Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Module I Alifa DC
Hochgeladen von
Laurie EvansOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Module I Alifa DC
Hochgeladen von
Laurie EvansCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Slide deck
FORWARD Advisory
Board
Module I
Epidemiology, Pathogenesis,
Classification & Diagnosis of
Diabetes Mellitus (DM)
Objectives
Definition of type 2 diabetes mellitus (type 2 DM)
Epidemiology of diabetes mellitus
Classification and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus
Glucose homeostasis and pathogenesis
The term diabetes mellitus describes a metabolic
disorder of multiple etiology characterized by chronic
hyperglycemia with disturbances of carbohydrate, fat,
and protein metabolism resulting from defect in insulin
secretion, insulin action, or both.
The effects of diabetes mellitus include long-term
damage, dysfunction and failure of various organs
World Health Organization., http://www.who.int/ncd/dia/
Definition
Epidemiology of
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes Atlas, 3rd edition
IDF 2006. www.eatlas.idf.org/index2983.html
Global projections for diabetes
2007 2025
Diabetes
Comparative prevalence (%) 6.0 7.3
No. people with diabetes (millions) 246 380
Predicted diabetes epidemic greatest
prevalence
in AP (Asia Pacific) countries vs. rest of world
Ranking
2000 2030
Country
People with diabetes
(millions) Country
People with diabetes
(millions)
1 India 31.7 India 79.4
2 China 20.8 China 42.3
3 U.S.A. 17.7 U.S.A. 30.3
4 Indonesia 8.4 Indonesia 21.3
5 Japan 6.8 Pakistan 13.9
6 Pakistan 5.2 Brazil 11.3
7 Russian Fed. 4.6 Bangladesh 11.1
8 Brazil 4.6 Japan 8.9
9 Italy 4.3 Philippines 7.8
10 Bangladesh 3.2 Egypt 6.7
Wild S, et al. Diabetes Care 2004;27:1047
53
Indonesia prevalence= 5.7%
Riskesdas ,2007
Indonesia prevalence = 5.7%
Prevalence of Known Diabetes, Newly
Diagnosed Diabetes and IGT
9
Data from capital city of 33 provinces in Indonesia ,Riskesdas ,2007
Number of adults with diabetes in developed and developing
countries in 2010 and prediction in 2030, according to age-
group
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 87 (2010) 4-14
Age group (yrs)
250
200
150
100
50
0
N
o
.
o
f
p
e
o
p
l
e
w
i
t
h
d
i
a
b
e
t
e
s
(
m
i
l
l
i
o
n
s
)
Developing
Developed
2010 2030
20-39 40-59 60-79
2010 2030 2010 2030
Prevalence DM based on age
P
r
e
v
a
l
e
n
c
e
(
%
)
Age
RISKESDAS 2007
Risk factors
Age > 45 years old
Obesity
Physical inactivity
First -degree relative with diabetes
Women who delivered a baby weighing 4 kg or were
diagnosed with gestasional DM
Hypertension ( blood pressure 140/90mmHg)
Dyslipidemia ( TG> 250, HDL < 35mg/dL)
IFG (impaired fasting glucose) or IGT (impaired glucose
tolerance) on previous testing
History with coronary heart disease
History of polycystic ovarial syndrome (PCOS)
Diabetes care 32,suppl1,2009
How To Diagnose?
Criteria for the Diagnosis
1. Classic symptoms* of DM + random plasma glucose 200
mg/dL or
2. Classic symptoms of DM + Fasting plasma glucose 126
mg/dL or
(Fasting is defined as no caloric intake for at least 8 h)
2-h plasma glucose >200 mg/dL) during an OGTT. The test
should be performed as described by the World Health
Organization, using a glucose load containing the
equivalent of 75 g anhydrous glucose dissolved in 200 cc
water .
*Classic Symptoms of DM : polyuria, polydipsia,polyphagia, weight loss without any causes
Criteria for the Diagnosis
Normal Prediabetes DM
IFG IGT
FPG
(mg/dL)
< 100 100-125 <100 > 126
2-h PG
(mg/dL)
< 140
< 140
140-199*
> 200
FPG : Fasting Plasma Glucose
2-h PG : 2- hour Plasma Glucose
IFG : Impaired Fasting Glucose
IGT : Impaired Glucose Tolerance
OGTT : Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
* OGTT : post load 75 g
Classification of Diabetes
Type 1 Type 2
Other specific type
of diabetes due to
other causes
Gestational
Cells destruction
leading to absolute
insulin deficiency
Progressive insulin
secretory defect on
background of insulin
resistance
Genetic defect on
cell function
Genetic defects in
insulin action
Disease of the
exocrine pancreas
Drug or chemical
induced diabetes
Diabetes
diagnosed during
pregnancy
Glucose Homeostasis And
Pathogenesis
Glucose Homeostasis
Skeletal
Muscle
Fat
Brain
Insulin-independent
Glucose Uptake
Plasma Glucose
Insulin-dependent
Glucose Uptake
Insulin
Liver
Insulin Glucagon
Pancreas
Joslins Diabetes Mellitus,2005
The natural progression of type 2 diabetes
Adapted from Type 2 Diabetes BASICS. International Diabetes Center; 2000.
Years -10-5 0 5 10 15 20 25 30
350
300
250
200
150
100
50
Insulin
level
Insulin resistance
-cell failure
250
200
150
100
50
0 R
e
l
a
t
i
v
e
-
c
e
l
l
f
u
n
c
t
i
o
n
(
%
)
Fasting BG
Post-meal BG
G
l
u
c
o
s
e
(
m
g
/
d
L
)
DIAGNOSIS
Clinical
features
MACROVASCULAR CHANGES
Obesity IGT Diabetes
Uncontrolled
hyperglycaemia
MICROVASCULAR CHANGES
Mechanisms of Hyperglycemia
FFA Mobilization
Inherited / acquired factors/ overweight / inactivity
Hyperglycemia
GLP-1
GIP
GLP-1,
GIP
DPP-4 enzyme
Lipolysis
Gluconeogenesis
Glucagon
Glucose Uptake
Lipotoxicity
Insulin
The ominous octet
H Y P E R G L Y C E M I A
Decreased
Incretin Effect
Decreased
Glucose Uptake
Islet -cells
Neurotransmitter
Dysfunction
Increased
Lipolysis
Decreased Insulin
Secretion
Increased
Glucagon Secretion
Increased HGP
Increased
Glucose
Reabsorption
DeFronzo Ralph A Diabetes 2009; 58:773
Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes
Adapted from Yki-Jarvinen H. Textbook of Diabetes 1, third edition; 2003
Gluco-
lipotoxicity
Glucose production
in the liver
Overweight, inactivity
(inherited/acquired)
FFA
Type 2 diabetes
Inherited/acquired factors
Glucose
uptake
Insulin deficiency Insulin resistance
Hyperglycaemia
FFA=free fatty acid
Summary
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder characterized by
chronic hyperglycemia with resulting from defect in insulin
secretion, insulin action, or both.
Prevalence of type 2 DM tend to increase from 6% (2007)
to 7.3% (2025)
National Data of the prevalence diabetes: 5.7% , whereas
74% of them are newly diagnosed.
Most of the cases are type 2 diabetes.
The main factors of type 2 diabetes are insulin resistance
and insulin deficiency
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
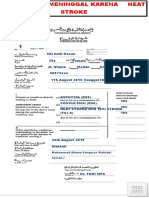
- CTH COD HEAT STROKEDokument1 SeiteCTH COD HEAT STROKELaurie EvansNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
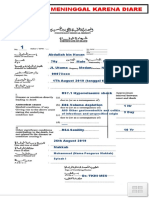
- Contoh Cod Meninggal Karena Diare: A09 Other Gastroenteritis and Colitis of Infectious and Unspecified OriginDokument1 SeiteContoh Cod Meninggal Karena Diare: A09 Other Gastroenteritis and Colitis of Infectious and Unspecified OriginLaurie EvansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Effective Patient-Physician Com (Bentuk PDFDokument5 SeitenEffective Patient-Physician Com (Bentuk PDFLaurie EvansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Module I Alifa DCDokument23 SeitenModule I Alifa DCLaurie EvansNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Securingrights Executive SummaryDokument16 SeitenSecuringrights Executive Summaryvictor galeanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Use Case Diagram ShopeeDokument6 SeitenUse Case Diagram ShopeeAtmayantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- AquaSorb PlantDokument2 SeitenAquaSorb Plantark6of7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Karla Beatriz Flores Ochoa 402-12 "C" 20 de Octubre de 2013Dokument1 SeiteKarla Beatriz Flores Ochoa 402-12 "C" 20 de Octubre de 2013Chabe CaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Minneapolis Police Department Lawsuit Settlements, 2009-2013Dokument4 SeitenMinneapolis Police Department Lawsuit Settlements, 2009-2013Minnesota Public Radio100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Historical Perspective of Financial Reporting Regulations in MalaysiaDokument2 SeitenHistorical Perspective of Financial Reporting Regulations in Malaysiauglore100% (6)
- XT 125Dokument54 SeitenXT 125ToniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Quiz MicrobiologyDokument65 SeitenQuiz MicrobiologyMedShare98% (51)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- CTY1 Assessments Unit 6 Review Test 1Dokument5 SeitenCTY1 Assessments Unit 6 Review Test 1'Shanned Gonzalez Manzu'Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- CV - Cover LetterDokument2 SeitenCV - Cover LetterMoutagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Appraisal System-Jelly BellyDokument13 SeitenPerformance Appraisal System-Jelly BellyRaisul Pradhan100% (2)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Spelling Power Workbook PDFDokument98 SeitenSpelling Power Workbook PDFTinajazz100% (1)
- Generator Faults and RemediesDokument7 SeitenGenerator Faults and Remediesemmahenge100% (2)
- Phase/State Transitions of Confectionery Sweeteners: Thermodynamic and Kinetic AspectsDokument16 SeitenPhase/State Transitions of Confectionery Sweeteners: Thermodynamic and Kinetic AspectsAlicia MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Vistas 1-7 Class - 12 Eng - NotesDokument69 SeitenVistas 1-7 Class - 12 Eng - Notesvinoth KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Affin Bank V Zulkifli - 2006Dokument15 SeitenAffin Bank V Zulkifli - 2006sheika_11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Ch5Dokument10 SeitenPractice Ch5Ali_Asad_1932Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- King of Chess American English American English TeacherDokument6 SeitenKing of Chess American English American English TeacherJuliana FigueroaNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Service Training Program 1Dokument13 SeitenNational Service Training Program 1Charlene NaungayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 1Dokument14 SeitenPart 1Jat SardanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Community Based Nutrition CMNPDokument38 SeitenCommunity Based Nutrition CMNPHamid Wafa100% (4)
- Power & Leadership PWDokument26 SeitenPower & Leadership PWdidato.junjun.rtc10Noch keine Bewertungen
- On Evil - Terry EagletonDokument44 SeitenOn Evil - Terry EagletonconelcaballocansadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Library PK - Library of Urdu BooksDokument8 SeitenThe Library PK - Library of Urdu Bookszamin4pakNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- V.S.B Engineering College, KarurDokument3 SeitenV.S.B Engineering College, KarurKaviyarasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal of Exceptional Experiences and PDokument62 SeitenJournal of Exceptional Experiences and Pbinzegger100% (1)
- Yds Deneme Sinavi PDFDokument16 SeitenYds Deneme Sinavi PDFodysseyyyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Timothy L. Mccandless, Esq. (SBN 147715) : Pre-Trial Documents - Jury InstructionsDokument3 SeitenTimothy L. Mccandless, Esq. (SBN 147715) : Pre-Trial Documents - Jury Instructionstmccand100% (1)
- The Municipality of Santa BarbaraDokument10 SeitenThe Municipality of Santa BarbaraEmel Grace Majaducon TevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Higher Order Differential EquationsDokument50 SeitenChapter 4 Higher Order Differential EquationsAlaa TelfahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)