit To A FarmAli YahyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chong Is Cycling at The Park.: Tina Is Dancing in Her RoomDokument3 SeitenChong Is Cycling at The Park.: Tina Is Dancing in Her RoomAli YahyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- D7Quiz Time!!Dokument10 SeitenD7Quiz Time!!Ali YahyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bitara 2010 Goh - EditDokument12 SeitenBitara 2010 Goh - EditAli YahyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theories of Instructional Management by Jacob KouninDokument14 SeitenTheories of Instructional Management by Jacob KouninNur Amira TeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR KizlikDokument5 SeitenDR KizlikAli Yahya100% (1)
- Dead Men's Path RujukanDokument4 SeitenDead Men's Path RujukanAli YahyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essay EsaimenDokument7 SeitenEssay EsaimenAli YahyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Physical Education Lesson 1Dokument2 SeitenTeaching Physical Education Lesson 1RonethMontajesTavera100% (1)
- Bpa Cover Letter FinalDokument1 SeiteBpa Cover Letter Finalapi-444413529Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bernal Raymond V. 18000102300 XM - PDFDokument1 SeiteBernal Raymond V. 18000102300 XM - PDFRaymond Veridiano BernalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis Proposal Guide 2-3-15Dokument4 SeitenThesis Proposal Guide 2-3-15ullallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume Guadalupe Garcia-2Dokument2 SeitenResume Guadalupe Garcia-2api-457167363Noch keine Bewertungen
- Responsible Safe and Ethical Use of Ict at School and Home - Educ 3628 - LeoDokument3 SeitenResponsible Safe and Ethical Use of Ict at School and Home - Educ 3628 - Leoapi-483734281Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bahan Ajar Asking and Giving OpinionDokument3 SeitenBahan Ajar Asking and Giving OpinionEdison ManaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University, Lucknow: "Family Law and The Indian Consitution"Dokument5 SeitenDr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University, Lucknow: "Family Law and The Indian Consitution"Anushi SaraswatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genres of LiteratureDokument90 SeitenGenres of Literaturejohn rey adizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Language Theories and ProponentsDokument1 SeiteLanguage Theories and ProponentsPaul Romano Benavides RoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily Lesson Log: CheerdanceDokument6 SeitenDaily Lesson Log: Cheerdanceprinces molina100% (1)
- Introduction To International Legal English Teachers Book Sample PDFDokument10 SeitenIntroduction To International Legal English Teachers Book Sample PDFSam Nguyen100% (1)
- Science Technology and SocietyDokument9 SeitenScience Technology and SocietyNita Teresa BagaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMEPA Ko ToDokument27 SeitenSMEPA Ko ToKlaris Reyes100% (1)
- The Spanish Black LegendDokument2 SeitenThe Spanish Black LegendAlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Christian Coping & Psychological Functioning in PrisonDokument540 SeitenChristian Coping & Psychological Functioning in PrisonRev.Dr.Roy Catchpole0% (1)
- Beyond The 5 Paragraph EssayDokument3 SeitenBeyond The 5 Paragraph EssayDanika BarkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Astecas) Feeding The Gods (Estudo Science)Dokument6 Seiten(Astecas) Feeding The Gods (Estudo Science)Pedro Henrique Leite100% (1)
- Naga Mandala and Women's EmancipationDokument5 SeitenNaga Mandala and Women's EmancipationAyesha UroojNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine Indigenous Arts by Carlo FranciaDokument5 SeitenPhilippine Indigenous Arts by Carlo FranciaWeLove RezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Das PoGE 8e SI LB PPT - Chapter 12 ExamplesDokument32 SeitenDas PoGE 8e SI LB PPT - Chapter 12 ExamplesTan Kai XianNoch keine Bewertungen
- CANAANITES BECOME THE 'BLACK NOBILITY' of Later Europe PDFDokument5 SeitenCANAANITES BECOME THE 'BLACK NOBILITY' of Later Europe PDFPeter100% (2)
- Textual Criticism Seminar ReflectionDokument2 SeitenTextual Criticism Seminar Reflectionapi-272647058Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cad Desk Student Fee's ReceiptDokument2 SeitenCad Desk Student Fee's ReceiptPushpendra LodhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RealismDokument2 SeitenRealismAnonymous 6pmKUrMTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explaining Islam in Central Asia-An Anthropological Approach For UzbekistanDokument10 SeitenExplaining Islam in Central Asia-An Anthropological Approach For UzbekistanCristina BobocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethnography As MethodDokument33 SeitenEthnography As MethodJULIANINoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Colors PPDokument12 SeitenTeaching Colors PPapi-510591078Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Study of Musical Instruments in IfugaoDokument114 SeitenA Study of Musical Instruments in IfugaoTine AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Dimensions of MeaningDokument4 SeitenThe Dimensions of MeaningKhadin Pendipa100% (7)