Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
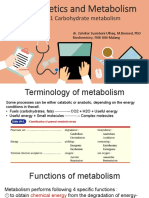
Non Energy Role of Carbohydrates
Hochgeladen von
Dr. M. Prasad NaiduCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Non Energy Role of Carbohydrates
Hochgeladen von
Dr. M. Prasad NaiduCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
M.
PRASAD NAIDU
MSc MEDICALBIOCHEMISTRY,
Ph.D. RESEARCH SCHOLAR
Definition
Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones or their
derivatives .
Digested Absorbed
Diet Monosaccharide Portal
circulation
Enters
systemic Glucose Liver
circulation Enters Converted
Mainly meant for energy .
There are other special functions of this molecule .
FATE OF GLUCOSE & ITS UTILISATION
OXIDATION STORAGE LIPOGENESIS CONVERSION CONVERSION
-GLYCOLYSIS GLYCOGEN INTO AMINO INTO OTHER
-HMP SHUNT ACIDS CARBOHYDRATES
-URONIC ACID
PATHWAY
-RAPOPORT
LUEBERING
CYCLE
GLUCOSE
HEXOSE MONO PHOSPHATE (HMP) SHUNT
Alternate oxidative pathway for GLUCOSE
Mainly meant for production of NADPH and PENTOSE
SUGARS
Occurs in special tissues for special function eg :- Liver, RBC,
Adrenal cortex, Lactating mammary gland.
1. NADPH
Used as electron donor in many reductive synthesis in the
body .
eg:- -Extra mitochondrial de novo fatty acid synthesis.
-Synthesis of Cholesterol
- To keep Glutathione in reduced state ( RBC, Lens)
-Phagocytosis
ROLE IN ERYTHROCYTES
-To maintain cell membrane integrity
Role in Phagocyosis
Role of HMP pathway in Lens
10% of glucose is oxidized in this pathway to
produce NADPH to keep G-SH in reduced form
,which is necessary for maintenance of lens
proteins.
Ribonucleotide reductase
Ribonucleotide Deoxyribonucleotide
Thiroredoxine Thiroredoxine
(Red ) (Oxi )
NADP NADPH + H
+
HMP
2. TO PROVIDE PENTOSE
For Nucleotide and Nucleic acid synthesis
In denovo synthesis , purines are built on R-5-P
molecule to form nucleotides .
Component of important molecules like ATP ,ADP,
cAMP ,cGMP
and co enzymes like NAD, NADP ,FMN , FAD . CoA
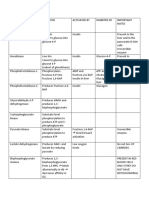
Uronic acid pathway
Biomedical importance
Production of D-Glucuronic acid ------mainly utilised
for detoxification of foreign substances
(Xenobiotics)
----also used for synthesis of MPS
Functions of Glucuronic acid
1. Conjugation
UDP Glucuronic acid is a active form
Conjugation takes place in liver & enzyme which
catalises is Glucuronyl transferase
various Xenobiotics like drugs ,chemicals ,
pollutants ,food additives , carcinogens &
endogeneous hormones . are converted into
corresponding Glucuronides which are more polar
& soluble , excreted in urine .
Eg :- Bile pigments (bilirubin )mono &
diglucuronoides
Aromatic amino acids -----Benzoic acid
Drugs & other xenobiotics------ First hydroxylated by
mono oxygenase Cyt P450 system & then conjugated
with D-Glucuronic acid .
Hormones-----Thyroid hormones ,derivatives of certain
steroid hormones are detoxified by D-Glucuronic acid
.
2. Synthesis of MPS
-composed of amino sugars and uronic acid .
-amino sugar may be glucosamine or galactosamine
which is acetylated .
-uronic acid may be D-glucuronic acid or L-iduronic
acid
-some may contain only galactose with glucosamine
Eg:- Hyaluronic acid , Chondroitin sulphate ,Keratan
sulphate , Heparin .
Functions of MPS
As a constituents of extra cellular matrix interacts
with collagens and elastins
Acts as polyanions ---binds to polycations and
cations (Na+, K+ ) ,thus attracts water by osmotic
pressure into extra cellular matrix contributing to
its turgor .
Acts as a barrier in tissues ---Hyaluronic acid
permits metabolites to pass through but resists
penetration of bacteria and other infective agents
.Also acts as lubricant and shock absorber .
Heparin acts as a anticoagulant and also as co-
enzyme for Lipoprotein lipase enzyme
Dermatan sulphate present in sclera of the eye
maintains the overall shape of the eye .
Keratan sulphate present in cornea of the eye and
lie between the collagen fibrils and play an
important role in maintaining corneal transperancy
.
Rapoport Leubering cycle in RBC
mutase
1,3 BPG
SLP 2,3 BPG
Glycolysis ATP
phosphatase
3PG
Functions of 2,3 BPG
2,3 BPG is the most abundant organic phosphate in
RBC ,where its concentration is roughly equals to that
of Hb
One molecule of 2,3 BPG binds to a pocket in the
center of the deoxy Hb tetramer ,formed by the 2
globin chains .
This preferrential binding stabilises the taut form.
This reduces the affinity of Hb for oxygen thus
enables Hb to release oxygen at tissue level .
Cell membrane --- Glycolipids and Glycoproteins
Glycoproteins
Located on the extracellular side of plasma membrane
2%-10%------are contributed by the sugar residues
of their glcoproteins
Membrane bound glycoproteins participate in a broad
range of cellular phenomena including cell surface
recognition , cell adhesion , blood group antigens .
GLYCOPHORINS
Transmembrane protein with carbohydrate coat .
Single polypeptide chain with 16 attached
oligosaccharide units .
These carbohydrate units are rich in sialic acid a
negatively charged sugar .
The carbohydrate units of glycophorins give RBC a
very hydrophilic , anionic coat , which enables them
to circulate with out adhering to other cells and vessel
walls .
Cell-Cell recognition
1. Eg:- Asialoglycoprotein receptor
Many newly synthesized glycoprotein , such as
immunoglobulin , peptide hormones contain
carbohydrate units with sialic acid residues .
In course of hours or days ,depending upon the
particular protein, these groups are removed by
SIALASES protruding from the surface of blood
vessels .
The exposed galactose residues from the trimmed
glycoprotein is detected by
ASIALOGLYCOPROTEIN RECEPTOR in the
plasma membrane of the liver cells .
The complex of the glycoprotein and receptor is
then internalised by the liver cells
ABO Substances
These are glycosphingolipids and glycoproteins
sharing common oligosaccharide chains .
On RBC membrane oligosaccharide that determines
the specific nature of ABO substance is present in
glycosphingolipid .
In secretions ----the same oligosaccharide is present in
glycoprotein .
H substance is the biosynthetic precursor of both A
and B substance .
Fucose -Gal-GlaNAc-R
A
GalNAc
Fucose-Gal-GlaNAc-R
H
Fucose-Gal-GlaNAc
B
Gal
Glycosides
Glycosides are formed when hemiacetal or hemiketal
hydroxyl group ( of anomeric carbon ) of a carbohydrate
reacts with a hydroxyl group of another carbohydrate or a
non carbohydrate ( aglycone )
Aglycone can be ---methanol , glycerol , sterol , phenol , or
bases like adenine .
They are important in medicine due to their action on
cardiac muscle . ( steroids as aglycone )
Cardiac glycoside
Used in cardiac insufficiency .
Steroids as aglycone .
Derivatives of Digitalis ,strophanthus , squill plants .
Eg:-Digitonin 4Galactose +Xylulose +
Digitogenin(aglycone )
Ouabain
Inhibits active transport of Na+ in cardiac muscle
(sodium pump inhibitor )
Sucrose
If introduced parentally cannot be utilised , but changes
osmotic condition of the blood and causes a flow of water
from the tissue into the blood .
Thus can be used in edema like cerebral edema .
Homopolysaccharides
Inulin
-polymer of D Fructose .
-Used in renal function test to determine GFR .
Cellulose
-polymer of D Glucose .
-not digested in humans .
-adds bulk to the intestinal substance and stimulate
peristalsis and elimination of indigested food
residues .
Dextrins
- partial hydrolysed product of starch .
- used as mucilages .
Dextrans
- polymer of D Glucose ( alpha 1-6 ,1-4 , 1-3
linkages in each unit )
-molecular weight 75000
-used as plasma expander due to their high
viscosity , low osmotic pressure, slow disintegration,
utilisation and elimination .
Agar
-made up of repeated units of Galactose which is
sulphated .
-purified agar dissolves in hot water and on cooling it
sets like a gel which is used in agar plates for culture
of bacteria .
Agarose
-Galactose combined with 3,6 anhydro galactose
units
-used as a support medium in Electrophoresis .
Conversion into aminoacids
Synthesis of non essential amino acidsby
transamination reaction .
Eg:-pyruvate alanine
oxaloacetate aspartate
C skeletons of nonessential aminoacids are derived
from glucose or its metabolites .
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 13 - GluconeogenesisDokument23 Seiten13 - GluconeogenesischeckmateNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2023-2024-B3502-Lecture 17-Carbohydrate Metabolism-Gluconeogenesis and Oxidative Pentose Phosphate PathwayDokument15 Seiten2023-2024-B3502-Lecture 17-Carbohydrate Metabolism-Gluconeogenesis and Oxidative Pentose Phosphate Pathwaypitsolerato60Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3-HMP and Glucuronic Acid PathwaysDokument40 Seiten3-HMP and Glucuronic Acid Pathwayslou765500Noch keine Bewertungen
- Content Will Be Covered:: Fructose Metabolism Galactose Metabolism Uronic Acid PathwayDokument21 SeitenContent Will Be Covered:: Fructose Metabolism Galactose Metabolism Uronic Acid PathwaygaasheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glycolysis: How Cells Extract Energy from GlucoseDokument10 SeitenGlycolysis: How Cells Extract Energy from GlucosechanudiGajadeeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOCHEMISTRY QUESTIONSDokument5 SeitenBIOCHEMISTRY QUESTIONSperssivesimangavwa2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Glycolysis 3MD (3)Dokument48 SeitenGlycolysis 3MD (3)gostrider0093sNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Lec. Biochemistry (4th)Dokument18 Seiten9 Lec. Biochemistry (4th)Doctor SonuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1599663221Dokument5 Seiten1599663221Kausik SenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Catabolism Blok 7 2018Dokument136 SeitenCarbohydrate Metabolism Catabolism Blok 7 2018N A Anggriani WulandariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 GlycolysisDokument41 Seiten2 Glycolysislou765500Noch keine Bewertungen
- GlycolysisDokument31 SeitenGlycolysisrafea_naffa8326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry of The EyeDokument38 SeitenBiochemistry of The EyeYusuf Almalik SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- GluconeogenesisDokument31 SeitenGluconeogenesisRajakannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Debanjana Chakraborty 2 Semester MSC BiotechnologyDokument20 SeitenDebanjana Chakraborty 2 Semester MSC Biotechnologydebanjana2009Noch keine Bewertungen
- HMP & Uronic Acid PathwaysDokument30 SeitenHMP & Uronic Acid PathwaysAastha SinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uronic Acid PathwayDokument26 SeitenUronic Acid PathwayAbdul Jabbar Abdul JabbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hexose Monophosphate PathwayDokument19 SeitenHexose Monophosphate Pathwayspdharanimaran001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gluconeogenesis: The Pathway and RegulationDokument31 SeitenGluconeogenesis: The Pathway and RegulationMunachande KanondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FTNS-3101 Nutritional Biochemistry-1: Rahanur AlamDokument80 SeitenFTNS-3101 Nutritional Biochemistry-1: Rahanur AlamMd. Muhaiminul IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 10 Second PPP PDFDokument16 SeitenLecture 10 Second PPP PDFMadani TawfeeqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pentose Phosphate PathwayDokument10 SeitenPentose Phosphate PathwaySania SaeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDokument61 SeitenOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreYoAmoNYCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrate Metabolism: NotesDokument15 SeitenCarbohydrate Metabolism: Notesarmin509Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lect # 3 GluconeogenesisDokument40 SeitenLect # 3 GluconeogenesisUbaid ur Rahman100% (1)
- Backwards ReasoningDokument40 SeitenBackwards Reasoningharshit chaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDokument56 SeitenCarbohydrate MetabolismPradini SugihartoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asy GlycolysisDokument69 SeitenAsy GlycolysisErdem AltunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem CombinedDokument758 SeitenBiochem CombinedTheBoss 20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolism GlycolysisDokument55 SeitenMetabolism GlycolysisDavid Dc ChristianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unacademy 2 PDFDokument26 SeitenUnacademy 2 PDFANUPAM ANAND KUMAR PANDEY MBA-INoch keine Bewertungen
- GlycolysisDokument35 SeitenGlycolysisAastha SinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioenergetics and Lipid MetabolismDokument34 SeitenBioenergetics and Lipid MetabolismM Daffa Abhista ReviansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- HMP ShuntDokument14 SeitenHMP Shuntامجد حسين جواد كاظمNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 2Dokument29 SeitenClass 2Roy Anderson Oropeza ClavoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 - Carbohydrate MetabolismDokument68 Seiten11 - Carbohydrate MetabolismcheckmateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrate Metabolism and BiosynthesisDokument44 SeitenCarbohydrate Metabolism and BiosynthesisEmman RegondolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry - Enzymes Shuttles Proteins Summary 1Dokument8 SeitenBiochemistry - Enzymes Shuttles Proteins Summary 1Samuel NafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbo ChemDokument123 SeitenCarbo ChemHan MichelNoch keine Bewertungen
- (CO8) Chemistry of VisionDokument7 Seiten(CO8) Chemistry of VisionCardoge DalisayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.2 Pentose and Uronic PathwayDokument28 Seiten2.2 Pentose and Uronic PathwayYared gebremedhinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry - Chapter 17 Dr. Bongon: Glycolysis & Oxidation of PyruvateDokument6 SeitenBiochemistry - Chapter 17 Dr. Bongon: Glycolysis & Oxidation of PyruvateChaze WaldenNoch keine Bewertungen
- (3.19) CarbosMetab (PPP, Other Sugars & GAGs)Dokument74 Seiten(3.19) CarbosMetab (PPP, Other Sugars & GAGs)pamelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioenergetics & Metabolism GuideDokument56 SeitenBioenergetics & Metabolism GuideAww AddNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbial MetabolismDokument49 SeitenMicrobial MetabolismOmelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDokument38 SeitenCarbohydrate Metabolismwidya nurrohmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GlucolysisDokument11 SeitenGlucolysisMohamed SalahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrate digestion and glucose metabolism pathwaysDokument4 SeitenCarbohydrate digestion and glucose metabolism pathwaysJeremy EvansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolic Adaptation During Prolonged StarvationDokument18 SeitenMetabolic Adaptation During Prolonged StarvationThabrish rish1234Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2.2 Carbohydrate Metabolism Part 2Dokument13 Seiten2.2 Carbohydrate Metabolism Part 2John Louis PulidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 03. Carbohydrate Metabolism. Common Pathway, Regulation and PathologyDokument80 SeitenLecture 03. Carbohydrate Metabolism. Common Pathway, Regulation and PathologyВіталій Михайлович НечипорукNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gluconeogenesis: Synthesizing Glucose from Non-Carbohydrate PrecursorsDokument31 SeitenGluconeogenesis: Synthesizing Glucose from Non-Carbohydrate Precursorsemery100% (1)
- PentosephosphateDokument38 SeitenPentosephosphatesreya ghosalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment For Blood - PaysonDokument25 SeitenAssignment For Blood - PaysonRodrigo Joseph PaysonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regulation of glucose metabolism by hormonesDokument15 SeitenRegulation of glucose metabolism by hormonesSoji PhilipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glycogen Synthesis and DegradationDokument6 SeitenGlycogen Synthesis and DegradationClara HerlinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolic Pathway of Carbohydrate and GlycolysisDokument22 SeitenMetabolic Pathway of Carbohydrate and GlycolysisDarshansinh MahidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 CHO Metabolism 2Dokument32 Seiten2021 CHO Metabolism 2xb2k9gzkc9Noch keine Bewertungen
- BCH421 2019-20 Harmattan 1Dokument7 SeitenBCH421 2019-20 Harmattan 1idriscognitoleadsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enteric FeverDokument42 SeitenEnteric FeverDr. M. Prasad NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vitamin-A: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDokument42 SeitenVitamin-A: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDr. M. Prasad NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- STUDENT T-TestDokument20 SeitenSTUDENT T-TestDr. M. Prasad NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signal TransductionDokument77 SeitenSignal TransductionM.PRASAD NAIDUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Parametric Tests: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDokument15 SeitenNon-Parametric Tests: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDr. M. Prasad NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDokument23 SeitenM.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDr. M. Prasad NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weight ManagementDokument30 SeitenWeight ManagementDr. M. Prasad NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Soluble VitaminsDokument55 SeitenWater Soluble VitaminsDr. M. Prasad Naidu100% (1)
- Thyroid HormonesDokument63 SeitenThyroid HormonesDr. M. Prasad NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Translation: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDokument33 SeitenTranslation: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDr. M. Prasad NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urea CycleDokument8 SeitenUrea CycleDr. M. Prasad Naidu100% (1)
- Uro Modul inDokument36 SeitenUro Modul inDr. M. Prasad NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid GlandDokument14 SeitenThyroid GlandDr. M. Prasad NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemisty, Ph.D.Research ScholarDokument33 SeitenTranscription: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemisty, Ph.D.Research ScholarDr. M. Prasad NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thin Layer ChromatographyDokument16 SeitenThin Layer ChromatographyDr. M. Prasad Naidu100% (1)
- M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDokument17 SeitenM.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDr. M. Prasad NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- TGF-β Signalling From CellDokument14 SeitenTGF-β Signalling From CellDr. M. Prasad NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- RIPKADokument40 SeitenRIPKAM.PRASAD NAIDUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spectro PhotometryDokument36 SeitenSpectro PhotometryDr. M. Prasad NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Serum Protein Electrophoresis & Their Clinical ImportanceDokument44 SeitenSerum Protein Electrophoresis & Their Clinical ImportanceDr. M. Prasad NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReplicationDokument64 SeitenReplicationDr. M. Prasad NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sex HormonesDokument10 SeitenSex HormonesM.PRASAD NAIDUNoch keine Bewertungen
- RFTDokument41 SeitenRFTDr. M. Prasad NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Serum Ferritin and Diabetes Mellitus Type LLDokument21 SeitenSerum Ferritin and Diabetes Mellitus Type LLM.PRASAD NAIDUNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDS PageDokument6 SeitenSDS PageDr. M. Prasad NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protien Mutation& Cystic FibrosisDokument28 SeitenProtien Mutation& Cystic FibrosisDr. M. Prasad NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sequence DatabaseDokument36 SeitenSequence DatabaseDr. M. Prasad NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rna Processing: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDokument33 SeitenRna Processing: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDr. M. Prasad NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peptides and Proteins: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDokument30 SeitenPeptides and Proteins: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDr. M. Prasad NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recombinant DNA TechnologyDokument34 SeitenRecombinant DNA TechnologyDr. M. Prasad NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral Nutrition Support NotesDokument28 SeitenOral Nutrition Support Notesleemon.mary.alipao8695Noch keine Bewertungen
- Young Women's Sexuality in Perrault and CarterDokument4 SeitenYoung Women's Sexuality in Perrault and CarterOuki MilestoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maureen L. Walsh - Re-Imagining Redemption. Universal Salvation in The Theology of Julian of NorwichDokument20 SeitenMaureen L. Walsh - Re-Imagining Redemption. Universal Salvation in The Theology of Julian of NorwichAni LupascuNoch keine Bewertungen
- FP-XH PGRG eDokument936 SeitenFP-XH PGRG ebvladimirov85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tds G. Beslux Komplex Alfa II (25.10.19)Dokument3 SeitenTds G. Beslux Komplex Alfa II (25.10.19)Iulian BarbuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 2 Debussy - LifejacketsDokument7 SeitenChap 2 Debussy - LifejacketsMc LiviuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D Area Clearance Strategies for Roughing ComponentsDokument6 Seiten3D Area Clearance Strategies for Roughing ComponentsMohamedHassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compare Blocks - ResultsDokument19 SeitenCompare Blocks - ResultsBramantika Aji PriambodoNoch keine Bewertungen
- JY Series Single-Phase Capacitor Induction MotorsDokument1 SeiteJY Series Single-Phase Capacitor Induction MotorsAditya PrasetyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Natural Aplicacion Industria y OtrosDokument319 SeitenGas Natural Aplicacion Industria y OtrosLuis Eduardo LuceroNoch keine Bewertungen
- T9001 T9002 T9003 T9004: Tecn# Originator Title Aging Status of TecnDokument2 SeitenT9001 T9002 T9003 T9004: Tecn# Originator Title Aging Status of TecnThanalachmy GopiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypophosphatemic Rickets: Etiology, Clinical Features and TreatmentDokument6 SeitenHypophosphatemic Rickets: Etiology, Clinical Features and TreatmentDeysi Blanco CohuoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telco XPOL MIMO Industrial Class Solid Dish AntennaDokument4 SeitenTelco XPOL MIMO Industrial Class Solid Dish AntennaOmar PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection 2: WHAT DOES It Mean To Be A Pacific Islander Today and in The Future To Me?Dokument5 SeitenReflection 2: WHAT DOES It Mean To Be A Pacific Islander Today and in The Future To Me?Trishika NamrataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effective Time ManagementDokument61 SeitenEffective Time ManagementTafadzwa94% (16)
- Proposal Anguria Pasta NewDokument24 SeitenProposal Anguria Pasta NewNOOR IRDINA HAFIZAH BT TAUPISNoch keine Bewertungen
- OpenROV Digital I/O and Analog Channels GuideDokument8 SeitenOpenROV Digital I/O and Analog Channels GuidehbaocrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emerson EPC48150 1800 FA1EPC48300 3200 FA1 V PDFDokument26 SeitenEmerson EPC48150 1800 FA1EPC48300 3200 FA1 V PDFRicardo Andrés Soto Salinas RassNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap06 (6 24 06)Dokument74 SeitenChap06 (6 24 06)pumba1234Noch keine Bewertungen
- Evolutionary PsychologyDokument10 SeitenEvolutionary PsychologyShreya MadheswaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Baseline Program Rev 3A Presentation 25 July 2020Dokument24 SeitenBaseline Program Rev 3A Presentation 25 July 2020Shakti Sourava RautrayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discuss The Challenges For Firms To Operate in The Hard-Boiled Confectionery Market in India?Dokument4 SeitenDiscuss The Challenges For Firms To Operate in The Hard-Boiled Confectionery Market in India?harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- PC3 The Sea PeopleDokument100 SeitenPC3 The Sea PeoplePJ100% (4)
- Final Decision W - Cover Letter, 7-14-22Dokument19 SeitenFinal Decision W - Cover Letter, 7-14-22Helen BennettNoch keine Bewertungen
- AI Model Sentiment AnalysisDokument6 SeitenAI Model Sentiment AnalysisNeeraja RanjithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sibuyan Island ResiliencyDokument12 SeitenSibuyan Island ResiliencyEndangeredSpeciesNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Art of Now: Six Steps To Living in The MomentDokument5 SeitenThe Art of Now: Six Steps To Living in The MomentGiovanni AlloccaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naukri LalitaSharma (3y 4m)Dokument2 SeitenNaukri LalitaSharma (3y 4m)rashika asraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lathe - Trainer ScriptDokument20 SeitenLathe - Trainer ScriptGulane, Patrick Eufran G.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar Spesifikasi Teknis Pembangunan Gedung Kantor BPN BojonegoroDokument6 SeitenDaftar Spesifikasi Teknis Pembangunan Gedung Kantor BPN BojonegoroIrwin DarmansyahNoch keine Bewertungen