Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
A Bearing Is A Device To Permit Constrained Relative Motion Between Two Parts, Typically Rotation or Linear Movement
Hochgeladen von
Sreedhar Madhana100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
83 Ansichten18 Seitencontains different types of rolling element bearings, Terminology and geometry of rolling bearings
Originaltitel
Rolling Bearings
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldencontains different types of rolling element bearings, Terminology and geometry of rolling bearings
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
83 Ansichten18 SeitenA Bearing Is A Device To Permit Constrained Relative Motion Between Two Parts, Typically Rotation or Linear Movement
Hochgeladen von
Sreedhar Madhanacontains different types of rolling element bearings, Terminology and geometry of rolling bearings
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 18
INTRODUCTION
A Bearing is a device to permit constrained relative motion between two
parts, typically rotation or linear movement.
When there is a relative motion between two machine parts, one of
which supports the others.The supporting member is called Bearing.
TERMINOLOGY
Inner race
Outer race
Inner and outer
diameters
Width
Geometry of Rolling Contact
Bearings
SELECTION OF BEARING
TYPE
Each bearing type displays characteristic properties, based on its design which makes it
more, or less appropriate for a given application
The most important factors to be considered when selecting a standard bearing type and
thus a facilitate an appropriate choice :
Available space
Loads
Misalignment
Precision
Speed
Quiet running
Stiffness
Axial displacement
Mounting and dismounting
Integral seals
LOADS
MAGNITUDE OF LOAD :-
The magnitude of the load is one of the factors that usually determines the size of the
bearing to be used. Generally, roller bearing are available to support heavier loads than
similar size ball bearing and bearings having a full compliment of rolling elements can
accommodate heavier loads than the corresponding caged bearing.
DIRECTION OF LOAD
Radial load :-
The load which comes perpendicular on the
shaft called redial load.
Cylindrical roller
bearing, needle roller bearing, and
toroidal roller bearing can only support
pure Radial loads.
DIRECTION OF LOAD
Axial load :-
The load which comes axis on the shaft
called Axial load.
Thrust ball bearing and four point contact
ball bearing are suitable for light or
moderate loads that are purely axial.
DIRECTION OF LOAD
Combined load :-
A combined load comprises a redial and an
axial load acting simultaneously
For combined loads, single and double row
angular contact ball bearing, and single
row taper roller bearing are most
commonly used, although deep groove
ball bearing and spherical roller bearing
are suitable.
SPEED
The permissible operating temperature limits the speed at which rolling
bearings can be operated. Bearing types with low friction and correspondingly
low heat generation inside the bearing are therefore the most suitable for
high - speed operation.
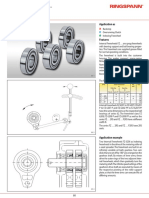
BALL BEARING
A Ball bearing is a common type
of rolling element bearing.
-Point contact; support radial
and axial loads.
ANGULAR CONTACT BALL
BEARING
Designed for axial loading;
used in pairs
These bearing are used where the thrust
load is equal to or greater than radial load.
THRUST BALL BEARING
Designed for pure
axial loading
This type comprises a row of balls
running between two flat groove washers
with balls track designed to absorbed
thrust load in one direction this does not
with stand any radial loads, also with this
is not suitable for higher speeds.
ROLLER BEARING
Roller bearings are used in rotary
applications to replace sliding movement
with low friction, rolling motion. The
principal types of roller bearings are
cylindrical, spherical, and tapered. In
general, roller bearings offer higher load
capacities than ball bearings of the same
size
CYLINDRICAL ROLLER BEARING
Supports high radial
loads; slower speed ratings
TAPERED ROLLER
BEARING
High radial and axial load
ratings; used in pairs
These bearings carry heavy loads
at moderate speed. There should
always be mounted in pairs with
opposed taper because in each
bearing the radial load produced an
axial component which needs
counter balance
SPHERICAL ROLLER BEARING
Allows for misalignment
These bearings are suitable for use with
independent support housing and
wherever there is possibility of a lack of
alignment. It can carry medium or heavy
redial or combined load.
NEEDLE ROLLER
BEARING
Thrust and radial types; typically
no inner race
These bearings are used in plans
where the speed in low or oscillation
takes place as in wrist pin, rocker arm,
universal joint etc.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Bearings: BEARING: It Is Device WhichDokument23 SeitenBearings: BEARING: It Is Device WhichPranjal Dogra100% (1)
- Lecture 1Dokument8 SeitenLecture 1Debabrat SaikiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering DrawingDokument41 SeitenEngineering DrawingKinfe MehariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Dan MetalurgiDokument32 SeitenMaterial Dan MetalurgiPrengki WijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big Island Bliss - Anita CarminDokument3 SeitenBig Island Bliss - Anita CarminAnitaCarminNoch keine Bewertungen
- VolcanoDokument17 SeitenVolcanoanm1207Noch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus TestDokument3 SeitenCalculus TestMark EichenlaubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lubrication of Wire RopeDokument14 SeitenLubrication of Wire RopegauthamNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrigonometryDokument60 SeitenTrigonometryjobeth_garcia10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rolling Contact Bearings - DMEDokument28 SeitenRolling Contact Bearings - DMESumitNoch keine Bewertungen
- HHT FFT DifferencesDokument8 SeitenHHT FFT Differencesbubo28Noch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Nitrous Oxide in AutomobilesDokument14 SeitenApplication of Nitrous Oxide in AutomobilesmandykapoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Golden Ratio, Fibonacci Series and Continued FractionsDokument23 SeitenThe Golden Ratio, Fibonacci Series and Continued FractionsDr Srinivasan Nenmeli -KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yield Stress Von MIses Stress Strength of Materials - Mechanics of MaterialsDokument3 SeitenYield Stress Von MIses Stress Strength of Materials - Mechanics of MaterialsGnabBangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Opportunities For Mobile Telecommunication ServicesDokument18 SeitenRadio Frequency Identification (RFID) Opportunities For Mobile Telecommunication ServicesAmit NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spoke Tension - The Definitive Guide To Spoke Tensioning - Spokecalc - IoDokument8 SeitenSpoke Tension - The Definitive Guide To Spoke Tensioning - Spokecalc - IoJose Luis Sabino100% (1)
- Leaf SpringDokument15 SeitenLeaf SpringAjay SengarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post Pouring BeltDokument5 SeitenPost Pouring BeltlouiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gear Ratio Calculations PDFDokument4 SeitenGear Ratio Calculations PDFrechingatuputamadreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gear Teeth: Clocks and ShipsDokument16 SeitenGear Teeth: Clocks and ShipsČika BrkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Homogeneous Boundary Value Problems: Dr. P. DhanumjayaDokument19 SeitenLinear Homogeneous Boundary Value Problems: Dr. P. DhanumjayapurijatinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Static Analysis of A Bycycle FrameDokument24 SeitenStatic Analysis of A Bycycle FrameADARSH SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 1 4 A PulleydrivessprocketsDokument4 Seiten1 1 4 A Pulleydrivessprocketsapi-30839565067% (3)
- Coupling: This Article Is About A Mechanical Connection Between Two Objects. For Other Uses, SeeDokument24 SeitenCoupling: This Article Is About A Mechanical Connection Between Two Objects. For Other Uses, Seerupesh8989Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quora MechanicalDokument14 SeitenQuora MechanicalRj SakthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Analysis Procedures For Shafts and Splines: Paul E. BurkeDokument21 SeitenDesign and Analysis Procedures For Shafts and Splines: Paul E. BurkeBalasrinivasan Murugan100% (3)
- Lab Report 5:: Compound PendulumDokument12 SeitenLab Report 5:: Compound PendulumAymen JavaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Design With Precision BallscrewsDokument10 SeitenHow To Design With Precision BallscrewsRichard CapewellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drive ShaftDokument8 SeitenDrive ShaftAkshat SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing ReliabilityDokument3 SeitenBearing ReliabilityWayu100% (1)
- Shaft Alignment Guide - E-Jan05Dokument12 SeitenShaft Alignment Guide - E-Jan05Brian FreemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab ManualDokument25 SeitenLab ManualFarhan Khan NiaZi100% (1)
- Lecture Slides: Shigley's Mechanical Engineering DesignDokument108 SeitenLecture Slides: Shigley's Mechanical Engineering DesignHamza SultanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tech-03 Springs-Roll Stiffness-4 PDFDokument9 SeitenTech-03 Springs-Roll Stiffness-4 PDFMibsão EsdrasNoch keine Bewertungen
- RequestDokument22 SeitenRequestOmar MuñozNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSK Rollneck Bearing ManualDokument36 SeitenNSK Rollneck Bearing ManualFaizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self-Locking Gear - Design and Potential ApplicationsDokument7 SeitenSelf-Locking Gear - Design and Potential ApplicationsVikram BalajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Mechatronics OverviewDokument13 Seiten1 Mechatronics OverviewPaul WallsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 Rolling Contact Bearing-2Dokument33 SeitenChapter 7 Rolling Contact Bearing-2Abaziz Mousa OutlawZzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design & Analysis of Steering System Drag Link Against Buckling Loads For Tipper ApplicationDokument7 SeitenDesign & Analysis of Steering System Drag Link Against Buckling Loads For Tipper ApplicationIJIERT-International Journal of Innovations in Engineering Research and TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Analysis of Leaf SpringDokument9 SeitenDynamic Analysis of Leaf SpringTHEBESTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimization of Planetary Gear Box For High Reduction RatioDokument12 SeitenOptimization of Planetary Gear Box For High Reduction RatioNovriansyah BrianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iowa Class - Armor ProtectionDokument3 SeitenIowa Class - Armor Protectionsworks69100% (1)
- 07 MolesDokument3 Seiten07 MoleshiepwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abstract Precision Gear Boxes and Geared Motors ReportDokument2 SeitenAbstract Precision Gear Boxes and Geared Motors Reportsandy17377Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 11 SlidesDokument77 SeitenCH 11 SlidestasrifNoch keine Bewertungen
- F1 CARS ChassisDokument27 SeitenF1 CARS ChassisNikhil Goyal100% (2)
- Optimization of Gear To Improve Performance of GearboxDokument4 SeitenOptimization of Gear To Improve Performance of Gearboxijaert100% (1)
- Types of GearsDokument22 SeitenTypes of GearsAnonymous 2RbW9dNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screwthread and Gear MeasurementDokument19 SeitenScrewthread and Gear MeasurementseenuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ptitchener Gearboxreport FullDokument25 SeitenPtitchener Gearboxreport Fullapi-244906204Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of PendulumDokument5 SeitenTypes of PendulumExpertsmindEdu100% (2)
- Thesis On Ball BearingsDokument196 SeitenThesis On Ball BearingsSudheer Reddy TenaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foote-Jones Spiral Bevel Helical ReducerDokument21 SeitenFoote-Jones Spiral Bevel Helical Reducerbwelz100% (1)
- An Investigation of The Fatigue and Fretting PerformanceDokument19 SeitenAn Investigation of The Fatigue and Fretting PerformanceKrishna PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harmonic Drive GearingDokument22 SeitenHarmonic Drive GearingManoj Kumar SarangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study On Tribological & Statistical Investigation of PTFE, Tin Bronze and White MetalDokument9 SeitenA Study On Tribological & Statistical Investigation of PTFE, Tin Bronze and White MetalIJRASETPublicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Analysis of Wheel Assembly For FSAE F3 VehicleDokument4 SeitenDesign and Analysis of Wheel Assembly For FSAE F3 VehicleEditor IJTSRD100% (1)
- 20 Design of Helical Springs For Variable LoadDokument16 Seiten20 Design of Helical Springs For Variable LoadPRASAD326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Microstructure and Defects in NanomaterialsDokument32 SeitenMicrostructure and Defects in NanomaterialsSreedhar MadhanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UnitDokument2 SeitenUnitSreedhar MadhanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TH THDokument1 SeiteTH THSreedhar MadhanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian GeographyDokument446 SeitenIndian GeographySreedhar Madhana100% (5)
- IC Engine Components (Autosaved)Dokument5 SeitenIC Engine Components (Autosaved)Sreedhar MadhanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursery RhymesDokument3 SeitenNursery RhymesSreedhar Madhana100% (1)
- Sketch ModuleDokument6 SeitenSketch ModuleSreedhar MadhanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Drawing1Dokument11 SeitenMachine Drawing1Sreedhar MadhanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Design - IntroductionDokument9 SeitenMachine Design - IntroductionSreedhar MadhanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- S3SD/S4SD & Sb3Sd/Sb4Sd: Submersible Sewage Dual Seal PumpsDokument8 SeitenS3SD/S4SD & Sb3Sd/Sb4Sd: Submersible Sewage Dual Seal PumpsulisesgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screw Pumps ACG-UCGDokument11 SeitenScrew Pumps ACG-UCGmohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Freewheels FZ : With Ball Bearing PropertiesDokument6 SeitenInternal Freewheels FZ : With Ball Bearing Propertiesmohammed kareemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coal Feeding AreaDokument75 SeitenCoal Feeding AreaAamir HayatNoch keine Bewertungen
- RKB Bearings Catalogue Light BetaDokument352 SeitenRKB Bearings Catalogue Light BetaHector MaldonadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SKF Bearings Master InterchangeDokument452 SeitenSKF Bearings Master InterchangeAamir AshinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing Technology Topics TR-113059-V2Dokument149 SeitenBearing Technology Topics TR-113059-V2anesi67100% (2)
- Viking Serie 4197 Sec - 164!12!06screenDokument5 SeitenViking Serie 4197 Sec - 164!12!06screenneoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Die Set Engineering Handbook and CatalogDokument144 SeitenDie Set Engineering Handbook and CatalogEduardo Medel50% (2)
- Bearing TypesDokument33 SeitenBearing TypesFaisal TariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- ED261d01 Alta VelocidadDokument48 SeitenED261d01 Alta Velocidadoctavio lugoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Egger Impeller Brochure PDFDokument10 SeitenEgger Impeller Brochure PDFnbharath1988100% (1)
- Linear BearingDokument3 SeitenLinear BearingyahsooyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing Units Catalog A-21000-IDokument374 SeitenBearing Units Catalog A-21000-Iardiansyah arfahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing Replacement Guide UkDokument264 SeitenBearing Replacement Guide UkLeroyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Android Game Programming For DummiesDokument127 SeitenAndroid Game Programming For DummiesbillyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Main Shaft AssemblyDokument6 SeitenMain Shaft AssemblyFrancis MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalog ZKL-ZRL PLC InfoDokument32 SeitenCatalog ZKL-ZRL PLC InfoVolodymyrNoch keine Bewertungen
- BearingDokument18 SeitenBearingBudhaditya Goswami89% (45)
- Ball TimkenDokument216 SeitenBall Timken5723820Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sintech Pumps For Sugar Processing PlantDokument18 SeitenSintech Pumps For Sugar Processing Plantsahildhingra100% (2)
- FAG Bearing DamageDokument91 SeitenFAG Bearing Damagesamir8albinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hub City Beveal Gear DrivesDokument5 SeitenHub City Beveal Gear DrivesJuan CaceresNoch keine Bewertungen
- NbnterehDokument459 SeitenNbnterehmeghasyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alfa Laval Complement To Service Manual SU Separation 01811064Dokument106 SeitenAlfa Laval Complement To Service Manual SU Separation 01811064André Heunis100% (1)
- Juntas EsfericasDokument12 SeitenJuntas EsfericasHenrique Ribeiro OliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project ReportDokument59 SeitenProject ReportKarthi M100% (2)
- MV Motor Publication Jan 2012Dokument16 SeitenMV Motor Publication Jan 2012safinditNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thrust Bearing Selector - InA-85-178Dokument94 SeitenThrust Bearing Selector - InA-85-178ebeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 ST Assignment Section-A&B 3-1 Semester Dmm-2: Sir CR Reddy College of EngineeringDokument3 Seiten1 ST Assignment Section-A&B 3-1 Semester Dmm-2: Sir CR Reddy College of EngineeringChadaram JagadishNoch keine Bewertungen