Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
7 - Apresentacao Gianlucca Gabetotto - II SBCASP
Hochgeladen von
Carolina Queiroz0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
12 Ansichten29 SeitenXBRL is "self-defining?" to a computer (XML parser), they are the same the tags (element names) provide no semantic knowledge to the program. What if financial documents included both content (eur75,453) and structure (EUR75,453=net income for Q1 / 2011)?
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenXBRL is "self-defining?" to a computer (XML parser), they are the same the tags (element names) provide no semantic knowledge to the program. What if financial documents included both content (eur75,453) and structure (EUR75,453=net income for Q1 / 2011)?
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
12 Ansichten29 Seiten7 - Apresentacao Gianlucca Gabetotto - II SBCASP
Hochgeladen von
Carolina QueirozXBRL is "self-defining?" to a computer (XML parser), they are the same the tags (element names) provide no semantic knowledge to the program. What if financial documents included both content (eur75,453) and structure (EUR75,453=net income for Q1 / 2011)?
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 29
A Experincia do Projeto SICONFI
II Seminrio Brasileiro de Contabilidade Aplicada ao Setor Pblico SBCASP
Gianluca Garbellotto
Braslia, 19 de Maio de 2014
Agenda
Introduo ao XBRL e XBRL Global Ledger
Introduo (rpida) ao Projeto SICONFI - Mais depois
O DATA Act em os EUA
Introduo ao XBRL e
XBRL Global Ledger
O Valor dos Padres
Combine a Infra-Estrutura com o Padro
Correspondente
1. Rail Road
2. Electricity
3. Telephone
4. Shipping
5. Product
6. Networking
7. Internet
8. Information
1. RJ 11
2. 40 x 8.5 x 8
3. UPC
4. HTML / SOAP / Web Services
5. 4 8.5
6. RJ 45
7. Rosettanet, MDDL, XBRL
8. 220V, 50Hz
9. Business data transparency
9. XBRL
XML Family
XML
Rules for text and angle brackets
XML Schema
Validation tool for XML
Namespaces
Same words, different schemas
XLink
Ties XML to internal and external
references
XSL and CSS
XML with Style
XML Without Agreement
XML is self-defining?
Sure, this looks simple:
is just SYNTAX
But how self-defining is this?
To a computer (XML parser), they
are the same
The tags (element names)
provide no semantic knowledge
to the program
Today over 65,000 International public
companies release financial results
half yearly and quarterly
But the contents are not organized.
The data must be reentered into
computer applications for
interpretation.
What if financial documents
included both content (75,453)
and structure
(75,453=net income for Q1/2011)?
ENTER XBRL
Catalyst: Standardizing Business Reporting
Catalyst: Standardize Management
Reporting
Transactional
data
Multiple departmental
Excel spreadsheets
Senior
Management
Consolidated spreadsheets
for management
SQL
SQL
System A
System B
System C
2000 elements = 6500 spreadsheets (this is not a typo)
Some Problems with Todays Model
Information goes in one direction
Information has no shared context
Analysis of the information is conducted via macros
that are embedded within the applications and are not
reusable by others .
Information labels are inconsistent from one application
to another
Information is not independently validated
Information is not connected to other related resources
across applications
Community
Accounting profession,
developers, regulators, users,
financial services, data aggregators 800+
Syntax and semantics
of taxonomies and instances
XML, Namespaces, XML Schema, XLink
Specification
US GAAP, IFRS, XBRL GL, SBR
and others
Taxonomies
XBRL: Three Primary Components
Multi-dimensional
Optimized for business
reporting
Discoverable
Reusable information
Extensible
More detail
Shared understanding
XML describes, XBRL
defines
Where is it relevant? The BRSC
US GAAP
IFRS
SBR
GRI G3
Statutory
MD&A
SCOA/Trial balance
AP/AR Ledgers
General Ledger
Fixed Assets, Inventory
Documents/Entries
Parties, entities
KPIs financial and not
Others
Accounting
Software
ERP systems
UBL
Rosettanet
ACORD
MISMO
FPML
Others
Processes
Crating the seamless interface
External
Business
Reporting
Business
Operations
Internal
Business
Reporting
Investment,
Lending,
Regulation
Economic
Policymaking
How Is It Used?
Transparency and greater analytical insight and capabilities SEC
in the US and similar global regulatory programs
Reduction of the reporting burden for businesses SBR programs
Efficient collection and dissemination of government information
SICONFI in Brazil, Open Government initiatives, such as the DATA
Act in the US
Automation, efficiency and cost reduction in data related
corporate processes
XBRL is More Than Just Tagging
Business Information
Multi-dimensional
business and
financial data
representations
Flexibility of
business reporting
vocabularies (i.e.
taxonomies)
Mathematical
relationships
between
concepts
Flexibility about
how to present
information to
users
XBRL FR and XBRL GL
XBRL for Financial Reporting (XBRL FR) or, more generally, XBRL for
End Reporting (XBRL ER)
Represents summarized reports
Loose data model composed by data points (fields in reports)
linked by arcs (linkbases) and referencing context and units
information defined in separate XML fragments within the XBRL
instance document
XBRL Global Ledger (XBRL GL)
Represents detailed, transactional data and its mappings to
data points in XBRL FR taxonomies
Structured data model (XML Schema) similar to structure of
information stored in accounting/ERP software
Easy to map to
Enables greater control on data quality in end reports
The Standards-Driven Paradigm Shift
No need to replace or modify existing systems
Software tools, lessons learned, business processes and knowledge
bases are reusable in different projects and domains
Application-independent data accuracy and consistency and
process automation
Data transparency
Minimally invasive, low cost technology
Projeto SICONFI
XBRL FR
XBRL GL
XBRL GL
How XBRL Is Used in SICONFI
MSC
COC
(Operations)
Source/Detailed Data Mappings Summarized Reports
DCASP
RGF
RREO
COC
(Reports)
DEFP
Outros PCASP
Information
Classification A
A.1
A.2
B.1
B.2
Agency X
Report X.1
Report X.2
Agency Y Agency
Report Y.1
Report Y.2
Definitional Taxonomy Common Dictionary
Reporting Taxonomies
Define the concept once
re-use on many reports
Address Wages & Salaries
Information
Classification B
How XBRL Is Used in SICONFI
Standard Business Reporting (SBR) Taxonomy Architecture
The Digital Accountability and
Transparency Act (DATA) in
the USA
Overview
Its all about open data
The transformation: Government-wide data
standards; comprehensive publication
requirements
The scope: Federal financial, assistance,
procurement, and performance reporting
The driver: Legislative mandate
Current Landscape
Financial reporting: Agencies to Treasury
Payment requests: Agencies to Treasury
Budget planning and actions: Agencies to OMB
Assistance: Agencies to Commerce, GSA
Procurement: Agencies to GSA
Grants: Awardees to agencies
Contracts: Awardees to agencies, GSA
Subawards: Prime awardees to OMB
GPRA: Agencies to Congress, OMB
Current Shortcomings
Information not available. The public, Congress,
Treasury and OMB, agency leaders, inspectors general,
and even program managers dont have the data they
need.
Information not accessible. Information is frequently
available only as documents or summaries.
Information not interoperable. Government-wide data
fields, even for basic concepts, dont exist. Formats
differ. There is no way to link spending and
performance.
DATA: the Basics
Treasury and OMB
Establish government-wide
identifiers
Establish government-wide
formats
Publish grants, contracts, and
internal spending on existing
USASpending.gov portal
Pilot program for
consolidated reporting by
grantees and contractors
Agencies
Apply the standards
wherever applicable
Data quality checks
Awardees
Standardized reporting
imposed by agencies
Recovery Board
Accountability platform to
Treasury
DATA: Desired Impact
Public Accountability. Citizens have access to
accurate, complete, searchable data on government
spending and performance
Better Management. Congress, Treasury, OMB, agency
leaders, inspectors general, program managers utilize
dashboards and analytics
Automated Compliance. Grantees and contractors
report to agencies without strain; agencies automate
reports to Treasury, OMB, Commerce, GSA, Congress
Implementation
Treasury and OMB to issue guidance 1 year after passage
Agencies to begin using data standards 2 years later
Grant/contract reporting consolidation pilot starts 1 year after
passage and lasts 2 years
Project SICONFI Helped
Significant XBRL implementation in the G2G space in a major
economy
Government SCOA used in both countries
Use of XBRL GL in conjunction with XBRL reports to
Simplify implementation for Government entities
Enhance data quality through pre-defined mappings and the ability to
push validation rules at the USSGL (MSC) and transactional level
SBR taxonomy architecture
OBRIGADO!
Your Speaker:
Gianluca Garbellotto
IPHIX, CEO
XBRL Best Practices Board, member
XBRL Global Ledger Working Group, Chair
gg@iphix.net
Twitter: @iphixbrl
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Eine Liebesgeschichte PDFDokument49 SeitenEine Liebesgeschichte PDFCarolina Queiroz100% (3)
- Conversation - 1. I Live in Pasadena PDFDokument1 SeiteConversation - 1. I Live in Pasadena PDFCarolina QueirozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checking Into The Hotel - Conversation 3 PDFDokument1 SeiteChecking Into The Hotel - Conversation 3 PDFCarolina QueirozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checking Into The Hotel - Conversation 1 PDFDokument1 SeiteChecking Into The Hotel - Conversation 1 PDFCarolina QueirozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Building g5Dokument45 SeitenBuilding g5ammarsteel68Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plantas Con Madre Plants That Teach and PDFDokument15 SeitenPlantas Con Madre Plants That Teach and PDFJetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership Nursing and Patient SafetyDokument172 SeitenLeadership Nursing and Patient SafetyRolena Johnette B. PiñeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Milestone BillingDokument3 SeitenMilestone BillingJagadeesh Kumar RayuduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Program Need Analysis Questionnaire For DKA ProgramDokument6 SeitenProgram Need Analysis Questionnaire For DKA ProgramAzman Bin TalibNoch keine Bewertungen
- ParaphrasingDokument11 SeitenParaphrasingAntiiSukmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Highway Journal Feb 2023Dokument52 SeitenHighway Journal Feb 2023ShaileshRastogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yaskawa V7 ManualsDokument155 SeitenYaskawa V7 ManualsAnonymous GbfoQcCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day 2 - Evident's Official ComplaintDokument18 SeitenDay 2 - Evident's Official ComplaintChronicle Herald100% (1)
- SUNGLAO - TM PortfolioDokument60 SeitenSUNGLAO - TM PortfolioGIZELLE SUNGLAONoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL - English 5 - Q3 - W8Dokument8 SeitenDLL - English 5 - Q3 - W8Merlyn S. Al-osNoch keine Bewertungen
- RMC No. 122 2022 9.6.2022Dokument6 SeitenRMC No. 122 2022 9.6.2022RUFO BULILANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Templates in C++Dokument16 SeitenIntroduction To Templates in C++hammarbytpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Editorial WritingDokument38 SeitenEditorial WritingMelanie Antonio - Paino100% (1)
- TOK Assessed Student WorkDokument10 SeitenTOK Assessed Student WorkPeter Jun Park100% (1)
- Module 0-Course Orientation: Objectives OutlineDokument2 SeitenModule 0-Course Orientation: Objectives OutlineEmmanuel CausonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pin Joint en PDFDokument1 SeitePin Joint en PDFCicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trainer Manual Internal Quality AuditDokument32 SeitenTrainer Manual Internal Quality AuditMuhammad Erwin Yamashita100% (5)
- SCHEMA - Amsung 214TDokument76 SeitenSCHEMA - Amsung 214TmihaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Personal StatementDokument2 SeitenModel Personal StatementSwayam Tripathy100% (1)
- Calculus of Finite Differences: Andreas KlappeneckerDokument30 SeitenCalculus of Finite Differences: Andreas KlappeneckerSouvik RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 6 Product Disassembly ChartDokument5 SeitenActivity 6 Product Disassembly Chartapi-504977947Noch keine Bewertungen
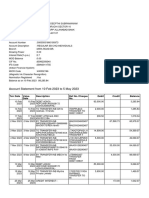
- Feb-May SBI StatementDokument2 SeitenFeb-May SBI StatementAshutosh PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case StudyDokument15 SeitenCase StudyChaitali moreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- M4110 Leakage Reactance InterfaceDokument2 SeitenM4110 Leakage Reactance InterfaceGuru MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Car Section 2 Series (H) Part-IiDokument6 SeitenCar Section 2 Series (H) Part-Iipandurang nalawadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccie R&s Expanded-BlueprintDokument12 SeitenCcie R&s Expanded-BlueprintAftab AlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normal Consistency of Hydraulic CementDokument15 SeitenNormal Consistency of Hydraulic CementApril Lyn SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asian Paints Final v1Dokument20 SeitenAsian Paints Final v1Mukul MundleNoch keine Bewertungen
- IJISRT23JUL645Dokument11 SeitenIJISRT23JUL645International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen