Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Thyroid Gland
Hochgeladen von
Sheena Mae Atienza100%(2)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (2 Abstimmungen)
767 Ansichten10 SeitenThe thyroid gland is located in the neck below the thyroid cartilage. It is butterfly-shaped with right and left lobes connected by an isthmus. The gland produces thyroid hormones T3 and T4 which regulate metabolism and are regulated by TSH from the pituitary gland. The most common thyroid disorders are hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) and hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid). Hyperthyroidism causes excessive thyroid hormone production and symptoms like rapid heartbeat and weight loss, often due to Graves' disease. Hypothyroidism is caused by insufficient hormone production and results in fatigue, weight gain, and intolerance to cold. Both disorders are treated with medication to regulate thyroid hormone levels.
Originalbeschreibung:
**
Originaltitel
Thyroid Gland PPT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe thyroid gland is located in the neck below the thyroid cartilage. It is butterfly-shaped with right and left lobes connected by an isthmus. The gland produces thyroid hormones T3 and T4 which regulate metabolism and are regulated by TSH from the pituitary gland. The most common thyroid disorders are hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) and hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid). Hyperthyroidism causes excessive thyroid hormone production and symptoms like rapid heartbeat and weight loss, often due to Graves' disease. Hypothyroidism is caused by insufficient hormone production and results in fatigue, weight gain, and intolerance to cold. Both disorders are treated with medication to regulate thyroid hormone levels.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(2)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (2 Abstimmungen)
767 Ansichten10 SeitenThyroid Gland
Hochgeladen von
Sheena Mae AtienzaThe thyroid gland is located in the neck below the thyroid cartilage. It is butterfly-shaped with right and left lobes connected by an isthmus. The gland produces thyroid hormones T3 and T4 which regulate metabolism and are regulated by TSH from the pituitary gland. The most common thyroid disorders are hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) and hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid). Hyperthyroidism causes excessive thyroid hormone production and symptoms like rapid heartbeat and weight loss, often due to Graves' disease. Hypothyroidism is caused by insufficient hormone production and results in fatigue, weight gain, and intolerance to cold. Both disorders are treated with medication to regulate thyroid hormone levels.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 10
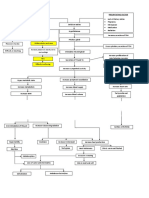
Thyroid Gland
found in the neck, below the thyroid cartilage
The bridge between the two lobes of the thyroid
is the Isthmus
Its a butterfly- shape organ, lobus dexter, right
lobe, lobus sinister, left lobe
Composed of Follicular and Parafollicular cells
Follicular Cells produce the Thyroxine (T4) and
Triiodothyronine(T3)
Parafollicular Cells produce and secrete
Thyrocalcitonin, w/c helps regulate serum
calcium level in the blood in response to
Hypercalcemia and serum Phosphorous
levels by reducing bone resorption
Up to 80% of the T
4
is converted to T
3
by
peripheral organs such as the liver, kidney
and spleen.
T
3
is several times more powerful than T
4
,
which is largely a pro hormone,
four or even ten times more active.
Hormonal output from the thyroid is
regulated by thyroid-stimulating
hormone (TSH)produced by the
anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated
by thyrotropin-releasing hormone(TRH)
produced by the hypothalamus.
The most common problems of the
thyroid gland
Overactive thyroid gland,
Hyperthyroidism
Underactive thyroid gland
Hypothyroidism.
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, or overactive thyroid, is
the overproduction of the thyroid hormones
T
3
and T
4
, and is most commonly caused
by the development of Graves' disease, an
autoimmune disease in which antibodies
are produced which stimulate the thyroid to
secrete excessive quantities of thyroid
hormones.
The disease can result in the formation of
a toxic goiter as a result of thyroid growth
in response to a lack of negative feedback
mechanisms.
Typical symptoms of hyperthyroidism
thyroid goiter
protruding eyes (exopthalmos)
palpitations
excess sweating
diarrhea
weight loss
muscle weakness
unusual sensitivity to heat.
appetite is often increased.
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is the underproduction
of the thyroid hormones T
3
and T
4
.
Autoimmune disorders such
as Hashimoto's thyroiditis, iodine
deficiency or the removal of the
thyroid following surgery to treat severe
hyperthyroidism and/or thyroid cancer,
causes hypothyroidism
Typical symptoms of hypothyroidism
abnormal weight gain
tiredness
baldness
cold intolerance and
bradycardia
Hypothyroidism is treated with hormone
replacement therapy such
levothyroxine,
Psychosocial Assessment of
Hyperthyroidism
-Mood swings
-Decrease attention span
-Manic behavior
Diagnostic Assessment of Hyperthyroidism
-Thyroid Scan-Evaluates the position,
size and functions
-Ultrasonography- To determine its
size, composition of masses and
nodules
-Electrocardiography- Usually shows
tachycardia, atrial fibrillation and changes
in P and T waveforms
Drug Therapy Hyperthyroidism
-Propylthiouracil (PTU)
-Methimazole (Tapazole)
-Carbimazole (Neo-Mercazole)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Thyroid GlandDokument30 SeitenThyroid GlandahmedkomranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clerking TemplateDokument4 SeitenClerking TemplateNur Atiqah Mohd Azli100% (1)
- Endocrine System Pathology 2009Dokument195 SeitenEndocrine System Pathology 2009SofiaemanginteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Endocrine DisordersDokument46 SeitenAssessment and Management of Patients With Endocrine Disordersamal100% (1)
- History and Physical ExaminationDokument17 SeitenHistory and Physical ExaminationNur Fatima SanaaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- History Taking Cheat SheetDokument1 SeiteHistory Taking Cheat SheetLaura ForsythNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic History Taking: Tim Communication Skill FKUBDokument30 SeitenBasic History Taking: Tim Communication Skill FKUBnarulita_94Noch keine Bewertungen
- Presenter-Dr. Tesita SherryDokument109 SeitenPresenter-Dr. Tesita SherryTesitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathology of Thyroid DiseasesDokument5 SeitenPathology of Thyroid DiseasesNur Kamalia KamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacologic TX For Idiopathic Parkinsons: Strategy Class / Drug MOA Side Effects USEDokument2 SeitenPharmacologic TX For Idiopathic Parkinsons: Strategy Class / Drug MOA Side Effects USEnicdeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid DisordersDokument34 SeitenThyroid DisordersAbdulhameed Mohamed100% (1)
- Sacrococcygeal Teratoma (SCT)Dokument5 SeitenSacrococcygeal Teratoma (SCT)IOSRjournalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Toxic GoiterDokument17 SeitenNon-Toxic Goiterabigaille chua100% (1)
- Case Presentation Og HyperthyroidismDokument7 SeitenCase Presentation Og HyperthyroidismMegan Mendoza0% (2)
- Adrenal DisordersDokument29 SeitenAdrenal DisordersSuliman Garalleh100% (1)
- Adrenal DisordersDokument48 SeitenAdrenal DisordersMubeenUrRehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid DisordersDokument21 SeitenThyroid DisordersSuliman GarallehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital HypothyroidismDokument37 SeitenCongenital HypothyroidismAwaluddin SalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperemesis GravidarumDokument5 SeitenHyperemesis GravidarumsalamredNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Family Planning (4400)Dokument27 SeitenReport On Family Planning (4400)Bikram KushaalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hormon GDSDokument23 SeitenHormon GDSBRI KUNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Lower Female Genital Tract InfectionsDokument42 Seiten12 Lower Female Genital Tract InfectionsAwal Sher khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MenorrhagiaDokument3 SeitenMenorrhagiajermie22100% (1)
- SCHIZODokument25 SeitenSCHIZOQuinonez Anna MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bronchial AsthmaDokument54 SeitenBronchial AsthmaSehar162100% (2)
- Testicular CancerDokument48 SeitenTesticular Cancerluckyswiss7776848Noch keine Bewertungen
- Polyhydramnios and Oligohydramnios Clinical Presentation - Physical ExaminationDokument2 SeitenPolyhydramnios and Oligohydramnios Clinical Presentation - Physical ExaminationAhmad FahroziNoch keine Bewertungen
- mhGAP Humanitarian Intervention Guide (mhGAP-HIG) - English VersionDokument68 SeitenmhGAP Humanitarian Intervention Guide (mhGAP-HIG) - English VersionПламен МинчевNoch keine Bewertungen
- DIABETIC COMA - Clinical Features and ManagementDokument54 SeitenDIABETIC COMA - Clinical Features and ManagementRitesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- History TakingDokument51 SeitenHistory TakingJAMES TONNY OKINYINoch keine Bewertungen
- Diseases of The Thyroid Gland PDFDokument72 SeitenDiseases of The Thyroid Gland PDFKay BristolNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Thyroid PDFDokument4 SeitenNew Thyroid PDFCrystal Gayle Nario SabadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catatonia Kaplan PDFDokument3 SeitenCatatonia Kaplan PDFJuan Sebastian LozanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical AppraisalDokument6 SeitenCritical AppraisalRevina AmaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antepartum Haemorrhage: BY: Ms. R. Liangkiuwiliu Assistant Professor, Obg SSNSR, SuDokument44 SeitenAntepartum Haemorrhage: BY: Ms. R. Liangkiuwiliu Assistant Professor, Obg SSNSR, SuLiangkiuwiliuNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAMDokument108 SeitenSAMAlimyon Abilar MontoloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdominal Pain PDFDokument23 SeitenAbdominal Pain PDFSahil DhamijaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothyroidism - Practice Essentials, Background, PathophysiologyDokument17 SeitenHypothyroidism - Practice Essentials, Background, PathophysiologyprobowurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperthyroidism: A Practical Approach To Diagnosis and ManagementDokument70 SeitenHyperthyroidism: A Practical Approach To Diagnosis and ManagementMutiara Manuella TambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheehan's SyndromeDokument12 SeitenSheehan's SyndromePawpaw ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Causes of Mental IllnessDokument4 SeitenCauses of Mental IllnessRima Pigar Goza MeleloaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperthyroidism History TakingDokument11 SeitenHyperthyroidism History TakingmokkailinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pud Case StudyDokument8 SeitenPud Case Studyapi-346620455Noch keine Bewertungen
- Oral Case PresentationDokument6 SeitenOral Case PresentationMD PraxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care of Patient With Cushing Syndrome and PheochromocytomaDokument43 SeitenNursing Care of Patient With Cushing Syndrome and PheochromocytomaMaica LectanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Presentation - GASTRODokument46 SeitenCase Presentation - GASTROalidudeNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Make An Oral Case Presentation To Healthcare ColleaguesDokument5 SeitenHow To Make An Oral Case Presentation To Healthcare ColleaguesYuliana Citra AnggraeniNoch keine Bewertungen
- GP Reg - Asthma and Spirometry 2011Dokument114 SeitenGP Reg - Asthma and Spirometry 2011minerva_stanciuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Endocrine SystemDokument37 SeitenPathophysiology of Endocrine SystemRodriguez Vivanco Kevin DanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multinodular Goitre Case PresentationDokument19 SeitenMultinodular Goitre Case PresentationTamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of Endocrine System: History TakingDokument14 SeitenAssessment of Endocrine System: History TakingNida Naaz100% (2)
- SC2 2015 HyperthyroidismDokument38 SeitenSC2 2015 HyperthyroidismShafern TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Case 1: Language Centre of Malahayati University at 2010Dokument16 SeitenMedical Case 1: Language Centre of Malahayati University at 2010putri1114Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To HematologyDokument61 SeitenIntroduction To HematologyThis is PonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Hepatitis BDokument9 SeitenChronic Hepatitis Bmits98Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothyroidism - Harrison Copy-PasteDokument4 SeitenHypothyroidism - Harrison Copy-PasteJoseph De Joya100% (1)
- Hypothyroidism: Regulation of Thyroid HormoneDokument4 SeitenHypothyroidism: Regulation of Thyroid HormoneAmer Abdulla SachitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Availability & Accessibility of The DrugsDokument1 SeiteAvailability & Accessibility of The DrugsSheena Mae AtienzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Individual Rotation PlanDokument2 SeitenIndividual Rotation PlanSheena Mae AtienzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discharge Management For CholecystojejunostomyDokument1 SeiteDischarge Management For CholecystojejunostomySheena Mae AtienzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Individual Rotation Plan. LEVEL IV. GROUP4Dokument2 SeitenIndividual Rotation Plan. LEVEL IV. GROUP4Sheena Mae AtienzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Conditions Requiring SurgeryDokument3 SeitenBasic Conditions Requiring SurgerySheena Mae AtienzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Programme For SocializationDokument1 SeiteProgramme For SocializationSheena Mae AtienzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TAHBSODokument14 SeitenTAHBSOSheena Mae Atienza100% (1)
- Fanconi AnemiaDokument41 SeitenFanconi AnemiaSheena Mae AtienzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volcanic Eruption.1Dokument31 SeitenVolcanic Eruption.1Sheena Mae AtienzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Desirable Body WeightDokument15 SeitenDesirable Body WeightSheena Mae AtienzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnteralDokument1 SeiteEnteralSheena Mae AtienzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Concept of Economics: Prepared By: Atienza, Sheena Mae M. Basas, Kristine MDokument28 SeitenThe Concept of Economics: Prepared By: Atienza, Sheena Mae M. Basas, Kristine MSheena Mae AtienzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Typical Synovial JointDokument8 SeitenA Typical Synovial JointSheena Mae AtienzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RLE (Instruments)Dokument5 SeitenRLE (Instruments)Sheena Mae AtienzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Substance Abuse OverviewDokument2 SeitenSubstance Abuse OverviewSheena Mae AtienzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2,4-Diaminoanisole and Its Salts: 1.1 Chemical and Physical DataDokument25 Seiten2,4-Diaminoanisole and Its Salts: 1.1 Chemical and Physical DatakhoachiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MethimazoleDokument5 SeitenMethimazoleapi-300595323Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 1Dokument3 SeitenQuiz 1Micah Magallano100% (1)
- Endocrinology InterpretationDokument382 SeitenEndocrinology InterpretationHernanda Adi Purwangga100% (7)
- PdfText - 2022-12-15T172553.484Dokument1 SeitePdfText - 2022-12-15T172553.484Himanshu MaheshwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry of HormoneDokument58 SeitenBiochemistry of HormoneHaamim Sya'bani0% (1)
- Hormones, ClassificationDokument10 SeitenHormones, ClassificationMenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bible 2018Dokument183 SeitenBible 2018monday125Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 16 Test Bank AnswersDokument13 SeitenChapter 16 Test Bank AnswersLauraLaine100% (3)
- Tulajabahvani StotrDokument2 SeitenTulajabahvani StotrHema DhaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine Disorders and PregnancyDokument32 SeitenEndocrine Disorders and PregnancyChristine Marie BudlaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete-Issue Critical PDFDokument92 SeitenComplete-Issue Critical PDFNndaydnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 16 - The Endocrine SystemDokument73 SeitenChapter 16 - The Endocrine SystemAbdullah AlghamdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 Hormones and Hormone Antagonists Complete PDF NotesDokument12 SeitenChapter 10 Hormones and Hormone Antagonists Complete PDF NotesJio InNoch keine Bewertungen
- SK Singh Lab Report 09042018Dokument8 SeitenSK Singh Lab Report 09042018Iasam Groups'sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normal Laboratory ValuesDokument2 SeitenNormal Laboratory ValuesSBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Egg Quality in Fish - What Makes A Good EggDokument30 SeitenEgg Quality in Fish - What Makes A Good EggShahbaz AkhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MineralsDokument3 SeitenMineralsrawnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ana PharynDokument23 SeitenAna PharynJenu SuwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abcde DietDokument18 SeitenAbcde Dietcraig1014Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bruyette, Canine HypothyroidismDokument5 SeitenBruyette, Canine Hypothyroidismlindsaybarbara7552Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elzohry+Exam LabsDokument88 SeitenElzohry+Exam Labsnaira100% (5)
- Chapter 39 Endorcrine and Reproductive SystemDokument20 SeitenChapter 39 Endorcrine and Reproductive SystemgjaenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-5 The Micronutrients-II MineralsDokument12 SeitenUnit-5 The Micronutrients-II MineralsStanley WangchokNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05.11.02 Thyroid and ParathyroidDokument10 Seiten05.11.02 Thyroid and Parathyroidbo gum parkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sharma 2017Dokument6 SeitenSharma 2017asfwegereNoch keine Bewertungen
- FastingDokument21 SeitenFastingtpau6272100% (1)
- Physio Lab 4 Endocrine in PhysioExDokument7 SeitenPhysio Lab 4 Endocrine in PhysioExfadhilfwazazssdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specialized Products From Amino Acids - Part 2Dokument16 SeitenSpecialized Products From Amino Acids - Part 2Leon WarrenNoch keine Bewertungen