Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
13 Emf Equation
Hochgeladen von
Pradeep RajasekeranOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
13 Emf Equation
Hochgeladen von
Pradeep RajasekeranCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
EMF EQUATION
&
TRANSFORMATI
ON RATIO
EMF EQUATION:-
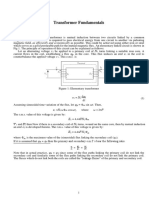
Consider the fig. shown:-
Let the voltage V1 applied to the primary of a
transformer, with secondary open circuited, be
sinusoidal.
Then the current Ie, due to applied voltage V1,
will also be a sinusoidal wave.
The mmf NI.Ie and therefore the core flux will
also follow the variation of Ie very closely.
Therefore if the voltage V has a sine waveform,
the flux must also have a sine waveform.
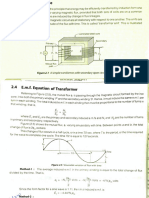
Let the sinusoidal variation of the flux be
shown as:-
Where max is the maximum value of the flux
and =2f.
Now the emf e1 in volts, induced in the primary
N1 turns by the alternating flux is given by:-
t sin
max
) 2 / sin(
cos
max 1
max 1
1 1
t N
t N
dt
d
N e
Its maximum value E1max occurs when Sin(-/2)
is equal to one.
Therefore
And
Therefore the RMS value of emf E1 induced in
primary winding is given by:-
---------(a)
Hence above is the required eqn. for EMF..
max 1 max 1
N E
) 2 / sin(
max 1 1
t E e
max 1 1
max 1
max 1
1
2
2
2
2
f N E
f N
E
E
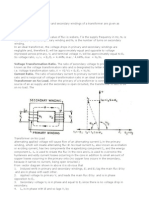
TURN RATIO:-
Consider the fig. shown:
The current Ie in the primary is assumed to flow
along the path abcda, as shown in fig.
The emf e1 induced in N1 turns of primary, must
be in such a direction as to oppose the cause, Ie.
Hence, by Lenz law, e1 will oppose V1.
Since primary winding resistance is negligible,e1
at every instant, must be equal and opposite to
V1:-
V1= = - E1
and max -------(a)
Similarly the emf induced in the secondary is:-
RMS value of E2 is given by:-
--------(b)
) 2 / sin(
) 2 / sin(
cos
max 2
max 2
max 2 2 2
t E
t N
t N
dt
d
N e
max 2
max 2
2
2
2
fN
E
E
1 1
2 fN E
From the eqns (a) and (b) we have:-
Or -------(c)
Hence
EMF per turn in primary= EMF per turn in
secondary.
max
2
2
1
1
2
1
2
1
2
f
N
E
N
E
N
N
E
E
In the fig shown, the secondary mmf F2 being
opposite to , tends to reduce the alternating
mutual flux .
Any reduction in would reduce E1. For an ideal
transformer, V1=-E1. if the applied voltage V1 is
constant, flux should also remain constant.
This can only happen if the primary draws
more current I1 from the source in order to
neutralize the demagnetizing effect of F2. I1 is
known as Load component of primary current.
The total primary current is then given by:-
If the magnetizing current Ie is neglected, then
the above equation becomes:-
Since this load component of primary current
will neutralise the secondary mmfTherefore
Or ---------(d)
e
I I I
'
1 1
'
1 1
I I
2 2 1 1
N I N I
1
2
2
1
I
I
N
N
Thus from Eqn (c) and (d) we have:-
-------(e)
The above eqn is known as the Transformation
ratio of transformers.
1
2
2
1
2
1
2
1
I
I
N
N
E
E
V
V
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Basic Transformer NotesDokument32 SeitenBasic Transformer Noteskarthime0889% (129)
- Steinmetz CP Symbolic Representation of General Alternating Waves and Double Frequency Vectors 1Dokument29 SeitenSteinmetz CP Symbolic Representation of General Alternating Waves and Double Frequency Vectors 1alpcruz100% (1)
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsVon EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (4)
- TD12 CompleteDokument110 SeitenTD12 Completemadina1386100% (2)
- Form One Integrated Science End of Year ExamDokument10 SeitenForm One Integrated Science End of Year ExamMiss Rambaran100% (2)
- Sustained Stress Indices (SSI) in The B31.3 2010 EditionDokument9 SeitenSustained Stress Indices (SSI) in The B31.3 2010 Editiont_rajith1179100% (2)
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsVon EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Investigate Relation Between The Ratio of Input and Output Voltage and Number of Turns of A Self Designed TransformerDokument15 SeitenTo Investigate Relation Between The Ratio of Input and Output Voltage and Number of Turns of A Self Designed Transformersuhayb96% (46)
- Convergence IndicatorDokument21 SeitenConvergence Indicatorsikandar100% (1)
- Liebherr STS Ship To Shore Container Gantry Cranes Technical Description 12469-0Dokument4 SeitenLiebherr STS Ship To Shore Container Gantry Cranes Technical Description 12469-0sheron100% (2)
- Unit 1 TransformersDokument39 SeitenUnit 1 TransformersAyush Khandelwal100% (1)
- CH2Dokument42 SeitenCH2etayhailu100% (2)
- Finite Element Analysis of Steel CordDokument6 SeitenFinite Element Analysis of Steel CordSanjiv Kumar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journey To The Edge of ReasonDokument337 SeitenJourney To The Edge of ReasonFrancesco CavinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single Phase TransformerDokument8 SeitenSingle Phase TransformerKrishna KorankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- EM1 - Unit 1 NotesDokument37 SeitenEM1 - Unit 1 NotesNIHAL GUPTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter TwoDokument61 SeitenChapter Twokifle203Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 2Dokument35 SeitenChap 2far remNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 1 Single PhaseTransformerDokument37 SeitenChap 1 Single PhaseTransformerKritika MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4,5. Transformers (1 Phase & 3 Phase)Dokument48 Seiten4,5. Transformers (1 Phase & 3 Phase)nakkasrinuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformers MergedDokument79 SeitenTransformers MergedPraneetha InumarthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer FundamentalsDokument6 SeitenTransformer FundamentalsAditya TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Fig. 1.1) (Fig. 1.2) Built Around A Ring-Shaped Core (Fig. 1.3)Dokument7 Seiten(Fig. 1.1) (Fig. 1.2) Built Around A Ring-Shaped Core (Fig. 1.3)Калоян ТотевNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer Fundamentals NoteDokument31 SeitenTransformer Fundamentals NoteSankara nathNoch keine Bewertungen
- ET UNIT-1 TransformerDokument16 SeitenET UNIT-1 TransformerHacking SomethingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 TransformersDokument79 SeitenUnit 2 Transformersmtgt1892Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1transformer VkmehtaDokument5 Seiten1transformer VkmehtadtrhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 2.PDF ClourDokument34 SeitenChap 2.PDF Clourfar remNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 Transformer PhasorsDokument13 Seiten14 Transformer PhasorsShahnawaz AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- c2Dokument52 Seitenc2royclhorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter TwoDokument75 SeitenChapter Twosm7526359Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 TransformersDokument24 SeitenChapter 2 TransformersFahrettin Beyazıt TokatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single - Phase TransformerDokument3 SeitenSingle - Phase TransformeraradhyamanitNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 2.machineDokument27 SeitenCH 2.machineTeshale AlemieNoch keine Bewertungen
- PT2 (18 Pages)Dokument19 SeitenPT2 (18 Pages)sampath kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Electrical Machines: Step-Up Transformer. When The Secondary Winding Has Less Turns Than TheDokument53 SeitenIntroduction To Electrical Machines: Step-Up Transformer. When The Secondary Winding Has Less Turns Than TheDamion McdowellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer: School of Computer and Communication Engineering, UnimapDokument53 SeitenTransformer: School of Computer and Communication Engineering, UnimapRajeev Valunjkar100% (1)
- TransformerDokument54 SeitenTransformerdubuli123Noch keine Bewertungen
- EMF EquationDokument2 SeitenEMF EquationEddie CowanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics, Maintenance, and Diagnostics 22Dokument1 SeiteBasics, Maintenance, and Diagnostics 22imcoolmailme2Noch keine Bewertungen
- SSM E3Dokument3 SeitenSSM E3Roy VeseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Two Transformer NewDokument63 SeitenChapter Two Transformer NewRekik AlemuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp2 SheetDokument8 SeitenExp2 SheetMajdy gamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antenna & Wave PropogationDokument4 SeitenAntenna & Wave PropogationAditya SamavedulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines IIDokument49 SeitenElectrical Machines IISuram Dileep ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- TransfrormerDokument91 SeitenTransfrormerArial96Noch keine Bewertungen
- Full Pitch Coil:: C P P PDokument12 SeitenFull Pitch Coil:: C P P PAkashman ShakyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee003 Expt2Dokument10 SeitenEe003 Expt2praveenshridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 Single Phase TransformersDokument8 SeitenModule 3 Single Phase TransformersGun ghrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alternator at Various Loads, Armature Reaction & Voltage RegulationDokument3 SeitenAlternator at Various Loads, Armature Reaction & Voltage RegulationYash BansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single Phase TransformerDokument53 SeitenSingle Phase TransformerGurpreet Singh100% (2)
- Transformers PDFDokument30 SeitenTransformers PDFMichael Williams100% (1)
- Sample Investigatory ProjectDokument13 SeitenSample Investigatory ProjectDhruv ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7358 التقرير النهائي للتدريب الهندسي PDFDokument3 Seiten7358 التقرير النهائي للتدريب الهندسي PDFمنتظر احمد حبيترNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single-Phase Transformers: 6. Insulating DC Circuits From AC CircuitsDokument21 SeitenSingle-Phase Transformers: 6. Insulating DC Circuits From AC CircuitsLin ChongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Result:: Clearly E /E N /N Within Experiment ErrorDokument7 SeitenResult:: Clearly E /E N /N Within Experiment Erroraman rajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Circuit and Short Circuit Tests On Single Phase Transformer 1 AimDokument7 SeitenOpen Circuit and Short Circuit Tests On Single Phase Transformer 1 AimRudra SimhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TransformersDokument26 SeitenTransformersgireeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 NotesDokument42 SeitenUnit 1 Notesganesh ganeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 3 Single-Phase Transformer Construction and WorkingDokument20 SeitenUNIT 3 Single-Phase Transformer Construction and WorkingSamrudhi PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOPIC 2 - Working Principles of Transformer, EMF and Turns RatioDokument34 SeitenTOPIC 2 - Working Principles of Transformer, EMF and Turns RatioRandred GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OriginalDokument13 SeitenOriginalSonic HedgehogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mutual InductanceDokument3 SeitenMutual InductanceManuel FordNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines (1phase T - F (31-141 Page)Dokument32 SeitenElectrical Machines (1phase T - F (31-141 Page)Pratibha KumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 22 For Paper SavingDokument10 SeitenLecture 22 For Paper Savingعبد المهيمن احمد قصيNoch keine Bewertungen
- Causes For The Rise of Jainism and BuddhismDokument1 SeiteCauses For The Rise of Jainism and BuddhismPradeep RajasekeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mesolithic or Middle Stone AgeDokument1 SeiteMesolithic or Middle Stone AgePradeep RajasekeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Indo-Gangetic Plain: Thar DesertDokument1 SeiteThe Indo-Gangetic Plain: Thar DesertPradeep RajasekeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cropping Seasons in IndiaDokument1 SeiteCropping Seasons in IndiaPradeep RajasekeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aluminum Die Cast Construction (ADC)Dokument1 SeiteAluminum Die Cast Construction (ADC)Pradeep RajasekeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acceleration Time Must Be Shorter Than The Safe Stall Time in Order To Prevent Rotor Thermal DamageDokument1 SeiteAcceleration Time Must Be Shorter Than The Safe Stall Time in Order To Prevent Rotor Thermal DamagePradeep RajasekeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stall Time Is CalculatedDokument1 SeiteStall Time Is CalculatedPradeep RajasekeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sudheer Bio Products PVT LTDDokument1 SeiteSudheer Bio Products PVT LTDPradeep RajasekeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Aided Electrical Drawing (CAED) 10EE65Dokument1 SeiteComputer Aided Electrical Drawing (CAED) 10EE65Pradeep RajasekeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- V 6300 Xd 1.2318 I 814.6 E 6720.924 cos φ 0.9 sin φ 0.43589 % Regulation 6.68133 %Dokument1 SeiteV 6300 Xd 1.2318 I 814.6 E 6720.924 cos φ 0.9 sin φ 0.43589 % Regulation 6.68133 %Pradeep RajasekeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Convection Heat TransferDokument1 SeiteConvection Heat TransferPradeep RajasekeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Internal Generated Voltage of ADokument1 SeiteThe Internal Generated Voltage of APradeep RajasekeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Montsinger RuleDokument1 SeiteMontsinger RulePradeep RajasekeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Influence of A Skin EffectDokument1 SeiteInfluence of A Skin EffectPradeep RajasekeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- SKIN DepthDokument1 SeiteSKIN DepthPradeep RajasekeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Mathematical Model For ThermalDokument1 SeiteThe Mathematical Model For ThermalPradeep RajasekeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forced Convection End-Space RegionsDokument1 SeiteForced Convection End-Space RegionsPradeep RajasekeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forced Convection Air-Gap Heat TransferDokument1 SeiteForced Convection Air-Gap Heat TransferPradeep RajasekeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Description and ComputationDokument1 SeiteMachine Description and ComputationPradeep RajasekeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cuff ManometerDokument1 SeiteCuff ManometerAlejandro Cardona100% (1)
- Fiber Optic CatalogueDokument25 SeitenFiber Optic Catalogueapi-3815405100% (2)
- Alexandre Grothendieck (1928-2014) Germany, FranceDokument13 SeitenAlexandre Grothendieck (1928-2014) Germany, FranceDer CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Paper 3 TZ1 SL MarkschemeDokument17 SeitenPhysics Paper 3 TZ1 SL MarkschemeRᴇᴀʟ RᴜᴋʜsᴀʀNoch keine Bewertungen
- FST v41 n3P2 Toc PDFDokument11 SeitenFST v41 n3P2 Toc PDFSulabh GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental and Numerical Analysis of Steel and Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Concrete Beams Under Transverse LoadDokument14 SeitenExperimental and Numerical Analysis of Steel and Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Concrete Beams Under Transverse LoadErnie SitanggangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mactor Report - Taller de Prospectiva D 2Dokument39 SeitenMactor Report - Taller de Prospectiva D 2Giovani Alexis Saez VegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 Physicsbowl Exam Equations: Continued On Next PageDokument3 Seiten2021 Physicsbowl Exam Equations: Continued On Next PageThe Entangled Story Of Our WorldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jenway 74 76 Series BrochureDokument6 SeitenJenway 74 76 Series BrochureSadik OunisNoch keine Bewertungen
- For Online Practice Exam Visit Us atDokument12 SeitenFor Online Practice Exam Visit Us atscribd scribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attachment PDFDokument2 SeitenAttachment PDFYunita RamadhantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- WT Chapter 6 2Dokument21 SeitenWT Chapter 6 2kanchanabalajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProjectDokument2 SeitenProjectWaqas MaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Various Types of Surfaces: Made By:-Nilesh Bhojani Guided By: - Prof. B.K. PatelDokument15 SeitenVarious Types of Surfaces: Made By:-Nilesh Bhojani Guided By: - Prof. B.K. Patelnilesh bhojaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lutensol TO Types: Technical InformationDokument15 SeitenLutensol TO Types: Technical InformationLjupco AleksovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar Report SampleDokument22 SeitenSeminar Report SampleDhruve EBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kanako Detailed ManualDokument74 SeitenKanako Detailed ManualastikaprasiddhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration Analysis, Control and Optimum Accelerometer Placement For Successful Vibrations TestsDokument44 SeitenVibration Analysis, Control and Optimum Accelerometer Placement For Successful Vibrations TestsVyankatesh AshtekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sorge 2015Dokument18 SeitenSorge 2015Masih LoghmaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet BSS66Dokument1 SeiteDatasheet BSS66Diego DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis of Nata de Coco Fiber Composite With Conductive Filler As An Eco-Friendly Semiconductor MaterialDokument7 SeitenSynthesis of Nata de Coco Fiber Composite With Conductive Filler As An Eco-Friendly Semiconductor MaterialDevit Hari AshariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18-Division 2-Section 02900 PP Pipelines, Materials, Installation & TestingDokument19 Seiten18-Division 2-Section 02900 PP Pipelines, Materials, Installation & TestingAvaan IvaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dvp-Es2 Ss2 Sa2 Sx2-Program o en 20110302Dokument14 SeitenDvp-Es2 Ss2 Sa2 Sx2-Program o en 20110302yasinNoch keine Bewertungen