Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Topic 3 Controlled Sources
Hochgeladen von
omairakhtar12345Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Topic 3 Controlled Sources
Hochgeladen von
omairakhtar12345Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Controlled Sources With
Op Amp
Voltage Controlled Voltage Source
(VCVS)
I I O
kv v
R
R
v = =
1
2
I O
kv v =
VCVS (Voltage Amplifier)
Inverting Configuration Example
+
_
R
L
+
-
v
in
+
_
R
1
i
1
R
F i
F
Given: v
in
= 0.6 V, R
F
= 20 kO
R
1
= 2 kO , A
OL
= 400k
R
in
= 8 M O , R
o
= 60 O
Find: v
o
, i
F
, A
v
v
O
Solution:
v
o
= -i
F
R
F
= -v
in
R
F
/R
1
= -(0.6*20,000)/2000 = 12 V
i
F
= i
1
= v
in
/R
1
= 1 / 2000 = 0.5 mA
A
v
= R
F
/R
1
= 20,000 / 2000 = 10
VCVS (Voltage Amplifier) Summary
Inverting Configuration
+
_
R
L
v
O
+
-
v
in
+
_
R
1 i
1
R
F i
F
The same
assumptions used to
find the equations for
the noninverting
configuration are
also used for the
inverting
configuration.
General Equations:
i
1
= v
in
/R
1
i
F
= i
1
v
o
= -i
F
R
F
= -v
in
R
F
/R
1
A
v
= R
F
/R
1
VCVS (Voltage Amplifier) Summary
Noninverting Configuration
+
_
v
in
+
+
-
v
O
v
id
i
(+)
i
(-)
i
O
i
F
R
F
R
L
R
1
i
1
v
id
= v
o
/A
OL
Assuming A
OL
v
id
=0
Also, with the
assumption that R
in
=
i
(+)
= i
(-)
= 0
_
v
F
+
_
v
1
+
_
v
L
+
_
i
L
Applying KVL the
following equations
can be found:
v
1
= v
in
v
O
= v
1
+ v
F
= v
in
+ i
F
R
F
This means that,
i
F
= i
1
Therefore: i
F
= v
in
/R
1
Using the equation to the left the output
voltage becomes:
v
o
= v
in
+ v
in
R
F
= v
in
R
F
+ 1
R
1
R
1
VCVS (Voltage Amplifier)
Noninverting Configuration Example
+
_
v
in
+
+
-
v
O
v
id
i
(+)
i
(-)
i
O
i
F
R
F
R
L
R
1
i
1
_
v
F
+
_
v
1
+
_
v
L
+
_
i
L
Given: v
in
= 0.6V, R
F
= 200 kO
R
1
= 2 kO , A
OL
= 400k
R
in
= 8 M O , R
o
= 60 O
Find: v
o
, i
F
, A
v
V V
V
V
A
mA .
R
V
i V V
R
R
V
in
o
v
in
F in
f
o
/ 101
3 0 6 . 60 1
1 1
= =
= = =
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
I
O
I
i
I I O
kv v
R
I = =
1
1
I O
kv I =
Voltage Controlled Current Source
(VCCS)
Floating Load
R
L
VCCS (Transconductance Amplifier) Summary
Voltage to Current Converter
+
_
Load
i
L
R
1 i
1
v
in
+
_
OR
+
_
Load
i
L
R
1 i
1
v
in
+
_
v
in
+
_
General Equations:
i
L
= i
1
= v
1
/R
1
v
1
= v
in
The transconductance, g
m
= i
o
/v
in
= 1/R
1
Therefore, i
L
= i
1
= v
in
/R
1
= g
m
v
in
The maximum load resistance is determined by:
R
L(max)
= v
o(max)
/i
L
VCCS (Transconductance Amplifier)
Voltage to Current Converter Example
+
_
Load
i
L
R
1 i
1
v
in
+
_
Given: v
in
= 2 V, R
1
= 2 kO
v
o(max)
= 10 V
Find: i
L
, g
m
and R
L(max)
Solution:
i
L
= i
1
= v
in
/R
1
= 2 / 2000 = 1 mA
g
m
= i
o
/v
in
= 1/R
1
= 1 / 2000 = 0.5 mS
R
L(max)
= v
o(max)
/i
L
= 10 V / 1 mA
= 10 k O
Note:
If R
L
> R
L(max)
the op amp
will saturate
The output current, i
L
is
independent of the load
resistance.
CCVS (Transresistance Amplifier) Summary
Current to Voltage Converter
Transresistance Amplifiers are used for low-power
applications to produce an output voltage proportional to
the input current.
Photodiodes and Phototransistors, which are used in the
production of solar power are commonly modeled as
current sources.
Current to Voltage Converters can be used to convert these
current sources to more commonly used voltage sources.
VCCS (Transresistance Amplifier)
Current to Voltage Converter Example
+
_
i
F
i
in
R
F
v
O
+
-
Given: i
in
= 10 mA
R
F
= 200 O
Find: i
F
, v
o
and r
m
Solution:
i
F
= i
in
= 10 mA
v
o
= -i
F
R
F
= 10 mA * 200 O = 2 V
r
m
= v
o
/i
in
= R
F
= 200
Application VCCS : Volt-Meter
(m-volt Range)
Moving Coil Meter
Coil Resistance
R
in
=
I I O
kv v
R
I = =
1
1
Full Scale Deflection depends on R
1
.
I
m
1 2
i I i
o
= +
4 3
R
V V
I
R
V
x o
o
x
= +
1 2
i I i
O
= +
I
O
Grounded Load
V
X
V
X
i
x
i
x
i
1
i
2
2
R i V V
x x o
=
Application VCCS
1 2
i I i
o
= +
i
i
o
x
o
x i
kV
R
V
I
R
R i
I
R
R i
R
V
= = = +
3 4
2
3
1
3
1
R i V V
x i x
=
3
4
1
2
R
R
R
R
=
i o
kV I =
Current controlled Voltage Source
CCVS
Ii
Ii
Floating Load
i i L o
kI I R V = =
Current Source Resistance is In-effective ?????
CCCS(Current Amplifier) Summary
Not commonly done using operational amplifiers
+
_
Load
i
in
i
L
Similar to the voltage
follower shown below:
Both these amplifiers have
unity gain:
A
v
= A
i
= 1
+
_
i
in
= i
L
v
in
= v
o
v
in
+
_ +
-
v
O
Voltage Follower
1 Possible
CCCS
Operational
Amplifier
Application
Current Controlled Current Source :
CCCS
I
o
I
i
I
2
V
x
i i
i
i o
x
i o
i o
kI
R
R
I
R
R I
I I
R
V
I I
I I I
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
=
=
=
2
1
2
1
2
2
1
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsVon EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Operational Amplifiers: Kristin Ackerson, Virginia Tech Ee Spring 2002 - Vtech - Calvin Project For Prof. RibeiroDokument29 SeitenOperational Amplifiers: Kristin Ackerson, Virginia Tech Ee Spring 2002 - Vtech - Calvin Project For Prof. Ribeirodheep_infotel3985100% (1)
- Op AmpDokument29 SeitenOp AmpvhinzsanguinaryNoch keine Bewertungen
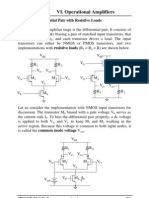
- ELEC 3400 VI. Operational Amplifiers: 1. MOS Differential Pair With Resistive LoadsDokument21 SeitenELEC 3400 VI. Operational Amplifiers: 1. MOS Differential Pair With Resistive Loadskidus100% (1)
- Ntu Ee2002Dokument198 SeitenNtu Ee2002Aaron Bourne Lee100% (1)
- OpAmp ExampleDokument16 SeitenOpAmp ExampleYi Ming Tan100% (1)
- Electronics Circuit IIDokument69 SeitenElectronics Circuit IIMtende MosesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Files-3-Lesson Notes Lecture 11Dokument9 SeitenFiles-3-Lesson Notes Lecture 11RekhyttolemyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 2 - 2021AAPS3021HDokument9 SeitenExperiment 2 - 2021AAPS3021Hasheshverma2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Power Source.Dokument12 SeitenPower Source.SaritechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1. B. Operational AmplifierDokument21 SeitenUnit 1. B. Operational AmplifierRonald ConstantinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buck Boost Regulator PresentationDokument6 SeitenBuck Boost Regulator PresentationBoutros MongareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics CircuitDokument0 SeitenElectronics Circuitwww.bhawesh.com.npNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 1 2021 Lecture Note - OpamplifierDokument20 SeitenWeek 1 2021 Lecture Note - OpamplifierBenjamin HungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 5 SolutionsDokument102 SeitenChapter - 5 SolutionsForrest LingNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Wattmeter MethodDokument8 Seiten2 Wattmeter Methodahg#0% (1)
- 9 Op-Amps and TransistorsDokument36 Seiten9 Op-Amps and TransistorsthuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Op Amp Lab ReportDokument7 SeitenFinal Op Amp Lab Reportmehrin12367% (3)
- Sistec: Sagar Group of InstitutionsDokument28 SeitenSistec: Sagar Group of InstitutionsdeeptimalviyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 - OpAmpDokument7 SeitenChapter 6 - OpAmpOm PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feedback Feedback Topologies PDFDokument12 SeitenFeedback Feedback Topologies PDFOrlando Jose Heredia0% (1)
- Lic Combined SlidesDokument288 SeitenLic Combined SlidesMadhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operational AmplifierDokument29 SeitenOperational AmplifierAlit WinayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp)Dokument26 SeitenOperational Amplifier (Op-Amp)Md ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE101 Operational AmplifierDokument117 SeitenEE101 Operational AmplifierAnish PuthurayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opa An AssDokument8 SeitenOpa An Assgvkreddyg100% (1)
- Module 7 Operational AmplifierDokument10 SeitenModule 7 Operational Amplifierjohnlester maggayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opamp Applications: Session 10: Prakash Biswagar Asst. Professor E&C Engg. Dept RV College of Engineering, BangaloreDokument35 SeitenOpamp Applications: Session 10: Prakash Biswagar Asst. Professor E&C Engg. Dept RV College of Engineering, BangaloreSatya Prasad AkkinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8Dokument34 SeitenChapter 8Abhinav GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog MeterDokument31 SeitenAnalog MeterAnooshe Asadian100% (1)
- Makalah Signal ConditioningDokument64 SeitenMakalah Signal Conditioningw4w4n_s3mk4n1s4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Op Amp ApplicationDokument24 SeitenOp Amp ApplicationPutra ArisandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Operational Amplifier EnglishDokument16 Seiten4 Operational Amplifier EnglishD4JTD Zaghlul YudafieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devices Experiment 1 - Inverting and Non-InvertingDokument16 SeitenDevices Experiment 1 - Inverting and Non-InvertingYanique GibbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analogue EEC436Dokument46 SeitenAnalogue EEC436Akachi OkoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELE 2603 AssignmentDokument16 SeitenELE 2603 AssignmentハヤNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2 AnsDokument9 SeitenTutorial 2 AnsKemproof100% (3)
- The "Operational" Amplifier: Eng - Ahmed HeskolDokument27 SeitenThe "Operational" Amplifier: Eng - Ahmed HeskoladilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 7 Power Amplifier BBN 10205 (Done)Dokument6 SeitenLab 7 Power Amplifier BBN 10205 (Done)Zhamir ZhakwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dasar OpampDokument54 SeitenDasar OpampAdri Muhaimin AfifNoch keine Bewertungen
- AtomsDokument23 SeitenAtomsAnand KNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10ESL37 - Analog Electronics Lab ManualDokument69 Seiten10ESL37 - Analog Electronics Lab ManualVinita AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operational Amplifier LAbDokument17 SeitenOperational Amplifier LAbAhmad DboukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nama: Herwin Sitanggang NIM: 14S17055 Kelas: 13 TE 2Dokument4 SeitenNama: Herwin Sitanggang NIM: 14S17055 Kelas: 13 TE 2manahanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dasar OpampDokument54 SeitenDasar OpampMaulana HidayatullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transitor 2Dokument22 SeitenTransitor 2HpA SaúlNoch keine Bewertungen
- D6 ME2143-2 Linear-Circuits ReportDokument8 SeitenD6 ME2143-2 Linear-Circuits ReportMd. Mahabubul HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Op Amp Lab ReportDokument7 SeitenFinal Op Amp Lab ReportmostfaalokezxNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC LAB EXP 02 (Study of Series Circuit and Verification of Kirchoff's Voltage Law (KVL) )Dokument7 SeitenDC LAB EXP 02 (Study of Series Circuit and Verification of Kirchoff's Voltage Law (KVL) )MishibaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectronicCircuit IILABDokument48 SeitenElectronicCircuit IILABSajith SrambikkalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Ideal Opamp Circuits: 1.1 The Voltage FollowerDokument7 Seiten1 Ideal Opamp Circuits: 1.1 The Voltage FollowerKunal KaushikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lect26 OMP AMPDokument14 SeitenLect26 OMP AMPJason LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Op AmpDokument9 SeitenOp AmpMahmoud Eldabah100% (1)
- Chapter 11Dokument14 SeitenChapter 11Johnny Lee Worthy IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 OpAmps CircuitsDokument59 Seiten5 OpAmps CircuitsDeepa ShreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC Circuits LAB 1Dokument4 SeitenAC Circuits LAB 1sarsm56Noch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft Word - Lic LabmanualDokument52 SeitenMicrosoft Word - Lic Labmanualaarish-ramesh-5468Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 9.39: /2 Spacing Is Excited With EqualDokument1 SeiteProblem 9.39: /2 Spacing Is Excited With Equalomairakhtar12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 9.34: SolutionDokument1 SeiteProblem 9.34: Solutionomairakhtar12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 5 - Channel Coding, Error Control - MEngDokument3 SeitenTutorial 5 - Channel Coding, Error Control - MEngomairakhtar12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- ENS2456 Solutions 4Dokument9 SeitenENS2456 Solutions 4omairakhtar12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 9.22: SolutionDokument1 SeiteProblem 9.22: Solutionomairakhtar12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- ENS5253 Chapter-1 Review Questions - Quiz-1Dokument3 SeitenENS5253 Chapter-1 Review Questions - Quiz-1omairakhtar12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial-SOLUTIONS-Feedback Control Systems March2017Dokument13 SeitenTutorial-SOLUTIONS-Feedback Control Systems March2017omairakhtar12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- ENS6146 Project Report TemplateDokument6 SeitenENS6146 Project Report Templateomairakhtar12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- ENS5253 Chapter-1 Review Questions - Quiz-1Dokument3 SeitenENS5253 Chapter-1 Review Questions - Quiz-1omairakhtar12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- ENS5253 Chapter-3 Review Questions - Quiz-3Dokument3 SeitenENS5253 Chapter-3 Review Questions - Quiz-3omairakhtar12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- Training PresentationDokument80 SeitenTraining Presentationomairakhtar12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hafeez Anwar Chairman Pakistan Cotton Ginners AssociationDokument20 SeitenHafeez Anwar Chairman Pakistan Cotton Ginners Associationomairakhtar12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation To IEEDokument17 SeitenPresentation To IEEomairakhtar12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4 International Conference On Advances in Energy Research Indian Institute of Technology BombayDokument30 Seiten4 International Conference On Advances in Energy Research Indian Institute of Technology Bombayomairakhtar12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- Date: 25-Jun-2014 Fateh Jhang Center Observations For Improvement of Battery Backup TimeDokument2 SeitenDate: 25-Jun-2014 Fateh Jhang Center Observations For Improvement of Battery Backup Timeomairakhtar12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- VLSI Design (MOSFET Structure) : Waqar AhmadDokument46 SeitenVLSI Design (MOSFET Structure) : Waqar Ahmadomairakhtar12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ecture: Vlsi DDokument44 SeitenEcture: Vlsi Domairakhtar12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 Op AmpDokument12 SeitenAssignment 1 Op Ampomairakhtar12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fluorescence MicroscopeDokument41 SeitenFluorescence MicroscopePraveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To Proteomics: The Protein Complement of The GenomeDokument40 SeitenAn Introduction To Proteomics: The Protein Complement of The GenomeJohn Louie BarquerosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Standard: Specificati-OnDokument14 SeitenIndian Standard: Specificati-On661982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Backend Physical Design InterviewDokument10 SeitenBackend Physical Design InterviewRohith Raj50% (2)
- Nastran DST Group TN 1700Dokument69 SeitenNastran DST Group TN 1700Minh LeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 2Dokument5 SeitenLab 2Adeem Hassan KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2017 - OPUS Quant Advanced PDFDokument205 Seiten2017 - OPUS Quant Advanced PDFIngeniero Alfonzo Díaz Guzmán100% (1)
- An Elin Load Tap Changer Diagnosis by DgaDokument4 SeitenAn Elin Load Tap Changer Diagnosis by Dgamartinez_joselNoch keine Bewertungen
- Universidad Cooperativa de Colombia: Calculo Vectorial Graficas FuncionesDokument11 SeitenUniversidad Cooperativa de Colombia: Calculo Vectorial Graficas FuncionesDavid TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week11 Turton - Cost of ManufacturingDokument32 SeitenWeek11 Turton - Cost of ManufacturingNrl Nbl Rmln100% (1)
- Press Tool ReportDokument40 SeitenPress Tool ReportIshu Bassan100% (2)
- AppNote 07 FPSO and Offshore PlatformsDokument4 SeitenAppNote 07 FPSO and Offshore PlatformsRao MadepalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermo 2, Lecture1 PDFDokument99 SeitenThermo 2, Lecture1 PDFMaricar HababagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sieve Analysis of Soil: By: Muhammad Firdaus, ST, MTDokument12 SeitenSieve Analysis of Soil: By: Muhammad Firdaus, ST, MTdaus_parisi100% (1)
- Failure Modes of Bolt and Nut Assemblies Under Tensile LoadingDokument11 SeitenFailure Modes of Bolt and Nut Assemblies Under Tensile LoadingclevercogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constant Effort SupportsDokument31 SeitenConstant Effort SupportsKen SidhartaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 4 Chemistry Yearly Plan 2019Dokument2 SeitenForm 4 Chemistry Yearly Plan 2019Jenny WeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guyton and Hall Medical PhysiologyDokument34 SeitenGuyton and Hall Medical PhysiologyFul VianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is 2974 Part 4 1979 Indian Standard Code of Practice For Design and Construction of Machine Foundations - Part 4 Foundations For Rotary Type Machines of Low Frequency PDFDokument23 SeitenIs 2974 Part 4 1979 Indian Standard Code of Practice For Design and Construction of Machine Foundations - Part 4 Foundations For Rotary Type Machines of Low Frequency PDFBibhu DattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boilere Solare Cu Serpentina Elbi Combi Quick Fisa PrezentareDokument2 SeitenBoilere Solare Cu Serpentina Elbi Combi Quick Fisa PrezentaresilvercristiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE 371JB Lecture 3Dokument38 SeitenECE 371JB Lecture 3yassinebouazziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wave Propagation in Shallow Water: Ert - C WDokument24 SeitenWave Propagation in Shallow Water: Ert - C WMarco QuirozNoch keine Bewertungen
- A1040 MiraDokument4 SeitenA1040 MiramichelditommasoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Submit by 1 May Humidification Operations: H A K ADokument2 SeitenAssignment Submit by 1 May Humidification Operations: H A K AHarshil ChangelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCS Quad Beams SeriesDokument4 SeitenSCS Quad Beams SeriesJeffrey BaldwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Condensate System ProtectionDokument8 SeitenCondensate System ProtectionmnasiroleslamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Design Roof Purlins - A Solved Example - StructvilleDokument16 SeitenHow To Design Roof Purlins - A Solved Example - StructvilleLavanyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contax t3Dokument64 SeitenContax t3desmauroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Semester Latest 21Dokument75 Seiten2nd Semester Latest 21Mugars Lupin ArseneNoch keine Bewertungen
- 413 Impurities Testing in MedicalDokument2 Seiten413 Impurities Testing in MedicalIsmail MathakiyaNoch keine Bewertungen