Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
03-13 Mimics of Appendicitis
Hochgeladen von
eosfieldOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
03-13 Mimics of Appendicitis
Hochgeladen von
eosfieldCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Mimics of Appendicitis: Alternative Nonsurgical Diagnoses with Sonography and CT
OBJECTIVE
To
illustrate the imaging features of alternative nonsurgical disorders in patients presenting with clinical signs of appendicitis.
Normal and Inflamed Appendix
Normal appendix
Maximum outer diameter : 6mm Homogeneous noninflamed fat Compressible on US Often contains intraluminal gas
1. 2. 3. 4.
Inflamed appendix
1. Outer diameter : 6mm 2. Surrounded by hyperechoic inflamed fat on US 3. Extramural changes with fat stranding on CT 4. Presence of an appendicolith 5. Cecal apical thickening 6. Hypervascularity of the appendix wall on color Doppler sonography
Normal appendix
Inflamed Appendix
Nonsurgical Mimics of Appendicitis : Gastrointestinal Tract
1.
2. 3.
Gastrointestinal Tract
Mesenteric adenitis Infectious enterocolitis Epiploic appendages Omental infarction Right-sided colonic diverticulitis Crohns disease Ileocecal intussusception
4.
5. 6. 7.
Nonsurgical Mimics of Appendicitis : Gastrointestinal Tract
1.
Mesenteric adenitis
The second most common cause of RLQ pain after appendicitis US & CT : Cluster of enlarged mesenteric lymph nodes and no other abnormalities
Nonsurgical Mimics of Appendicitis : Gastrointestinal Tract
2. Infectious enterocolitis
Bacterial ileocecitis caused by Yersinia, Campylobacter, or Salmonella spp. US & CT : Mural thickening of the terminal ileum and cecum without inflammation of the surrounding fat and moderate mesenteric adenopathy
Nonsurgical Mimics of Appendicitis : Gastrointestinal Tract
3. Epiploic appendagitis
Epiploic appendage may undergo torsion and secondary inflammation. US & CT : An inflamed fatty mass adjacent to the colon containing a characteristic hyperattenuating ring of thickened visceral peritoneal lining Occasional dense central focus caused by a thrombosed vessel or hemorrhagic changes on CT.
Nonsurgical Mimics of Appendicitis : Gastrointestinal Tract
3. Omental infarction
Pathophysiology and clinical presentation similar to that of epiploic appendagitis Both have a similar benign natural history CT : A cakelike inflamed fatty mass larger than in epiploic appendagitis and lacking a hyperattenuating ring
Nonsurgical Mimics of Appendicitis : Gastrointestinal Tract
4. Right-sided colonic diverticulitis
In comparison with sigmoid diverticula, rightsided colonic diverticula are usually true diverticula Explain the essentially benign selflimiting character of right-sided diverticulitis US & CT : Inflammatory changes in pericolic fat Segmental thickening of the colonic wall at the level of an inflamed diverticulum
Nonsurgical Mimics of Appendicitis : Gastrointestinal Tract
5. Crohn's disease
Up to one-third of patients with ileocecal Crohn's disease present with initial symptoms so acute that they are misdiagnosed as appendicitis US & CT : Transmural bowel wall thickening, often predominantly of the submucosal layer, with frequent inflammatory changes of the surrounding fat in the acute active phase.
Nonsurgical Mimics of Appendicitis : Gastrointestinal Tract
6. Ileocecal intussusception
Peak age between 3 and 9 months Enlarged mesenteric lymph nodes or lymphoid hyperplasia of the distal ileum often acts as a lead point for intussusception US : A bowel-within-bowel configuration with a targetlike mass on sonography consisting of multiple concentric rings related to the invaginating layers of the bowel wall
Nonsurgical Mimics of Appendicitis : Genitourinary Tract
1.
2. 3.
Genitourinary Tract
Pelvic inflammatory disease Hemorrhagic functional ovarian cyst Urolithiasis
Nonsurgical Mimics of Appendicitis : Genitourinary Tract
1. Pelvic inflammatory disease
The imaging findings vary according to the severity of the disease and may be normal in early conditions. US & CT : Enlargement of the internal genital organs with indistinct contours and free pelvic fluid in more advanced stage.
Nonsurgical Mimics of Appendicitis : Genitourinary Tract
2. hemorrhagic ovarian cyst
Frequent cause of lower abdominal pain in the pubertal population
US & CT : A complicated cyst on sonography and a high-attenuation adnexal mass on unenhanced CT
Nonsurgical Mimics of Appendicitis : Genitourinary Tract
3. Urolithiasis
US & CT : Unenhanced CT is more accurate in detecting ureteral stones than sonography Hydronephrosis and a hydroureter as signs of obstruction
Nonsurgical Mimics of Appendicitis : Musculoskeletal Tract
1. Rectus sheath hematoma
Easy to diagnose in patients presenting with a painful palpable mass under anticoagulant therapy Small nonpalpable hematomas can clinically masquerade as appendicitis US & CT : Hemorrhagic mass within the sheath of the rectus abdominis muscle
CONCLUSION
A correct imaging diagnosis of these alternative disorders may have a major impact on patient management because it prevents an unnecessary operation or hospitalization.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Alteration in Elimination BowelDokument140 SeitenAlteration in Elimination BowelBayu Kxiikdx Lskd100% (1)
- Overview of Lower GastroIntestinal Bleeding 1.1Dokument42 SeitenOverview of Lower GastroIntestinal Bleeding 1.1Raja Ain100% (1)
- Duodenal ObstructionDokument53 SeitenDuodenal ObstructionBoby ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 판독 양식 (사랑 병원에서 쓰던거)Dokument24 Seiten판독 양식 (사랑 병원에서 쓰던거)eosfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- MR TempleteDokument3 SeitenMR TempleteeosfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- 판독 양식Dokument9 Seiten판독 양식eosfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- BI-RADS CategoryDokument1 SeiteBI-RADS CategoryeosfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Factor of Small Bowel Cancer in Crohn PTDokument2 SeitenRisk Factor of Small Bowel Cancer in Crohn PTeosfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Small Bowel Cancer in Crohn's Disease PatientDokument3 SeitenSmall Bowel Cancer in Crohn's Disease PatienteosfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
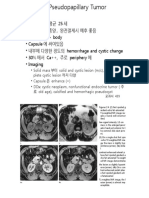
- - 젊은 여성, 평균 25 세 - 저등급 악성종양, 완전절제시 예후 좋음 - Tail > head> body - Capsule 에 싸여있음 - 내부에 다양한 정도의 hemorrhage and cystic change - 30% 에서 Ca++, 주로 periphery 에 - ImagingDokument2 Seiten- 젊은 여성, 평균 25 세 - 저등급 악성종양, 완전절제시 예후 좋음 - Tail > head> body - Capsule 에 싸여있음 - 내부에 다양한 정도의 hemorrhage and cystic change - 30% 에서 Ca++, 주로 periphery 에 - ImagingeosfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lateral EpicondylitisDokument3 SeitenLateral EpicondylitiseosfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paraduodenal HerniaDokument5 SeitenParaduodenal HerniaeosfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
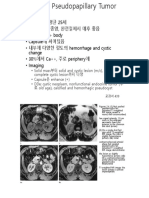
- - 젊은 여성, 평균 25세 - 저등급 악성종양, 완전절제시 예후 좋음 - Tail > head> body - Capsule에 싸여있음 - 내부에 다양한 정도의 hemorrhage and cystic change - 30%에서 Ca++, 주로 periphery에 - ImagingDokument2 Seiten- 젊은 여성, 평균 25세 - 저등급 악성종양, 완전절제시 예후 좋음 - Tail > head> body - Capsule에 싸여있음 - 내부에 다양한 정도의 hemorrhage and cystic change - 30%에서 Ca++, 주로 periphery에 - ImagingeosfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9월 1월례집담회 토픽데이 (IBD and mimickers) 새 케이스 추가Dokument27 Seiten9월 1월례집담회 토픽데이 (IBD and mimickers) 새 케이스 추가eosfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Small Bowel LymphomaDokument30 SeitenSmall Bowel LymphomaeosfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lateral EpicondylitisDokument3 SeitenLateral EpicondylitiseosfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiology - AFIP - 2006-2007 Lecture NotesDokument1.594 SeitenRadiology - AFIP - 2006-2007 Lecture Notesjvmeyer100% (1)
- Case 6Dokument1 SeiteCase 6eosfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Radiology of PleuraDokument122 SeitenThe Radiology of PleuraAimandu ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0418 발표용Dokument12 Seiten0418 발표용eosfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRI and CT Insufficiency Fractures of Pelvis and Proximal FemurDokument17 SeitenMRI and CT Insufficiency Fractures of Pelvis and Proximal FemureosfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mucinous Cystadenoma 0708Dokument12 SeitenMucinous Cystadenoma 0708eosfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osf Major Case StudyDokument19 SeitenOsf Major Case Studyapi-509667406Noch keine Bewertungen
- UC Case StudyDokument1 SeiteUC Case StudyDolly MadisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frequently Asked Questions On Digestive Health (English) : What Is The Digestive System?Dokument6 SeitenFrequently Asked Questions On Digestive Health (English) : What Is The Digestive System?Ronn BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Long Cases ADokument24 SeitenLong Cases Amieraf mesfinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDokument8 SeitenInflammatory Bowel Diseasevmc6gyvh9gNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st LE - Surgery 2Dokument3 Seiten1st LE - Surgery 2Valerie Gonzaga-CarandangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Choledocholithiasis: Prevalence IncidenceDokument9 SeitenCholedocholithiasis: Prevalence IncidenceMike GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease: DefinitionDokument4 SeitenInflammatory Bowel Disease: Definitionkarl abiaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buku Saku UrologiDokument33 SeitenBuku Saku UrologisitisarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver Cirrhosis Treatment in Kochi IndiaDokument3 SeitenLiver Cirrhosis Treatment in Kochi IndiaLiver Surgery IndiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irritable Bowel SyndromeDokument5 SeitenIrritable Bowel Syndromedrnareshkumar3281Noch keine Bewertungen
- InvaginasisDokument18 SeitenInvaginasisVanny FolandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Case StudyDokument3 SeitenAssignment Case StudyMian Waqar MunawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 6 Appendicitis and Diverticular Disease PDFDokument4 SeitenSession 6 Appendicitis and Diverticular Disease PDFGracia Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLD FinalDokument17 SeitenCLD FinalHervis FantiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar Power PointDokument20 SeitenSeminar Power PointNoor KhaiatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intestinal Obstruction PDFDokument4 SeitenIntestinal Obstruction PDFKiiza AloysiusNoch keine Bewertungen
- QirurgiaDokument132 SeitenQirurgiadex menkesNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCRN-PCCN Review GastrointestinalDokument23 SeitenCCRN-PCCN Review GastrointestinalGiovanni MictilNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 116 - RLE Activity#1 - VALDEZ PDFDokument6 SeitenNCM 116 - RLE Activity#1 - VALDEZ PDFDexel Lorren ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ROJoson PEP Talk: Liver Cancer and Viral Hepatitis AwarenessDokument70 SeitenROJoson PEP Talk: Liver Cancer and Viral Hepatitis AwarenessrojosonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estimasi Biaya Bedah DigestifDokument2 SeitenEstimasi Biaya Bedah DigestifDei RahayuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdominal Pains in Children Under 12Dokument5 SeitenAbdominal Pains in Children Under 12clubsanatateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Gallstone Disease in Adults - UpToDateDokument22 SeitenOverview of Gallstone Disease in Adults - UpToDateJoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heg PDFDokument18 SeitenHeg PDFannisarachmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hepatobiliary Disorders 2Dokument21 SeitenHepatobiliary Disorders 2KatrinaJimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- GastritisDokument10 SeitenGastritisMario100% (2)