Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Edema Hyperemia Congestion
Hochgeladen von
raanja2Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Edema Hyperemia Congestion
Hochgeladen von
raanja2Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
oedema
2oed definition
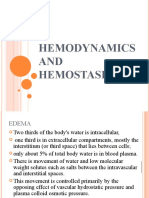
Increased fluid in interstitial spaces
Anasarca -- severe generalized
oedema with profound subcutaneous
tissue swelling
Fluid collection in various cavities is named
Hydrothorax
Hydroperitonium (ascities)
hydropericardium
3oed classification
Increase hydrostatic pressure
Reduced plasma osmotic pressure
(hypoproteinemia)
Lymphatic obstruction
Sodium retention
inflammation
4oed increased hydrostatic pressure
Impaired venous return
Congestive heart failure
Constrictive pricarditis
Ascities (liver cirrhosis)
Venous obstruction
Thrombosis
External pressure (mass)
Inactivity with prolonged dependency
Arteriolar dilation
heart
5oed hyoproteinemia
Reduced plasma osmotic pressure
Protein loosing glomerulopathies
(nephrotic syndrome)
Liver cirrhoses (ascities)
malnutrition
protein loosing gastro-entero pathy
6oed lymphatic obstruction
Inflammatory
Neoplastic
post surgical
Post irradiation
7oed sodium retention
Excessive salt intake ,with renal
insufficiency
Increase tubular reabsorption of sodium
Renal hyoperfusion
Increased renin-angiotensin-aldosteron
secretion
8oed inflammation
Acute inflammation
Chronic inflammation
angiogenesis
9oed variables of pressures
Affecting fluid transit across capillary wall
Capillary hydrostatic & osmatic forces are
balanced
No net loss or gain of fluid across capillary bed
Increase hydrostatic pressure or decreased
plasma osmotic pressure leads to
net accumulation of extra vascular fluid (oedema)
As the interstitial fluid pressure increases
tissue lymphatics remove much of the excess fluid
Eventually returning it to circulation via thoracic duct
pathways leading
To systemic
oedema
Heart failure
Cardiac output
Effective arterial
Blood volume
rennin
aldosteron
Renal sodium
reabsorption
Rena retention
Of Na
+
, H
2
O
Plasma
volume
transudation
oedema
MALNUTRITION
Hepatic SYNTHEIS
NEPHROTIC SYNDROM
PLASMA
Osmotic pressure
Blood volume
Ascities
Other effusions
Renal
vasoconstriction
Tubular reabsorption
Na
+
, H
2
O
GFR
CVP
capillary
pressure
11oed clinical presentation
Ranges from annoying to fatal
Signals the underlying disease
Impairs wound healing & clearance of
infection
Pulmonary oedema interferes with
ventilation & can cause death
Brain oedema is serious and can be fatal
by herniation or pressure ischemia
MORPHOLOGY
SUBCUTANEOUS EDEMA
Dependent, site of higher osmotic pressure
Prominent feature of right heart failure
NEPHROTIC EDEMA
PERIORBITAL EDEMA
PULMONARY EDEMA
Frothy blood tinged fluid, with air
BRAIN EDEMA
Swollen brain,narrow sulci distended gyri
12hyp
Hyperaemia
and congestion
13hyp definition
Both indicate a local increased volume of blood
in particular tissue
Hyperemia is
an active process
augmented tissue inflow
arteriolar dilatation
skeletal muscle in exercise
place of inflammation
Congestion is
passive process
impaired outflow
cardiac failure
14hyp hyperemia versus congestive
In both cases there is
Increased volume
and pressure of blood
in a given tissue with
associated capillary dilatation and
potential for fluid extravasations
15hyp hyperemia versus congestion
hyperemia
Increased inflow leads to
Engorgement with oxygenated blood
Resulting in erythema
Congestion
Diminished out flow leads to
Capillary be swollen
With deoxygenated venous blood
Resulting in cyanosis
MORPHOLOGY
Cut surfacewet and hemorrhagic
Alveolar capillaries engorged with blood
Focal intra alveolar hemorrhage
HEPATIC CONGESTION
Hepatocyte degeneration
Chronic congestion.nutmeg liver
Centrilobular necrosis
Hepatic fibrosisin severe cases
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hemodynamic Disorders, Thromboembolic Disease and ShockDokument13 SeitenHemodynamic Disorders, Thromboembolic Disease and Shockpjcanero100% (5)
- Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock GWAIDokument102 SeitenHemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock GWAIkavindukarunarathnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OedemaDokument44 SeitenOedemaNadia MaisaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 7Dokument27 SeitenLec 7helenyakhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid and Hemodynamic DisordersDokument19 SeitenFluid and Hemodynamic DisordersapplesncoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11) Circulatory DisturbancesDokument42 Seiten11) Circulatory DisturbancesRavishan De AlwisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap4 Hemodynamics F2Dokument12 SeitenChap4 Hemodynamics F2Twinkle Salonga100% (3)
- Hemodynamic Disorders: Ma. Minda Luz M. Manuguid, M.DDokument59 SeitenHemodynamic Disorders: Ma. Minda Luz M. Manuguid, M.Dchocoholic potchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Edema HemorrhDokument44 Seiten2 Edema HemorrhshmirtbNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Hemodynamic Disorders, Thromboembolism and ShockDokument162 Seiten5 Hemodynamic Disorders, Thromboembolism and Shocksinte beyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemodynamic Disturbance: Dr. Usha.MDokument77 SeitenHemodynamic Disturbance: Dr. Usha.MOlumide Omotola AjayiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemodynamic DisordersDokument16 SeitenHemodynamic DisordersHussein Al SaediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gangguan Hemodinamik, Trombosis Dan Syok: Fk-Uncen JayapuraDokument67 SeitenGangguan Hemodinamik, Trombosis Dan Syok: Fk-Uncen Jayapuramarsal25Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 EdemaDokument33 Seiten1 EdemaSawera RaheemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemodynamics - PDF 20 21Dokument172 SeitenHemodynamics - PDF 20 21ayahnaser20Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1.4 Circulatory DisturbanceDokument162 Seiten1.4 Circulatory DisturbanceКатя ШаповалNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edema Hyperemia & Congestion: Miriam Al Battal, MDDokument20 SeitenEdema Hyperemia & Congestion: Miriam Al Battal, MDHassoun hassounNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis and ShockDokument127 SeitenHemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis and ShockMowlidAbdirahman Ali madaaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemodynamic Disorders-RevisedDokument118 SeitenHemodynamic Disorders-Revisedspringding0% (1)
- Chapter 4 For PathologyDokument47 SeitenChapter 4 For PathologycocoramziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemodynamic Disturbances: Dr. Dhamyaa Al-RahalDokument74 SeitenHemodynamic Disturbances: Dr. Dhamyaa Al-RahalAmmar Bany AtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edema: Pendrik Tandean Internal Medicine, Medical Faculty of Hasanuddin University, MakassarDokument31 SeitenEdema: Pendrik Tandean Internal Medicine, Medical Faculty of Hasanuddin University, MakassarLIEBERKHUNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Path 3Dokument26 SeitenPath 3رؤى مصطفىNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemodynamic DisordersDokument20 SeitenHemodynamic Disordersbpt2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Pulmonary Edema: Purwoko Sugeng HDokument25 SeitenAcute Pulmonary Edema: Purwoko Sugeng HBee DanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemodynamic Disorders ThrombosisDokument106 SeitenHemodynamic Disorders ThrombosisRamez AnaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid and Hemo Dynamic Imbalances W 2Dokument49 SeitenFluid and Hemo Dynamic Imbalances W 2erwilli5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edema MultisistemDokument47 SeitenEdema Multisistem123someone123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kuliah BMD Pathomechanism DemaDokument30 SeitenKuliah BMD Pathomechanism DemaSelebriti Indonesia100% (1)
- A Patient With Oedema PresentationDokument35 SeitenA Patient With Oedema PresentationWasswaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOL 2292 NotesDokument12 SeitenBIOL 2292 Notesfglo188Noch keine Bewertungen
- CHP 4 HemodynamicsDokument29 SeitenCHP 4 HemodynamicsmaryannejkiemNoch keine Bewertungen
- OedemaDokument23 SeitenOedemaTavleen KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemodynamic DysorderDokument158 SeitenHemodynamic DysorderTemesgen EndalewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary Edema: Prepared By: South West Education CommitteeDokument65 SeitenPulmonary Edema: Prepared By: South West Education CommitteedanradulescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5) Circulatory Disturbance BPT - 093303Dokument106 Seiten5) Circulatory Disturbance BPT - 093303Crystal GamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- OedemaDokument6 SeitenOedemajayanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Shock: Cardiovascular Dysfunction Chapter 48Dokument1 SeiteTypes of Shock: Cardiovascular Dysfunction Chapter 48meeeenonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of EdemaDokument7 SeitenPathophysiology of EdemaTaniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oedema 122456Dokument33 SeitenOedema 122456Divya Prakash SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemodynamic Disorder PC1Dokument227 SeitenHemodynamic Disorder PC1Bereket weybaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperemia CongestionDokument40 SeitenHyperemia CongestionBikash PuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemodynamics ModifiedDokument175 SeitenHemodynamics ModifiedAyele AsefaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemodynamic PathologyDokument9 SeitenHemodynamic PathologyjoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edema: Pendrik Tandean Subdivison Cardiology of Internal Medicine, Medical Faculty of Hasanuddin University, MakassarDokument37 SeitenEdema: Pendrik Tandean Subdivison Cardiology of Internal Medicine, Medical Faculty of Hasanuddin University, MakassarLIEBERKHUNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5Dokument5 SeitenLecture 5Isak ShatikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathmorphology Oral 2021-Converted GUJJUDokument138 SeitenPathmorphology Oral 2021-Converted GUJJUHarsh NimavatNoch keine Bewertungen
- EdemaDokument4 SeitenEdemaWanchung ZienNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 - Congestion and ThrombosisDokument67 Seiten4 - Congestion and ThrombosisIsuri GanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Under Supervision DR/ Mariam Sabry: Ulmonary DemaDokument28 SeitenUnder Supervision DR/ Mariam Sabry: Ulmonary DemaMohamed ElsyaedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 26 Patofisiologi Edema FK Unhas TGL 5 Mei 2015Dokument65 Seiten26 Patofisiologi Edema FK Unhas TGL 5 Mei 2015sri ayu lestari wulandariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-3 Haemodinamicpart1 PDFDokument64 Seiten1-3 Haemodinamicpart1 PDFSetiawan SukmadjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shock NotesDokument7 SeitenShock NotesAnitha NoronhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Aspect of Heart FailureDokument67 SeitenClinical Aspect of Heart FailureAri Bandana TasrifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edema: Dr. Bernardo Dámaso MataDokument55 SeitenEdema: Dr. Bernardo Dámaso MataDeivis Dan ErickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approach To Patient With Generalized Body OedemaDokument7 SeitenApproach To Patient With Generalized Body OedemaAbdulJabar RiadhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemodynamic DisordersDokument8 SeitenHemodynamic DisordersRedhwan85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtVon EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- (Monir Ahmed) BSC in Medical TechnologyDokument125 Seiten(Monir Ahmed) BSC in Medical Technologyraanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Labconco BSCpresentationDokument35 SeitenLabconco BSCpresentationkabardeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Laboratory Safety: Summary of The Main FactorsDokument27 SeitenGeneral Laboratory Safety: Summary of The Main FactorsvirparaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Technology 1Dokument110 SeitenMedical Technology 1Anjali MohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dancey ScoreDokument27 SeitenDancey ScoreAltus GoldenNoch keine Bewertungen
- RTB LeachingDokument11 SeitenRTB Leachingraanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Lab Assignment 1Dokument2 SeitenBasic Lab Assignment 1raanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- MCG 2009 03 Raman 200954 SDC1Dokument14 SeitenMCG 2009 03 Raman 200954 SDC1raanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hemostasis:: (Stoppage of Blood Flow After Damage)Dokument5 SeitenHemostasis:: (Stoppage of Blood Flow After Damage)raanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- PHD Res Topics With NamesDokument1 SeitePHD Res Topics With Namesraanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Practical HandoutDokument16 SeitenBlood Practical Handoutraanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ph.D. Research Proposal Formate March 17Dokument1 SeitePh.D. Research Proposal Formate March 17raanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Random BodDokument17 SeitenRandom Bodraanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- University of Azad Jammu & Kashmir, Muzaffarabad Performa For Details of Faculty Staff Name of DepartmentDokument2 SeitenUniversity of Azad Jammu & Kashmir, Muzaffarabad Performa For Details of Faculty Staff Name of Departmentraanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Biology 2Dokument41 SeitenMolecular Biology 2raanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 - Molecular Mechanism of Human Disease - Fragile X SyndromeDokument12 SeitenLecture 1 - Molecular Mechanism of Human Disease - Fragile X Syndromeraanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2 - Molecular Mechanism of Human Disease - Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)Dokument16 SeitenLecture 2 - Molecular Mechanism of Human Disease - Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)raanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Hewaida Fadel Dr. Tarek El Sewedy: Department of Medical Laboratory Technology Faculty of Allied Medical SciencesDokument45 SeitenDr. Hewaida Fadel Dr. Tarek El Sewedy: Department of Medical Laboratory Technology Faculty of Allied Medical Sciencesraanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- I.A Jimoh, Rudyk S.N and Søgaard E.GDokument28 SeitenI.A Jimoh, Rudyk S.N and Søgaard E.Graanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hazards RTB 0804Dokument26 SeitenHazards RTB 0804raanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hospital Waste March 25Dokument30 SeitenHospital Waste March 25raanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 10 Bio1 Nutrition 26-12-2013Dokument39 SeitenLec 10 Bio1 Nutrition 26-12-2013raanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hazards RTB 0804Dokument26 SeitenHazards RTB 0804raanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Improving Biodegradation Potential of Dioxin-Degrading BacteriaDokument30 SeitenImproving Biodegradation Potential of Dioxin-Degrading Bacteriaraanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Objective: Muhammad ImranDokument2 SeitenObjective: Muhammad Imranraanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- CharcoalProcess DoItDokument10 SeitenCharcoalProcess DoItErik ÖqvistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extremophiles - RTB 11.3Dokument43 SeitenExtremophiles - RTB 11.3raanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- ExtremophileDokument10 SeitenExtremophileraanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dengue PaperDokument2 SeitenDengue Paperraanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Practical HandoutDokument16 SeitenBlood Practical Handoutraanja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stenorol® Crypto - OS - Brochure - EN - v01 - 1020 PDFDokument2 SeitenStenorol® Crypto - OS - Brochure - EN - v01 - 1020 PDFDrivailaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sea BuckthornDokument5 SeitenSea BuckthornLidiana Burlacu100% (1)
- RCL Employment Medical Examination Form A (New-Returning) Revised 2015-03Dokument2 SeitenRCL Employment Medical Examination Form A (New-Returning) Revised 2015-03Ahmad ShodiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- All You Need To Know About Antibiotics: Tariq A. Madani, MBBS, FRCPCDokument89 SeitenAll You Need To Know About Antibiotics: Tariq A. Madani, MBBS, FRCPCMansour AltalhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument135 SeitenUntitledDr.younes95 RekaaneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample MCQ'SDokument4 SeitenSample MCQ'SHerman SehmbiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stress Management Objectives Stree Illness and Adaptaion OriginalDokument49 SeitenStress Management Objectives Stree Illness and Adaptaion OriginalKhizar AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Claw Diseases - WSAVA 2014 Congress - VINDokument4 SeitenClaw Diseases - WSAVA 2014 Congress - VINAndrea VargaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dory in The Lens of PsychologyDokument3 SeitenDory in The Lens of PsychologyPoetic PandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preventive Care Health Check Plans Wellness Services & Disease PreventionDokument2 SeitenPreventive Care Health Check Plans Wellness Services & Disease PreventionMihir DakwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peptic Ulcer Case Study 1Dokument9 SeitenPeptic Ulcer Case Study 1Alejandro Daniel Landa MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cord Presentation and ProlapseDokument4 SeitenCord Presentation and ProlapseAnnapurna Dangeti100% (2)
- Penyakit Kulit Dan KelaminDokument97 SeitenPenyakit Kulit Dan KelaminSelvi Putri Oktari100% (1)
- Pathogenesis of PcosDokument14 SeitenPathogenesis of PcosMitali Narurkar100% (1)
- Effect of Textile Industry On Health FinalDokument2 SeitenEffect of Textile Industry On Health FinalSudhir Jain100% (1)
- Antibiotics Chart 2Dokument10 SeitenAntibiotics Chart 2Vee MendNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is in ParacetamolDokument5 SeitenWhat Is in Paracetamolloremhel barrogaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Diseases and Epidemics: PolioDokument7 SeitenCommon Diseases and Epidemics: PolioTheAwein ChannelNoch keine Bewertungen
- SELECTIVIDAD Inglés-2004Dokument3 SeitenSELECTIVIDAD Inglés-2004JabiportuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prometric Exam Sample QuestionsDokument9 SeitenPrometric Exam Sample QuestionsDe Dios JV100% (5)
- RNC Content and Study GuideDokument11 SeitenRNC Content and Study GuideNicole CanadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malnutrition in India.2Dokument45 SeitenMalnutrition in India.2Afsha ChevelwallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Periodical Test Grade 9Dokument5 Seiten1st Periodical Test Grade 9Nhoj Kram Alitnacnosalliv80% (51)
- Fork Over Knives 2017 MagazineDokument101 SeitenFork Over Knives 2017 Magazinemygacon97% (36)
- Sub07 - MR Bruce SuttonDokument45 SeitenSub07 - MR Bruce SuttonditeABCNoch keine Bewertungen
- SIP 2016 Abstract & Background Booklet V.6 PDFDokument187 SeitenSIP 2016 Abstract & Background Booklet V.6 PDFJimboreanu György PaulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Nursing Exam Board Type-1Dokument15 SeitenPediatric Nursing Exam Board Type-1CINDY� BELMESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Typhoid FeverDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan Typhoid Feverderic87% (68)
- Glossary of Psychiatry WikipediaDokument153 SeitenGlossary of Psychiatry WikipediaAkio OzaragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument14 SeitenDrug StudyCj LowryNoch keine Bewertungen