Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Attacks On Traditional Metaphysics
Hochgeladen von
Archie Dei MagaraoOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Attacks On Traditional Metaphysics
Hochgeladen von
Archie Dei MagaraoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Philosophy Synthesis I
Prepared by
Archie R. Magarao
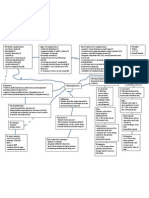
Phase I
Turn to the
Subject
Phase II
Turn to
Historicism
Phase III
Turn to
Language
Key
Figures
Descartes
Kant,
Locke
Hume
Key
Thoughts
Emphasis on
epistemology over
metaphysics
Since the time of Locke, metaphysics has been challenged as extending beyond the
capacities of human reason
Locke maintains that in books of metaphysics we find an infinite number of
propositions that nevertheless tells us nothing of the nature or reality of things
existing without us so that metaphysical propositions are not tautological, they are
merely trifling.
For Hume, metaphysics is not properly a science but arises either from fruitless
efforts of human vanity which would penetrate into subjects
Key Figures
Post-Hegelians
Marx, Engels, etc.
Key Thought(s)
The attack is on what it is
that metaphysics claimed
to know.
the primacy or the
possibility of metaphysics
is under criticism
All human knowledge
was socially constructed
or context-bound, or that
there were no natures or
ultimate reality to be
known.
All human knowledge
was socially
constructed or context-
bound, or that there
were no natures or
ultimate reality to be
known.
What a thing is cannot
be separated from its
historical context.
Key Figures
Wittengenstein,
de Saussure,
Frege, Cassirier,
Levi-Strauss,
Heidegger
Key Thoughts
Insistence of the
importance of
language in
relation to
thought
Thought requires
language to be
even possible.
If something cannot be
coherently expressed or
articulated in language, it
makes no sense to affirm
or deny anything about
it.
In the 20
th
century, the
linguistic turn called
into question any attempt
to talk of metaphysical
truthparticularly
whether metaphysical
propositions could be
true.
Everything or
the reality of
things need no
explanation or
accounting for
PRAGMATISM
EXISTENTIA-
LISM
NATURALISM,
POSITIVISM,
MARXISM
We have no reason to claim that there is a cross-cultural standard of rationality
or a single, universal model of reason.
Reason is a tool that without warrant marginalizes certain aspects of experience
and certain groups and thus hegemonic and oppressive.
Mistrust in reason and rationality (Feminism,
Marxism, Deconstructionism etc.)
One of Karl Poppers concern about metaphysics from Plato to Hegel is that
comprehensive metaphysical accounts have tended to bring with them political
systems that allegedly leave no room for human (political) freedom and
autonomy.
If there is no stable core of philosophical problems, if reality is in large part,
or wholly socially constructed and if knowledge and categories of knowing
are ultimately historical , a systematic metaphysics would be not only beside
the point but impossible.
If there can be a metaphysics, what method or methods might one use?
Suspicion of any systematic
metaphysics
What is your assessment to the
contemporary challenges on
metaphysics?
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- White IgnoranceDokument27 SeitenWhite IgnorancejakilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Assault Against Logic by Steve YatesDokument28 SeitenThe Assault Against Logic by Steve YatesDeea MilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Models of The ChurchDokument8 SeitenModels of The ChurchArchie Dei Magarao100% (2)
- Case Conceptualization BowenDokument2 SeitenCase Conceptualization BowenJovencio Marquez0% (1)
- Rob Lucas - Feeding The InfantDokument16 SeitenRob Lucas - Feeding The InfantEge ÇobanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bourdieu Pierre 1967 Sociology and Philosophy in France Since 1945 Death and Resurrection of A Philosophy Whitout Subject en Social Research VoDokument52 SeitenBourdieu Pierre 1967 Sociology and Philosophy in France Since 1945 Death and Resurrection of A Philosophy Whitout Subject en Social Research VoRaúl Cavero100% (1)
- GAD 7 Anxiety Updated 0Dokument1 SeiteGAD 7 Anxiety Updated 0Shintya DewiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icd 11Dokument22 SeitenIcd 11Shubhangi Vats100% (1)
- MaterialismDokument187 SeitenMaterialismAntony Lopez VilcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sociology of KnowledgeDokument8 SeitenSociology of KnowledgeCAREL FAITH M. ANDRESNoch keine Bewertungen
- The End of Progress: Decolonizing the Normative Foundations of Critical TheoryVon EverandThe End of Progress: Decolonizing the Normative Foundations of Critical TheoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical MRCPSYCH Passing The CascDokument353 SeitenClinical MRCPSYCH Passing The Cascsherief marouf100% (3)
- Biblical Pronunciations GuideDokument14 SeitenBiblical Pronunciations GuideArchie Dei Magarao100% (1)
- Approaches To PsychotherapyDokument4 SeitenApproaches To PsychotherapyHassan.shehri100% (7)
- Feminist Standpoint Theory - Internet Encyclopedia of PhilosophyDokument17 SeitenFeminist Standpoint Theory - Internet Encyclopedia of PhilosophySESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Warner Fear of A Queer PLanetDokument15 SeitenWarner Fear of A Queer PLanetJeroozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychodrama TherapyDokument6 SeitenPsychodrama TherapyMahrukhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Raymond Geuss - Reality and Its Dreams (2016, Harvard University Press)Dokument313 SeitenRaymond Geuss - Reality and Its Dreams (2016, Harvard University Press)Carlos Eduardo Jiménez RubianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bible Quiz QuestionsDokument2 SeitenBible Quiz QuestionsArchie Dei MagaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1: What Is Postmodernism? 2: (Blank Slide) 3: History of PostmodernismDokument5 Seiten1: What Is Postmodernism? 2: (Blank Slide) 3: History of PostmodernismKaye Jiane Espanillo MatulacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Debating Humanity. Towards A Philosophical Sociology: Daniel CherniloDokument20 SeitenDebating Humanity. Towards A Philosophical Sociology: Daniel CherniloEka Wahyudi NggoheleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Nature: Justice Versus Power: The Chomsky-Foucault DebateVon EverandHuman Nature: Justice Versus Power: The Chomsky-Foucault DebateNoch keine Bewertungen
- After Queer Theory: The Limits of Sexual PoliticsVon EverandAfter Queer Theory: The Limits of Sexual PoliticsBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (3)
- Trauma Recovery and Empowerment ModelDokument12 SeitenTrauma Recovery and Empowerment Modeljimmiefking_64670597Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Are The Main Features of PostmodernismDokument4 SeitenWhat Are The Main Features of PostmodernismSMCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Against Dryness Iris MurdochDokument6 SeitenAgainst Dryness Iris MurdochAdriana Bădoi100% (4)
- Speaking Hermeneutically: Understanding in the Conduct of a LifeVon EverandSpeaking Hermeneutically: Understanding in the Conduct of a LifeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gáspár Miklós Tamás About ClassDokument41 SeitenGáspár Miklós Tamás About ClassHistorica VariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poststructuralism GenealogiesDokument24 SeitenPoststructuralism GenealogiesPeter FormanNoch keine Bewertungen
- What If Truth Was PersonalDokument27 SeitenWhat If Truth Was PersonalJohn JiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classical Philosophical Text. Textual & Contexual Method.Dokument9 SeitenClassical Philosophical Text. Textual & Contexual Method.Shatabdi Duttapol sc2nd yearNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument4 SeitenAssignment 1ASHNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Liberal HumanismDokument4 Seiten1 Liberal Humanismazmat.pti.ikNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Anything Goes?" Theology and Science in A Culture Marked by Postmodern ThinkingDokument7 Seiten"Anything Goes?" Theology and Science in A Culture Marked by Postmodern Thinkingmatrik88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Criticism Is The Theory of Literature': Theory Is The Criticism of Literature RODERICK MCGILLISDokument10 SeitenCriticism Is The Theory of Literature': Theory Is The Criticism of Literature RODERICK MCGILLISLaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- HistoricismDokument18 SeitenHistoricismManal SaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ideology and Political IdeologyDokument5 SeitenIdeology and Political Ideologym-7383186Noch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophical View of ManDokument12 SeitenPhilosophical View of ManGis Siti Rodrigo Sevilla100% (1)
- Ideology: The Problem-Child of Political AnalysisDokument3 SeitenIdeology: The Problem-Child of Political AnalysisEnrico SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pragmatism by Murray, D. L., 1888-1962Dokument33 SeitenPragmatism by Murray, D. L., 1888-1962Gutenberg.org100% (1)
- Final Ansfor Classical Political PhilosophyDokument70 SeitenFinal Ansfor Classical Political PhilosophyKevin AntonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ferguson, Stephen C. 2007 'Social Contract As Bourgeois Ideology' Cultural Logic (19 PP.)Dokument19 SeitenFerguson, Stephen C. 2007 'Social Contract As Bourgeois Ideology' Cultural Logic (19 PP.)voxpop88Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Five Languages of Utopia: Cercles 30 (2013)Dokument8 SeitenThe Five Languages of Utopia: Cercles 30 (2013)felipee20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mills - White IgnoranceDokument26 SeitenMills - White IgnoranceCarlos DeutscheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telling The Truth About ClassDokument41 SeitenTelling The Truth About ClassIgor CvejicNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Specter of Materialism Review EssayDokument8 SeitenThe Specter of Materialism Review EssayImene BouguesriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Berger Luckman Social Construction of Reality SummaryDokument4 SeitenBerger Luckman Social Construction of Reality SummaryPrasansa SaikiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elias MetahistoricalRomanceDokument15 SeitenElias MetahistoricalRomanceMoh FathoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classical Pol PhilosophyDokument7 SeitenClassical Pol PhilosophySanchi GangwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surber 1998 Materialist Critique of CultureDokument37 SeitenSurber 1998 Materialist Critique of Culturebilal.salaamNoch keine Bewertungen
- FCLT - Knowledge - For ClassDokument2 SeitenFCLT - Knowledge - For Classrupal aroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vários Autores - Immanent Materialisms and The Unbounded Earth (Angelaki Volume 19, Number 1)Dokument189 SeitenVários Autores - Immanent Materialisms and The Unbounded Earth (Angelaki Volume 19, Number 1)Benjamim GomesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stuart Hall's Theory of Ideology: A Frame For Rhetorical CriticismDokument21 SeitenStuart Hall's Theory of Ideology: A Frame For Rhetorical CriticismIatridis Elisavet NikosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Titusland,+SR 2006 SanbonmatsuDokument32 SeitenTitusland,+SR 2006 Sanbonmatsuhakan eyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elías Palti - The Return of The SubjectDokument27 SeitenElías Palti - The Return of The SubjectAnonymous pcYaAFwlINoch keine Bewertungen
- The Psychology of Society (Barnes & Noble Digital Library)Von EverandThe Psychology of Society (Barnes & Noble Digital Library)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lotman S Scientific Investigatory BoldneDokument24 SeitenLotman S Scientific Investigatory Boldnewellington Neves VieiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arguments For ADokument4 SeitenArguments For AsNoch keine Bewertungen
- TviturintiDokument30 SeitenTviturintibeepishNoch keine Bewertungen
- IdeologiesDokument17 SeitenIdeologiesmaleskunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phi Lo WhyDokument8 SeitenPhi Lo WhyAmy Cecilia LeighNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0201 Aron GB 2Dokument18 Seiten0201 Aron GB 2Anahi GimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Script: Do You Know That?? Descartes Was Also Known Among TheDokument8 SeitenScript: Do You Know That?? Descartes Was Also Known Among TheEugene Franz SantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foucault - S Encounter With MarxismDokument58 SeitenFoucault - S Encounter With MarxismStefanTanasijevićNoch keine Bewertungen
- A "Conversation" With Richard RortyDokument26 SeitenA "Conversation" With Richard RortyderoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rorty Post Metaphysical CultureDokument9 SeitenRorty Post Metaphysical CultureJesúsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions of DiscourseDokument6 SeitenFunctions of DiscoursejenniferclaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Terry Eagleton Marx and FreedomDokument26 SeitenTerry Eagleton Marx and FreedomBodhisatwa RayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes On The PostmodernDokument5 SeitenLecture Notes On The PostmodernKam Ho M. WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creation PsalmsDokument7 SeitenCreation PsalmsArchie Dei MagaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALAY SA DIYOS Lyrics OnlyDokument2 SeitenALAY SA DIYOS Lyrics OnlyArchie Dei MagaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BibliographyDokument3 SeitenBibliographyArchie Dei MagaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Citations and Bibliography StylesDokument6 SeitenCitations and Bibliography StylesArchie Dei MagaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LST Academic Calendar 2019-2020Dokument7 SeitenLST Academic Calendar 2019-2020Archie Dei MagaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Goal of Man: To Give Glory To God, To Know Him and To Love HimDokument13 SeitenThe Goal of Man: To Give Glory To God, To Know Him and To Love HimArchie Dei MagaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Altar Serving SeminarDokument9 SeitenAltar Serving SeminarArchie Dei MagaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Altar Serving SeminarDokument9 SeitenAltar Serving SeminarArchie Dei MagaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inspirational SongDokument16 SeitenInspirational SongArchie Dei MagaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SVPS HymnDokument1 SeiteSVPS HymnArchie Dei MagaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 25 Years of Piarist Life Song LyricsDokument1 Seite25 Years of Piarist Life Song LyricsArchie Dei MagaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To The Holy Rosary: Wharton Catholic ClubDokument29 SeitenIntroduction To The Holy Rosary: Wharton Catholic ClubArchie Dei Magarao100% (1)
- Life and Dignity of The Human PersonDokument2 SeitenLife and Dignity of The Human PersonArchie Dei MagaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Human Person and OthersDokument16 SeitenThe Human Person and OthersArchie Dei MagaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Philosophy: "Know Thyself."Dokument24 SeitenIntroduction To Philosophy: "Know Thyself."Archie Dei MagaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pyschological DisorderDokument2 SeitenPyschological DisorderFatin AfyqahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding The SelfDokument18 SeitenUnderstanding The SelfNerish Plaza0% (1)
- Personality DisorderDokument26 SeitenPersonality Disordergem72100% (2)
- Describe The Major Stressors in Teens EssayDokument2 SeitenDescribe The Major Stressors in Teens EssaySaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sinhgad College of Nursing: IndexDokument2 SeitenSinhgad College of Nursing: IndexAmit TamboliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychological Services BrochureDokument1 SeitePsychological Services BrochureRhalfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of Work Related Stress (Self Reporting Questionnaire-20)Dokument12 SeitenAssessment of Work Related Stress (Self Reporting Questionnaire-20)Keyne ChristaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bipolar I Disorder Case ExampleDokument6 SeitenBipolar I Disorder Case ExampleGrape JuiceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dmnorusis Resume (Updated)Dokument1 SeiteDmnorusis Resume (Updated)DainaNorusisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Letter For Wayne McGuinness' Ride For Mental HealthDokument2 SeitenLetter For Wayne McGuinness' Ride For Mental Healthscribd-jNoch keine Bewertungen
- Depression in Men OPED - Dr. MugambiDokument3 SeitenDepression in Men OPED - Dr. MugambiCosmas MugambiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic Depression in Pakistan, Causes and EffectsDokument9 SeitenTopic Depression in Pakistan, Causes and EffectsMubasair MubeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept MapDokument1 SeiteConcept Mapmwhite21100% (5)
- Integrative CBTDokument4 SeitenIntegrative CBTeoinstephens100% (3)
- Outline and Evaluate Definitions of AbnormalityDokument1 SeiteOutline and Evaluate Definitions of Abnormalityadam3250100% (1)
- 6 Fsiqiatria-1524041346Dokument48 Seiten6 Fsiqiatria-1524041346მირანდა გიორგაშვილიNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Health of JesusDokument4 SeitenMental Health of Jesusscribd.river89228Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adult Needs and Strengths Assessment (Ansa) 18 +Dokument4 SeitenAdult Needs and Strengths Assessment (Ansa) 18 +mysteryvan1981Noch keine Bewertungen
- Constructing Food Choice Decisions Sobal 2009Dokument10 SeitenConstructing Food Choice Decisions Sobal 2009Mario SánchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychological Disorder (Schizophrenia)Dokument31 SeitenPsychological Disorder (Schizophrenia)Farah Bashir0% (1)
- A Case of AgoraphDokument5 SeitenA Case of AgoraphMari LynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Mental Health Is ImportantDokument1 SeiteWhy Mental Health Is ImportantRisky KadamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBT-I Provider List - Updated 06-20-17Dokument32 SeitenCBT-I Provider List - Updated 06-20-17AnupNoch keine Bewertungen