Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Case Presentation - CKD
Hochgeladen von
Amanda Padma50%(2)50% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (2 Abstimmungen)
466 Ansichten27 SeitenA 35-year-old male presented with abdominal pain and shortness of breath due to fluid in the abdomen. He has a history of chronic kidney disease stage 5 and has been undergoing hemodialysis for about a year. On examination, he had abdominal swelling and shifting dullness consistent with ascites. Laboratory tests showed anemia. He was diagnosed with chronic kidney disease stage 5 with ascites and anemia. He received ascites puncture which improved his symptoms.
Originalbeschreibung:
chronic kidney disease
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenA 35-year-old male presented with abdominal pain and shortness of breath due to fluid in the abdomen. He has a history of chronic kidney disease stage 5 and has been undergoing hemodialysis for about a year. On examination, he had abdominal swelling and shifting dullness consistent with ascites. Laboratory tests showed anemia. He was diagnosed with chronic kidney disease stage 5 with ascites and anemia. He received ascites puncture which improved his symptoms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
50%(2)50% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (2 Abstimmungen)
466 Ansichten27 SeitenCase Presentation - CKD
Hochgeladen von
Amanda PadmaA 35-year-old male presented with abdominal pain and shortness of breath due to fluid in the abdomen. He has a history of chronic kidney disease stage 5 and has been undergoing hemodialysis for about a year. On examination, he had abdominal swelling and shifting dullness consistent with ascites. Laboratory tests showed anemia. He was diagnosed with chronic kidney disease stage 5 with ascites and anemia. He received ascites puncture which improved his symptoms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 27
Felix Hansen (1015101)
Amanda Padma (1015058)
Indra Josua (0715092)
Case Presentation
Identity of Patient
Name : Tn. R
Age : 35 years old
Gender : Male
Occupation : Not working
Status : Single
Room/Bed : Gideon/4
Date : 09-06-2014
Diagnose : CKD Stage 5 on Hemodialysis
+ Acites
Resume
A male 35 years old came with pain in all parts
of abdomen. The pain wasnt radiate and patient
also complained having breathless because of
fluid in abdomen that press the chest. Patient
confessed having treatment with the kidney
disease and had hemodialysis for almost a
year. Patient also complained having swolen in
pair of feet.
Past medical history : UTI on 2010 => progress
to renal disease on 2012 => having
hemodialysis since then, asthma (-), diabetes
mellitus (-), hypertension (-)
Family medical history : -
Allergic history : -
Physical Examination
Vital Signs
BP : 120/80 mmHg
Heart rate : 120 x/minute
Respiration : 32x/minute
Temperature : 36,9C
Skin : cyanosis (-), jaundice (-)
Head
Eye : Conjunctiva anemic (+/+), sclera jaundice (-/-)
ENT : secretions (-)
Neck : lymph node not palpable, trachea
central
Thorax
Heart : heart sound S1S2 regular, murmur (-)
Pulmo : move symetric, vbs (+/+), ronchi (-/-),
wheezing (-/-)
Abdomen : raised, soepel, gut sound (-), palpable pain
(-), shifting dullness (+), fluid wave (+)
Extremities : swolen in pair of feet, non pitting,
muscle atrophy in pair of feet.
Lab Result (09-06-2014)
Hb : 9,4 gr/dl (<<)
Ht : 28,5 % (<<)
Leucocyte : 6.560 / mm3
Thrombocyte : 340.000 / mm3
Erythrocyte : 3.8 million / mm3 (<<)
MCV : 75 fl (<<)
MCH : 25 pg/ml
MCHC : 33 gr/dl
USG (03-06-2014)
R-Kidney
Smaller with length around 70mm, uneven
surfaces, thin parenchym, higher echogenesity
L-Kidney
Smaller with length around 77mm, thin
parenchym, higher echogenesity
Intraperitoneal free fluid
Minimal pleural effusion
Diagnose
Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 5 + Acites +
Anemia
Follow up
09-06-2014
BP: 120/80 mmHg
HR: 120x/minute
RR: 32x/minute
T : 36,9C
Breathless (+), fluid
intraperitoneal (+),
abdominal pain (+)
Bed rest, nasal cannule
O2 5 litres/minute,
prepare for ascites
punction
10-06-2014
BP: 110/80 mmHg
HR: 100x/minute
RR: 22x/minute
T : 36,4C
Breathless (-), fluid
intraperitoneal minimal,
abdominal pain (-)
Ascites punction +- 2-
2,5 litres
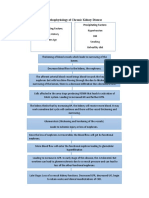
Chronic Kidney Disease
Is define as abnormalities of kidney structure or
function, present for more than 3 months with
implication for help
Staging of CKD
Why CKD??
Because the patient having abnormalities
structure (from the USG imaging)
The patient having history of hemodialysis for 2
years so we assume he had abnormality of renal
function more than 3 months
Why stage 5??
We assume he had CKD stage 5 because
dialysis is typically initiated when eGFR falls
bellow 10mL/minute/1,73 m2 but in this patient
we didnt have the last result of eGFR but he had
hemodialysis twice a week for 2 years
Why Ascites??
The etiology of ascites is still uncertain. The
pathogenesis seems to be multifactorial:
1. Chronic fluid overload with hepatic congestion resulting
in increased hepatic vein hydrostatic pressure is usual
2. Change in the permeability of the peritoneal membrane
have been shown in patients receiving CAPD
3. Impaired lymphatic peritoneal reabsorption was
proposed as a pathogenic mechanism and confirm by
lymphatic flow rate studies. The fact that the rate of
removal is much slower in ureamic patients compare to
non ureamic
4. Contributing causes include hypoproteinemia,
congestive heart failure, or liver cirrhosis with portal
hypertension
Why Anemia??
CKD leads to normocytic anemia due to
inadequate renal production of erythropoietin.
3.2.1: Diagnose anemia in adult and children > 15
years with CKD when Hb Concentration is < 13
g/dl in males and <12 g /dl
In Patient Hb is 9,4 g/dl
Management CKD
Hemodialysis 5 hours three times a week
If possible to doing renal transplant procedure
Refer to nephrologist
Management of anemia
In general, erythropoiesis stimulating agents are
used to maintain a hemoglobin level of 11 to 12
g/dl.
In patient receiving this treatment, iron stores
should be assessed and replenished as needed
to avoid apparent erythropoietin resistance.
Complication
Prognosis
Daftar Pustaka
http://www.pathophys.org/ckd/#Pathophysiology
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/170907-
treatment
KDIGO 2012 Clinical Pratice Guideline for the
Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney
Disease. Kidney Disease Improving Global
Outcomes. 1, January 2013, Vol. 3.
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation. Franz, M.
and Horl, W.H. 1997.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Construction Agreement SimpleDokument3 SeitenConstruction Agreement Simpleben_23100% (4)
- Pathophysiolgoy Coronary Artery DiseaseDokument3 SeitenPathophysiolgoy Coronary Artery DiseaseNursesLabs.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Renal FailureDokument34 SeitenAcute Renal Failureaibaloca67% (9)
- The Structure of The Nazi Economy - Maxine Yaple SweezyDokument273 SeitenThe Structure of The Nazi Economy - Maxine Yaple Sweezygrljadus100% (2)
- CKDDokument48 SeitenCKDJuniorNoch keine Bewertungen
- End Stage Renal DiseaseDokument62 SeitenEnd Stage Renal DiseaseMae Navidas DigdiganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corrugated Board Bonding Defect VisualizDokument33 SeitenCorrugated Board Bonding Defect VisualizVijaykumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Directory of Schools For The Deaf in The PhilippinesDokument6 SeitenDirectory of Schools For The Deaf in The PhilippinesVERA Files100% (1)
- Obectives of Case Study: General ObjectivesDokument42 SeitenObectives of Case Study: General Objectivesganesh0% (1)
- Skylab Our First Space StationDokument184 SeitenSkylab Our First Space StationBob AndrepontNoch keine Bewertungen
- CirrhosisDokument56 SeitenCirrhosisJerson IngnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study ESRDDokument30 SeitenCase Study ESRDreginebenedicte100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney Disease: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of Chronic Kidney Disease: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsReina Samson0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Dokument1 SeitePathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2faula rocamora100% (3)
- Community Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandCommunity Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study On End Stage Renal FailureDokument19 SeitenCase Study On End Stage Renal Failurelenecarglbn100% (1)
- OrderFlow Charts and Notes 19th Sept 17 - VtrenderDokument9 SeitenOrderFlow Charts and Notes 19th Sept 17 - VtrenderSinghRaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- CaseStudy ChronicRenalFailureDokument29 SeitenCaseStudy ChronicRenalFailureCarlcedrick ManlapusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sportex 2017Dokument108 SeitenSportex 2017AleksaE77100% (1)
- Acute Renal FailureDokument59 SeitenAcute Renal Failurepaul_v_44440% (1)
- Acute PyelonephritisDokument24 SeitenAcute Pyelonephritismayey22100% (3)
- Case StudyDokument37 SeitenCase StudyAnonymous t78m8ku100% (1)
- Case Study CKD DM Type 2Dokument7 SeitenCase Study CKD DM Type 2Brian Cornel0% (3)
- ESRD Secondary To Diabetic Nephropathy CASE STUDY Docx 2Dokument42 SeitenESRD Secondary To Diabetic Nephropathy CASE STUDY Docx 2Eyerusalem100% (1)
- End Stage Renal Disease Case StudyDokument8 SeitenEnd Stage Renal Disease Case StudyNikko Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map On CVA Bleed Left Thalamo-Ganglionic Bleed Patient Name: Mr. DGDDokument1 SeiteConcept Map On CVA Bleed Left Thalamo-Ganglionic Bleed Patient Name: Mr. DGDBert Brian Bolido100% (1)
- Case StudyDokument34 SeitenCase StudyBSNNursing101Noch keine Bewertungen
- Non-St Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (Nstemi)Dokument24 SeitenNon-St Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (Nstemi)MHIEMHOINoch keine Bewertungen
- CellulitisDokument16 SeitenCellulitisMhOt AmAd100% (1)
- Case Study On Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokument101 SeitenCase Study On Chronic Kidney DiseaseZNEROL100% (6)
- Hypovolemic Shock 09Dokument58 SeitenHypovolemic Shock 09Joanne Bernadette Aguilar100% (2)
- A Case Study On Chronic Renal DiseaseDokument17 SeitenA Case Study On Chronic Renal Diseasematucojulio100% (1)
- End-Stage Renal DiseaseDokument3 SeitenEnd-Stage Renal DiseaseAkira Pongchad B100% (1)
- CKD (F&e)Dokument110 SeitenCKD (F&e)Al-nazer Azer Al100% (1)
- A Case Study On Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokument103 SeitenA Case Study On Chronic Kidney DiseaseLouella Mae CoraldeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHF Group 3 Ncmb312 RleDokument39 SeitenCHF Group 3 Ncmb312 RleMaica Lectana50% (2)
- Acute Renal FailureDokument54 SeitenAcute Renal FailureNiala Almario100% (1)
- CHF Case StudyDokument38 SeitenCHF Case StudyMelissa David100% (1)
- Case Study On Bilateral NephrolithiasisDokument85 SeitenCase Study On Bilateral NephrolithiasisShoixi ⎝⓿⏝⓿⎠100% (1)
- Case Presentation CKDDokument27 SeitenCase Presentation CKDSapna thakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study 18 CKDDokument7 SeitenCase Study 18 CKDapi-301049551Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes MellitusDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of Diabetes MellitusJerene67% (3)
- Case Study EsrdDokument4 SeitenCase Study EsrdSTEPHANIE JOSUENoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study 18Dokument4 SeitenCase Study 18api-271284613Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case Presentation On Chronic Kidney Disease1Dokument18 SeitenCase Presentation On Chronic Kidney Disease1d100% (1)
- Chronic Kidney Disease Case PresDokument32 SeitenChronic Kidney Disease Case Presnnaesor_1091Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study On Bilateral NephrolithiasisDokument84 SeitenCase Study On Bilateral NephrolithiasisSteph BulanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysio CRF RevisedDokument2 SeitenPathophysio CRF Revisedroseanne18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Congestive Heart FailureDokument18 SeitenCongestive Heart FailureAisha Rashed100% (1)
- Chronic Kidney Disease Case PresentationDokument14 SeitenChronic Kidney Disease Case PresentationEmi EspinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Predisposing Conditions, Management and Prevention of Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokument52 SeitenPredisposing Conditions, Management and Prevention of Chronic Kidney DiseaseSaad MotawéaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study - Chronic Kidney Disease Treated With DialysisDokument7 SeitenCase Study - Chronic Kidney Disease Treated With Dialysisapi-387604918100% (1)
- CKD PresentationDokument51 SeitenCKD PresentationBasneyatPragyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case StudyDokument17 SeitenCase StudyEarl Viray JulaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Renal FailureDokument28 SeitenChronic Renal FailurePatricia Nadine Sarcadio NeffeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemorrhagic StrokeDokument12 SeitenHemorrhagic StrokeManggara Surya DharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk For Bleeding - Cirrhosis NCPDokument2 SeitenRisk For Bleeding - Cirrhosis NCPPaula AbadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver CirrhosisDokument60 SeitenLiver CirrhosisCamilla Zharine P. BantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study ReportDokument23 SeitenCase Study Reportapi-290866384Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Renal FailureDokument37 SeitenChronic Renal Failuredorkiebaby100% (10)
- Case StudyDokument26 SeitenCase Studyamazing grace mejia carlos100% (2)
- Nasopharyngeal CarcinomaDokument26 SeitenNasopharyngeal CarcinomahazaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Efusi Pleura Ec Ca ParuDokument33 SeitenEfusi Pleura Ec Ca ParuRahma Putri KinasihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caseeeee Egaaa IrbasssDokument27 SeitenCaseeeee Egaaa IrbasssIrbasMantiniSyaifulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final CaseDokument45 SeitenFinal Case_carido_Noch keine Bewertungen
- Meig SyndromeDokument42 SeitenMeig SyndromeWenny Artha MuliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Morning Report Tuesday Night Shift, FEBRUARY 12, 2019: Dr. / Dr. / Dr. / Dr. /dr. Dr. Dr. / DRDokument32 SeitenMorning Report Tuesday Night Shift, FEBRUARY 12, 2019: Dr. / Dr. / Dr. / Dr. /dr. Dr. Dr. / DRHafizhan MuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Management System - Full DocumentDokument46 SeitenStudent Management System - Full DocumentI NoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evolution of Designed Industrial Symbiosis Networks in The Ulsan Eco-Industrial Park - Research and Development Into Business ADokument10 SeitenEvolution of Designed Industrial Symbiosis Networks in The Ulsan Eco-Industrial Park - Research and Development Into Business Asanyukta sinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMP Step 2 6 Week CalendarDokument3 SeitenEMP Step 2 6 Week CalendarN VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of Physicochemical Pollutants in Wastewater and Some Food Crops Grown Along Kakuri Brewery Wastewater Channels, Kaduna State, NigeriaDokument5 SeitenDetermination of Physicochemical Pollutants in Wastewater and Some Food Crops Grown Along Kakuri Brewery Wastewater Channels, Kaduna State, NigeriamiguelNoch keine Bewertungen
- EFL Listeners' Strategy Development and Listening Problems: A Process-Based StudyDokument22 SeitenEFL Listeners' Strategy Development and Listening Problems: A Process-Based StudyCom DigfulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Living in IT Era OutputDokument6 SeitenLiving in IT Era OutputDanica Rose SaludarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 3 Quest-Answer 2014Dokument8 Seiten1 3 Quest-Answer 2014api-246595728Noch keine Bewertungen
- Inventory Management Final ProjectDokument65 SeitenInventory Management Final ProjectMAHESH MUTHYALANoch keine Bewertungen
- Byron and The Bulgarian Revival Period - Vitana KostadinovaDokument7 SeitenByron and The Bulgarian Revival Period - Vitana KostadinovavitanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2U6 S4HANA1909 Set-Up EN XXDokument10 Seiten2U6 S4HANA1909 Set-Up EN XXGerson Antonio MocelimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apush Leq Rubric (Long Essay Question) Contextualization (1 Point)Dokument1 SeiteApush Leq Rubric (Long Essay Question) Contextualization (1 Point)Priscilla RayonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar PustakaDokument6 SeitenDaftar PustakaSeptian UtamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safe Britannia PDFDokument2 SeitenSafe Britannia PDFeden4872Noch keine Bewertungen
- Powerpoints 4 4up8Dokument9 SeitenPowerpoints 4 4up8Ali KalyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- أثر البحث والتطوير على النمو الاقتصادي - دراسة قياسية لحالة الجزائر (1990 -2014)Dokument17 Seitenأثر البحث والتطوير على النمو الاقتصادي - دراسة قياسية لحالة الجزائر (1990 -2014)Star FleurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sona Koyo Steering Systems Limited (SKSSL) Vendor ManagementDokument21 SeitenSona Koyo Steering Systems Limited (SKSSL) Vendor ManagementSiddharth UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indiabix PDFDokument273 SeitenIndiabix PDFMehedi Hasan ShuvoNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Governance Horizon Report 2007 PDFDokument240 SeitenE-Governance Horizon Report 2007 PDFtouhedurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Referensi PUR - Urethane Surface coating-BlockedISO (Baxenden) - 20160802 PDFDokument6 SeitenReferensi PUR - Urethane Surface coating-BlockedISO (Baxenden) - 20160802 PDFFahmi Januar AnugrahNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Notified Bodies Under Directive - 93-42 EEC Medical DevicesDokument332 SeitenList of Notified Bodies Under Directive - 93-42 EEC Medical DevicesJamal MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANTH 222 Syllabus 2012Dokument6 SeitenANTH 222 Syllabus 2012Maythe S. HanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ham (Son of Noah) - WikipediaDokument3 SeitenHam (Son of Noah) - Wikipediamike bNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neolms Week 1-2,2Dokument21 SeitenNeolms Week 1-2,2Kimberly Quin CanasNoch keine Bewertungen