Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Operating Systems Chapter-01
Hochgeladen von
Felipe EspositoOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Operating Systems Chapter-01
Hochgeladen von
Felipe EspositoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 What is an operating system 1.2 History of operating systems 1.3 The operating system zoo 1.4 Computer hardware review 1.5 Operating system concepts 1.6 System calls 1.7 Operating system structure
1
Introduction
A computer system consists of
hardware system programs application programs
2
What is an Operating System
It is an extended machine
Hides the messy details which must be performed Presents user with a virtual machine, easier to use
It is a resource manager
Each program gets time with the resource Each program gets space on the resource
History of Operating Systems (1)
Early batch system
bring cards to 1401 read cards to tape put tape on 7094 which does computing put tape on 1401 which prints output
4
History of Operating Systems (2)
First generation 1945 - 1955
vacuum tubes, plug boards
Second generation 1955 - 1965
transistors, batch systems
Third generation 1965 1980
ICs and multiprogramming
Fourth generation 1980 present
personal computers
5
History of Operating Systems (3)
Structure of a typical FMS job 2nd generation
6
History of Operating Systems (4)
Multiprogramming system
three jobs in memory 3rd generation
7
The Operating System Zoo
Mainframe operating systems Server operating systems Multiprocessor operating systems Personal computer operating systems Real-time operating systems Embedded operating systems Smart card operating systems
Computer Hardware Review (1)
Monitor
Bus
Components of a simple personal computer
9
Computer Hardware Review (2)
(a) A three-stage pipeline (b) A superscalar CPU
10
Computer Hardware Review (3)
Typical memory hierarchy
numbers shown are rough approximations
11
Computer Hardware Review (4)
Structure of a disk drive
12
Computer Hardware Review (5)
One base-limit pair and two base-limit pairs
13
Computer Hardware Review (6)
(a)
(b)
(a) Steps in starting an I/O device and getting interrupt (b) How the CPU is interrupted
14
Computer Hardware Review (7)
Structure of a large Pentium system
15
Operating System Concepts (1)
A process tree
A created two child processes, B and C B created three child processes, D, E, and F
16
Operating System Concepts (2)
(a) A potential deadlock. (b) an actual deadlock.
17
Operating System Concepts (3)
File system for a university department
18
Operating System Concepts (4)
Before mounting,
files on floppy are inaccessible
After mounting floppy on b,
files on floppy are part of file hierarchy
19
Operating System Concepts (5)
Two processes connected by a pipe
20
Steps in Making a System Call
There are 11 steps in making the system call
read (fd, buffer, nbytes)
21
Some System Calls For Process Management
22
Some System Calls For File Management
23
Some System Calls For Directory Management
24
Some System Calls For Miscellaneous Tasks
25
System Calls (1)
A stripped down shell:
while (TRUE) { type_prompt( ); read_command (command, parameters) if (fork() != 0) { /* Parent code */ waitpid( -1, &status, 0); } else { /* Child code */ execve (command, parameters, 0); } } /* repeat forever */ /* display prompt */ /* input from terminal */ /* fork off child process */ /* wait for child to exit */
/* execute command */
26
System Calls (2)
Processes have three segments: text, data, stack
27
System Calls (3)
(a) Two directories before linking /usr/jim/memo to ast's directory (b) The same directories after linking
28
System Calls (4)
(a) File system before the mount (b) File system after the mount
29
System Calls (5)
Some Win32 API calls
30
Operating System Structure (1)
Simple structuring model for a monolithic system
31
Operating System Structure (2)
Structure of the THE operating system
32
Operating System Structure (3)
Structure of VM/370 with CMS
33
Operating System Structure (4)
The client-server model
34
Operating System Structure (5)
The client-server model in a distributed system
35
Metric Units
The metric prefixes
36
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chapter-01 TanenbaumDokument36 SeitenChapter-01 TanenbaumBekir GülerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-01 TanenbaumDokument18 SeitenChapter-01 TanenbaumKrooks CostanzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIX Internals: Rohit JnagalDokument36 SeitenUNIX Internals: Rohit Jnagalshery_agNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.2 Computer Hardware Review 1.3 Operating System ConceptsDokument94 Seiten1.2 Computer Hardware Review 1.3 Operating System ConceptsDo Cao Dat (K15 HL)Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1.2 Computer Hardware Review 1.3 Operating System ConceptsDokument98 Seiten1.2 Computer Hardware Review 1.3 Operating System ConceptsDo Cao Dat (K15 HL)Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 1Dokument60 SeitenCH 1Yahya AlqadhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Systems Design and Implementation: Third Edition Andrew S. Tanenbaum Albert S. WoodhullDokument33 SeitenOperating Systems Design and Implementation: Third Edition Andrew S. Tanenbaum Albert S. Woodhullbhammack-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Real Time Operating System Based Design-1Dokument121 SeitenReal Time Operating System Based Design-1Prajna S BhatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Le-6 System CallsDokument9 SeitenLe-6 System CallsHarshit AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Systems: Steven Hand Michaelmas / Lent Term 2008/09Dokument11 SeitenOperating Systems: Steven Hand Michaelmas / Lent Term 2008/09Sanjeev KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- IntroductionDokument37 SeitenIntroductionSharan SPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Systems Design - Session 3 PDFDokument21 SeitenOperating Systems Design - Session 3 PDFSai susheel gupta sanagapalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- OS Lecture1 INtroductionDokument37 SeitenOS Lecture1 INtroductionFurious FiveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec2 Lec3 Cpuvirt FullDokument67 SeitenLec2 Lec3 Cpuvirt FullamulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 10 UNIXDokument48 SeitenCH 10 UNIXAnusha BikkineniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Systems Design: Session 3: OS InterfaceDokument21 SeitenOperating Systems Design: Session 3: OS InterfaceAvinash AllaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5 - Embedded SystemDokument58 SeitenUnit 5 - Embedded Systemsujith100% (1)
- Ch1 IntroductionDokument34 SeitenCh1 Introduction221810303009 BUSSA RUTHVIKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating System & Data Storage Lec 2Dokument79 SeitenOperating System & Data Storage Lec 2vantom85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Operating System IntroductionDokument35 SeitenOperating System IntroductionFurious FiveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Name-Operating System Course Code-COM-302 Lecture No-2 Topic - Booting SystemDokument17 SeitenCourse Name-Operating System Course Code-COM-302 Lecture No-2 Topic - Booting SystemGulshan SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ke FandaDokument32 SeitenKe FandaPra TamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5 - Intro To OS - PrinciplesDokument25 SeitenLecture 5 - Intro To OS - PrinciplespomalNoch keine Bewertungen
- IoDokument26 SeitenIoSourav SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Control Blocks Linux PCBS: Operating Systems Operating Systems 2Dokument4 SeitenProcess Control Blocks Linux PCBS: Operating Systems Operating Systems 2Muhammad RizwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Input/outputDokument63 SeitenInput/outputrecompactedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Linux OverviewDokument81 Seiten02 Linux OverviewLmehyaoui TalalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Introduction p1Dokument7 Seiten1 Introduction p1Mohi Gpt4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Government College of Engineering, Nagpur: Operating System III Semester/ CSE (2021-2022)Dokument60 SeitenGovernment College of Engineering, Nagpur: Operating System III Semester/ CSE (2021-2022)Vishal KesharwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 5 System Software NotesDokument46 SeitenWeek 5 System Software Notesmesin basuhNoch keine Bewertungen
- It2354 2Dokument63 SeitenIt2354 2lnisarahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating System NotesDokument168 SeitenOperating System Notesishahma100% (1)
- Chapter 1Dokument32 SeitenChapter 1Fariha Nuzhat MajumdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solaris AdminDokument256 SeitenSolaris Adminsubhrajitm47Noch keine Bewertungen
- Inf583 3Dokument14 SeitenInf583 3Pocho GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Operating SystemsDokument33 SeitenIntroduction To Operating SystemsLennys Andés Vargas ValderramaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 System CallsDokument22 SeitenModule 1 System CallsJoseph PrasanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wa0016Dokument55 SeitenWa0016Naeem AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introductiontooscopy 20053013110Dokument27 SeitenIntroductiontooscopy 20053013110Balaji RamachandrakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 How Computers WorkDokument49 Seiten03 How Computers WorkBhagyashreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument14 SeitenChapter 3azwar charisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Introduction p3Dokument10 Seiten1 Introduction p3Mohi Gpt4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Operating System 4Dokument33 SeitenOperating System 4Seham123123Noch keine Bewertungen
- System Structure PDFDokument23 SeitenSystem Structure PDFh4nnrtmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Operating Systems Sixth EditionDokument70 SeitenUnderstanding Operating Systems Sixth EditionBSIT3_IT116Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2Dokument38 SeitenModule 2sueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dukungan Sistem OperasiDokument40 SeitenDukungan Sistem OperasiGamer PendekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-II Services and Components of Operating SystemDokument39 SeitenUnit-II Services and Components of Operating Systemrhythm -Noch keine Bewertungen
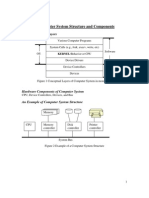
- Computer System Structure and ComponentsDokument5 SeitenComputer System Structure and ComponentsLucas ChengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 01Dokument9 SeitenLecture 01api-3801184Noch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Systems Lecture-1 OS Concepts: Tahira Alam University of Asia PacificDokument24 SeitenOperating Systems Lecture-1 OS Concepts: Tahira Alam University of Asia PacificMd SaifullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unix System Kernel: Instructor: S. Kiptoo Computer Science & IT Kimathi University College of TechnologyDokument79 SeitenUnix System Kernel: Instructor: S. Kiptoo Computer Science & IT Kimathi University College of TechnologyRamadhan Hassan NzuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating SystemDokument22 SeitenOperating SystemYashika MadanNoch keine Bewertungen
- File System Calls PPTDokument63 SeitenFile System Calls PPTpower starNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marking Scheme For Ris 958Dokument7 SeitenMarking Scheme For Ris 958Geay PeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aos - W03Dokument21 SeitenAos - W03GES ISLAMIA PATTOKINoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction Components Evolution and TYPES of OSDokument53 SeitenIntroduction Components Evolution and TYPES of OSPratibha BahugunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS2257Dokument43 SeitenCS2257ramauma100% (1)
- Operating Systems Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesVon EverandOperating Systems Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agile Key With Answers-Consolidated PDF Scrum (Software Development) Agile Software DevelopmentDokument1 SeiteAgile Key With Answers-Consolidated PDF Scrum (Software Development) Agile Software DevelopmentReena DewanganNoch keine Bewertungen
- PI Server Applications User Guide PI3 Server Version 3.4.370Dokument406 SeitenPI Server Applications User Guide PI3 Server Version 3.4.370vervesolar100% (1)
- Rundown Pembukaan (Kamis Siang) ADokument3 SeitenRundown Pembukaan (Kamis Siang) ARizky JPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generate Yearly Report - Walkthrough Hints PDFDokument23 SeitenGenerate Yearly Report - Walkthrough Hints PDFPablo Giordy Sánchez0% (1)
- WFC814 APIQuickStartDokument229 SeitenWFC814 APIQuickStartscribd_renjithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Library Management System ReportDokument23 SeitenLibrary Management System ReportUdupiSri groupNoch keine Bewertungen
- A10 Ddos DatasheetDokument12 SeitenA10 Ddos DatasheetAnilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yacto Errors PDFDokument98 SeitenYacto Errors PDFChinnathambi MuthusamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 22Dokument80 SeitenChapter 22Kushagra TiwaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- N00-341 IEC 60870-5-101 Protocol Technical Manual CAPM4-5Dokument88 SeitenN00-341 IEC 60870-5-101 Protocol Technical Manual CAPM4-5ndtdlhagiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.package - Installations - List - DMZ Prod PDFDokument3 Seiten6.package - Installations - List - DMZ Prod PDFAchour SiadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft Announces First Windows CE Shared Source Program To Allow Commercial Distribution of Modified Source Code - StoriesDokument11 SeitenMicrosoft Announces First Windows CE Shared Source Program To Allow Commercial Distribution of Modified Source Code - StoriesMariusz PruszowskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Production Process Has Two Machines. The First M...Dokument2 SeitenA Production Process Has Two Machines. The First M...Saiful IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Es I Sap Admin GuideDokument110 SeitenEs I Sap Admin GuideGuruprasad Tiptur Nagaraja0% (1)
- KVR32S22S8/16: Memory Module Specifi CationsDokument2 SeitenKVR32S22S8/16: Memory Module Specifi CationsJefry Gutiérrez CelisNoch keine Bewertungen
- nGeniusPULSE Virtual Install GuideDokument23 SeitennGeniusPULSE Virtual Install Guidemodather nadyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 93025409V1.1.R10 - V1 - 7210 Sas M Os 1.1 - R10Dokument20 Seiten93025409V1.1.R10 - V1 - 7210 Sas M Os 1.1 - R10DAGNUXNoch keine Bewertungen
- SW0D5-ALVLS-EUL License CD-ROMDokument11 SeitenSW0D5-ALVLS-EUL License CD-ROMGennaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monitor Logic Apps With Azure Monitor Logs - Azure Logic Apps - Microsoft DocsDokument19 SeitenMonitor Logic Apps With Azure Monitor Logs - Azure Logic Apps - Microsoft DocsasdfwefaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProjectDokument6 SeitenProjectAyush ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Format For Collecting Bank Details by Dating PDFDokument1 SeiteFormat For Collecting Bank Details by Dating PDFdianenicolle77Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab ExerciseDokument9 SeitenLab ExerciseSheila Mae FajutaganaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Python OopDokument10 SeitenPython OopRatsietsiMoketeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Software Performance Testing Handbook - A Comprehensive Guide For BegineersDokument124 SeitenSoftware Performance Testing Handbook - A Comprehensive Guide For BegineersNageshNoch keine Bewertungen
- T D L H: Echnical Ocumentation Ibrary ELPDokument32 SeitenT D L H: Echnical Ocumentation Ibrary ELPMohamed SalhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ar101 Week-5 PPTDokument28 SeitenAr101 Week-5 PPTGerong Jerome MarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aggl - Work Book - Etapa 1Dokument8 SeitenAggl - Work Book - Etapa 1alan guillermoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cliniview 10.0: User ManualDokument189 SeitenCliniview 10.0: User ManualSohail AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loops and Conditionals in MATLABDokument6 SeitenLoops and Conditionals in MATLABawais anwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Python Set Methods: Tutorials References Exercises Menu Paid CoursesDokument1 SeitePython Set Methods: Tutorials References Exercises Menu Paid CoursesKittin KaglaiNoch keine Bewertungen