Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Steven Lee M.S. Pathology FTCC
Hochgeladen von
jnnfrleighOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Steven Lee M.S. Pathology FTCC
Hochgeladen von
jnnfrleighCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
vomer
mandible
Frontal bone
maxilla
Zygomatic
bone
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
Supraorbital
Foramen
(frontal bone)
Middle nasal concha
(ethmoid bone)
Inferior nasal concha
Infraorbital foramen
(maxillary bone)
Perpendicular plate
(ethmoid bone)
vomer
mandible
Frontal bone
maxilla
Alveoli processes
(maxillary bone)
Alveoli processes
(mandible)
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
P
e
r
p
e
n
d
i
c
u
l
a
r
p
l
a
t
e
(
e
t
h
m
o
i
d
b
o
n
e
)
vomer
Infraorbital foramen
(maxillary bone)
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
Optic foramen or canal (sphenoid bone)
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
When the supraorbital foramen is not completely
enclosed by bone, there is a supraorbital notch, rather
than a foramen, on the orbital rim, as is the case for
this specimen.
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
Optic canals permit passage of the
optic nerves from the eyes to the brain.
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
The inferior orbital fissure
permits passage of cranial
nerves and blood vessels.
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
The superior orbital fissure
permits passage of cranial
nerves and blood vessels to the orbit
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
Frontal
bone
Parietal bone
Temporal bone
Zygomatic
bone
mandible
O
c
c
i
p
i
t
a
l
b
o
n
e
maxilla
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
Frontal
bone
Parietal bone
Zygomatic process
(Temporal bone)
Temporal process
Zygomatic bone
mandible
O
c
c
i
p
i
t
a
l
b
o
n
e
maxilla
Mastoid process
(temporal bone)
Styloid process
(temporal bone)
External occipital
protuberance
External auditory meatus
(temporal bone)
angle
ramus
Zygomatic process
(frontal bone)
Frontal process
(zygomatic bone)
Condylar process
(mandible)
Coronoid process
(mandible)
Coronal suture
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
Frontal bone
Zygomatic bone
mandible
Zygomatic process
(frontal bone)
Frontal process
(zygomatic bone)
Zygomatic arch
Sphenoid bone
Ethmoid
bone
Condylar process
(mandible)
Coronoid process
(mandible)
maxilla
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
Parietal bone
Parietal bone
Occipital bone
Lambdoidal
suture
External occipital
protuberance
Sagittal suture
Mastoid process
(temporal bone)
Styloid process
(temporal bone)
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
Coronal suture
Frontal bone
Parietal bone
Parietal bone
Occipital bone
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
Lesser wing (sphenoid bone)
Greater wing
(sphenoid bone)
Foramen magnum surrounds
the connection between the
brain and spinal cord.
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
Foramen
magnum
Lesser wing (sphenoid bone)
Foramen ovale
(sphenoid bone)
Foramen spinosum
(sphenoid bone)
Foramen lacerum
(sphenoid bone)
Location of foramen rotundum (sphenoid bone), although not shown on this model
Greater wing
(sphenoid bone)
Internal occipital
protuberance
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
Crista galli
(ethmoid bone)
Cribiform plate
(ethmoid bone)
Lesser wing (sphenoid bone)
Sella turcica
(sphenoid bone)
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
Crista galli
(ethmoid bone)
Lesser wing (sphenoid bone)
Sella turcica
(sphenoid bone)
The falx cerebri, a membrane that stabilizes the
position of the brain, attaches to this ridge.
Greater wing
(sphenoid bone)
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
Optic canal
(sphenoid bone)
The hypophyseal fossa,
the depression within the
sella turcica houses and
protects the pituitary gland.
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
nasal
mandible
Mastoid process (temporal bone)
Internal acoustic canal
(temporal bone)
Petrous portion
(temporal bone)
angle
ramus
body
Alveoli processes
(maxillary bone)
Lesser wing
(sphenoid bone)
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
Internal auditory meatus
(temporal bone)
The internal auditory canal (meatus) carries
blood vessels and nerves to the
inner ear.
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
Foramen
magnum
Palatine process
(maxilla)
Palatine bones
Zygomatic arch
External occipital
ptotuberance
Occipital condyles
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
Occipital condyles
Occipital condyles are the site of
articulation between the skull and
the 1st cervical vertebrae (atlas).
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
Palatine
bone
Palatine
bone
Palatine process
(maxillary bone)
mandible
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
vomer
Pterygoid plates
(sphenoid bone)
lateral
lateral
medial
medial
Foramen magnum
Pterygoid processes
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
mandible
maxilla
Mandibular notch
ramus
body
Mandibular alveoli processes
Maxillary alveoli processes
Mental protuberance
Mental
foramen
Oblique line
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
Maxillary bone
Alveoli processes
mandible
Alveoli processes
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
FETAL
SKULL
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
At birth, there are 2 frontal bones
that articulate along the metopic
suture. Although the suture
generally disappears by age 8 as
the bones fuse, the adult skull
commonly retains traces of the
suture line.
Metopic suture
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
Frontal fontanel
(anterior)
Parietal bone
Parietal bone
Frontal bone
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
Parietal bone
Parietal bone
Occipital bone
Occipital fontanel
(posterior)
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
Parietal bone
Sphenoidal fontanel
(anterolateral)
Mastoidal fontanel
(posterolateral)
steven lee
M.S. Pathology
FTCC
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Diaphragm Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandDiaphragm Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells and TissuesVon EverandCells and TissuesArthur W. PollisterNoch keine Bewertungen
- MeiosisVon EverandMeiosisPeter MoensBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- 2023.neuroscience - Trans10.posterior Fossa Level Brainstem Cranial Nuclei and NervesDokument7 Seiten2023.neuroscience - Trans10.posterior Fossa Level Brainstem Cranial Nuclei and NervesstellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vernon MouncastleDokument40 SeitenVernon MouncastleCarla Guixé SendiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- EmbryologyDokument68 SeitenEmbryologyانس ابوهيبةNoch keine Bewertungen
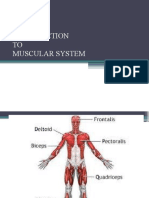
- UNIT-6 Muscular SystemDokument48 SeitenUNIT-6 Muscular SystemChandan ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- D. Brainstem: PONS (Ventral Metencephalon) 1. External Consideration A. Ventral ViewDokument39 SeitenD. Brainstem: PONS (Ventral Metencephalon) 1. External Consideration A. Ventral ViewMarvic SueltoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Year Basic BSC Nursing Anatomy Word Notes in DetailsDokument2 Seiten1st Year Basic BSC Nursing Anatomy Word Notes in DetailsShreyas WalvekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology: Chapter 3-Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument7 SeitenBiology: Chapter 3-Human Anatomy and PhysiologyMaahrukh Shifa KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of The Nervous SystemDokument31 SeitenAnatomy of The Nervous SystemXKnightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Musculoskeletal QuestionsDokument4 SeitenMusculoskeletal QuestionsJen Del Mundo100% (1)
- Pres1 Intro To KinesiologyDokument31 SeitenPres1 Intro To KinesiologyShahina Sherani100% (2)
- Higher Center - Dr. BarbonDokument5 SeitenHigher Center - Dr. BarbonMelissa SalayogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy TMJ CinioDokument3 SeitenAnatomy TMJ CinioGren May Angeli MagsakayNoch keine Bewertungen
- OPP Lecture 1Dokument7 SeitenOPP Lecture 1Lenny CostantiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Development of Infants and ToddlersDokument36 SeitenPhysical Development of Infants and ToddlersJOHN PURANoch keine Bewertungen
- The Prenatal Origin of Behavior by Davenport Hooker, PH.D., Sc.D. - University of Kansas Press, Lawrence, Kansas, 1952Dokument148 SeitenThe Prenatal Origin of Behavior by Davenport Hooker, PH.D., Sc.D. - University of Kansas Press, Lawrence, Kansas, 1952Tamás DunavölgyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP MusclesDokument14 SeitenAP MusclesAlexandra NadinneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy & Physiology Syllabus For Community CollegesDokument312 SeitenAnatomy & Physiology Syllabus For Community CollegesRenz EspinosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System ReviewDokument6 SeitenNervous System Reviewtherenam825Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sciences 6 - Sample PagesDokument12 SeitenSciences 6 - Sample PagesLili Muñoz Mendoza100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Muscles Power PointDokument102 SeitenChapter 7 Muscles Power PointNurseReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21-Spinal Cord TractsDokument23 Seiten21-Spinal Cord TractsALFAHRUL CAHYADINoch keine Bewertungen
- Students Clinical Case AnalysisDokument5 SeitenStudents Clinical Case Analysisjacc_282Noch keine Bewertungen
- PhysiologyDokument31 SeitenPhysiologyraza20100% (1)
- The Axilla: Norah AlmudawiDokument14 SeitenThe Axilla: Norah AlmudawiF-med440 imamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument46 SeitenHuman Anatomy and PhysiologyBegumHazinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument8 SeitenHuman Anatomy and PhysiologyDanielle AguilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalyst O True Catalyst: ExampleDokument9 SeitenCatalyst O True Catalyst: ExampleAshley SaronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology of The Nervous System 2011Dokument33 SeitenHistology of The Nervous System 2011Ng Bing JueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology (1-Ya)Dokument108 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology (1-Ya)Rhelina MinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health, Wellness, and IllnessDokument22 SeitenHealth, Wellness, and Illnessjasnate84100% (1)
- Neuro Assessment ReviwerDokument51 SeitenNeuro Assessment ReviwerKim RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction of Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument27 SeitenIntroduction of Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDebora Intan D. LarashatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- OPP Course Review: John Garlitz, DO Deborah Schmidt, DO Opp 2 April 15, 2015 8:10 AMDokument248 SeitenOPP Course Review: John Garlitz, DO Deborah Schmidt, DO Opp 2 April 15, 2015 8:10 AMmina botross100% (1)
- Autonomic Nervous System in The Head & NeckDokument22 SeitenAutonomic Nervous System in The Head & Neckبراءة أحمد السلامات33% (3)
- Lower Limb InjuriesDokument47 SeitenLower Limb InjuriesDaisyyhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions and AnswersDokument15 SeitenQuestions and AnswersTanveerAli01Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Signficance of RespirationDokument12 SeitenThe Signficance of RespirationApril Dawn100% (1)
- Embryogenesis (Week 4-8) & Fetal Period (Week 9-Birth)Dokument30 SeitenEmbryogenesis (Week 4-8) & Fetal Period (Week 9-Birth)مالك مناصرةNoch keine Bewertungen
- M. Rowane - Core Concepts in Osteopathic Manipulative MedicineDokument55 SeitenM. Rowane - Core Concepts in Osteopathic Manipulative Medicinedruidsamsung100% (1)
- Identify Your MuscleDokument89 SeitenIdentify Your MuscleProdosh Chatterjee100% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument999 SeitenAnatomy and PhysiologyNacel CelesteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Learning Assessment 3Dokument13 SeitenAnatomy Learning Assessment 3Jay Lure Gomez BaguioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology of Balance: Kunal ShahDokument18 SeitenPhysiology of Balance: Kunal ShahKunal ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.ascending PathwaysDokument27 Seiten11.ascending PathwaysdenekeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Guide To LU3 PDFDokument54 SeitenA Guide To LU3 PDFMigs MedinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Physiology - Kapitola 21 PDFDokument41 SeitenHuman Physiology - Kapitola 21 PDFpummygNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing DepartmentDokument15 SeitenNursing DepartmentJaylord VerazonNoch keine Bewertungen
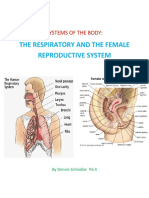
- Systems of The BodyDokument10 SeitenSystems of The BodyKatrina SchindlarNoch keine Bewertungen
- VIII. Special SensesDokument21 SeitenVIII. Special SensesSkyNayvieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnostic Exam - Bio1215 - Bio1214 PDFDokument15 SeitenDiagnostic Exam - Bio1215 - Bio1214 PDFCarla AngelesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4th Lecture HeadNeck and LympaticsDokument77 Seiten4th Lecture HeadNeck and LympaticsJeffrey Valdez Esteron100% (1)
- Human Development SyllabusDokument5 SeitenHuman Development SyllabusbeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Introduction To Autonomic PharmacologyDokument68 Seiten6 Introduction To Autonomic Pharmacologynids100% (1)
- Dermatome Myotome SclerotomeDokument4 SeitenDermatome Myotome SclerotomeAdhya TiaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Head & Neck - Deep Cervical Fascia &cervical PlexusDokument9 SeitenHead & Neck - Deep Cervical Fascia &cervical PlexusKomang Tri Adi SuparwatiNoch keine Bewertungen
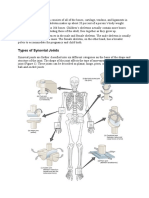
- Types of Synovial JointsDokument7 SeitenTypes of Synovial Jointsaulia nurfadillahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Living GraceDokument227 SeitenLiving GraceÁdám NógrádiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative Analysis of Selected Medicinal Plants, Tamilnadu, IndiaDokument3 SeitenQualitative Analysis of Selected Medicinal Plants, Tamilnadu, IndiaDiana RaieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Strategy 3rd Edition Peng Solutions ManualDokument16 SeitenGlobal Strategy 3rd Edition Peng Solutions ManualJenniferThompsonxergb100% (13)
- Convention Concerning The Protection of The WorldDokument41 SeitenConvention Concerning The Protection of The WorldMonica Ardeleanu100% (1)
- Modfied Indian Systems of MedicineDokument8 SeitenModfied Indian Systems of MedicineNishamolKSNoch keine Bewertungen
- STD 12 Accountancy1Dokument264 SeitenSTD 12 Accountancy1Chetan KhonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Digest 2 S.C. MEGAWORLD CONSTRUCTIONDokument3 SeitenCase Digest 2 S.C. MEGAWORLD CONSTRUCTIONRomualdo CabanesasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Journal 2Dokument60 SeitenFinal Journal 2Swetha NikaljeNoch keine Bewertungen
- WearebecausewebelongDokument3 SeitenWearebecausewebelongapi-269453634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Catherine Davies - Modernity, Masculinity, and Imperfect Cinema in CubaDokument16 SeitenCatherine Davies - Modernity, Masculinity, and Imperfect Cinema in CubakahlilchaarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Competencies: Table of SpecificationDokument2 SeitenLearning Competencies: Table of Specificationyolanda renos0% (1)
- UNIX Introduction 1Dokument18 SeitenUNIX Introduction 1Akash SavaliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (EN) Google Developer Policy - September 1, 2021Dokument56 Seiten(EN) Google Developer Policy - September 1, 2021JimmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Physician V CIRDokument24 SeitenUniversity of Physician V CIROlivia JaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Biography of Hazrat Shah Qamaos Sahib in One PageDokument3 SeitenThe Biography of Hazrat Shah Qamaos Sahib in One PageMohammed Abdul Hafeez, B.Com., Hyderabad, IndiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method Statement Free Download: How To Do Installation of Suspended False CeilingsDokument3 SeitenMethod Statement Free Download: How To Do Installation of Suspended False Ceilingsmozartjr22100% (1)
- Ap Government Imperial PresidencyDokument2 SeitenAp Government Imperial Presidencyapi-234443616Noch keine Bewertungen
- Internship Proposal FormDokument3 SeitenInternship Proposal FormMuhammad FidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mutants Genetic Gladiators Hack PDFDokument2 SeitenMutants Genetic Gladiators Hack PDFFercho GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wavoo Wajeeha Women's College - Annual Report - 2013-14Dokument29 SeitenWavoo Wajeeha Women's College - Annual Report - 2013-14kayalonthewebNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSC User GuidelinesDokument64 SeitenDSC User Guidelineslinus200Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fractal Blaster Trading Strategy ReportDokument22 SeitenFractal Blaster Trading Strategy ReportIcky IckyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Melo V PeopleDokument1 SeiteMelo V PeoplejjangNoch keine Bewertungen
- BArch Thesis Proposal Form - 27march 2023 1 PDFDokument3 SeitenBArch Thesis Proposal Form - 27march 2023 1 PDFDevkalpaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sistem Informasi Pencatatan Data Pelanggan Pada Telkomsel Grapari Banda AcehDokument6 SeitenSistem Informasi Pencatatan Data Pelanggan Pada Telkomsel Grapari Banda AcehJurnal JTIK (Jurnal Teknologi Informasi dan Komunikasi)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Settlement Geography: Unit No-1&2Dokument11 SeitenSettlement Geography: Unit No-1&2Arindam RoulNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Social Policy and Social Welfare AdministrationDokument284 Seiten3 Social Policy and Social Welfare AdministrationJoseph Kennedy100% (5)
- October 2014 1413376166 06 PDFDokument3 SeitenOctober 2014 1413376166 06 PDFDineshNoch keine Bewertungen
- E5170s-22 LTE CPE - Quick Start Guide - 01 - English - ErP - C - LDokument24 SeitenE5170s-22 LTE CPE - Quick Start Guide - 01 - English - ErP - C - LNelsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Denso HP4Dokument87 SeitenDenso HP4Abraham Janco Janco100% (2)