Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Electromyography (EMG)
Hochgeladen von
Esome SharmaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Electromyography (EMG)
Hochgeladen von
Esome SharmaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Electromyography (EMG)
Recording of action potentials of muscle fibers near the needle electrode in a muscle. The equipment for EMG consists of: -electrodes ( disc electrodes or needle electrodes) -Amplifier -Displayer ( visual)/ printer
basic unit of EMG
The basic unit of EMG signals is motor unit action potential (MUP). It is the sum of the action potentials produced in the muscle supplied by an anterior horn. Amplitude of MUP is 0.5-3mv, duration is 5-12 ms, frequency up to 500Hz and it is mostly triphasic.
analysis
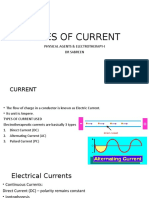
3 types of signals observed in EMG Insertional activity Spontaneous activity Voluntary activity
Applications of EMG
Mainly used to diagnose nerve and muscle injury. Neurogenic disease like anterior horn cell disease, Amylotropic lateral sclerosis Myogenic disease like Duchennes muscular dystrophy, muscle trauma, muscle cramps etc.
Fibrillation
contraction of individual muscle fiber which cannot be seen through skin. Abnormal spontaneous activity are seen in EMG It may be due to denervation of motor neuron Amplitude 10-100mv, duration 12ms , frequency 10 Hz
Fasiculation
Coarse contraction of individual motor units; 50-500mv, 2-4ms, 220Hz Can be visible through skin Occasionally it can be seen normally like in muscle cramps. Occurs in anterior motor neuron disease like poliomyelitis
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Recent Advances in PhysiotherapyVon EverandRecent Advances in PhysiotherapyCecily PartridgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- EmgDokument49 SeitenEmgarmin2200100% (1)
- EMG Signal ProcessingDokument38 SeitenEMG Signal ProcessingAbdi TeferiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Electro Physiological TestingDokument22 SeitenClinical Electro Physiological TestingPaul VkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interpreting EMG and NCS ResultsDokument4 SeitenInterpreting EMG and NCS ResultsnadiyasyadinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Needle EMG 2Dokument77 SeitenNeedle EMG 2Shauki AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muscle StimulationDokument15 SeitenMuscle StimulationApoorvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nerve Conduction Velocity: Karunakaran K MPT (Neuro) ., PGDMT Associate Professor, SvcoptDokument30 SeitenNerve Conduction Velocity: Karunakaran K MPT (Neuro) ., PGDMT Associate Professor, SvcoptSineka 19170239Noch keine Bewertungen
- PAE 5 Techniques of The Treatment With Faradic Type Current-1Dokument35 SeitenPAE 5 Techniques of The Treatment With Faradic Type Current-1Huzaifa HabibNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMG Summary: Muscle MNDokument12 SeitenEMG Summary: Muscle MNanjelikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMGDokument53 SeitenEMGgauravmahabal100% (1)
- BTL CardioPoint CPET CLIN Treadmill Load Protocol For Athletes EN100Dokument3 SeitenBTL CardioPoint CPET CLIN Treadmill Load Protocol For Athletes EN100stoicea catalinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interferential Therapy: DefinitionDokument9 SeitenInterferential Therapy: DefinitionLowell QuadrosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proprioception in Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation. Part 2: Clinical Assessment and InterventionDokument10 SeitenProprioception in Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation. Part 2: Clinical Assessment and InterventionAlejandra VasquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time Code Title Author: Date: 30-07-2021Dokument4 SeitenTime Code Title Author: Date: 30-07-2021siddhartha senNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interferential Therapy Sept 08Dokument8 SeitenInterferential Therapy Sept 08api-19753815100% (1)
- Interferential (IFT) TherapyDokument25 SeitenInterferential (IFT) Therapymohd100100% (2)
- Arm, Forearm, Hand MuscleDokument18 SeitenArm, Forearm, Hand MusclerabeyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nerve Pathways - Functions, Lesions and AdhesionsDokument33 SeitenNerve Pathways - Functions, Lesions and Adhesionshajra habibNoch keine Bewertungen
- EmgDokument25 SeitenEmgAdelina MusaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Functional Electrical StimulationDokument14 SeitenIntroduction To Functional Electrical StimulationJia HuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrotherapy On The Web - Pulsed Shortwave TherapyDokument10 SeitenElectrotherapy On The Web - Pulsed Shortwave Therapyakheel ahammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMG ManualDokument2 SeitenEMG ManualOmar Manzano CaceresNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHT 1261C Tests and Measurements Dr. KaneDokument17 SeitenPHT 1261C Tests and Measurements Dr. Kanenico7christian100% (1)
- Regional Meeting NCS and EMGDokument35 SeitenRegional Meeting NCS and EMGhop2e08etqknumzfxzsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Therapybook Interferencial TherapyDokument34 SeitenTherapybook Interferencial TherapyBrian RaymondNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELECTROMYOGRAPHYDokument10 SeitenELECTROMYOGRAPHYSapna DhankharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Russian Current 2011Dokument14 SeitenRussian Current 2011Faisal Qureshi100% (1)
- Eccentric Vs Concentric Training Muscle GrowthDokument8 SeitenEccentric Vs Concentric Training Muscle GrowthAres Santiago R. NoguedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of CurrentDokument24 SeitenTypes of Currentsabreen hires100% (1)
- Sense Organ:vestibular OrganDokument55 SeitenSense Organ:vestibular OrganivanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Kinetic Chain Approach To PainDokument4 SeitenThe Kinetic Chain Approach To PaincharbelhannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technique of Electromyography andDokument41 SeitenTechnique of Electromyography andRizalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interferential TherapyDokument31 SeitenInterferential TherapyFaisal Qureshi89% (9)
- Spasticity ManagementDokument17 SeitenSpasticity ManagementLowell QuadrosNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMG Trigerred StimulationDokument3 SeitenEMG Trigerred StimulationralphholingsheadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shockwave Therapy MZUEDokument21 SeitenShockwave Therapy MZUELove & HumanityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of EMG in Clinical and Sports MedicineDokument412 SeitenApplications of EMG in Clinical and Sports Medicineteju1996coolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomechanics of GaitDokument48 SeitenBiomechanics of GaitSania SaeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diseases of Spine andDokument37 SeitenDiseases of Spine andgunawan djayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 - Mahima Bhatia - MyalgiaDokument14 Seiten15 - Mahima Bhatia - MyalgiaApoorvNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Fundamentals of PNFDokument5 SeitenThe Fundamentals of PNFAri SudarsonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intramuscular EMG QuizDokument60 SeitenIntramuscular EMG QuizMike Pascoe50% (2)
- HeliotherapyDokument20 SeitenHeliotherapyDodo JuniorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foot DropDokument30 SeitenFoot Dropdr_s_ganesh100% (1)
- Practical Skills On PalpationDokument6 SeitenPractical Skills On PalpationsudersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurostimulation For Stroke RehabilitationDokument11 SeitenNeurostimulation For Stroke Rehabilitationisos.mporei.vevaios.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electrotherapy: DR Ramaiah Choudhary PhysiotherapistDokument13 SeitenElectrotherapy: DR Ramaiah Choudhary Physiotherapistvenkata ramakrishnaiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 7-BiofeedbackDokument32 SeitenChap 7-Biofeedbackaarya12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Aerobic ExerciseDokument35 SeitenPrinciples of Aerobic ExerciseSherin KNoch keine Bewertungen
- DownloadDokument11 SeitenDownloadChristopher Chew Dian MingNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESWTDokument16 SeitenESWTPrahoveanu IoanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Didynamic+Current+Lecture GOODDokument16 SeitenDidynamic+Current+Lecture GOODkrishnamoorthy abiramanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instruction Manual FOR 3-In-1 Combo Electrotherapy Device: Model: R-C1Dokument40 SeitenInstruction Manual FOR 3-In-1 Combo Electrotherapy Device: Model: R-C1najjaciNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELECTROMYOGRAPHYDokument120 SeitenELECTROMYOGRAPHYAyyappan Jayavel100% (1)
- MSK Us ProtocolsDokument40 SeitenMSK Us Protocolsjamir59Noch keine Bewertungen
- Properties of Skeletal MuscleDokument72 SeitenProperties of Skeletal MuscleAakash GohilNoch keine Bewertungen
- EmgDokument6 SeitenEmgDhabia AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single Fi Bre: ElectromDokument4 SeitenSingle Fi Bre: ElectromShauki AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromyogram 151012062827 Lva1 App6891Dokument26 SeitenElectromyogram 151012062827 Lva1 App6891Bima IyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biocompatibility of Dental MaterialsDokument51 SeitenBiocompatibility of Dental MaterialsEsome Sharma100% (1)
- Biocompatibility of Dental MaterialsDokument51 SeitenBiocompatibility of Dental MaterialsEsome Sharma100% (1)
- Complications of FractureDokument19 SeitenComplications of FractureEsome Sharma100% (1)
- Vitamin D and CalcitoninDokument28 SeitenVitamin D and CalcitoninEsome SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calcium HomeostasisDokument19 SeitenCalcium HomeostasisEsome SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RSDokument1 SeiteRSEsome SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen