Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Depreciation
Hochgeladen von
Ankit Jain0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
53 Ansichten12 SeitenDepreciation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenDepreciation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
53 Ansichten12 SeitenDepreciation
Hochgeladen von
Ankit JainDepreciation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 12
Amity Business School
Amity Business School
MBA Class of 2015,
Semester I
Amity Business School
Depreciation means a fall in the value of an asset.
Every Fixed Asset is liable to lose its value ,once it
begin to be used for production purpose
Accounting Concept of Depreciation
Accounting concept of depreciation means to
distribute the cost of fixed asset over its estimated
life in a reasonable manner.
Amity Business School
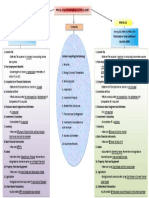
Plant
Assets
Natural
Resources
Intangible
Assets
Depreciation Depletion Amortization
Amity Business School
1. Wear and tear
wearing out of the asset on account of its constant use is
called wear & tear.
2. Lapse of time
With passage of time there is reduction in the value of
fixed assets .
3. Obsolescence
Due to acquisition of an improved model which is more
economic and works more quickly then the existing
machine will become obsolete.
Causes of Depreciation
Amity Business School
Objective of Charging Depreciation
1. To Ascertain the Profit or Loss Properly
2. To show the Asset at its proper Value
3. To Retain out of Profit Funds for Replacement
Basic Factors Consider for calculating the Depreciation
1. Original cost of the Asset
2. Scrap Value at the End of its Life
3. Estimated effective or Commercial life or legal life which ever is shorter
Amity Business School
Methods of Depreciations
1. Straight Line Method or Fixed installment Method
2. Diminishing Balance or Written Down Value Method
3. Annuity Method
4. Sinking Fund Method
5. Sum of the Digits Method
6. Insurance policy Method
7. Revaluation Method
Amity Business School
Straight Line Method
Under this method, an equal portion (amount) of the cost of the
Asset is allocated as Depreciation to each accounting year over a
period of its effective life. This is done so to reduce the value of the
asset equal to zero or its salvage or scrap value
This method is based on the assumption that depreciation is the Function of Time
Rather than of use and service potential of the Asset
It is also called as Fixed or Equal instalment method
Amity Business School
The Annual depreciation charge will be computed as follows
Annual Depreciation = Cost of Asset + Erection charges Scrap Value
Estimated life of the Asset
Question 1
A machine is purchased for Rs 50000 & Rs 5000 is incurred as erection charges.
The machine has a life of 5 years with a salvage value of Rs 10,000.
Compute the annual depreciation.
Question 2
A firm bought a machinery for Rs 38000 on 1
st
January 2009 and its life was
Estimated to be 8 years. Its estimated scrap value at the end of the period was
Rs 6000. Calculate the amount of depreciation.
Amity Business School
Ram & Sons acquired a machine on 1
st
July 2008 at a cost of Rs 14000 and spent
Rs 1000 on its installation. The firm write off depreciation at 10% on the original
Cost every year. The Books are closed on 31
st
December every year. Show the
Machinery Account & Depreciation Account for three years.
Question 3.
Question 4.
On 1st January 2000, Z Ltd purchased a plant costing Rs 41000 and spent Rs 4000
On its erection. The estimated effective life of the plant is 10 year with scrap value of
Rs 5000. Calculate depreciation on the SLM for three years.
Amity Business School
Advantages of Fixed installment
method
It is easily understandable & is simply to apply.
Amount of depreciation does not vary from year
to year.
Under this method the book value of asset is
reduced either to zero or scrap value as the case
may be.
Amity Business School
Disadvantages of fixed installment method
It does not reflect correct charge on a/c of
depreciation where effective utilization of asset varies
from year to year.
It does not recognize the reality that as an asset
becomes older the amount spent for repairs.
Sometime in this method, book value of asset become
zero but yet the assets are used in the business.
Amity Business School
Written Down Value Method
Under this Method depreciation is charged at fixed rate on the reducing balance
(i.e. cost less depreciation) every year.
Advantages of diminishing balance method
Simple to understand
Easy to follow
Ensures a fairly even charge to
profit and loss A/c
Disadvantages
Value of an asset cannot be brought down to zero
There is a difficult task to ascertain the proper rate of depreciation
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Role of Personal Core Skills in The Working Life Competency of GraduatesDokument6 SeitenThe Role of Personal Core Skills in The Working Life Competency of GraduatesAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICARO QuestionnaireDokument9 SeitenICARO QuestionnaireAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotated - UNICEF Comprehensive-Lifeskills-FrameworkDokument44 SeitenRotated - UNICEF Comprehensive-Lifeskills-FrameworkAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz QuestionsDokument4 SeitenQuiz QuestionsAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of Conversational PrinciplesDokument12 SeitenBasics of Conversational PrinciplesCrystal HillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Practices in Soft Skills Assessment 1 PDFDokument20 SeitenBest Practices in Soft Skills Assessment 1 PDFJuan Camilo Ardila100% (1)
- Training Strategy Process FlowDokument3 SeitenTraining Strategy Process FlowAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz QuestionsDokument4 SeitenQuiz QuestionsAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automation of PIP and Internal Transition Guidelines: by Saransh GargDokument15 SeitenAutomation of PIP and Internal Transition Guidelines: by Saransh GargAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz QuestionsDokument4 SeitenQuiz QuestionsAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Future of HRDokument28 SeitenFuture of HRArathy KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer Durable HRDokument1 SeiteConsumer Durable HRAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amity Business School: Legal Aspects of BusinessDokument40 SeitenAmity Business School: Legal Aspects of BusinessAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- TATA PowerDokument7 SeitenTATA PowerAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spanish - Ii: Course Code: MBA 246 Credit Units: 02 Course ObjectiveDokument1 SeiteSpanish - Ii: Course Code: MBA 246 Credit Units: 02 Course ObjectiveAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- HR Audit CaseDokument9 SeitenHR Audit CaseAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Access 2007 TutorialDokument52 SeitenAccess 2007 TutorialRamesh GurumoorthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- LLPDokument15 SeitenLLPAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managing CareerDokument13 SeitenManaging CareerAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Companies Act SummaryDokument34 SeitenCompanies Act SummaryAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amity Business School: MBA Class of 2015, Semester IDokument32 SeitenAmity Business School: MBA Class of 2015, Semester IAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- IPRsDokument28 SeitenIPRsAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marginal CostingDokument9 SeitenMarginal CostingAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recruitment and SelectionDokument26 SeitenRecruitment and SelectionAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- RecuritmentDokument14 SeitenRecuritmentAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning TheoriesDokument9 SeitenLearning TheoriesAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRPDokument37 SeitenHRPAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summer Training (M.I.L. (A.d.) )Dokument16 SeitenSummer Training (M.I.L. (A.d.) )Ankit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Position Trading Plan TemplateDokument2 SeitenPosition Trading Plan TemplateEmmanuel MasindaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tax - AssignmentDokument29 SeitenTax - Assignmentjai_thakker7659Noch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Capital Structure on ProfitabilityDokument8 SeitenEffect of Capital Structure on ProfitabilitysuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Finance Assignment 1Dokument6 SeitenCorporate Finance Assignment 1Kûnãl SälîañNoch keine Bewertungen
- PFRS of SME and SE - Concept MapDokument1 SeitePFRS of SME and SE - Concept MapRey OñateNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Sample Papers Accountancy 2Dokument10 Seiten11 Sample Papers Accountancy 2AvcelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Slides - Chapter 9 & 10Dokument103 SeitenLecture Slides - Chapter 9 & 10Phan Đỗ QuỳnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - GDP Per CapitaDokument28 Seiten1 - GDP Per CapitaTrung TạNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phil. Home Assurance Corp vs. CADokument1 SeitePhil. Home Assurance Corp vs. CACaroline A. LegaspinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSN School of Management: Final Semester Project-Internship in The Mba ProgramDokument14 SeitenSSN School of Management: Final Semester Project-Internship in The Mba ProgramSmart BalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study - Track SoftwareDokument6 SeitenCase Study - Track SoftwareRey-Anne Paynter100% (14)
- Arn Receipt GST Rfd-01a 10ctupk3011q1zh ExbclDokument1 SeiteArn Receipt GST Rfd-01a 10ctupk3011q1zh ExbclRAHUL AGGARWALNoch keine Bewertungen
- RATIO ANALYSIS MCQsDokument9 SeitenRATIO ANALYSIS MCQsAS GamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- FR Concept Book Jai ChawlaDokument280 SeitenFR Concept Book Jai ChawlatharishbabubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shane and AssociatesDokument2 SeitenShane and AssociatesCheryl MountainclearNoch keine Bewertungen
- HJR 192.original 1933 06 05Dokument4 SeitenHJR 192.original 1933 06 05WeberSteve90% (79)
- Financial ManagementDokument96 SeitenFinancial ManagementAngelaMariePeñarandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delegated Regulation Annex enDokument20 SeitenDelegated Regulation Annex enNickNoch keine Bewertungen
- HandoutDokument12 SeitenHandoutDaniela AvelinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- INDUE LIMITED - Current & Historical Company ExtractDokument28 SeitenINDUE LIMITED - Current & Historical Company ExtractclarencegirlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Account - STMT 2Dokument5 SeitenAccount - STMT 2Be HappyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting Cycle Review ProblemDokument10 SeitenAccounting Cycle Review Problemapi-25737554778% (9)
- History of Cooperation in IndonesiaDokument8 SeitenHistory of Cooperation in IndonesiakudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Payslip Nov - Sailu1 fINALDokument2 SeitenPayslip Nov - Sailu1 fINALChristine HallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting ConceptsDokument32 SeitenAccounting ConceptsSarika KeswaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pangea Mortgage Capital Closes $8.5 Million LoanDokument3 SeitenPangea Mortgage Capital Closes $8.5 Million LoanPR.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Richard W. Ellson: February 2016: Ellson Consulting, LLC: Raleigh, NCDokument4 SeitenRichard W. Ellson: February 2016: Ellson Consulting, LLC: Raleigh, NCNick HuronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ge Capital Mar19-09 PresentationDokument88 SeitenGe Capital Mar19-09 PresentationCarneades100% (2)
- A Project Report On Bharti-AXA Life Insurance Co.Dokument66 SeitenA Project Report On Bharti-AXA Life Insurance Co.sushobhanbirtia85% (20)
- MFD Exam 500 QusDokument40 SeitenMFD Exam 500 QusArvindKumarNoch keine Bewertungen