Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chemistry: An Introduction: CHY 105: Fundamentals of Chemistry
Hochgeladen von
Nandha KumarOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chemistry: An Introduction: CHY 105: Fundamentals of Chemistry
Hochgeladen von
Nandha KumarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 1
Chemistry: An Introduction
CHY 105: Fundamentals of
Chemistry
Chapter Outline
Chemistry defined
Examples of chemistry in everyday life
Chemistry in context
The natural sciences
Branches of chemistry
Chemistry in history
Methods of science
Basic vs. applied science
Public vs. private funding
Chemistry
Chemistry study of the matter (materials)
of the universe and the changes that this
matter undergoes
Matter anything that has mass and occupies
space
Examples of matter and non-matter
Chemistry
What chemists study about the matter:
Composition
Structure
Properties
Related to composition and structure
Chemical changes the matter will undergo
Relationship between the matter and:
The environment
Human health
Chemistry and Everyday Life
Better (?) living through chemistry
Wrinkle-free cotton
Dr. Ruth Benerito
CFCs and the ozone layer
Lead paint
Chemistry in Context
Natural Sciences
Physical Sciences
Study of matter and
How energy affects
matter
Biological Sciences
Study of living
organisms
Chemistry in Context
Physical Sciences
Biological Sciences
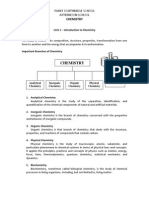
Branches of Chemistry
Inorganic
Study of matter this is primarily of mineral
(non-living origin)
Organic
Study of carbon containing compounds
Once believed that all carbon containing
compounds were of living origin
Branches of Chemistry
Analytical
Study of matter to determine the identity and
quantity of its components
Forensic chemistry is a sub-branch
Physical
Study of the structure of matter and the
influence of energy on matter
Materials chemistry is a sub-branch
Kevlar Inventor Joins Women's
Hall of Fame
Chemical Week, October 8, 2003 Retired DuPont
scientist Stephanie Kwolek, whose research led to the
discovery of Kevlar aramid fiber, was inducted into the
National Women's Hall of Fame in Seneca Falls, NY,
on October 4. Kwolek joined DuPont in 1946 as
laboratory chemist in Buffalo, NY and spent 40 years
with the company, mostly at its experimental station at
Wilmington, DE. DuPont says nearly 3,000 law
enforcement officers have survived potentially fatal or
disabling injuries because they were wearing body
armor made from aramid fiber. All U.S. combat soldiers
have worn Kevlar helmets since the 1991 Gulf War, it
says.
Branches of Chemistry
Environmental Chemistry
Study of pollutants to identify their sources, to
determine the quantities present , and to
discover ways to address the issues
associated with them
Often considered a branch of _____________
Branches of Chemistry
Biochemistry
Study of reactions that take place in living
organisms
Links the biological and physical sciences
Branch of science most important to the medical
sciences
History of Chemistry
Metals
Gold, copper (3000 BCE), bronze (copper/tin
alloy, 2000 BCE), iron (1500 BCE)
History of Chemistry
Chemical Arts
Pottery
Ceramics
Dyes
Embalming techniques
Perfumes
Brewing of alcoholic beverages
History of Chemistry
Greek Philosophers, ~400 300 BCE
First to speculate about the nature of matter
Proposed that all matter is composed of 4
elements
Air, earth, fire, water
Aristotle added a 5
th
element
Ether to glow
History of Chemistry
Greek Philosophers, ~400 300 BCE
Democritus proposed an alternate explanation
of the matter of the universe
All matter is composed of tiny indivisible particles
called atomus
theory not well supported by Aristotle
Therefore, Democritus theory was not widely
accepted at the time
History of Chemistry
Alchemy - Two pursuits
1. Search for a means to convert base metals
into gold
2. Search for the elixir of life
Substance that would lead to immortality
History of Chemistry
Advances from Alchemy
Many new substances where identified
Plaster of Paris, nitric acid.
New lab techniques and equipment
developed
New medicines identified
History of Chemistry
Modern Chemistry, ~1600 on
First to use scientific method
Methodical approach to problem solving
Based on hypothesis testing
Modern Chemistry, ~1600 on
Boyle (1600s)
Studied the affect of pressure on the volume of
gases
Priestly (1700s)
Among other things, first to discover and study the
properties of oxygen
Came to US to avoid religious persecution
Some give Schele in Sweden credit for discovering
oxygen
Modern Chemistry
Lavoisier (mid/late 1700s)
Called the father of modern chemistry
Proposed the law of conservation of matter
matter can neither be created nor destoyed
Modern Chemistry
John Dalton (1800s)
Proposed atomic theory
Marie and Pierre Curie (1890 -1900s)
First to study radioactivity
Identified several new radioactive elements
Polonium and radium
Neils Bohr (1900)
Proposed theory of atomic structure
The Curies Niels Bohr
Scientific Method
Make observations
Observations must be recordable and
repeatable
Observations may be:
Quantitative
or
Qualitative
Scientific Method
Develop hypotheses to explain the
observations
Hypothesis tentative explanation of the
observations
Scientific Method
Perform Experiments
Make predictions based on the hypothesis
If the hypothesis is truewhat else will be true
Test accuracy of the prediction
Repeat for all hypotheses
Experiments often lead to new observations
and more hypotheses to test
Scientific Method
Analyze results and share findings and
conclusions
Publish results in journals
Present findings at conferences..
Public versus Private Research
Natural Laws and Theories
From scientific research come theories
and laws
Theory (also called a model) - explanation of
observed behavior based on significant data
Natural Law - statement/summary of
observed behavior
Law of conservation of matter
Types of Scientific Research
Basic research
scientific research for the sake of knowledge,
no immediate application in mind.
Applied research
scientific research with the short-term goal of
solving a specific problem
begin the research with an application in mind.
Chapter 1 Questions
#9 and #13 on page 13
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chemical Reactions!: With 25 Science Projects for KidsVon EverandChemical Reactions!: With 25 Science Projects for KidsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atoms and Alchemy: Chymistry and the Experimental Origins of the Scientific RevolutionVon EverandAtoms and Alchemy: Chymistry and the Experimental Origins of the Scientific RevolutionBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (5)
- Week 1 Module 1 LectDokument8 SeitenWeek 1 Module 1 LectAtilano RenzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 (Introduction)Dokument32 SeitenChapter 1 (Introduction)Kathrine Kae Ibe RosarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-1 Introduction To Chemistry For EngineersDokument27 Seiten1-1 Introduction To Chemistry For EngineersCtstrphy100% (1)
- Intro To Chem2Dokument28 SeitenIntro To Chem2mm.vince21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gen ChemDokument226 SeitenGen ChemKemal PujabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemisty Notes Class 9 IxDokument70 SeitenChemisty Notes Class 9 IxMuhammad Iqbal72% (43)
- 9th Class-Chapter-1-Chemistry Notes-Sindh Board PDFDokument14 Seiten9th Class-Chapter-1-Chemistry Notes-Sindh Board PDFMohsin AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit I: Introduction To Chemistry: LEARNING OUTCOMES: After Successful Completion of This Unit, You Should Be Able ToDokument23 SeitenUnit I: Introduction To Chemistry: LEARNING OUTCOMES: After Successful Completion of This Unit, You Should Be Able ToMabale, Joyce Danielle H.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2023 Chem For Engineering v3 MIDTERMSDokument79 SeitenModule 2023 Chem For Engineering v3 MIDTERMSmarkeepetesentuineNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Chemistry?Dokument48 SeitenWhat Is Chemistry?Ellaine IlaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 General View of Chemistry and MatterDokument17 SeitenChapter 1 General View of Chemistry and MatterJoshua Kulot100% (1)
- Class Ix Chemisty NotesDokument70 SeitenClass Ix Chemisty NotesBasim blouchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Unit1Q1Dokument14 SeitenChem Unit1Q1Miguel CosnadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 +ChapterAboutScienceDokument23 Seiten1 +ChapterAboutSciencembangesibabalwe03Noch keine Bewertungen
- ChemistryDokument84 SeitenChemistryMaria Regina SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 1 Lecture NotesDokument87 SeitenChem 1 Lecture NotesGlenn ClementeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 - The Nature of ChemistryDokument12 SeitenModule 1 - The Nature of ChemistryElhamae Sindatoc100% (1)
- Chemistry (From Egyptian Kēme (Chem), MeaningDokument15 SeitenChemistry (From Egyptian Kēme (Chem), Meaningkhiane_25114Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science Is A Search For Order in NatureDokument3 SeitenScience Is A Search For Order in NaturehildaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3 - Atomos, Aristotle and Alchemy (Chemistry Before Modern History)Dokument18 SeitenLesson 3 - Atomos, Aristotle and Alchemy (Chemistry Before Modern History)Eji Alcoreza100% (1)
- Chemistry Chapter1 FinalDokument18 SeitenChemistry Chapter1 FinalNaveed Ur Rehman LuckyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Biology, Chemistry, and PhysicsDokument30 SeitenIntroduction To Biology, Chemistry, and PhysicsJamesInocencioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Chapter1 FinalDokument18 SeitenChemistry Chapter1 FinalHassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Chemistry: AckleyDokument39 SeitenIntroduction To Chemistry: AckleyCoachAckNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biodiversity - Level 1 - 1 - 2020Dokument20 SeitenBiodiversity - Level 1 - 1 - 2020tanatswaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To ChemistryDokument17 SeitenIntroduction To ChemistryLeovihilda BalalangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Notes For Students SECONDARY SDokument70 SeitenChemistry Notes For Students SECONDARY Skcgno72Noch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To ChemDokument27 SeitenIntro To ChemPhoebe Ruth Ligoy Ligoy-GuintoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 1Dokument114 SeitenChap 1ababiya mulugetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To General Physics 1Dokument59 SeitenIntroduction To General Physics 1Ariane Dionisio100% (1)
- The Chemical World: Introductory Chemistry, 3Dokument20 SeitenThe Chemical World: Introductory Chemistry, 3farooq_bagbanNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Chemistry (Chem. 1012)Dokument138 SeitenGeneral Chemistry (Chem. 1012)mekibeb yichenekuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Chemistry Sindhi Text BoardDokument4 SeitenChapter 1 Chemistry Sindhi Text BoardMansoorAliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 1Dokument10 SeitenSection 1EAGLE GAMERSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Chemistry: Mrs. CoyleDokument39 SeitenIntroduction To Chemistry: Mrs. CoyleElisabeta StamateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument5 SeitenChapter 1Mark Euan B. DolosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To ChemistryDokument13 SeitenIntroduction To Chemistryaika smithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 Lesson 1Dokument3 SeitenModule 1 Lesson 1Nataniel DoctoleroNoch keine Bewertungen
- The History of Chemistry Can Be Divided Into Four Periods.Dokument7 SeitenThe History of Chemistry Can Be Divided Into Four Periods.Diana AnchetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 205 Week 1 To 3Dokument24 SeitenChem 205 Week 1 To 3REAN KEM CUTAMORANoch keine Bewertungen
- REVIEWERDokument10 SeitenREVIEWERNathasha Marie BanalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical ScienceDokument206 SeitenPhysical SciencecasimiroaltheaeuniceNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.0 ChemistryDokument9 Seiten1.0 ChemistryShanna Leigh MerquitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Chemistry: Mrs. CoyleDokument39 SeitenIntroduction To Chemistry: Mrs. CoyleharahrNoch keine Bewertungen
- TitleDokument9 SeitenTitleRommel DesuyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- History: Chemistry Is TheDokument4 SeitenHistory: Chemistry Is TheKim Caitlin Carbolico ClasieteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 Introduction To ChemistryDokument5 SeitenLesson 1 Introduction To ChemistryEnrico Sapitula Del RosarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of AtomDokument16 SeitenTheory of AtomMICHAEL MESIASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Chemistry 101Dokument39 SeitenIntroduction To Chemistry 101Romeo Altaire GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction of ChemistryDokument4 SeitenIntroduction of ChemistryAgatha OfrecioNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 1Dokument5 SeitenCH 1Muqadas NazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Origin of LifeDokument22 SeitenOrigin of LifeApril RicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Introduction - To - Chemistry 1Dokument19 Seiten1 - Introduction - To - Chemistry 1Hosnie AlfonsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Unit 1Dokument17 SeitenBio Unit 1EyamgualeleNoch keine Bewertungen
- l1.2 The Scientific MethodDokument30 Seitenl1.2 The Scientific MethodAngela Marie PalamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inorganic ChemistryDokument2 SeitenInorganic ChemistryNicole LaquilacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Sci. 1Dokument24 SeitenEarth Sci. 1Lester Eslava OrpillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General and Inorganic ChemistryhandoutDokument25 SeitenGeneral and Inorganic ChemistryhandoutleapapayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classified - Internal UseDokument18 SeitenClassified - Internal UseNandha KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 100: Fundamentals For Chemistry: Chapter 1: Introduction Lecture NotesDokument132 SeitenCH 100: Fundamentals For Chemistry: Chapter 1: Introduction Lecture NotesNandha KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2007 Ch158 A3 Basicsorg Update For 2010Dokument40 Seiten2007 Ch158 A3 Basicsorg Update For 2010Nandha KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic ChemistryDokument14 SeitenBasic ChemistryAtul DwivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Waste Heat Recovery: Alfred PiggottDokument9 SeitenIndustrial Waste Heat Recovery: Alfred PiggottNandha KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Power ApplicationsDokument2 SeitenFluid Power ApplicationsNandha KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Maritime Dangerous Goods CodeDokument45 SeitenInternational Maritime Dangerous Goods Codequanghoa18121973100% (2)
- Empirical Formula For Magnesium OxideDokument6 SeitenEmpirical Formula For Magnesium OxidesophiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nucleic Acid: Group 2 ReportDokument20 SeitenNucleic Acid: Group 2 ReportDiePalAPieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1Dokument7 SeitenLab 1Gagan GautamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Low Temp Separation Unit PDFDokument2 SeitenLow Temp Separation Unit PDFMaribel Apaza MamaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sinus C User Manual Knuth C3000Dokument124 SeitenSinus C User Manual Knuth C3000Tamas RaduNoch keine Bewertungen
- CompassDokument139 SeitenCompassErick Olano100% (1)
- Chapter 7 PDFDokument38 SeitenChapter 7 PDFfuatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry End of Chapter QuestionsDokument3 SeitenChemistry End of Chapter QuestionsHershil SawlaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrogen Combustion Engine Project Theory and UsageDokument61 SeitenHydrogen Combustion Engine Project Theory and UsageChetanSavandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 247-E RoboticsDokument4 Seiten247-E RoboticsFlavioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water-Soluble Polymers For Petroleum Recovery PDFDokument355 SeitenWater-Soluble Polymers For Petroleum Recovery PDFKovacs MariusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan ColloidDokument5 SeitenLesson Plan ColloidShaina MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcritical Carbon Dioxide Based Heat Pumps For Simultaneous Cooling and Heating ApplicationsDokument217 SeitenTranscritical Carbon Dioxide Based Heat Pumps For Simultaneous Cooling and Heating ApplicationssyedsameermechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiences With Fires and ExplosionsDokument10 SeitenExperiences With Fires and ExplosionsmrudhulrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1005 Answerkey PDFDokument16 Seiten1005 Answerkey PDFmadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- BNi-7 TDSDokument2 SeitenBNi-7 TDSQuang Thuận NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Structure of AtomDokument48 SeitenChapter 2 Structure of AtomRehan AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLP - BIOMOLECULES (Castro, Abegail C.)Dokument6 SeitenDLP - BIOMOLECULES (Castro, Abegail C.)Abby Castro100% (2)
- Hafiz Rehan: Technical ResponsibilitiesDokument8 SeitenHafiz Rehan: Technical ResponsibilitiesAdnan AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- محاضرة 8 استكمال الابارDokument30 Seitenمحاضرة 8 استكمال الابارSherif MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pallet Stacker CranesDokument20 SeitenPallet Stacker CranesDangAnhDuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Articol 18Dokument6 SeitenArticol 18RaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative Estimation of Amino Acids by NinhydrinDokument4 SeitenQuantitative Estimation of Amino Acids by Ninhydrinbhuvana_eee0% (1)
- Ajpcr PDFDokument6 SeitenAjpcr PDFAndrianna NastasyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visible Spectroscopy of Methylene Blue On HectoriteDokument11 SeitenVisible Spectroscopy of Methylene Blue On HectoriteEstefanía VelásquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 030 Intro To Secondary Metabolism and BiosynthesisDokument64 Seiten030 Intro To Secondary Metabolism and BiosynthesisRadi TyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dental CeramicsDokument26 SeitenDental CeramicsVikas Aggarwal50% (2)
- 4PH1 2P Que 20210304Dokument24 Seiten4PH1 2P Que 20210304Nuh Zaman Chistee100% (1)
- Assignment 1 WeldingDokument11 SeitenAssignment 1 WeldingLee Eyyh DeeNoch keine Bewertungen