Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Unit - Ii: Process Planning
Hochgeladen von
Jackson ..Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Unit - Ii: Process Planning
Hochgeladen von
Jackson ..Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
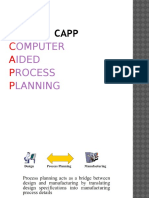
UNIT -II
PROCESS PLANNING
By
N.E.Godwin Pithalis
PROCESS PLANNING
DEFINITION:
Process planning can be defined as an act of
preparing a detailed processing documentation
for the manufacture of a piece part or assembly
Process planning is a detailed specification
which lists the operation, tools, and facilities
Usually accomplished in manufacturing
department
Also known as operations planning
Systematic determination of the engineering
processes and systems to manufacture a
product competitively and economically
APPROACHES TO PROCESS PLANNING
1. Manual Process planning
2. Computer Aided Process planning
(CAPP)
a. Retrieval CAPP system
b. Generative CAPP system
MANUAL PROCESS PLANNING
Manually prepared
Task involves examining and interrupting
engineering drawings, making decisions on
machining process selection, equipment
selection, operation sequence, and shop
practices
Dependent on judgment and experience of
process planner
Advantages
Very much suitable for small scale
companies
Highly flexible
Low investment costs
Disadvantages Of MANUAL
PROCESS PLANNING
Very complex
Time consuming
Requires large amount of data
Requires skilled process planner
More possibilities for human error
Increases paper work
Inconsistent process plans results in
reduced productivity
COMPUTER AIDED PROCESS
PLANNING (CAPP)
To overcome drawbacks of manual process planning
Computer Aided Process planning (CAPP) is used
Provides interface between CAD and CAM
Benefits
Process rationalization and standardization
Productivity improvement
Product cost reduction
Elimination of human error
Reduction in time
Reduced clerical effort and paper work
Improved legibility
Faster response to engineering changes
Incorporation of other application programs
RETRIEVAL CAPP SYSTEM
It is also called as variant CAPP,
widely used in machining applications
Basic idea behind is, similar parts will
have similar process plans
Process plan for new part is created
by recalling, identifying and retrieving
an existing plan for a similar part, and
making necessary modification for
new part
PROCEDURE FOR RETRIEVAL
CAPP SYSTEM
Retrieval CAPP system is based on
principles of group technology (GT) and
part classification and coding
For each part family, standard process
plan is prepared and stored in computer
files
Through classification and coding, code
number is generated
Standard plan is retrieved and edited
for new part
RETRIEVAL CAPP SYSTEM
Advantages
Once a standard plan has been written, variety
of parts can be planned
Requires simple programming and installation
Understandable, and planner has control of final
plan
Easy to learn and easy to use
Disadvantages
Components to be planned are limited to similar
components previously planned
Requires experienced process planners to
modify the standard plan for specific component
GENERATIVE CAPP SYSTEM
In this approach computer is used to
synthesize or generate each individual process
plan automatically without reference to any
prior plan
Generates the process plan based on decision
logics and pre-coded algorithms. Computer
stores the rules of manufacturing and
equipment capabilities
Specific process plan for specific part can be
generated without any involvement of process
planner
Components of Generative
CAPP system
Part descriptor
Subsystem to identify machine parameters
Subsystem to select and sequence individual operations
Database
Report generator
Advantages
Generate consistent process plan rapidly
New components can be planned as easily as existing
components
It has potential for integrating with automated manufacturing
facility to provide detailed control information
Drawbacks
Complex and very difficult to develop
PROCESS PLANNING
ACTIVITIES
Specific activities involved in Process planning
are
Analysis of the finished part requirements as
specified in the engineering design
Determining the sequence of operation
required
Selecting the proper equipment to
accomplish the required operations
Calculating the specific operation setup times
and cycle times on each machine
Documenting the established process plans
Communicating the manufacturing
knowledge to the shop floor
1. Analyze finished part
requirements
Component drawing should be
analyzed to identify its features,
dimensions, and tolerance
specifications
Parts requirement defined by its
features, dimensions, and tolerance
specifications will determine
corresponding processing
requirements
2. Determine operating
sequence
Basic aim is to determine the type of processing
operation that has the capability to generate
various types of features, given the tolerance
requirements
There are two ways of viewing decision process
First view is to consider processing evaluation of
part from rough state to finished final state. In
this view material is removed or modified on
rough part in stages in order to transform it into
finished part
Second view is to consider part evaluation from
finished state back to rough/ initial state. In this
view material is added back onto the part.
3. Select machines
Machine selection requires determining how the part would be
processed on each of the alternative machines so that best machine
can be selected
At this phase, firm has to decide whether to make or buy the
component part
Break even analysis is most convenient method for selecting
optimum method of manufacture or machine amongst the competing
ones
Factures which influence the selection of machine are,
Economic considerations
Production rate and unit cost of production
Durability and dependability
Lower process rejection
Minimum set-up and put away times
Longer productive life of machines or equipment
Functional versatility
4. Material selection parameters
Function
Appearance
Reliability
Service life
Environment
Compatibility
Productivity
Cost
5. Calculate processing time
Determination of set-up times requires knowledge of
available tooling and sequence of steps necessary to
prepare the machine for processing given work piece
For establishing accurate set-up times, detailed
knowledge of equipment capacity, tooling, and shop
practice required
Calculation of part processing time requires
determination of sequence of processing steps on each
machine. This is called as OUTPLANNING
After calculation of processing time, appropriate times
for loading, part unloading, machine indexing, and other
factors involved in one complete cycle for processing a
part must be included to compute the expected
machine cycle time
Allowances are added with machine cycle time to
calculate standard cycle time for processing one piece
Appropriate machine rates are added with calculated
cycle time to calculate expected standard cost for given
operation
6. Document process
planning
Process plan is documented as job routing or operation sheet
Operation sheet also called route sheet, instruction sheet, traveler,
planner
Information provided by route sheet are,
Part identification
Description of processing steps in each operation
Operation sequence and machines
Standard set-up and cycle times
Tooling requirements for each operation
Production control information showing the planning lead time at each
operation
Reasons for documentation
To have a record on a part is processed in order to plan future parts with
similar design requirements in a consistent manner
To provide a record for future job quoting, cost estimating, and standard
costing systems
To act as a vehicle for communication
7. Communicate process
knowledge
Communication is essential to ensure
that part will be processed according to
most economical way
Process documentation and
communication provide basis for improved
part consistency and quality in
manufacturing
DEVELOPING MANUFACTURING
LOGIC AND KNOWLEDGE
To support process planning system, the acquisition
and documentation of manufacturing knowledge is very
essential
Knowledge structure should be determined prior to any
type of program coding or data presentation
Knowledge structure will help to ensure error reduction,
debugging case, clarity, and future modification
Production engineers need a tool to develop
Knowledge structure format that can be used in an
interactive process and will emphasis what questions to
ask and what data to collect to support standardized
format
Commonly used tools are,
1. Flow charts
2. Decision tables
3. Expert system shells
1. FLOW CHARTS
Most commonly used tool for
collection and display of
manufacturing knowledge
Disadvantages of flow charts
It focus on process rather than on the
structure decision logic
Provides no check against
incompleteness, and redundancy
2. DECISION TABLE
It is a system / logic tool to bring together, analyze, and display
complex decision logic in such a way that its meaning can be easily
grasped
IF portion of table shows various condition that may apply
THEN portion of table indicates appropriate available actions
Left portion of table contains stub in which each of the conditions
or actions is stated
Right portion lists various entries that are possible for each of the
stub conditions and actions
Benefits
It assists the production engineers in thinking through a problem
thoroughly and presenting its resolution in a systematic and
rationally structured format
Ensure accuracy, eliminate redundancy, and avoid contradiction
It assists in stating problem, agreeing on criteria, stating
alternatives, and accepting actions between criteria and alternatives
Provide knowledge structure and readable documentation as by-
product
3. EXPERT SYSTEM SHELLS
Using this tool, knowledge engineers can
collect information to develop knowledge
base within predefined decision structure
of shell
Expert system shells format is similar to
decision table format
Like decision table format, knowledge
base is formatted in structures of if this
condition then this action, or if this
condition then this action, or else this
action
SELECTION OF PROCESS
PLANNING SYSTEM
Factors to be considered while selecting
best process planning system are,
Environment in which process
planning is conducted
Organizational structure of company
Technical expertise available to the
company
Needs and objective of company
regarding generation of manufacturing
information and process plans
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Need For Study 3: S.N O. Topic Covered Page NoDokument15 SeitenNeed For Study 3: S.N O. Topic Covered Page NoRohit BharveshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recent Trends in CappDokument23 SeitenRecent Trends in CappharimankadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Ii: Process Planning by Dr. A. Asha Professor/Mechanial Engineering Kamaraj College of Engineering & TechnologyDokument28 SeitenUnit Ii: Process Planning by Dr. A. Asha Professor/Mechanial Engineering Kamaraj College of Engineering & TechnologyShailesh ShirguppikarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Aided Process PlanningDokument6 SeitenComputer Aided Process Planningaqtu12fucNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book Series Increasing Productivity of Software Development, Part 2: Management Model, Cost Estimation and KPI ImprovementVon EverandBook Series Increasing Productivity of Software Development, Part 2: Management Model, Cost Estimation and KPI ImprovementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me 6703-Cim-Mech-Viist-Au-Unit-IiDokument29 SeitenMe 6703-Cim-Mech-Viist-Au-Unit-IiSiva RamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Aided Process Planning For Milling Operation: PritiDokument8 SeitenComputer Aided Process Planning For Milling Operation: PritiWahyu WidiantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPCE U 1 NotesDokument10 SeitenPPCE U 1 NotesJeevanandam ShanmugasundaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process PlanningDokument10 SeitenProcess PlanningSudeep Kumar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 & Chapter 2Dokument16 SeitenChapter 1 & Chapter 2pragyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Lecture 4 Computer Aided Process PlanningDokument18 SeitenChapter 2 Lecture 4 Computer Aided Process PlanningsinghsujitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2 - Process Planning PDFDokument30 SeitenLecture 2 - Process Planning PDFFoxsoer100% (5)
- CIMSDokument24 SeitenCIMSAaryan MoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer-Aided Process PlanningDokument3 SeitenComputer-Aided Process PlanningAbdul-wahab RiyadhNoch keine Bewertungen
- CaPP MainDokument9 SeitenCaPP MainSulficker AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAPPDokument25 SeitenCAPPshubham_arora_19Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-8 Computer Aided Process Planning (Capp)Dokument16 SeitenChapter-8 Computer Aided Process Planning (Capp)olyad ahmedinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computerized Manufacturing Planning Systems (Computerized Production)Dokument15 SeitenComputerized Manufacturing Planning Systems (Computerized Production)Aravind IlangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Aided Process Planning Full Seminar ReportDokument32 SeitenComputer Aided Process Planning Full Seminar ReportSarath Chandran100% (7)
- Cad Module 2Dokument3 SeitenCad Module 2JithumonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Aided Process Planning (CAPP)Dokument30 SeitenComputer Aided Process Planning (CAPP)brijkishor2017100% (1)
- Computer Aided Process PlanningDokument10 SeitenComputer Aided Process PlanningyashwanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - 2 Process Planning Process PlanningDokument21 SeitenUnit - 2 Process Planning Process PlanningRAJAGOPAL MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Aided Process Planning: Date: 2/27/03 Room: MSE Computer Lab Presenters: Cem Toma Anthony NguyenDokument23 SeitenComputer Aided Process Planning: Date: 2/27/03 Room: MSE Computer Lab Presenters: Cem Toma Anthony NguyenRjose PortilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cop Milling 4Dokument9 SeitenCop Milling 4Naseeb Ullah TareenNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAPPDokument27 SeitenCAPPRajeshwar DeshmukhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Selection: Influence That Process Has On An OrganizationDokument8 SeitenProcess Selection: Influence That Process Has On An OrganizationCarla Jamina IbeNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDPP Unit - 5 PDFDokument25 SeitenPDPP Unit - 5 PDFShreya KumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAPP Final PPT 2.0Dokument21 SeitenCAPP Final PPT 2.0Navya MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 CAPPDokument31 SeitenChapter 6 CAPPtrần thị ngọc trâmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Aided Process Planning For Milling Operation: September 2016Dokument9 SeitenComputer Aided Process Planning For Milling Operation: September 2016guptaamitalwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7: Process PlanningDokument6 SeitenChapter 7: Process Planningஅன்புடன் அஸ்வின்Noch keine Bewertungen
- Me8793 Qb.Dokument38 SeitenMe8793 Qb.YUVA RAJA BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me6703 2 Mark Questions Slow LearnersDokument10 SeitenMe6703 2 Mark Questions Slow LearnersKanagarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generative Approach Under Computer Aided Process Planning (Dokument14 SeitenGenerative Approach Under Computer Aided Process Planning (asprillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 3 (B)Dokument38 SeitenCHAPTER 3 (B)daneshnedaieNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT-5: Omputer Ided Rocess LanningDokument28 SeitenUNIT-5: Omputer Ided Rocess LanningDarbhalaPavanKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 9 Computer Aided Process Planning (Capp) : StructureDokument21 SeitenUnit 9 Computer Aided Process Planning (Capp) : StructureRajueswarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CappDokument19 SeitenCappSumanAgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument6 SeitenAssignment 1MUTHUKKANNU KRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 6 PP and CAPPDokument28 SeitenLec 6 PP and CAPPMuhammadImranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost CH - 1Dokument23 SeitenCost CH - 1mihiretugetinet41Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Aided Process Planning-IDokument19 SeitenComputer Aided Process Planning-IShamsir Ibni ShukriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer-Aided Process Planning - CAPP: 110 Manufacturing Methods 99Dokument1 SeiteComputer-Aided Process Planning - CAPP: 110 Manufacturing Methods 99Anonymous qRbPsLpuNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production Flow AnalysisDokument24 SeitenProduction Flow AnalysisSelva Shri NathNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME6005 Ppce QBDokument18 SeitenME6005 Ppce QBKamalakkannan Krishnan100% (1)
- Ppce Essay Two MarksDokument29 SeitenPpce Essay Two Markskarthiksubramanian94Noch keine Bewertungen
- Operations Management: Lecture NotesDokument49 SeitenOperations Management: Lecture NotesKajal NainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Aided Process Planning-IDokument19 SeitenComputer Aided Process Planning-IPrabha KaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Aided Process Planning CAPPDokument32 SeitenComputer Aided Process Planning CAPPعبدالله عبداللهNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Aided Process Planning-I 23Dokument19 SeitenComputer Aided Process Planning-I 23familyumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Lec CIM Route Sheet and CAPPDokument28 Seiten11 Lec CIM Route Sheet and CAPPM ARQAM WaheedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process PlanningDokument32 SeitenProcess PlanningBalto YesurethnamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proces wp001 - en P PDFDokument16 SeitenProces wp001 - en P PDFReinaldo GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 MarksDokument12 Seiten2 MarksVijaya Prabhu KumarasamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Aided Process Planning-IDokument19 SeitenComputer Aided Process Planning-IAnantha KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME6712 Mechatronics Lab ManualDokument50 SeitenME6712 Mechatronics Lab ManualJackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- CREO-Student List - AttendanceDokument1 SeiteCREO-Student List - AttendanceJackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- FormulaDokument12 SeitenFormulaJackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- PumpDokument38 SeitenPumpJackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit IDokument5 SeitenUnit IJackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- Name List PDFDokument2 SeitenName List PDFJackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fea 6Dokument11 SeitenFea 6Jackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus CoverageDokument1 SeiteSyllabus CoverageJackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-V: Isoparametric FormulationDokument9 SeitenUnit-V: Isoparametric FormulationJackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- Presented By: Sagar Narula - 121 Amit Navghare - 122 Priydarshini Nawar - 123 Suraj Nilekar - 124 Reeta Pal - 125Dokument18 SeitenPresented By: Sagar Narula - 121 Amit Navghare - 122 Priydarshini Nawar - 123 Suraj Nilekar - 124 Reeta Pal - 125Jackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus R2013 PDFDokument105 SeitenSyllabus R2013 PDFlogeshboy007Noch keine Bewertungen
- TUT1Unit: 10 TUT2Unit: 10 TUT3Unit: 30 TUT4Unit: 30 TUT5Unit: 30 TUT6Unit: 30 TUT7Unit: 40Dokument1 SeiteTUT1Unit: 10 TUT2Unit: 10 TUT3Unit: 30 TUT4Unit: 30 TUT5Unit: 30 TUT6Unit: 30 TUT7Unit: 40Jackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ie433 Cad/Cam Computer Aided Design and Computer Aided Manufacturing Part-1 Introduction To CAD/CAMDokument27 SeitenIe433 Cad/Cam Computer Aided Design and Computer Aided Manufacturing Part-1 Introduction To CAD/CAMJackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- ME2353 Finite Element Analysis NovDec 2015 QPDokument3 SeitenME2353 Finite Element Analysis NovDec 2015 QPJackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- Joining ProcessDokument122 SeitenJoining ProcessJackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Finite Element MethodDokument202 SeitenIntroduction To Finite Element MethodPrithviraj Daga80% (15)
- Fea Data Book 1Dokument3 SeitenFea Data Book 1Jackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Semester SjhjkyllabusDokument13 Seiten1st Semester SjhjkyllabusJackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Materials and Metallurgy Notes PDFDokument0 SeitenEngineering Materials and Metallurgy Notes PDFSenthilkumar Subbiah50% (2)
- Front PageDokument9 SeitenFront PageJackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Introduction MechatronicsDokument77 Seiten1 Introduction MechatronicsJeewan AtwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manufacturing IDokument28 SeitenManufacturing IJackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- Text BooksDokument2 SeitenText BooksJackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- Front PageDokument9 SeitenFront PageJackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- M T 1Dokument2 SeitenM T 1sumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course: ME 2252 - Manufacturing Technology - II - Class: BEMEC-2012-4-A Course Objective(s)Dokument7 SeitenCourse: ME 2252 - Manufacturing Technology - II - Class: BEMEC-2012-4-A Course Objective(s)Jackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDokument2 SeitenNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentJackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- Process Planning & Cost Estimation Question BankDokument12 SeitenProcess Planning & Cost Estimation Question Banksanbharani4242100% (2)
- Lesson List PpceDokument2 SeitenLesson List PpceJackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- SyallabusDokument3 SeitenSyallabusJackson ..Noch keine Bewertungen
- GD&T StandardDokument100 SeitenGD&T StandardsudhirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fs 4041 TG Package, Rev-0Dokument88 SeitenFs 4041 TG Package, Rev-0Othman RejabNoch keine Bewertungen
- AS10169Dokument11 SeitenAS10169JOECOOL67Noch keine Bewertungen
- IRS Specification For Composite GRSP (6.2mm Thick) With Amendment 2 of 2017Dokument27 SeitenIRS Specification For Composite GRSP (6.2mm Thick) With Amendment 2 of 2017RAJKUMARINoch keine Bewertungen
- en 32 - HCPPDokument9 Seitenen 32 - HCPPsoniya RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso 10683 2000Dokument9 SeitenIso 10683 2000VIJAYANTHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gear Technology 511Dokument84 SeitenGear Technology 511sosu_sorin3904Noch keine Bewertungen
- Is 3459-2004Dokument12 SeitenIs 3459-2004Anonymous 0v9zwXz6hFNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tolerancias FEM y Autoportantes 1Dokument53 SeitenTolerancias FEM y Autoportantes 1ybusomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm B16 PDFDokument5 SeitenAstm B16 PDFpilo111100% (3)
- B473 07Dokument7 SeitenB473 07Srinivasan KrishnamoorthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fdocuments - in The Formwork Experts Timber Formwork Beams 4 999791002 022020 User InformationDokument20 SeitenFdocuments - in The Formwork Experts Timber Formwork Beams 4 999791002 022020 User InformationNitish BansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is-5382-1998 Specification-for-Rubber-Sealing-Rings-for-Gas-Mains-Water-Mains-and-Sewage PDFDokument23 SeitenIs-5382-1998 Specification-for-Rubber-Sealing-Rings-for-Gas-Mains-Water-Mains-and-Sewage PDFDeven Patle0% (1)
- Unit 23:: Control ChartsDokument11 SeitenUnit 23:: Control ChartstarrteaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SNT Plummer Block CatalogDokument120 SeitenSNT Plummer Block CatalogRickson PhilipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Instructions: BA 3600 EN 08.98Dokument24 SeitenOperating Instructions: BA 3600 EN 08.9896652529Noch keine Bewertungen
- 11 RunoutDokument14 Seiten11 RunoutImranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fits and TolerancesDokument18 SeitenFits and TolerancesShahid MehmudNoch keine Bewertungen
- EML2322L Design For Manufacturing Examples PDFDokument13 SeitenEML2322L Design For Manufacturing Examples PDFNitinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalog A9: Sealing Rings Retaining RingsDokument48 SeitenCatalog A9: Sealing Rings Retaining Ringsshrikant mishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ansi-Nicts 322Dokument72 SeitenAnsi-Nicts 322enriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Bridge Group - TolerancesDokument5 SeitenSteel Bridge Group - TolerancesIshmael WoolooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product CatalogDokument14 SeitenProduct CatalogAndrei IngelbergNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bsen 10029 1991 PDFDokument17 SeitenBsen 10029 1991 PDFPinkuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Bolting GuideDokument24 SeitenStructural Bolting GuideJoseph BookerNoch keine Bewertungen
- d4753 15 Standard Guide For Evaluating Selecting and Specifying Balances and Standard Masses For Use in Soil Rock and Construction Materials TestingDokument6 Seitend4753 15 Standard Guide For Evaluating Selecting and Specifying Balances and Standard Masses For Use in Soil Rock and Construction Materials TestingAfra AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iec60404 8 7 (Ed3.0) BDokument42 SeitenIec60404 8 7 (Ed3.0) BMor GreenbergNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Organization For Standardization StandardsDokument17 SeitenInternational Organization For Standardization Standardsek chumni786Noch keine Bewertungen
- F2658 PDFDokument10 SeitenF2658 PDFAhmad Zubair RasulyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modelo 357Dokument3 SeitenModelo 357Marco Antonio Esquivel BarretoNoch keine Bewertungen