Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
The Chemical Composition of Organisms: What Makes Compounds Inorganic or Organic?
Hochgeladen von
Mohd NizamOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The Chemical Composition of Organisms: What Makes Compounds Inorganic or Organic?
Hochgeladen von
Mohd NizamCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The Chemical Composition of
Organisms
What makes compounds inorganic or
organic?
ELEMENTS IN THE CELL
There are about 92 element occurring naturally in
nature.
From these 92 element, only about 25 element
are needed to build living organisms.
Not all these element found in all living cell.
Main elements (CHON) are the most frequently
found elements in cells, forming about 96% of the
human body mass.
Trace-elements are the elements are found in
small quantity in cells, but are important in
biological processes.
CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS IN THE CELL
ORGANIC INORGANIC
Chemical compounds contain
carbon (exception are carbon
monoxide, carbon dioxide,
carbides and carbonates which
are typically considered as
inorganic)
Are usually found in and
originate from living organism.
Usually consist of
macromolecules (large
molecules)
Chemical compounds that do not
contain carbon
Usually a smaller and simpler
than organic compounds
Founds in cells water, acids,
alkalis and mineral salts
There are 4 main group of organic
compounds in cells
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic acids
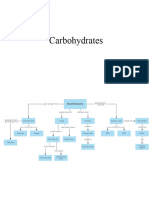
CARBOHYDRATES
The carbohydrates are made up of carbon,
hydrogen and oxygen. The ratio of hydrogen to
oxygen atoms in a molecule usually 2:1.
Many carbohydrates have the general formula
CX(H2O)Y, where x is approximately equal to y.
Three basic types of carbohydrates are
monosaccharide, disaccharides and
polysaccharides
Monosaccharide's
Monosaccharide also called simple sugar
The common monosaccharide are six-carbon
sugar
Examples of monosaccharide are glucose,
fructose (fruit sugar) and galactose
Glucose is the most common monosaccharide
Monosaccharide are sweet-tasting crystalline
substances which are soluble in water
Disaccharides
Disaccharides are formed from two monosaccharide
molecules combining together with the elements of a
molecule of water. The chemical reaction of the
formation is known as condensation.
Disaccharides also called double sugar.
Disaccharides can be broken down to their
constituent monosaccharide by a chemical reaction
involving the addition of water. The reaction is know
as hydrolysis.
Like monosaccharide, they are sweet-tasting
crystalline substances that are soluble in water.
The most common disaccharides are maltose, lactose
and sucrose.
Polysaccharides
Many monosaccharide molecules join together in
a condensation reaction (with the removal of
water molecules) to form a large polysaccharides
molecules.
Polymerisation is the process of condensing
many individual monosaccharide molecules to
form a large polysaccharides molecules.
In polymerisation, the individual monosaccharide
molecule are called monomers.
Polymerisation of monosaccharide forms:
Glycogen in humans and animals
Starch and cellulose in plants
Hydrolysis
Condensation
C
12
H
22
O
11
sucrose
+ H2 O
water
C
6
H
12
O
6
fructose
C
6
H
12
O
6
glucose
+
Starch structure
glucose
Sub unit: Glucose
Molecules with many side branches
Major storage of carbohydrates in animals and fungi, for
examples, in muscle cells and liver cells
glycogen
glucose
cellulose
Straight unbranched chain of glucose units
Plant cell wall
Proteins
Proteins are compounds of these element:
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen sulphur and
phosphorus.
Amino acids are the subunits of all proteins.
Each amino acids carries two functional group:
A carboxyl group (- COOH) which is acidic and
An amino group (-NH2) which is basic.
Types of Proteins
Two amino acids can combine together to form a
dipeptide by a condensation reaction between
the carboxyl group of one and the amino group of
the other. The resulting a bond linking the two
amino acids that is called a peptide bond.
Long chains of amino acids are called
polypeptides.
A polypeptide is formed by the condensation
reaction of many amino acids, with the removal of
water.
A polypeptide chain can also be hydrolysed, with
the addition of water molecules to form individual
amino acids.
cooh Hn c n
C C c c
NH
2
hooc nh
2
hooc
O h
h
H
2
O
condensation
Peptide bond
LIPIDS
Lipids a diverse group of substance that contain
carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, but in different
proportions to carbohydrate's.
All lipids are insoluble in water
Lipids dissolve readily in other lipids and in
organic solvent such as ether and ethanol.
The main types of lipids are:
Fats, energy-storing molecule
Oils, energy-storing molecule
Phospholipids, an important component of the cell
membrane
Steroids, act as hormones and vitamins
Vitamins
Organic molecules that are required for normal
functioning.
Animals are able to synthesise some vitamins but
most are sourced from diet
Vitamins are either water or lipid soluble
Water soluble vitamins are not stored in the body
Lipid soluble vitamins can be stored
Vitamins are essential for enzyme development
Nucleic Acids
Is genetic material, it codes what makes up an
organism
Deoxyribonucleic Acid, DNA, codes our genes
Ribonucleic acid, RNA, is DNA that has been
transcribed.
Inorganic Compounds
Water, where life evolved and reactions take
place
Oxygen (21%) and carbon dioxide (0.033%)
Nitrogen (78%) a key component of proteins
Minerals such as calcium and potassium
The skeletal structure contains 99% of the bodies
calcium, the phosphate salts in calcium provide the
mechanical rigidity bones need to bear loads.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chapter 4 Bio KasDokument84 SeitenChapter 4 Bio KasMiz KarstzNoch keine Bewertungen
- STB 111 Lecture Three Note 2012Dokument20 SeitenSTB 111 Lecture Three Note 2012Musa HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Xii Bio MoleculesDokument22 SeitenClass Xii Bio MoleculesSiddharth GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrate Lipids: Saturated Fatty Acid Unsaturated Fatty AcidsDokument53 SeitenCarbohydrate Lipids: Saturated Fatty Acid Unsaturated Fatty AcidsSyamila YusofNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worktext 1 - Biomol - Carbo & Lipids, PERALTADokument10 SeitenWorktext 1 - Biomol - Carbo & Lipids, PERALTAKelsi Kyla PeraltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry of Life: WaterDokument3 SeitenChemistry of Life: WaterRiy KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 4 Chemical Composition of CellDokument35 SeitenBiology Form 4 Chapter 4 Chemical Composition of Cellgregory gumbangNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiomoleculesDokument58 SeitenBiomoleculesLili MagossNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Compounds ExplainedDokument11 SeitenOrganic Compounds ExplainedDhimas MahardhikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological Molecules - For K-12 TrainingDokument187 SeitenBiological Molecules - For K-12 TrainingAlicia CatalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Remedial - 2Dokument54 SeitenBiology Remedial - 2Rediat GossayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Molecules PPT For P AP BiologyDokument34 SeitenBio Molecules PPT For P AP BiologyDivineDoctorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ilovepdf Merged PDFDokument12 SeitenIlovepdf Merged PDFharshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4-Biomolecules: Chemical Composition of Living FormsDokument6 SeitenModule 4-Biomolecules: Chemical Composition of Living Formsmpstme placementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 02 BIOLOGICAL MOLECULESDokument7 SeitenChapter 02 BIOLOGICAL MOLECULESAceTheLastFlameNoch keine Bewertungen
- RESEARCHDokument8 SeitenRESEARCHbun carNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiomoleculesDokument8 SeitenBiomoleculesOM SableNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio MoleculesDokument4 SeitenBio MoleculesShishir AcharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Substances of The CellDokument28 SeitenChemical Substances of The Cellorkid_ijaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CarbohydratesDokument13 SeitenCarbohydratesyr44grf94kNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Chemical Constituents of Cells1Dokument14 SeitenThe Chemical Constituents of Cells1ArnelBautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Project On BiomoleculesDokument28 SeitenChemistry Project On BiomoleculesGAMING WITH TGK YTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology ReviewerDokument14 SeitenBiology ReviewerForkensteinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbs: Definitions, Types, Functions & DigestionDokument29 SeitenCarbs: Definitions, Types, Functions & DigestionPiyali SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrates: Classification, Structures and FunctionsDokument35 SeitenCarbohydrates: Classification, Structures and FunctionsSunita SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- L 14 BiomoleculesDokument20 SeitenL 14 Biomoleculesshahin appuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2 - Introductory BiochemistryDokument15 SeitenLecture 2 - Introductory BiochemistryJana-Tae KerrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 Biomolecules: CarbohydratesDokument20 SeitenChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 Biomolecules: CarbohydratesSOUMYODEEP NAYAKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomolecules: Proteins Water LipidsDokument94 SeitenBiomolecules: Proteins Water LipidsRochelleCasador180Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Level BiologyDokument522 SeitenA Level BiologyJAMESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem SummaryDokument20 SeitenBiochem SummaryJAREL ALBERT PASCASIONoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrates and LipidsDokument8 SeitenCarbohydrates and Lipidshibadesi00Noch keine Bewertungen
- Walang MakakaseethisDokument3 SeitenWalang MakakaseethisAlissa YangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Reactions Part II: Week 7: Organic ChemistryDokument24 SeitenChemical Reactions Part II: Week 7: Organic Chemistrymia kris quiatchonNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Molecules of LifeDokument175 SeitenThe Molecules of LifeTiffany BheaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry of CellsDokument79 SeitenBiochemistry of CellsketakeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CarbohydratesDokument7 SeitenCarbohydratesAkib AbidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 BiomoleculesDokument67 Seiten5 BiomoleculesDarryl CalimlimNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Chemicals of LifeDokument12 SeitenThe Chemicals of LifeGabriel XuerebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macromolecules and Living ThingsDokument33 SeitenMacromolecules and Living ThingsDana AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Chemistry of Life Organic CompoundsDokument67 SeitenThe Chemistry of Life Organic CompoundsHahe HshdbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemicals of LifeDokument77 SeitenChemicals of LifeABEL JEDIDIAHNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHE 461 Module 1Dokument20 SeitenCHE 461 Module 1Danladi VictoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry: Biological MoleculesDokument18 SeitenBiochemistry: Biological MoleculesAnup Singh TanwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Essential Chemicals of Life PPTDokument82 Seiten3 Essential Chemicals of Life PPTBhoni KumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrate: CarbonDokument6 SeitenCarbohydrate: CarbonTrexie JaymeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Composition of The CellDokument45 SeitenChemical Composition of The CellDahliza Kamat100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Molecules of LifeDokument67 SeitenChapter 2 Molecules of LifeNatalie GraceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Assignment: BiomoleculesDokument28 SeitenChemistry Assignment: BiomoleculesShruthi GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomolecules Chemistry AssignmentDokument25 SeitenBiomolecules Chemistry Assignmentxelivo8277Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry: Molecules of LifeDokument20 SeitenBiochemistry: Molecules of Lifeapi-464344582Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry: Water Carbohydrates Lipids ProteinsDokument16 SeitenBiochemistry: Water Carbohydrates Lipids ProteinsryanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Substances.: CarbohydratesDokument9 SeitenOrganic Substances.: CarbohydratesLillianLinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrates OutlineDokument3 SeitenCarbohydrates OutlineKalka BoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Chemical Basis of LifeDokument68 SeitenThe Chemical Basis of LifeDiane Christel LundayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aadil BioChemistryDokument3 SeitenAadil BioChemistrySaira Falak SherNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM BIOLOGY SEMESTER 1 Chapter 1 CarbohydratesDokument9 SeitenSTPM BIOLOGY SEMESTER 1 Chapter 1 CarbohydratesMabel Lee Shan Shan100% (3)
- Organic vs Inorganic Compounds: Carbs, Lipids and Proteins ExplainedDokument10 SeitenOrganic vs Inorganic Compounds: Carbs, Lipids and Proteins ExplainedLyka Joy RedobleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics and Evolution: CarbohydratesDokument5 SeitenGenetics and Evolution: Carbohydratesmahreen akramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula 50 P3 2014 Zkof Sent Gbm-1Dokument12 SeitenFormula 50 P3 2014 Zkof Sent Gbm-1Mohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmoregulation Carried Out by Paramecium (Bilingual)Dokument1 SeiteOsmoregulation Carried Out by Paramecium (Bilingual)Mohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEIOSISDokument1 SeiteMEIOSISMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ba Ca Da Fa Ga Ha Ka La Manapa Ra Sa Ta Vawaya JaDokument16 SeitenBa Ca Da Fa Ga Ha Ka La Manapa Ra Sa Ta Vawaya JaMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endangeredkertas2 Soalan SkemaDokument13 SeitenEndangeredkertas2 Soalan SkemaMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmoregulation Carried Out by Paramecium (Bilingual)Dokument1 SeiteOsmoregulation Carried Out by Paramecium (Bilingual)Mohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter3heredity and VariationDokument75 SeitenChapter3heredity and VariationMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical composition of cellsDokument5 SeitenChemical composition of cellsMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOT431SDokument4 SeitenBIOT431SMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical composition of cellsDokument5 SeitenChemical composition of cellsMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Importance of Chemical Composition in CellsDokument4 SeitenImportance of Chemical Composition in CellsMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOT431TDokument4 SeitenBIOT431TMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOT442TDokument5 SeitenBIOT442TMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Importance of Chemical Composition in CellsDokument4 SeitenImportance of Chemical Composition in CellsMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOT442SDokument6 SeitenBIOT442SMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Floating Tabletop GluedDokument2 SeitenFloating Tabletop GluedMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOT441SDokument6 SeitenBIOT441SMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOT431RDokument4 SeitenBIOT431RMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 - Light - Colour and SightDokument9 SeitenChapter 7 - Light - Colour and SightHHK88893% (15)
- BIOT421TDokument7 SeitenBIOT421TMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOT421SDokument9 SeitenBIOT421SMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 4 - Biology NotesDokument59 SeitenForm 4 - Biology Notesshahmi200679% (28)
- Cell Chemical CompositionDokument14 SeitenCell Chemical CompositionMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Floating Tabletop SlottedDokument3 SeitenFloating Tabletop SlottedMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Two Tier Center Post Three Tier Center PostDokument3 SeitenTwo Tier Center Post Three Tier Center PostMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jadual BerkalaDokument18 SeitenJadual BerkalaMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exothermic and Endothermic ReactionsDokument13 SeitenExothermic and Endothermic ReactionsMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contoh Soalan Esei Dan Cara JawabDokument51 SeitenContoh Soalan Esei Dan Cara JawabMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical and Chemical ChangeDokument13 SeitenPhysical and Chemical ChangeMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Student EditionDokument54 SeitenChapter 6 Student EditionMohd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- XML JavascriptDokument62 SeitenXML Javascriptanon-506495Noch keine Bewertungen
- Session5 Automotive PackagingDokument72 SeitenSession5 Automotive PackagingShivprasad Savadatti100% (1)
- Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Program: Vibration Engineering Lab: KM31401: LAB IVDokument7 SeitenFaculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Program: Vibration Engineering Lab: KM31401: LAB IVhasmikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BasrahDokument19 SeitenBasrahDurban Chamber of Commerce and IndustryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Composition, Properties, and Standards of Steel Grade 42CrMo4 (1.7225Dokument1 SeiteChemical Composition, Properties, and Standards of Steel Grade 42CrMo4 (1.7225ADITYA_PATHAK100% (1)
- HP LaserJet 5P - 6P Service Manual (Proper)Dokument116 SeitenHP LaserJet 5P - 6P Service Manual (Proper)maroudasp100% (1)
- MSC Thesis Final Version Stephan de HoopDokument92 SeitenMSC Thesis Final Version Stephan de HoopSanjay singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- NFRC 200-2010Dokument45 SeitenNFRC 200-2010reynolds534100% (1)
- Review For Mastery: VocabularyDokument3 SeitenReview For Mastery: VocabularyHala EidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Nuts and Bolts: 2.1 Deterministic vs. Randomized AlgorithmsDokument13 Seiten2 Nuts and Bolts: 2.1 Deterministic vs. Randomized AlgorithmsEdmund ZinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Text Linguistics and Classical Studies - Facebook Com LinguaLIBDokument129 SeitenText Linguistics and Classical Studies - Facebook Com LinguaLIBEnglish Buzz100% (1)
- Blockchain Unconfirmed Transaction Hack Script Docx PDF FreeDokument2 SeitenBlockchain Unconfirmed Transaction Hack Script Docx PDF FreeHealing Relaxing Sleep Music100% (1)
- Engineering Chemistry Lab Osmania UniversityDokument83 SeitenEngineering Chemistry Lab Osmania UniversityMujtaba khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- hw12 ch11 2Dokument27 Seitenhw12 ch11 2Angela EvansNoch keine Bewertungen
- CT-1 (Paper-1) - 09-Aug-15Dokument63 SeitenCT-1 (Paper-1) - 09-Aug-15HhjNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Dimensional Engineering Process For ShipbuildingDokument11 SeitenA Dimensional Engineering Process For ShipbuildingWJccnNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHM 556 Experiment 5Dokument12 SeitenCHM 556 Experiment 5Amar Safwan100% (1)
- E 1340 - 96 - RtezndaDokument12 SeitenE 1340 - 96 - RtezndagheijoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Assigment 1Dokument32 SeitenData Assigment 1Sukhwinder Kaur100% (1)
- Cambridge O Level: PHYSICS 5054/03Dokument16 SeitenCambridge O Level: PHYSICS 5054/03Titan XosmosNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument135 SeitenUntitledtaraji dawlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Innovative Injection Rate Control With Next Generation Common Rail Fuel Injection SystemDokument8 SeitenInnovative Injection Rate Control With Next Generation Common Rail Fuel Injection SystemRakesh BiswasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prescurtari PDFDokument67 SeitenPrescurtari PDFהוד אנדרוNoch keine Bewertungen
- MediaanditsterilzationDokument15 SeitenMediaanditsterilzationAyushi MauryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework Labs Lecture01Dokument9 SeitenHomework Labs Lecture01Episode UnlockerNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Nijhoff International Philosophy Series) Stanislaw Lesniewski - S. J. Surma Et Al. (Eds.) - Collected Works. 1, 2-Springer (1991)Dokument408 Seiten(Nijhoff International Philosophy Series) Stanislaw Lesniewski - S. J. Surma Et Al. (Eds.) - Collected Works. 1, 2-Springer (1991)Aldana Fontana100% (4)
- Huawei Site Design GuidelineDokument7 SeitenHuawei Site Design GuidelineHeru BudiantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- XXXXX: Important Instructions To ExaminersDokument21 SeitenXXXXX: Important Instructions To ExaminersYogesh DumaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Methods in PsychologyDokument2 SeitenResearch Methods in PsychologyHillaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix B DAX ReferenceDokument174 SeitenAppendix B DAX ReferenceTomislav Mališ100% (1)