Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Preventive Pediatrics
Hochgeladen von
Deena Mcgee0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
65 Ansichten53 Seitenpedia
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenpedia
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
65 Ansichten53 SeitenPreventive Pediatrics
Hochgeladen von
Deena Mcgeepedia
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 53
Preventive Pediatrics
Celia T. Sy, M.D.
Pediatric Pulmonologist
Department of Pediatrics
Fatima Medical Center
Immunization
Vaccinations
Type of vaccine
Route of administration
Immune response
Post- exposure drug prophylaxis
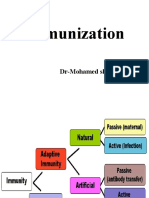
Immunization
Denotes the process of inducing or
providing immunity artificially by
administering an immunologic
substances
Active
Passive
Active Immunization
When it produces the desired beneficial
effects by stimulation of endogenous
antibody production by the patient
Tetanous toxoid
MMR
BCG
Passive Immunization
Administration of preformed human or
animal antibodies to individuals already
exposed or about to be exposed to
certain infectious agents
Tetanus antitoxins
Immune globulins
Vaccination
Denotes the physical act of
administrating any vaccine or toxoids
Immunobiologic Substances
Vaccine - a suspension of live or inactivated
microorganism or fractions thereof
administered to induce immunity and prevent
infectious disease or its sequela
Toxoid modified bacterial toxin that has
been made nontoxic but retains the ability to
stimulate the formation of antitoxins
Antitoxins a solution of antibodies
derived from the serum of animals
immunized with specific antigens
Passive immunization
Diphtheria antitoxin
Tetanus antitoxin
Immune globulin (IG) - a sterile
solution containing antibodies from
human blood. Intended for IM use
for passive immunization
Measles immune globulin
hepatitis b immune globulin
IV IG a product derived from blood
plasma from the donor pools similar to
the IG pool but prepared for IV used
Used in primary antibody-deficiency
disorders
- Kawasaki disease
- ITP
- Hypogammaglobulinemia
Immunologic Constituents
Suspending fluids sterile water, saline
Preservatives, Stabilizers, Antibiotics
used to inhibit or prevent bacterial growth
Stabilize the antigens or antibodies
albumin, phenols, neomycin, mercurial
Adjuvants evoke suboptimal immunologic
response
To enhance immunogenicity
Al hydroxide, Al phosphate
Vaccines & Toxoids
Live vaccines
BCG
MMR
Oral polio
Varicella
Oral typhoid
Killed antigens
Toxoids
DPT
Tetanus
Killed antigens
Inactivated Virus
IPV (inactived polio
virus)
Influenza
Rabies
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B
Killed antigens
Bacterial
polysaccharide
Hib
Route of Administration
Intramuscular (IM)
DPT
IPV (as DPT-IPV-HIB
combination)*
Hep A & B
HiB
Influenza
Pneumococcal
Meningococcal
Typhoid
Subcutaneous (SC)
Measles
Mumps
Rubella
MMR
Varicella
IPV
Pneumococcal
Meningococcal
Route of Administration
Oral
OPV
Typhoid
Intradermal
BCG
Where to inject?
General rules:
For children < 1 year old lateral thigh
For children > 1 year old - deltoid
Buttocks should not be used for active
vaccinations because of the potential
risk of injury to the sciatic nerve
If the buttocks are to used use only
the upper outer quadrant
Fever:
To give or not to give?
Minor febrile illness or malnutrition is
not a contraindication to immunization
Immunization is deferred in the
presence of severe febrile illness
Vomiting:
What to Do?
Regurgitated oral vaccine
If the child vomit or regurgitate within 5
10 mins after giving OPV another dose
should be given at the same visit
If repeated dose is not retained,
re-administered at the next visit
Diarrhea:
Could OPV be given?
Diarrhea should not be considered as a
contraindication for OPV but to ensure
full protection, doses given to children
with diarrhea SHOULD NOT BE
COUNTED as part of the series
Need to give 2 or more vaccines:
How to give?
Multiple vaccinations
Administer each vaccine at a different site
using different needles and syringes
If > 1 vaccine is to be used in a single
limb, use the thigh muscle and given at 1 -
2 inches apart
Interruption of Schedule
What to do?
Interruption with a delay between
doses does not interfere with the final
immunity achieved
No need to start the series again
Contraindications?
Live attenuated vaccines is
contraindicated in:
Pregnant woman
Immunocompromised person leukemia,
lymphoma, malignancy, therapy with
steroids, alkylating agents, antimetabolites
Radiotherapy
Trivia
Which of the following are live
vaccines?
DPT Measles
TOPV Pneumococcal
IPV Meningococcal
BCG Oral Typhoid
Hep B
MMR
Guidelines for Giving Live
vaccines and killed Antigens
2 or more killed antigens may be
administered simultaneously or at any
interval between doses
Example:
DPT and Hep B
DPT and Hib
Hep A and Hep B
Killed and live antigens may be
administered simultaneously or at any
interval between doses
Example:
DPT and OPV
Hep b and MMR
DPT and Measles
DPT and varicella
2 or more live antigens may administered
simultaneously or at 4 week minimum interval
if not given simultaneously
Example:
Measles and varicella
MMR and varicella
** OPV can be administered at any time before,
with or after MMR if indicated
Guidelines for administration
of IG & Vaccines
Simultaneous administration
IG and killed antigen given at the same
time or at any time between doses
Hepatitis B immune globulin and hepatitis B
vaccine
Tetanus antitoxins and anti-tetanus vaccine
IG and live antigen should generally NOT
BE ADMINISTERED simultaneously
GuidelinesIG & Vaccines
Non-simultaneous administration
First Second
IG Killed Ag No interval needed
IG Live Ag dose related
Killed Ag IG No interval needed
Live Ag IG 2 weeks
Interval between IG & Live
Measles Vaccine
IVIG Interval
ITP 400 mg/kg 8 month
ITP 1000 mg/kg 10 months
Kawasaki 11 months
Blood transfusion
Whole blood & packed RBC 6 months
Plasma/platelets 7 months
IntervalIG & live measles
vaccine
IG measles prophylaxis
Normal contact 0.25ml/kg 5 mons
Immunocompromised 0.50ml/kg 6 mons
Trivia
Which of the following vaccines can be
given simultaneously?
Hep B & Measles
BCG & DPT
Oral polio & measles
DPT & MMR
Measles & MMR
DPT & IPV + HiB
Immune Response
Immune response to one live virus
vaccine might be impaired if
administered within 30 days of another
live virus vaccine
Only OPV and MMR can be
administered at anytime before, with or
after each other
Immune Response
Live virus vaccines can interfere with
the response to a tuberculin test
Tuberculin testing can be done either
on the same day that live virus vaccines
are administered or 4 6 weeks later
Special Conditions
Special Considerations
Persons with hemophilia
Increased risk of hepatitis B & hematomas
Assess the patients bleeding risk
Use fine needle & apply pressure to the
site
Special considerations
Altered immunocompetence
Killed or inactivated vaccines can be
administered to all immunocompromised
patients
OPV should not be given to any household
contacts of an immunocompromised
patient
IPV can be given
Special considerations.
Altered immunocompetence
MMR is not contraindicated to close
contacts of immunocompromised persons
MMR vaccine is recommended for all
asymptomatic HIV-infected persons and
should be considered for all symptomatic
HIV-infected persons
Special consideratios
Preterm infants
Regardless of birth weight should be
vaccinated at the same chronological age
and according to the same schedule
Use full recommended dose except BCG
OPV should be deferred until discharge
from the nursery
Special considerations
Pregnancy
Combined tetanus and diphtheria toxoids
ARE THE ONLY vaccine indicated
Vaccines
BCG (Bacille-Calmette-Guerin)
Attenuated bovine strains of tubercle bacilli
Route: intradermal
Dose: 0.05 ml preterm
0.1 ml term
Complications
Abscess
Indolent ulcer
lymphadenopathy
BCG
Normal course
Wheal diappear in 30
mins
Induration after 2-
3 wks
Pustular formation
after 4 6 wks
Full scarification
after 6 12 wks
Accelerated
reaponse 91-
100% correlation
with TB infection
Induration after 2
3 days
Pustular formation
after 5 7 days
Scar after 2 -3 wks
Polio vaccine
OPV live attenuated vaccine
IPV inactive polio virus
Combination vaccine:
DPT + IPV + Hib
DPT
Toxoids of diphtheria & tetanus;
inactivated pertussis component
adsorbed into aluminum salts
Dose: 0.5 ml
Route: IM
Side effect: swelling at injection site
DTaP
Diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis
component
Decrease risk of neuroparalytic
reactions due to component of pertussis
Measles
Live attenuated vaccine
Freeze dried
Dose: 0.5 ml SQ
Side effects: fever between 5
th
-14
th
day after
injection, rashes, arthritis
Prophylaxis: may be given within 72
hours after measles exposure
Measles IG 0.25 ml/kg IM may be within 6
days of exposure
Hepatitis B Vaccine
Infant born to HBs Ag-positive mother
should received:
Hep b Vaccine + Hep B immune globulin
(HBIG) within 12 hours of birth at different
site
Next dose: Hep B at 1-2 months of age
and 3
rd
dose at 6
th
month of age
Schedule: 0, 1, 6
Hepatitis B Vaccine
Infant born to mother whose HBsAg
status is unknown:
Hep B vaccine within 12 hours of birth
Request for mothers HBsAg status if (+)
Infant should received HBIG Asap
(no later than 1 week of age)
Recommended Schedule
BCG
DPT, TOPV, IPV, Hib
Hepatitis B
Measles
At birth or anytime after
birth
2, 4, 6 month of age
0, 1, 6 month of age
0, 1, 3 month of age
(endemic country)
9 month of age
( can be given at 6
month of age)
Schedule.
MMR
Hepatits A
Pneumococcal (IPD
7 valent)
Pneumococcal (23-
valent)
Meningococcal
Typhoid
15 month of age
After 1 year of age
2, 4, 6 months up to
9 years of age
2 years of age
2 years of age
3 years of age
Post-exposure Drug
Prophylaxis
Diphtheria Erythromycin
Pertussis Erythromycin
Cholera Tetracycline
Plasmodia Chloroquine
N. gonorrhea Amoxicillin/Penicillin
Meningococcemia Rifampicin
Sulfisoxazole
Ceftriaxone
Tuberculosis Isoniazid
Case 1
A 3 y/o child was exposed to a person with measles. Past
immunization hx: he had received 1 dose of BCG, 3 doses of
DPT, TOPV & Hepatitis B. If you are the attending physician,
how are you going to manage the patient?
Give measles vaccine if the exposure is within 72 hours
Give measles immunoglobulin if the exposure is more than 72
hours
Give MMR if the exposure is within 72 hours
Give Mesles vaccine and immune globulin at the same time
Observe the patient
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Programmers GuideDokument94 SeitenProgrammers GuideDeena McgeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Miller SAW HandbookDokument76 SeitenMiller SAW HandbookDeena McgeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CT 7201309Dokument29 SeitenCT 7201309Deena McgeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hardening Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5Dokument42 SeitenHardening Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5sudhakarlinux5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Name of The ExperimentDokument3 SeitenName of The ExperimentDeena McgeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cme BookDokument1 SeiteCme BookDeena McgeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leonardo DiCaprioDokument8 SeitenLeonardo DiCaprioDeena Mcgee0% (1)
- Rhel5 Guide I731Dokument200 SeitenRhel5 Guide I731KorbenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Codominance: Some Genes Have Alleles That Are Both Expressed in The Heterozygote IndividualsDokument7 SeitenCodominance: Some Genes Have Alleles That Are Both Expressed in The Heterozygote IndividualsDeena McgeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiologyDokument24 SeitenBiologyDeena McgeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Text DocumentDokument1 SeiteNew Text DocumentDeena McgeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linux Audit Quick Start: SUSE Linux Enterprise 10 SP1Dokument5 SeitenLinux Audit Quick Start: SUSE Linux Enterprise 10 SP1Rahman Racha YpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moments Its Musical Age ExplainDokument2 SeitenMoments Its Musical Age ExplainDeena McgeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case DigestDokument4 SeitenCase DigestDeena McgeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audit sp2Dokument76 SeitenAudit sp2Deena McgeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALT CodesDokument1 SeiteALT CodesElle RalukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Study of MPPT ALGORTHIM DDokument16 SeitenComparative Study of MPPT ALGORTHIM DHalit YahyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Aided Analysis and Design of Multi-Storeyed BuildingsDokument66 SeitenComputer Aided Analysis and Design of Multi-Storeyed BuildingsPeter Saxena100% (1)
- Ann Other CV SummaryDokument10 SeitenAnn Other CV SummaryDr. TaubeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSUF Campus MapDokument1 SeiteCSUF Campus MapDeena McgeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- GD&TDokument70 SeitenGD&TKarthi KeyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- R IntroDokument105 SeitenR IntroManoj C PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Check-in for your Emirates flight with e-ticket barcode or numberDokument1 SeiteCheck-in for your Emirates flight with e-ticket barcode or numberDeena Mcgee33% (3)
- Guide To US Plastic AssemblyDokument118 SeitenGuide To US Plastic AssemblyrenebbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sri Lanka Airlines E-TicketDokument2 SeitenSri Lanka Airlines E-TicketDeena Mcgee50% (6)
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene: WWW - Ampaplastics.co - Za +27 11 398 8000Dokument2 SeitenAcrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene: WWW - Ampaplastics.co - Za +27 11 398 8000Deena McgeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smoking SpeechDokument5 SeitenSmoking SpeechDeena McgeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Media Shared Content Docs Factsheet2012 Jan2011 Dec20111331893943Dokument2 SeitenMedia Shared Content Docs Factsheet2012 Jan2011 Dec20111331893943Deena McgeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adv Tolerance 57 IndDokument5 SeitenAdv Tolerance 57 IndDeena McgeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lexan® 3412R Resin: Property Nominal Values Test MethodDokument1 SeiteLexan® 3412R Resin: Property Nominal Values Test MethodDeena McgeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Why Do We Fall IllDokument42 SeitenWhy Do We Fall IllExabyteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Communicable DiseasesDokument477 SeitenConcept Communicable DiseasesrimeoznekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brief History of ImmunologyDokument5 SeitenBrief History of Immunologyella SyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NOTES ON CHAP5 Food and HealthDokument4 SeitenNOTES ON CHAP5 Food and HealthSalvator XNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communicable Disease NursingDokument50 SeitenCommunicable Disease NursingChernobyle Tolentino BattadNoch keine Bewertungen
- WHO 2019 NCoV Vaccines SAGE Prioritization 2021.1 EngDokument23 SeitenWHO 2019 NCoV Vaccines SAGE Prioritization 2021.1 EngNeneng Aini KaruniawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunology & Immunotechnology - 1Dokument40 SeitenImmunology & Immunotechnology - 1jihovajayraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Health and Hygiene ChapterDokument10 SeitenPhysical Health and Hygiene ChapterBinu Kumar SNoch keine Bewertungen
- ImmunisationDokument42 SeitenImmunisationDr. Ajeta GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management and Discharge PlanDokument2 SeitenManagement and Discharge PlanZenny Marie B Dureza0% (1)
- All Degree Programs Taught in EnglishDokument14 SeitenAll Degree Programs Taught in EnglishCrowley AshtonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Community Health Nursing 2Dokument140 SeitenCommunity Health Nursing 2Bikash KandelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med-2017-Long-a025577 PDFDokument17 SeitenCold Spring Harb Perspect Med-2017-Long-a025577 PDFAurelia WetondieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tool's Inoculum CovidDokument5 SeitenTool's Inoculum CovidFritz FehlingNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ Adaptive and Innate Immunity SET-ADokument4 SeitenMCQ Adaptive and Innate Immunity SET-AParvathy Sarma100% (1)
- The Humoral Immune Response To BCG VaccinationDokument18 SeitenThe Humoral Immune Response To BCG VaccinationMario ChristopherNoch keine Bewertungen
- West Philippine SeaDokument4 SeitenWest Philippine SeaFrancheskalane ValenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alwadi International School Grade 9 Biology 10. Diseases and Immunity NotesDokument35 SeitenAlwadi International School Grade 9 Biology 10. Diseases and Immunity NotesMohammed HelmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antigen & Antibody: Structure, Function & Immune ResponseDokument48 SeitenAntigen & Antibody: Structure, Function & Immune Responsebook keedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ImmunizationDokument16 SeitenImmunizationShafie ElmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundations of Immunology in Ayurvedic Classics: Ram H SinghDokument12 SeitenFoundations of Immunology in Ayurvedic Classics: Ram H SinghgaurnityanandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dinthill Technical Biology SyllabusDokument5 SeitenDinthill Technical Biology SyllabussrtwgwfwwgwNoch keine Bewertungen
- DHI Course Papers and Exam GuidelinesDokument64 SeitenDHI Course Papers and Exam GuidelinesAmar ChandNoch keine Bewertungen
- 805Dokument27 Seiten805Amit GhadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of A Cholera EpidemicDokument231 SeitenManagement of A Cholera EpidemicNyi WynnNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIMS Doctor 0820 ID PDFDokument51 SeitenMIMS Doctor 0820 ID PDFGATOT WIDYATMO PRINGGODIGDONoch keine Bewertungen
- Determinants of HealthDokument29 SeitenDeterminants of HealthMayom Mabuong92% (12)
- 10 Anti InfectivesDokument29 Seiten10 Anti InfectivesFrançoise BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Innate ImmunityDokument29 SeitenInnate ImmunityAsad MirzaNoch keine Bewertungen