Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Liver Diseases: Dr. Avnish Upadhyay Senior Research Scientist, Patanjali Yog Peeth, Haridwar
Hochgeladen von
Dr. Avnish Upadhyay0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
213 Ansichten22 SeitenOriginaltitel
Liver Disease Avnish
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
213 Ansichten22 SeitenLiver Diseases: Dr. Avnish Upadhyay Senior Research Scientist, Patanjali Yog Peeth, Haridwar
Hochgeladen von
Dr. Avnish UpadhyayCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 22
Liver Diseases
Dr. Avnish Upadhyay
Senior Research Scientist, Patanjali Yog
Peeth, Haridwar
1. Introduction
a. anatomical Position and weight.
b. Functions- Processing most of the nutrients
absorbed from the intestine.
c. Removing drugs, Alcohol and harmful
substances from the blood stream.
d. Manufacturing bile, its storage in GB.
e. Produces cholesterol- Blood clotting factors
and certain other Proteins.
f. The liver may be Palpable in normal healthy
adult, 10 to 12% are such cases.
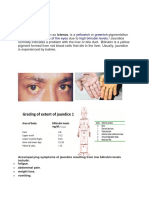
Healthy Liver
This is what a healthy
liver is supposed to
look like:
Damaged Liver
This is what a
damaged liver looks
like:
Damaged liver Continuation
2. Examination of Liver
1. On inspection if one sees
a. swelling in the Rt. Hypochondria which on
palpation seems to be in the liver the
common conditions are
1. Amoebic Liver Abscesses.
2. A malignancy
b. First palpate Right and then Lt Lobe of Liver.
c. Edge whether thin or thick, firm or soft.
d. Surface- smooth or nodular.
e. Pulsatile Tricuspid Regurgitation.
2. Examination of Liver Contd.
2. Look for Tenderness- it is very important Point to
consider. it is tender in 3 conditions.
a. Infective hepatitis.
b. Amoebic Hepatitis and Amoebic Abscess.
c. CCF
Exclude CCF by the presence of dyspnoea,
enlarged heart, engorged neck veins, edemas of
feet.
Now there remain 2 common causes
1. Hepatic Amoebiasis or Amoebic Liver Abscess.
2. Infective Hepatitis
3. Hepatic Amoebiasis
It includes Amoebic Hepatitis and Amoebic Liver
Abscess
a. main symptom is pain in hypochondria (Right) and /or
epigastria rarely in Rt Shoulder
b. it may be of dull ache or as severe as biliary colic
c. The duration of pain Could be from a few days to few
weeks.
d. The pain in increased on turning on the side, more on the
Rt Side.
e. The pain is increased on deep breathing.
f. Nausea. Vomiting, lose of appetite, jaundice are absent.
g. alcoholic are more prone to get disease.
h. Past history of dysentery may or may not be present
however a recent attack of diarrheas or dysentery if
present would favour the diagnosis very much.
4. Physical sign is Tenderness of the Liver
a. May be elicited by hammering over the liver area Or
by pressure on subcostal area after a deep
inspiration. Rarely tenderness may be only in the
epigastria in the area of left lobe. The liver may not
be enlarged or may be enlarged, slightly, moderately
or markedly, Therefore more time should be give in
eliciting tenderness than size of the liver.
b. A lump in the liver area is a rarity.
c. No investigations are required. The may be normal
raised.
d. The Rt dome of diaphragm may be raised or
immobile. Immobility is more important. It can be
seen on screening of the chest (Fluoroscopy)
e. Best is Therapeutic test with emetine Injection.
Treatment
1. Emetine 60 mg 1M for 8-10 days - Rest if Possible
2. Chloroguin or Metronidazole- 2 Tabs twice daily
for 2 days. After then 1 Tab twice daily for 21
days (May cause slight nausea)
Flagyl (Metronidazole):- 400 to 800 mg TD for 8
days may cause nausea and loss of appetite but
this is the effective dose, Dose of 200 mg TD is
only for infantile amoebiasis.
If pain, fever and tenderness of the liver persists
ever after emetine Tapping must not be delayed
finally, if an obvious lump is seen in the liver
area, it would always need aspiration.
INFECTIVE HEPATITIS
It is due to virus and therefore a single case can
infect many others, So it should be taken
seriously.
Incubation Period is about 3-4 weeks, history of
jaundice in any family member or any friend,
neighbor or locality during past one month is an
important point to be elicited in history taking.
One can get 2-3 attacks of viral hepatitis during
the life time
Disease is common in small children and young
adults, It is rare after the age of 45-50 yrs.
Dot Call This disease "Jaundice" because
Many People may suffer and recover without
jaundice. The patient get loss of appetite, slight
nausea and do not generally feel well for a week
or two. The only way to diagnose will be, by
eliciting history of jaundice in the family or
neighborhood during previous 3-4 weeks. An the
same time, in that particular patient, it is
impossible whether he is going to develop
jaundice or whether he would recover without
developing jaundice. Jaundice without jaundice
is called anicteric jaundice.
Fever with complete loss of appetite.
Surgical jaundice will have to be excluded,
surgical jaundice means jaundice caused by the
disease which produce obstruction the flow of
bile and the treatment is mainly surgical such as
bile duct obstruction due to stones.
Carcinoma head pancreas (leading to
obstructing common bile ducts) Presence of
one or more severe upper abdominal pain, while
colored stool and excessive pruritis would
favour for surgical jaundice.
Prolonged administration of hormones or
promazine group of drugs will favour the
diagnosis of drug hepatits.
Three stages
Stage 1
Complete loss of appetites, Patient does not
want even to see food. Nausea, vomiting,
Fever, body ache, general malaise. In the 1st
week there is no evidence of jaundice.
Towards the end of 1st week the patient
might notice very high colored urine.
In viral hepatitis patient don’t complain of pain
in the liver area, may complain vague
discomfort on questioning. Patient to may
lose 2-3 kg body weight.
Stage 2
Patient's relatives see jaundice.
As Jaundice deepens, the temperature
starts coming down and appetite starts
improving, So that by the end of 2nd week
the patient is left with deep Jaundice but
good appetite and no fever.
Stage 3
Recovering to normal. Resume his work
Appetite improve weight gains. Jaundice
clears up by the end of third week.
90-95% behave the above manner, 5 to 10
PC would die after going to hepatic coma
(specially Pregnant women)
Symptoms of Prehepatic coma
1. Presence of Drowsiness
2. Abnormal Behavior
3. Irritability
4- Tremors
Better to hospitalize
nothing can be done at this stage.
Signs of Infective hepatitis
Jaundice
Tender liver
may be enlarged and may bends
Enlarged.
Investigations
SGPT
SGOT
Serum Billirubin
Treatment
1. Inj Gamma Globulin .06 cc/LB body weight
should be given to all family members as
prophylaxis, but they are very costly but
should ideally be give to all family.
2. Tonics for appetite, Inj glucose 25 pc Iv. Cal.
gluconate iv, Inj B comp., vit c, vit k,
Antibiotics, Prednisolone 1 BD or TD, Inj.
liver ext., two drugs are harmful as they can
precipitate hepatic coma. only glucose iv or
orally is useful along with rest.
Drugs
Antihistaminic and IV glucose is sufficient.
In severe case prednisolone 40 to 60 mg/day
gradually tapered off very slowly
danger signals
The following are the danger signals, the
presence of any of them indicates on coming
hepatic coma and death
1. Drowsiness
2. Reversal of sleep rhythm
3. Irritability
4. Tremors
Deep Jaundice is not a sign of danger.
Thanks
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Acute Cholecystitis ER AdmissionDokument6 SeitenAcute Cholecystitis ER Admissionjessica100% (5)
- Case Study 101: Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm With Acute Kidney InjuryDokument8 SeitenCase Study 101: Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm With Acute Kidney InjuryPatricia Ann Nicole ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study On Jaundice With AnswersDokument4 SeitenCase Study On Jaundice With Answersabirami pNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Grey Nomads Guide To AustraliaDokument3 SeitenThe Grey Nomads Guide To AustraliaFreerangecamping60% (5)
- Case Study2Dokument11 SeitenCase Study2Jainet Aira S. AmanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Glomerular Nephritis V.S Nephrotic SyndromeDokument4 SeitenAcute Glomerular Nephritis V.S Nephrotic SyndromeYoussef AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver - Dr. Allam 2021 PDFDokument70 SeitenLiver - Dr. Allam 2021 PDFMohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkaloids AvnishDokument16 SeitenAlkaloids AvnishDr. Avnish Upadhyay100% (22)
- Ford 1982 3.8L V6Dokument22 SeitenFord 1982 3.8L V6sc100% (1)
- Template EbcrDokument7 SeitenTemplate EbcrNoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hepatobiliary DisorderDokument49 SeitenHepatobiliary DisorderAhmed KanemazeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nurse caring for patient with abdominal mass and bowel obstructionDokument12 SeitenNurse caring for patient with abdominal mass and bowel obstructionabezareljvenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 5 - Pancreatitis-1Dokument4 SeitenCase 5 - Pancreatitis-1ngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peeds Infection LecturesDokument190 SeitenPeeds Infection LecturesAli Al.JuffairiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gi SMB - Clin MedDokument5 SeitenGi SMB - Clin MedSohil PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hepatic FailureDokument37 SeitenHepatic FailureWinston Dela FuenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Diarrhea 678Dokument24 SeitenAcute Diarrhea 678Sheren GamaleldenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Git 3 PDFDokument9 SeitenGit 3 PDFAnonymous biAu5PONoch keine Bewertungen
- Chart Data:: - She Was Given A Diamicron 60mg/tab OD - Pritor Plus 40 MG OD and Lacipil 2 MG ODDokument4 SeitenChart Data:: - She Was Given A Diamicron 60mg/tab OD - Pritor Plus 40 MG OD and Lacipil 2 MG ODSkyla FiestaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gallbladder DisordersDokument59 SeitenGallbladder DisordersdrelvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diseases of The Stomach:-ObjectivesDokument14 SeitenDiseases of The Stomach:-Objectiveshussain AltaherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gallbladder & Liver Disorders GuideDokument82 SeitenGallbladder & Liver Disorders Guidem1k0e100% (2)
- Diarrhea 1Dokument5 SeitenDiarrhea 1Mohammed Taha Al-nuaimyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SurgDokument4 SeitenSurgSoumabho ParuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACUTE (Suddenly) CHRONIC (Gradually)Dokument6 SeitenACUTE (Suddenly) CHRONIC (Gradually)Kristiene Kyle AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estu LBM 2Dokument12 SeitenEstu LBM 2Roby SandeiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Betty JaundiceDokument6 SeitenBetty JaundicediniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgery: Small & Large IntestineDokument15 SeitenSurgery: Small & Large Intestineapi-3829364100% (1)
- GIT History TakingDokument7 SeitenGIT History TakingDarawan MirzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patofisiologi DiareDokument45 SeitenPatofisiologi DiareAngela Kristiana Intan100% (1)
- 2300 - Module 8 - Gastrointestinal and Genitourinary EmergenciesDokument14 Seiten2300 - Module 8 - Gastrointestinal and Genitourinary Emergenciesmegan.abbinkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perforated Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDokument2 SeitenPerforated Peptic Ulcer DiseaseRene John FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case ADokument2 SeitenCase Aapi-26938624Noch keine Bewertungen
- Git MRCGP 2015Dokument170 SeitenGit MRCGP 2015AlexandraOsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- What is acute pancreatitis? Causes, symptoms and treatmentDokument6 SeitenWhat is acute pancreatitis? Causes, symptoms and treatmentpanduranganraghuramaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ladja, Irish V. BSN 3-C Laboratory ResultsDokument13 SeitenLadja, Irish V. BSN 3-C Laboratory ResultsEzra LambarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Nausea and Vomiting: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDokument25 SeitenUnderstanding Nausea and Vomiting: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentYosr Samia Abou SediraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report Introduction GastritisDokument4 SeitenReport Introduction GastritisTanpa NamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Git 2Dokument18 SeitenGit 2Mateen ShukriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver Nursing NotesDokument7 SeitenLiver Nursing NotesHeather ShantaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMQs For Medical Students Volume 2 2eDokument30 SeitenEMQs For Medical Students Volume 2 2ePasTestBooks50% (2)
- Biliary System and PancreasDokument10 SeitenBiliary System and Pancreasjinkym123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive Symptoms Knowledge QuizDokument4 SeitenDigestive Symptoms Knowledge Quizajal hamzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What is Crohn's Disease? Understanding Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentDokument6 SeitenWhat is Crohn's Disease? Understanding Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentSami ShouraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alimentary and Biliary Conditions 3-1Dokument249 SeitenAlimentary and Biliary Conditions 3-1Mercy KeruboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ornopia - MS 2 PancreatitisDokument3 SeitenOrnopia - MS 2 PancreatitisORNOPIA, JOUELLA ANNE C.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Diverticulosis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesVon EverandDiverticulosis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- Jaundice, (Hyperbilirubinemia) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandJaundice, (Hyperbilirubinemia) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Salmonella, Campylobacter, Yersinia Enterocolitica and Shigella InfectionsDokument3 SeitenSalmonella, Campylobacter, Yersinia Enterocolitica and Shigella InfectionsKelvin BolusanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bowel Obstruction With Acute Renal Failure Central BaptistDokument13 SeitenBowel Obstruction With Acute Renal Failure Central BaptistJason SturgeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Report On CRF PrtatikDokument7 SeitenCase Report On CRF PrtatikOm PalekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- c-7 Case PresentatonDokument11 Seitenc-7 Case PresentatonRaja0% (1)
- EMQs for Medical Students Volume 2 GastroenterologyDokument30 SeitenEMQs for Medical Students Volume 2 Gastroenterologynob2011nob100% (1)
- Pancreatic Disease1Dokument24 SeitenPancreatic Disease1Hero StoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Mayo Clinic Proceedings, Jan 2022) - 75 Year Old Woman With Abdominal Pain and ConstipationDokument5 Seiten(Mayo Clinic Proceedings, Jan 2022) - 75 Year Old Woman With Abdominal Pain and ConstipationNigelyulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive Health Nursing Review QuestionsDokument37 SeitenDigestive Health Nursing Review QuestionsNorPhea - នភាNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managing Diverticulitis RecoveryDokument21 SeitenManaging Diverticulitis RecoveryTiffany AdriasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Typhoid Fever: by DR .. Magdi Elbaloola Ahmed Physcian & GastrohepatologistDokument25 SeitenTyphoid Fever: by DR .. Magdi Elbaloola Ahmed Physcian & GastrohepatologistÅbübâkêř Äbd-ëřhēēm BãřřîNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pembahasan To Online 5Dokument522 SeitenPembahasan To Online 5vanadiel4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis (IHPS) : IncidenceDokument9 SeitenInfantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis (IHPS) : IncidenceRaed AlhnaityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jaundice Natural RemediesDokument12 SeitenJaundice Natural RemediesprkshshrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sir Yahaya Memorial Hospital Birnin Kebbi: Nursing DepartmentDokument7 SeitenSir Yahaya Memorial Hospital Birnin Kebbi: Nursing DepartmentyusufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jaundice Symptoms, Causes and Treatment ExplainedDokument7 SeitenJaundice Symptoms, Causes and Treatment ExplainedKesyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNIS ProfileDokument7 SeitenDNIS ProfileDr. Avnish UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- BAMS, PGDCR, ROTP, Ph.D. (Pursuing)Dokument48 SeitenBAMS, PGDCR, ROTP, Ph.D. (Pursuing)Dr. Avnish UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aloe Berry Juice Relieves Psycho-Somatic DisordersDokument4 SeitenAloe Berry Juice Relieves Psycho-Somatic DisordersDr. Avnish UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of The Efficacy and Safety of Proprietary Ayurvedic CombinationDokument7 SeitenEvaluation of The Efficacy and Safety of Proprietary Ayurvedic CombinationDr. Avnish UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Other Liver Disease AvnishDokument21 SeitenOther Liver Disease AvnishDr. Avnish Upadhyay100% (1)
- AIDS ProtocolDokument24 SeitenAIDS ProtocolDr. Avnish UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- ModelProjectReport ICCrevised 030112Dokument15 SeitenModelProjectReport ICCrevised 030112Dr. Avnish UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rural Marketing & NGOsDokument26 SeitenRural Marketing & NGOsDr. Avnish UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- AshwashilaDokument3 SeitenAshwashilaDr. Avnish UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypertension Protocol Mukta VatiDokument18 SeitenHypertension Protocol Mukta VatiDr. Avnish UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asthma Protocol SwasariDokument21 SeitenAsthma Protocol SwasariDr. Avnish UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final PresentationDokument16 SeitenFinal PresentationDr. Avnish Upadhyay100% (3)
- Existing Processing UnitsDokument13 SeitenExisting Processing UnitsDr. Avnish UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Breast CancerDokument21 SeitenProject Breast CancerDr. Avnish UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mega Food Parks IndiaDokument2 SeitenMega Food Parks IndiaDr. Avnish UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Ayurved Research and DevelopmentDokument14 SeitenDepartment of Ayurved Research and DevelopmentDr. Avnish UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathological Parameters (LFT)Dokument1 SeitePathological Parameters (LFT)Dr. Avnish UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathological Parameters (LFT)Dokument1 SeitePathological Parameters (LFT)Dr. Avnish UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathological Parameters (LFT)Dokument1 SeitePathological Parameters (LFT)Dr. Avnish UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathological Parameters (LFT)Dokument1 SeitePathological Parameters (LFT)Dr. Avnish UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver Disease AvnishDokument25 SeitenLiver Disease AvnishDr. Avnish Upadhyay100% (1)
- Pathological Parameters (LIPID)Dokument1 SeitePathological Parameters (LIPID)Dr. Avnish UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation FOOTBALL-FDokument16 SeitenPresentation FOOTBALL-FDr. Avnish Upadhyay100% (1)
- Clinical Mechanics of PranayamDokument20 SeitenClinical Mechanics of PranayamDr. Avnish Upadhyay100% (3)
- Effect of PranayamaDokument37 SeitenEffect of PranayamaDr. Avnish Upadhyay100% (22)
- Role of Bramhacharya in Good HealthDokument1 SeiteRole of Bramhacharya in Good HealthDr. Avnish Upadhyay100% (3)
- Contact GRRSB Team for InquiriesDokument2 SeitenContact GRRSB Team for Inquiriesmsis81Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mahle KFWA MAIN Data SheetDokument4 SeitenMahle KFWA MAIN Data SheetRudnikNoch keine Bewertungen
- LOD Spec 2016 Part I 2016-10-19 PDFDokument207 SeitenLOD Spec 2016 Part I 2016-10-19 PDFzakariazulkifli92Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tap Yourself FreeDokument134 SeitenTap Yourself Freenguyenhavn100% (2)
- Termites and Microbial Biological Control StrategiesDokument30 SeitenTermites and Microbial Biological Control StrategiesMuhammad QasimNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Dedication of the Broken Hearted SailorDokument492 SeitenThe Dedication of the Broken Hearted SailorGabriele TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitchella Partridge Berry Materia Medica HerbsDokument3 SeitenMitchella Partridge Berry Materia Medica HerbsAlejandra GuerreroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Profile OMORIS - Presentation 2020-2Dokument20 Seiten2 Profile OMORIS - Presentation 2020-2lemuel bacsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPS and The Quest For Pizza: National Aeronautics and Space AdministrationDokument1 SeiteGPS and The Quest For Pizza: National Aeronautics and Space Administrationvijay maddiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 (Additional Notes) Thermodynamics Review (Power Plant Technology by M Wakil)Dokument29 SeitenChapter 7 (Additional Notes) Thermodynamics Review (Power Plant Technology by M Wakil)Aries SattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specs Mantilla UV BT8800 Oct 2014Dokument2 SeitenSpecs Mantilla UV BT8800 Oct 2014Julio MendezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qand ADokument5 SeitenQand AJoshua PascasioNoch keine Bewertungen
- DCI-2 Brief Spec-Rev01Dokument1 SeiteDCI-2 Brief Spec-Rev01jack allenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crimson Holdings Fact Sheet As of April 14Dokument3 SeitenCrimson Holdings Fact Sheet As of April 14WDIV/ClickOnDetroitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Symbols For Signalling Circuit DiagramsDokument27 SeitenSymbols For Signalling Circuit DiagramsrobievNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Composite Materials Design EngineeringDokument19 SeitenAdvanced Composite Materials Design EngineeringpanyamnrNoch keine Bewertungen
- State of The Art Penelitian - Chat GPT 2023Dokument137 SeitenState of The Art Penelitian - Chat GPT 2023restyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NarendraVani KallubaluVKV 2010-11Dokument144 SeitenNarendraVani KallubaluVKV 2010-11Vivekananda Kendra100% (1)
- Earthing Substation Earthing Guide Central NetworksDokument12 SeitenEarthing Substation Earthing Guide Central Networksshahkhan552000100% (1)
- 366 Community Service IdeasDokument5 Seiten366 Community Service IdeasAhmetYılmazVuralNoch keine Bewertungen
- r05320202 Microprocessors and Micro ControllersDokument7 Seitenr05320202 Microprocessors and Micro ControllersSri LalithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instruction Manual: E2M40 and E2M80 Rotary Vacuum PumpsDokument46 SeitenInstruction Manual: E2M40 and E2M80 Rotary Vacuum PumpsVicki NugrohoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sanchez 07 Poles and Zeros of Transfer FunctionsDokument20 SeitenSanchez 07 Poles and Zeros of Transfer FunctionsYasmin KayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speech for pecha kuchaDokument6 SeitenSpeech for pecha kuchaaira mikaela ruazolNoch keine Bewertungen
- 35.2 - ING - El Puente NewsletterDokument13 Seiten35.2 - ING - El Puente NewsletterIrmali FrancoNoch keine Bewertungen
- D6528-07 ASTM Standard Consolidated Undrained Direct Simple Shear Testing of Cohesive SoilsDokument9 SeitenD6528-07 ASTM Standard Consolidated Undrained Direct Simple Shear Testing of Cohesive SoilsDayana HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dahua Pfa130 e Korisnicko Uputstvo EngleskiDokument5 SeitenDahua Pfa130 e Korisnicko Uputstvo EngleskiSaša CucakNoch keine Bewertungen