Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Wide QRS Tachycardias
Hochgeladen von
Eduard Espeso Chiong-Gandul Jr.0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
17 Ansichten36 SeitenECG
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenECG
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
17 Ansichten36 SeitenWide QRS Tachycardias
Hochgeladen von
Eduard Espeso Chiong-Gandul Jr.ECG
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 36
Wide QRS tachycardia is a rhythm with a rate
of more than 100 beats/min and having a
QRS duration of > 120milliseconds (ms).
Any deviation in the normal pathway of
ventricular activation may cause
widening of the QRS complex.
Different pharmacologic management
For possible ablation
Prognostication
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) with
aberrant conduction
Pre-excited tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia (VT)
Pacemaker-mediated tachycardia
Conduction over the His-Purkinje system is
blocked in either the right or the left bundle
or the distal Purkinje system (intraventricular
conduction delay).
obtain a previous ECG if available
important clues to differentiate VT vs SVT
- AV dissociation
- fusion or capture beats
- QRS width
- QRS axis
- QRS regularity
- QRS concordance
- QRS morphology
independent atrial and ventricular activation
50% of patients with VT
rare in SVT
best seen in leads V
1
and inferior leads
Lewis lead amplifies P waves
dissociated P wave totally (capture) or
partially (fusion) activates the ventricle in
advance of the next VT cycle
premature narrow QRS complex during VT
highly specific for VT
consider VT if:
-RBBB pattern > 140 ms
-LBBB pattern > 160 ms
normal axis favors SVT
left or right axis deviation favors VT
extreme left or right axis deviation
(northwest) axis strongly favors VT
slight irregularity in the R - R interval may be seen
in SVT and VT
marked irregularity of R - R interval suggests atrial
fibrillation conducted via accessory pathway
strongly favors VT
positive concordance (positive QRS
in V
1
to V
6
) suggests posterobasal
origin
negative concordance (negative
QRS in V
1
to V
6
) suggests
anteroapical origin
Negative
Concordance
Positive Concordance
V
1
and V
6
most useful
typical RBBB or LBBB pattern more likely
to be SV
atypical pattern is more likely to be VT
abrupt change from one QRS morphology
to another during regular tachycardia
suggests VT
QRS morphology during tachycardia
similar to isolated PVC during sinus
rhythm suggests VT
RBBB morphology QRS
- triphasic pattern with rsR` or rR` in V
1
- qRs in V
6
LBBB morphology QRS
- rS (r < 30 ms; rapid downslope of S) or QS in V
1
- monophasic R in V
6
QRS Morphology Favoring VT
RBBB morphology QRS
-monophasic or biphasic in V
1
; R > R
-rS or QS in V
6
LBBB morphology QRS
-rightward axis
-broad R wave (> 40 ms); notching in the
downslope of the S wave in V
1
-qR or QS in V
1
Brugada's sign: The interval from the R wave to the bottom of the S ways = 0.10
sec---characteristic VT
Josephson's sign: a small notching near the low point of the S wave = an
indicator of VT
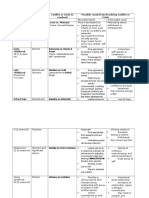
Favors SVT
Favors VT
RBBB
morphology
V1
Triphasic
rsR, rR
Monophasic
R>R
V6
qRs rS or QS
LBBB
morphology
V1 rS (r < 30 ms;)
or QS
broad R (> 40
ms); notching of
the S
qR or QS in V1
V6 monophasic R
if hemodynamically unstable, prompt
electrical cardioversion is indicated
if stable and tachycardia mechanism is
uncertain, therapeutic trial with:
- adenosine
- procainamide
- lidocaine
- Cardioversion
avoid verapamil unless VT has been
ruled out with certainty
When in doubt, the working
diagnosis is VT until proven
otherwise!
A. Supraventricular tachycardia
B. Ventricular Fibrillation
C. Ventricular Tachycardia
D. Atrial Fibrillation
A. Supraventricular tachycardia
B. Ventricular Fibrillation
C. Ventricular Tachycardia
D. Atrial Fibrillation with abberant
conduction
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- ACLS Pocket Card PDFDokument14 SeitenACLS Pocket Card PDFTmp Tmp60% (5)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Josephson - Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology Techniques AnDokument451 SeitenJosephson - Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology Techniques Anmobilica100% (5)
- DM 2018-0333 - ProjectedPop - BicolRegion - 2018-2022Dokument62 SeitenDM 2018-0333 - ProjectedPop - BicolRegion - 2018-2022Eduard Espeso Chiong-Gandul Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atrial FlutterDokument17 SeitenAtrial FlutterEdRobertArnadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Patients With Dysrhythmias and Conduction Problems Dr. SydioncoDokument15 SeitenManagement of Patients With Dysrhythmias and Conduction Problems Dr. SydioncoRoyce Vincent Tizon100% (1)
- August MALOBAGO AR 2022Dokument4 SeitenAugust MALOBAGO AR 2022Eduard Espeso Chiong-Gandul Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dec Malobago Ar 2022Dokument4 SeitenDec Malobago Ar 2022Eduard Espeso Chiong-Gandul Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- April Malobago ReportDokument4 SeitenApril Malobago ReportEduard Espeso Chiong-Gandul Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- SUN MON TUE WED THU FRI: Eduard E. Gandul JRDokument1 SeiteSUN MON TUE WED THU FRI: Eduard E. Gandul JREduard Espeso Chiong-Gandul Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Administrative Data Key To Health Policies and Programs: Philippine ExperienceDokument35 SeitenAdministrative Data Key To Health Policies and Programs: Philippine ExperienceEduard Espeso Chiong-Gandul Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Municipality Cataingan Year 2018 Barangay PopulationDokument21 SeitenMunicipality Cataingan Year 2018 Barangay PopulationEduard Espeso Chiong-Gandul Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- ACLS DrugsDokument4 SeitenACLS DrugsEduard Espeso Chiong-Gandul Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Enhanced Strategy: Department of Health, PhilippinesDokument28 SeitenEnhanced Strategy: Department of Health, PhilippinesEduard Espeso Chiong-Gandul Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stage Influential Conflict or Crisis To Resolved Possible Result From Resolving Conflict or Crisis Infancy Trust vs. MistrustDokument7 SeitenStage Influential Conflict or Crisis To Resolved Possible Result From Resolving Conflict or Crisis Infancy Trust vs. MistrustEduard Espeso Chiong-Gandul Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Perpetual Help Paramedical School: (Course&Year)Dokument1 SeitePerpetual Help Paramedical School: (Course&Year)Eduard Espeso Chiong-Gandul Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- BHW Registry FormDokument2 SeitenBHW Registry FormEduard Espeso Chiong-Gandul Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate of Participation: Erwin B. Bocalig Karen R. Binalingbing SSC President SSC AdviserDokument2 SeitenCertificate of Participation: Erwin B. Bocalig Karen R. Binalingbing SSC President SSC AdviserEduard Espeso Chiong-Gandul Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Campus Kween Board of JudgesDokument1 SeiteCampus Kween Board of JudgesEduard Espeso Chiong-Gandul Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Method of Acid Base Balance InterpretationDokument5 SeitenSimple Method of Acid Base Balance InterpretationEduard Espeso Chiong-Gandul Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- ECG For Beginners PDFDokument153 SeitenECG For Beginners PDFIonut MoisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sinus ArrhythmiaDokument6 SeitenSinus ArrhythmiaVincent Maralit MaterialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Paper For MD1 2021 - AnswersDokument10 SeitenPractice Paper For MD1 2021 - AnswersAlex TaylorNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECG For The Small Animal Practitioner PDFDokument110 SeitenECG For The Small Animal Practitioner PDFCarlos Pereida100% (1)
- VT CriteriaDokument8 SeitenVT CriterianitipatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normal Ecg, Infarction & Arrhythmias: Iqbal Lahmadi Departement of Internal Medicine Sintang - 2013Dokument98 SeitenNormal Ecg, Infarction & Arrhythmias: Iqbal Lahmadi Departement of Internal Medicine Sintang - 2013Maylisa ManurungNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECG Exercise, Insights, Ang HighlightsDokument5 SeitenECG Exercise, Insights, Ang HighlightsKerima Danica Lising GayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal Cardiac EmergenciesDokument4 SeitenNeonatal Cardiac EmergenciesEstellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Arrythmias: Prof. Maximin A. Pomperada, RN, MNDokument70 SeitenBasic Arrythmias: Prof. Maximin A. Pomperada, RN, MNRellie CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pub Family Practice Examination and Board ReviewDokument937 SeitenPub Family Practice Examination and Board ReviewMohammad PharaonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Idiopathic Fascicular LV Tachycardia Case Report - Kadek Agus Putra - Edit 1Dokument8 SeitenIdiopathic Fascicular LV Tachycardia Case Report - Kadek Agus Putra - Edit 1putra udayanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Picu Ready RecknerDokument2 SeitenPicu Ready RecknerPranitha Reddy0% (1)
- Miocarditis Por Clozapina Ronaldson2017 Revisión SistematicaDokument19 SeitenMiocarditis Por Clozapina Ronaldson2017 Revisión SistematicaAlejandro PiscitelliNoch keine Bewertungen
- EKG Rhythms2 PDFDokument7 SeitenEKG Rhythms2 PDFAya KamajayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flujogramas Europa 2010 Poster RCPDokument9 SeitenFlujogramas Europa 2010 Poster RCPMinina Delka MedinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChloroephedrineDokument9 SeitenChloroephedrineTyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Core V - Cardiovascular CoreDokument35 SeitenCore V - Cardiovascular CoreMatthew LeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac Rhythms and DysrhythmiasDokument14 SeitenCardiac Rhythms and DysrhythmiasShawn Gaurav Jha100% (1)
- Soal ArithmiaDokument13 SeitenSoal Arithmiaeka rahmawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Essentials: Essential Updates: Distinguishing Between Left-And Right-Sided Atrial TachycardiaDokument28 SeitenPractice Essentials: Essential Updates: Distinguishing Between Left-And Right-Sided Atrial TachycardiaRully SyahrizalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Principle, Operation and Maintenance: Aqeel Ahmed KhanDokument18 SeitenBasic Principle, Operation and Maintenance: Aqeel Ahmed KhanchanlalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rhythm Cheat SheetDokument1 SeiteRhythm Cheat Sheetjb cookiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ArrhythmiaDokument8 SeitenArrhythmiaPrecious Grace CabahugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Palpitation:evaluation, Ambulatory Monitoring, Mobile Telemetry Eg - MCOT@2012Dokument19 SeitenPalpitation:evaluation, Ambulatory Monitoring, Mobile Telemetry Eg - MCOT@2012Navojit ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUG STUDY AdenosineDokument1 SeiteDRUG STUDY Adenosinejulesubayubay5428100% (1)