Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Generate Electricity with Hydropower
Hochgeladen von
Pradeep Kumar MehtaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Generate Electricity with Hydropower
Hochgeladen von
Pradeep Kumar MehtaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
INTRODUCTION
In hydroelectric power station potential and kinetic energy of stored water is converted into electric energy . For hydro power station factors like rainfall,steam flow available head and storage facilities are studied. 25% of electricity generation capacity in world is provided by hydel power plant. In the countries like Norvey 99% electricity is produced by hydelpowerplant.
4% of the total hydel energy potential in world is in India.
In India 25.32% of total electricity generation capacity is produced by hydel power plant.
As per rocords of March-2000 23,816 MW electricity was generated by hydel power plant. It is increasing day by day because of the institutes like National Hydro Power Corporation Limited(NHPCL).
PURPOSES OF MULTIPURPOSE HYDROPROJECT
For
irrigation of agricultural land. For navigation. For fisheries and tourism. For flood control. For civil water supply. For generation of electricity.
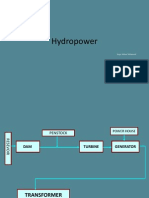
BASIC ELEMENTS OF HYDEL POWER PLANT
Reservoir Dam Trace
rack For bay Surge tank Penstock Spillway Turbine Powerhouse
CLASSIFICATION OF HYDEL POWER PLANT
According
to head :a) Low head plant b) Medium head plant c) High head plant According to load :a) Base load plant b) Peak load plant According to turbine specific speed:a) High specific speed plant b) Medium specific speed plant c) Low specific speed plant
WATER TURBINES USED IN HYDEL POWER PLANT
PELTON TURBINE
FRANCIS TURBINE
KAPLAN TURBINE
PELTON WHEEL
KAPLAN TURBINE
ADVANTAGES OF HYDEL POWER PLANT
This
plant is free from pollution. Its operation and maintenance cost is less. It has no stand by losses. Unit cost of power is less. Hydraulic turbines can be started speedily. The plant has longer service life. No fuel is required. No change in efficiency with the age.
DISADVANTAGES OF HYDEL POWER PLANT
Initial
cost of dam and plant is high. The availability of power from it is not much reliable. Loss of forest creates environmental problems. Due to evaporation , considerable water is lost. Time required for construction of hydroproject is more.
AUXILIARIES ATTACHED WITH HYDEL POWER PLANT.
(A)Electrical instruments Generator Exciter,transformers Switch gears Other instruments of control room (B)Mechanical instruments Shaft coupling,journal bearings,thrust bearings Lubricating oil system Cooling system Brake system for generatorturbine shaft
Lets see few of the International Hydel Power Plant Dam
Arch Dam Monticello Dam impounds Putah Creek west of Sacramento, California. The solid concrete structure stands 93 m (304 ft) tall. The dams arched upstream face transfers some of the pressure from its reservoir, Lake Berryessa, onto the walls of the canyon.
Kariba Arch Dam The Kariba Dam lies along the border between Zambia and Zimbabwe. The facility controls flooding and supplies hydroelectric power to both countries. A public road traces the rim of the dam, between reservoir Lake Kariba and the drop to the Zambezi River. The distinct arch shape distributes pressure evenly on the overall structure of the dam.
G and P Corrigan/Robert Harding Picture Library Hoover Dam The Hoover Dam is an arch-gravity dam on the Colorado River. Its reservoir, Lake Mead, lies between the states of Arizona and Nevada. As an arch-gravity dam, it depends on its shape and its own weight for stability.
Lake Mead Lake Mead, a vast artificial lake, straddles the border between Arizona and Nevada. The lake was formed by the construction of the Hoover Dam on the Colorado River. During wet periods, it stores excess water until it is needed. Lake Mead has also become a popular area for boating and other recreational activities.
Flat Slab Buttress Dam Lake Tahoe Dam impounds the Truckee River in northern California. Like all flat slab buttress dams, it has a flat slab upstream face supported by a series of buttresses on the downstream side. Lake Tahoe Dam measures 5.5 m (18 ft) tall and 33 m (109 ft) long. It was completed in 1913 to raise the water level in Lake Tahoe, a natural lake, to provide additional water for crop irrigation.
Multiple Arch Dam Bartlett Dam impounds the Verde River northeast of Phoenix, Arizona. Like all multiple arch dams, Bartlett Dam makes use of a series of arches supported by buttresses to withstand the pressure of the water in its reservoir, Bartlett Lake. Each of the dams 10 concrete arches has a 7-m (24ft) radius and measures 2 m (7 ft) at the base and just 0.6 m (2 ft) at the crest. The thick base provides additional strength at the bottom of the reservoir, where the water pressure is most intense.
Concrete Gravity Dam Shasta Dam impounds the Sacramento River in northern California. Like all concrete gravity dams, Shasta Dam holds back the water in its reservoir, Shasta Lake, by the sheer force of its weight. Built of solid concrete, the massive structure rises 183 m (602 ft). It measures 165 m (542 ft) at the base and just 9 m (30 ft) at the crest. This shape, typical of concrete gravity dams, counteracts the force of the water pressing against the dam at the bottom of the reservoir, where the pressure is most intense.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hydro Electric Power Plant 568a6d753e8bfDokument35 SeitenHydro Electric Power Plant 568a6d753e8bfAd Man GeTigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Training RestDokument35 SeitenPractical Training RestĎąŕ BäbăřNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parker DamDokument9 SeitenParker Damlana mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power of WaterDokument60 SeitenPower of WaterAdnan MehmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detail Study of Hydroelectric Power PlantDokument139 SeitenDetail Study of Hydroelectric Power PlantDivyansh Singh ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- HYDROPOWER GENERATION FROM MOVING WATERDokument32 SeitenHYDROPOWER GENERATION FROM MOVING WATERPrakhar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Larji Report Edited - 2Dokument37 SeitenLarji Report Edited - 2SachinSharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReprtDokument24 SeitenReprtDivyanshu PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magat DamDokument7 SeitenMagat DamJennie Vicenta0% (1)
- Hydroelectric Power Plants: Created By: Jasper Dickson Grade Level: High School Project Number: 38Dokument3 SeitenHydroelectric Power Plants: Created By: Jasper Dickson Grade Level: High School Project Number: 38Logu12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hydropower Seminar ReportDokument19 SeitenHydropower Seminar Reportmichealfajobi7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hydroelectric Power PlantDokument25 SeitenHydroelectric Power PlantPrasun BajracharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TIDAL AND HYDEL ENERGY - by MAHIMADokument22 SeitenTIDAL AND HYDEL ENERGY - by MAHIMAMahima KamraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydro Power PlantDokument93 SeitenHydro Power PlantAnonymous gb6ARMgNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Hydroelectric Power in IndiaDokument18 SeitenHistory of Hydroelectric Power in IndiaIshwari TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydral Power PlantDokument28 SeitenHydral Power PlantFarman AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report On Water TurbinesDokument62 SeitenProject Report On Water TurbinesIndranil Ganguly100% (1)
- UNIT-I Hydro and Thermal Power PlantsDokument114 SeitenUNIT-I Hydro and Thermal Power PlantsManish MadhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic EnergyDokument10 SeitenHydraulic EnergySameer KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydro Electric Power PlantDokument7 SeitenHydro Electric Power PlantMuhammad SaqlainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bakun DamDokument33 SeitenBakun DamChyNaluri8971% (7)
- HYDRO POWER PLANT GUIDEDokument9 SeitenHYDRO POWER PLANT GUIDEKorsa KorsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How hydropower works to generate renewable energyDokument11 SeitenHow hydropower works to generate renewable energyRichard ManongsongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Power EngineeringDokument14 SeitenWater Power EngineeringSAMIM100% (1)
- Hydro Technology FAQsDokument12 SeitenHydro Technology FAQsriteshreplyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument13 SeitenChapter 2Aung KhantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction Synopsis Hydro Power PlantDokument7 SeitenIntroduction Synopsis Hydro Power PlantSuresh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waterwheels, Turbines, and Mills: Hydropower TypesDokument4 SeitenWaterwheels, Turbines, and Mills: Hydropower TypesDiana AbalosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 08 Hydro PowerDokument65 Seiten08 Hydro PowerMuhammad BurhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydroelectric Power: Potential Energy Kinetic Renewable DamDokument5 SeitenHydroelectric Power: Potential Energy Kinetic Renewable Damsudeep9666Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tidal Energy Real 2Dokument26 SeitenTidal Energy Real 2Erman DeanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fact Sheet 6: Hydro Electricity: History and DevelopmentDokument9 SeitenFact Sheet 6: Hydro Electricity: History and DevelopmentbigadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Hydro Power PlantDokument17 SeitenReport On Hydro Power PlantVikas Kumar50% (2)
- Report On Hydro Power PlantDokument12 SeitenReport On Hydro Power PlantVishnu NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tidal EnergyDokument7 SeitenTidal EnergyMohit DalalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydro Power PlantDokument37 SeitenHydro Power PlantSaini YatendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydropower Plant Report - RemovedDokument8 SeitenHydropower Plant Report - RemovedBivash PanditNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generate Clean Energy from Flowing WaterDokument27 SeitenGenerate Clean Energy from Flowing Watershimoto18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hydro Electric PowerDokument78 SeitenHydro Electric PowerVamsi100% (1)
- Group No. 1 Energy Engineering PresentationDokument34 SeitenGroup No. 1 Energy Engineering PresentationTabi RajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydro Power StructuresDokument29 SeitenHydro Power StructuresVignesh TamilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science: Project inDokument11 SeitenScience: Project inMelissa Oliver MachicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tidal EnergyDokument9 SeitenTidal EnergydalerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydroelectric Power Stations Lecture (BEEDokument73 SeitenHydroelectric Power Stations Lecture (BEEMeezan StationersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydropower GenerationDokument6 SeitenHydropower Generationfgh.fhg751Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hydroelectric Power: Harnessing the FlowDokument17 SeitenHydroelectric Power: Harnessing the FlowAatif AltafNoch keine Bewertungen
- AENG 80 Microhydro NotesDokument39 SeitenAENG 80 Microhydro NotesRufina RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydroelectric Power Plant For TERIDokument41 SeitenHydroelectric Power Plant For TERIAnonymous nF09cqwNKNoch keine Bewertungen
- DEMONSTRATION OF A HYDRO POWER STATIONDokument5 SeitenDEMONSTRATION OF A HYDRO POWER STATIONsmh khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proiect Ces FinDokument11 SeitenProiect Ces FinMadalina MolnarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Selection of Turbines PPT BestDokument68 SeitenDesign and Selection of Turbines PPT BestAdhanom G.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hudro Electric Power PlantDokument84 SeitenHudro Electric Power PlantNilesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Power Plant PPE-UNIT-IIIDokument15 SeitenHydraulic Power Plant PPE-UNIT-IIISacet 2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- hydro and geo electric powerDokument54 Seitenhydro and geo electric powerTMedhin MisganawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydro Electric Power Plant 28012019Dokument85 SeitenHydro Electric Power Plant 28012019Rahul YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Hydropower TurbinesDokument11 SeitenTypes of Hydropower TurbinesfazarbadhushaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Incoming Resource Capital Resource: Winds Vegetation Solar RadiationDokument56 SeitenIncoming Resource Capital Resource: Winds Vegetation Solar RadiationVilash ShingareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity for the farm: Light, heat and power by inexpensive methods from the water wheel or farm engineVon EverandElectricity for the farm: Light, heat and power by inexpensive methods from the water wheel or farm engineNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effects of Supercharging On The Performance of C.I Engine Using Blends of Pre-Heated Cotton Seed Oil and Diesel As Alternate FuelDokument4 SeitenThe Effects of Supercharging On The Performance of C.I Engine Using Blends of Pre-Heated Cotton Seed Oil and Diesel As Alternate FuelPradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effects of Supercharging On The Performance and Exhaust Gas Emissions of A Dual-Fuel Engine Fueled With Producer Gas-Diesel and Palm Oil BlendsDokument8 SeitenThe Effects of Supercharging On The Performance and Exhaust Gas Emissions of A Dual-Fuel Engine Fueled With Producer Gas-Diesel and Palm Oil BlendsPradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Engineering Graphics Xii PDF For WebDokument180 SeitenFinal Engineering Graphics Xii PDF For WebRicha Sahni100% (1)
- MMM Lab Manual 10mel47bDokument108 SeitenMMM Lab Manual 10mel47bsimalaraviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Download MATLAB R2015aDokument6 SeitenDownload MATLAB R2015aPradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Residual Signal Techniques Used For Gear Fault DetectionDokument7 SeitenResidual Signal Techniques Used For Gear Fault DetectionPradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CricketDokument3 SeitenCricketPradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effects of Supercharging On The Performance and Exhaust Gas Emissions of A Dual-Fuel Engine Fueled With Producer Gas-Diesel and Palm Oil BlendsDokument8 SeitenThe Effects of Supercharging On The Performance and Exhaust Gas Emissions of A Dual-Fuel Engine Fueled With Producer Gas-Diesel and Palm Oil BlendsPradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 22-23-24 Time Domain Analysis of 2nd Order SystemsDokument73 SeitenLecture 22-23-24 Time Domain Analysis of 2nd Order SystemsPradeep Kumar Mehta100% (1)
- TM16 Experimental Vibration Using The Universal Vibration ApparatusDokument1 SeiteTM16 Experimental Vibration Using The Universal Vibration ApparatusPradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MatlabDokument93 SeitenMatlabPradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 Dynamic Modelling of A One Stage Spur Gear System and Vibration Based Tooth Crack Detection Analysis MohammedDokument13 Seiten2015 Dynamic Modelling of A One Stage Spur Gear System and Vibration Based Tooth Crack Detection Analysis MohammedPradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Universal Vibration (A)Dokument34 SeitenUniversal Vibration (A)shajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Create Object For Recording - MATLAB AudiorecorderDokument2 SeitenCreate Object For Recording - MATLAB AudiorecorderPradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gear Dof Fig.Dokument10 SeitenGear Dof Fig.Pradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010-Automatic Faults Diagnosis by Application of Neural Network System and Condition-Based Monitoring Using Vibration Signals-Adyles Arato JuniorDokument11 Seiten2010-Automatic Faults Diagnosis by Application of Neural Network System and Condition-Based Monitoring Using Vibration Signals-Adyles Arato JuniorPradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010-A Novel Method For The Optimal Band Selection For Vibration Signal Demodulation and Comparison With The Kurtogram-Tomasz BarszczDokument21 Seiten2010-A Novel Method For The Optimal Band Selection For Vibration Signal Demodulation and Comparison With The Kurtogram-Tomasz BarszczPradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 Effect of Backup Ratio and Cutter Tip Radius On Uniform Bending Strength Design of Spur Gears SekarDokument10 Seiten2014 Effect of Backup Ratio and Cutter Tip Radius On Uniform Bending Strength Design of Spur Gears SekarPradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010-Advantages and Drawbacks of Applying Periodic Time-Variant Modal Analysis To Spur Gear Dynamics-Rune PedersenDokument14 Seiten2010-Advantages and Drawbacks of Applying Periodic Time-Variant Modal Analysis To Spur Gear Dynamics-Rune PedersenPradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Below Is The Sectional Cutoff For IBPS PO 2014Dokument3 SeitenBelow Is The Sectional Cutoff For IBPS PO 2014Pradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 1 1 469 5945Dokument21 Seiten10 1 1 469 5945Pradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2009-Vibration-Based Fault Diagnosis of Spur Bevel Gear Box Using Fuzzy Technique-N. SaravananDokument17 Seiten2009-Vibration-Based Fault Diagnosis of Spur Bevel Gear Box Using Fuzzy Technique-N. SaravananPradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rate of Interest On Single Domestic Term DepositsDokument2 SeitenRate of Interest On Single Domestic Term DepositsPradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 100 Hindi Gkq1Dokument3 Seiten100 Hindi Gkq1javed alamNoch keine Bewertungen
- On The Capacity of A Cellular CDMA System.: - Anshul PopatDokument23 SeitenOn The Capacity of A Cellular CDMA System.: - Anshul PopatPradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MPPSC General Studies Question PapersDokument39 SeitenMPPSC General Studies Question PapersPradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General SocioDokument22 SeitenGeneral SocioPradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MP Forest PaperDokument21 SeitenMP Forest PaperPradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experience CertificatesDokument3 SeitenExperience CertificatesPradeep Kumar MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflammability and Health Risks of Lubricant Oil 5W30 SNDokument9 SeitenInflammability and Health Risks of Lubricant Oil 5W30 SNPerformance Lubricants, C.A.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Parliamentary Procedure in The Conduct of Business MeetingDokument14 SeitenParliamentary Procedure in The Conduct of Business MeetingEstephanie SalvadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydro Skimming Margins Vs Cracking MarginsDokument78 SeitenHydro Skimming Margins Vs Cracking MarginsWon Jang100% (1)
- Erasmo WongDokument3 SeitenErasmo WongGabriel GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge O Level: English Language 1123/21Dokument8 SeitenCambridge O Level: English Language 1123/21Fred SaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geo 2230 MJ 02Dokument8 SeitenGeo 2230 MJ 02Jason 402Noch keine Bewertungen
- Itc Diversification Case SolutionDokument40 SeitenItc Diversification Case SolutionDivya PujariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self-Certification and Medical Examiner's Certificate ReportingDokument2 SeitenSelf-Certification and Medical Examiner's Certificate ReportingcatrutterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banking Sector Project ReportDokument83 SeitenBanking Sector Project ReportHarshal FuseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Organization Climate On Innovative Work BehaviourDokument8 SeitenEffect of Organization Climate On Innovative Work BehaviourRaja .SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Accounting 1: Accounting Lab Module Uph Business SchoolDokument36 SeitenAdvanced Accounting 1: Accounting Lab Module Uph Business SchoolDenisse Aretha LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MJ1000-Motorola IncDokument4 SeitenMJ1000-Motorola IncFrancisco DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- BBEK4203 Principles of MacroeconomicsDokument20 SeitenBBEK4203 Principles of MacroeconomicskiranaomomNoch keine Bewertungen
- 26-200 kVA BrochureDokument16 Seiten26-200 kVA Brochureargo kuncahyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Win Server 2008 Manual Installation PDFDokument20 SeitenWin Server 2008 Manual Installation PDFFery AlapolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Access User GuideDokument49 SeitenAccess User GuideShivaji JagdaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biju Patnaik University of Technology MCA SyllabusDokument18 SeitenBiju Patnaik University of Technology MCA SyllabusAshutosh MahapatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- City Profil Addis AbabaDokument33 SeitenCity Profil Addis AbabaEyuale TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 The Nature of Strategic Management2Dokument8 SeitenModule 1 The Nature of Strategic Management2Julienne LobchoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approved Term of Payment For Updating Lower LagunaDokument50 SeitenApproved Term of Payment For Updating Lower LagunaSadasfd SdsadsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S1350630720317192 MainDokument16 Seiten1 s2.0 S1350630720317192 MainmaximNoch keine Bewertungen
- NFL 101 Breaking Down The Basics of 2-Man CoverageDokument10 SeitenNFL 101 Breaking Down The Basics of 2-Man Coveragecoachmark285Noch keine Bewertungen
- Prateek Chhabra - (C.V.) 22-08Dokument4 SeitenPrateek Chhabra - (C.V.) 22-08PrateekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth / Ground Test (Version 1) : Za'immul Na'imDokument4 SeitenEarth / Ground Test (Version 1) : Za'immul Na'imMd Rodi BidinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stare DecisisDokument7 SeitenStare DecisisBirolal Jamatia100% (1)
- Flyrock Prediction FormulaeDokument5 SeitenFlyrock Prediction FormulaeAmy LatawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MasterCard Approves PAX Card ReaderDokument2 SeitenMasterCard Approves PAX Card ReaderThinakaran RajamoorthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Completing The Accounting Cycle: © 2009 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights ReservedDokument57 SeitenCompleting The Accounting Cycle: © 2009 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights ReservedPham Thi Hoa (K14 DN)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Autox - December 2019 PDFDokument162 SeitenAutox - December 2019 PDFtae talNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Data Sheet for Anionic Polymer LiquidDokument6 SeitenSafety Data Sheet for Anionic Polymer LiquidZi Wei LeongNoch keine Bewertungen