Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Industrial Training at NTPC: Thermal Power Generation & Maintenance Division
Hochgeladen von
Charu MathurOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Industrial Training at NTPC: Thermal Power Generation & Maintenance Division
Hochgeladen von
Charu MathurCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
INDUSTRIAL TRAINING AT
NTPC
THERMAL POWER GENERATION &
MAINTENANCE DIVISION
BADARPUR POWER PLANT
NATIONAL THERMAL POWER
CORPORATION
ABOUT NTPC
NTPC, the largest power Company in India, was setup in 1975 to
accelerate power development in the country.
NTPC has installed capacity of 29,394 MW.
15 coal based power stations (23,395 MW)
7 gas based power stations (3,955 MW)
4 power stations in Joint Ventures (1,794 MW).
The company has power generating facilities in all major regions of
the country.
NTPC, was setup in 1975 worlds largest .
In Forbes list of Worlds 2000 Largest Companies for the year
2007, NTPC occupies 411th place.
NTPC - Vision and Mission
Vision
A world class integrated power major, powering
Indias growth, with increasing global presence
Mission
Develop and provide reliable power, related products
and services at competitive prices, integrating multiple
energy sources with innovative and eco-friendly
technologies and contribute to society
OVERVIEW
TYPE OF
POWER
STATION
NUMBER CAPACITY
(MW)
COAL
BASED
15 23395
GAS
BASED
7 3955
JOINT
VENTURE
4 1794
POWER GENERATION
CONTRIBUTION
INSTALLED CAPACITY &
GENRATION
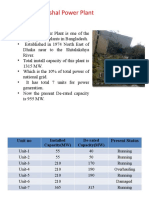
NTPC BADARPUR
Location: Mathura Road,
Badarpur, New Delhi
Status: Active
Commission date:
1973
Operator(s):
NTPC
Coal Source : Jharia Coal
Fields
Water Source : Agra
Canal
Primary fuel: Coal-fired
Generation units: 5
Installed capacity: 705
MW
BASIC PRINCIPLE
Three main units
of a thermal power
plant:
Steam Generator
or Boiler
Steam Turbine
Electric Generator
COAL TO ELECTRICITY
THERMAL POWER PLANT
.
A Thermal Power Station comprises all of the equipment and
a subsystem required to produce electricity by using a steam
generating boiler fired with fossil fuels or befouls to drive an
electrical generator.
A generating station which converts heat energy of coal
combustion into electrical energy is known as a steam power
station.
Steam is produced in the boiler by utilizing the heat of coal
combustion. The steam is then expanded in the steam turbine
and is condensed in a condenser to be fed into the boiler
again. The steam turbine drives the alternator which converts
mechanical energy of the turbine into electrical energy.
THERMAL POWER GENERATION
PROCESS
MAIN COMPONENTS
Steam generating equipment
Condenser
Prime mover
Cooling towers
Electrical equipment
COMPLETE PLANT
STATION
ELECTRIC MAINTENANCE
DIVISION-II
The training in this division was divided as
follows:
Generator and Auxiliaries
Transformer
Switchgear
GENERATOR
The transformation of mechanical energy into
electrical energy is carried out by the
Generator.
The A.C. Generator or alternator is based
upon the principle of electromagnetic induction
and consists generally of a stationary part
called stator and a rotating part called rotor.
When the rotor is rotated, the lines of magnetic
flux (viz magnetic field) cut through the stator
windings. This induces an electromagnetic
force (e.m.f.) in the stator windings.
GENERATOR COMPONENTS
ROTOR: The rotor(non-stationary part) consists of
coils(field windings) wound into slots cut in its
cylindrical iron surface. These windings are
arranged in pole pairs to form the magnetic field
which produces the flux. The rotor shaft is coupled
to a steam turbine, and rotates inside the stator
core.
STATOR: The stator(stationary part) consists of a
cylindrical steel frame, inside which is a cylindrical
iron core made of thin insulated laminations
mounted on a support system. The iron core has
equally spaced axial slots on its inside diameter,
and wound within the core slots is a stator
winding.
GENERATOR COOLING
SYSTEM
Rotor Cooling System: The rotor is cooled by
means of gap pick-up cooling, wherein the
hydrogen gas in the air gap is sucked through
the scoops on the rotor wedges and is directed
to flow along the sides of the rotor coil, to the
bottom of the slot where it takes a turn and
comes out on the other side of the rotor coil to
the hot zone of the rotor. The rotation of the
rotor assists a uniform gas flow which cools
the rotor.
Hydrogen Cooling System: Hydrogen is used as a cooling
medium in large capacity generator in view of its high heat
carrying capacity and low density.
The system is capable of performing the following functions:
Filling in and purging of hydrogen safely without bringing in
contact with air.
Maintaining the gas pressure inside the machine at the desired
value at all times.
Providing indication to the operator about the condition of the
gas inside the machine i.e. its pressure, temperature and
purity.
Continuous circulation of gas inside the machine through a
drier in order to remove any water vapor that may be present in
it.
Indication of liquid level in the generator and alarm in case of
high level.
Stator Cooling System: The stator winding is
cooled in by circulating demineralised water
(DM water) through hollow conductors. The
cooling water used for cooling stator winding
calls for the use of very high quality of cooling
water. For this purpose DM water of proper
specific resistance is selected. The system is
designed to maintain a constant rate of cooling
water flow to the stator winding at a nominal
inlet water temperature of 40C.
SWITCHGEAR
Switchgear is an electrical functional switch
used for starting any drive and provide
protection to the drive during on load
condition. It makes or breaks an electrical
circuit.
Classification of switchgear:
LT SWITCHGEAR
HT SWITCHGEAR
LT SWITCHGEAR
Operating voltage : 415 V
It is classified into:
Main Switch
Fuses
Contractors
Overload Relay
Air Circuit Breakers
HT SWITCHGEAR
Operating Voltage: 6.6 kV
It is classified into:
Minimum Oil Circuit Breaker
Air Circuit Breaker
SF6 Circuit Breaker
Vacuum Circuit Breaker
CONCLUSIONS
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Sullivan's Interpersonal TheoryDokument27 SeitenSullivan's Interpersonal TheoryJezalen GonestoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procedure Manual - IMS: Locomotive Workshop, Northern Railway, LucknowDokument8 SeitenProcedure Manual - IMS: Locomotive Workshop, Northern Railway, LucknowMarjorie Dulay Dumol80% (5)
- Full Summer Training Report On Power PlantDokument27 SeitenFull Summer Training Report On Power PlantAnurag Chand60% (5)
- Rajiv Gandhi Thermal Power Plant Training Report 2018Dokument21 SeitenRajiv Gandhi Thermal Power Plant Training Report 2018DeltaKill 1120% (1)
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationVon EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- BHELDokument38 SeitenBHELSharath Chandra100% (1)
- Aditya NTPCMMNDokument53 SeitenAditya NTPCMMNaditya34Noch keine Bewertungen
- NFL ProjectDokument35 SeitenNFL ProjectHomi_nathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Badarpur Thermal Power StationDokument23 SeitenBadarpur Thermal Power StationBhagyashree PachisiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NTPC Summer Training ReportDokument33 SeitenNTPC Summer Training Reportshivani chhabra83% (23)
- NTPC Training PresentationDokument26 SeitenNTPC Training Presentationapi-19621388100% (1)
- EEN - 499 Training SeminarDokument18 SeitenEEN - 499 Training SeminarSonu PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Power Plant IntroductionDokument51 SeitenThermal Power Plant IntroductiondheerumgiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lovely Professional University: Thermal Power PlantDokument26 SeitenLovely Professional University: Thermal Power PlantShivam GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summer Training Report NTPCDokument45 SeitenSummer Training Report NTPCChetan MeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final DcacDokument4 SeitenFinal DcacPEE JAYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Act.3-9 - Florida, Mark ChristianDokument26 SeitenAct.3-9 - Florida, Mark ChristianJOVELYN TACADINONoch keine Bewertungen
- Internship ReportDokument29 SeitenInternship Reportfarazahmad759Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rishu NewDokument37 SeitenRishu NewAbhay AswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- NTPC Kayamkulam Training ReportDokument18 SeitenNTPC Kayamkulam Training ReportAdam Weiss67% (3)
- NTPC BoilerDokument57 SeitenNTPC BoilerSami ZamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power PlantDokument27 SeitenPower PlantaloknegiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training Report Ktps FinalDokument45 SeitenTraining Report Ktps FinalVishal Singh Rahangdale75% (4)
- Training Report NTPCDokument16 SeitenTraining Report NTPCRajat ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presented By: NAVNEET KUMAR ME4 Year Sec B Roll No. 1516140126Dokument18 SeitenPresented By: NAVNEET KUMAR ME4 Year Sec B Roll No. 1516140126Anonymous 6aZ9MqlNoch keine Bewertungen
- NTPC Anta Training ReportDokument33 SeitenNTPC Anta Training Reportpradeep meenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Plant EngineeringDokument25 SeitenPower Plant EngineeringlitonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial SayariDokument14 SeitenIndustrial SayariSayari RoychoudhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generator and AlternatorDokument8 SeitenGenerator and Alternatorvirgilio mercadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water HarvestingDokument44 SeitenWater HarvestingTanmay KhuranaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sarni Power PlantDokument59 SeitenSarni Power Plantdev810995Noch keine Bewertungen
- PRESENTATION ON SUMMER INTERNSHIP NikhilDokument56 SeitenPRESENTATION ON SUMMER INTERNSHIP NikhilshayarigurunitinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Power Plant PDFDokument118 SeitenThermal Power Plant PDFdance77% (22)
- Thermal Plant Report MechatronicsDokument50 SeitenThermal Plant Report Mechatronicsहिमाँशु पालNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Work - Excitation SystemDokument58 SeitenProject Work - Excitation SystemKaranki DineshNoch keine Bewertungen
- NTPC Badarpur PPT 2012Dokument33 SeitenNTPC Badarpur PPT 2012hemantparjapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Plant Colour)Dokument44 SeitenPower Plant Colour)Er Anoop GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summer Training Report DLW VaranasiDokument84 SeitenSummer Training Report DLW VaranasiHemant MeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vocational Training (MOHIT)Dokument11 SeitenVocational Training (MOHIT)R SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BtpsDokument12 SeitenBtpschanchal2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vocational Training (SONU)Dokument11 SeitenVocational Training (SONU)R SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diesel GeneratorDokument21 SeitenDiesel GeneratoreiferjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sri Venkateswara Engineering College: SUYAPET, NALGONDA (DIST) - 508213Dokument35 SeitenSri Venkateswara Engineering College: SUYAPET, NALGONDA (DIST) - 508213Hitesh PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- NTPC Plant Dadri (2003) PlainDokument28 SeitenNTPC Plant Dadri (2003) PlainpalanilNoch keine Bewertungen
- N.T.P.C Summer Training Project Report: Submitted By: Neha Singh O4313503609 MAE IgitDokument91 SeitenN.T.P.C Summer Training Project Report: Submitted By: Neha Singh O4313503609 MAE IgitNeha SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- NTPCDokument25 SeitenNTPCPrakhar Rai TyagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CEB Trainig Report 1 - Progress Report - 1Dokument19 SeitenCEB Trainig Report 1 - Progress Report - 1Buddhika GonagalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ghora SalDokument25 SeitenGhora SalMehedi HimelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sahil Sharma (01625511115) 3rd Yr (NTPC PPT)Dokument23 SeitenSahil Sharma (01625511115) 3rd Yr (NTPC PPT)smriti sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Power Plant: " " NTPC (Dadri)Dokument17 SeitenThermal Power Plant: " " NTPC (Dadri)Kulvinder SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Training Report: Report On "Generation of Thermal Power" AT NTPC DadriDokument19 SeitenIndustrial Training Report: Report On "Generation of Thermal Power" AT NTPC DadriayushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Plant EngDokument93 SeitenPower Plant Engsenthilkumarece100% (1)
- Prepared By: Shubhra Dhyani Btech (EEE) III Year 0919221054Dokument28 SeitenPrepared By: Shubhra Dhyani Btech (EEE) III Year 0919221054Prashant KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Polygeneration Process Concept for Hybrid Solar and Biomass Power Plant: Simulation, Modelling, and OptimizationVon EverandA Polygeneration Process Concept for Hybrid Solar and Biomass Power Plant: Simulation, Modelling, and OptimizationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlVon EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Integration of Large Scale Wind Energy with Electrical Power Systems in ChinaVon EverandIntegration of Large Scale Wind Energy with Electrical Power Systems in ChinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetVon EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asm RevDokument2 SeitenAsm RevgunbrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM - Global System For Mobile Communication: Debby Nahl Fall 2004Dokument26 SeitenGSM - Global System For Mobile Communication: Debby Nahl Fall 2004Charu MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doordarshan Project ReportDokument2 SeitenDoordarshan Project ReportCharu MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM and 3G Security: Emmanuel GadaixDokument72 SeitenGSM and 3G Security: Emmanuel GadaixCharu MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global System For Mobile Communication: by Charu Mathur 090320Dokument25 SeitenGlobal System For Mobile Communication: by Charu Mathur 090320Charu MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- DTMF ReportDokument76 SeitenDTMF ReportRishavNoch keine Bewertungen
- AbstractDokument60 SeitenAbstractCharu MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doordarshan Project ReportDokument2 SeitenDoordarshan Project ReportCharu MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day 4 Wan Fundamentals, Frame Relay & NatDokument43 SeitenDay 4 Wan Fundamentals, Frame Relay & NatCharu MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day 5 - Switching and WirelessDokument131 SeitenDay 5 - Switching and WirelessCharu MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data FundamentalsDokument128 SeitenData FundamentalsCharu MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rip, Eigrp, Ospf and AclDokument105 SeitenRip, Eigrp, Ospf and AclCharu Mathur0% (1)
- Cellular Fdma Bandwidth Improved Mobile Telephone ServiceDokument1 SeiteCellular Fdma Bandwidth Improved Mobile Telephone ServiceCharu MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day 6 - Ipv6, VPNDokument33 SeitenDay 6 - Ipv6, VPNCharu MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Repote FileDokument42 SeitenRepote FileCharu MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- MacDokument22 SeitenMacCharu MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Line Follower Tutorial v1.1Dokument34 SeitenLine Follower Tutorial v1.1zanluphzahNoch keine Bewertungen
- ImsDokument36 SeitenImsCharu MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satellites For BeginnersDokument26 SeitenSatellites For BeginnersOctavio GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SemiconductorDokument64 SeitenSemiconductorCharu MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThreadsDokument42 SeitenThreadsCharu MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- AT89S52 Hardware-Software ManualDokument39 SeitenAT89S52 Hardware-Software ManualugocirriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doordarshan Project ReportDokument2 SeitenDoordarshan Project ReportCharu MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rip, Eigrp, Ospf and AclDokument105 SeitenRip, Eigrp, Ospf and AclCharu Mathur0% (1)
- Kübra Şendoğan CVDokument5 SeitenKübra Şendoğan CVKübra ŞendoğanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 4 - Energy Flow and Food WebDokument4 SeitenActivity 4 - Energy Flow and Food WebMohamidin MamalapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Horizon Public School, Airoli: Grade X: English: Poem: The Ball Poem (FF)Dokument42 SeitenNew Horizon Public School, Airoli: Grade X: English: Poem: The Ball Poem (FF)stan.isgod99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jmac TempDokument5 SeitenJmac TempDan GerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instruction Manual Il-Obct-R1: Slip-Over Current Transformer ObctDokument2 SeitenInstruction Manual Il-Obct-R1: Slip-Over Current Transformer Obctبوحميدة كمالNoch keine Bewertungen
- PresentationDokument6 SeitenPresentationVruchali ThakareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speaking Quý 1 2024Dokument43 SeitenSpeaking Quý 1 2024Khang HoàngNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZEROPAY WhitepaperDokument15 SeitenZEROPAY WhitepaperIlham NurrohimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Th-Sunday Magazine 6 - 2Dokument8 SeitenTh-Sunday Magazine 6 - 2NianotinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Report 2022 2Dokument48 SeitenAnnual Report 2022 2Dejan ReljinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes 3 Mineral Dressing Notes by Prof. SBS Tekam PDFDokument3 SeitenNotes 3 Mineral Dressing Notes by Prof. SBS Tekam PDFNikhil SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- JSSC JDLCCE 2021 (Civil Engineering) Official Pape 230615 233342Dokument39 SeitenJSSC JDLCCE 2021 (Civil Engineering) Official Pape 230615 233342Bhuban KumbhakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carpentry NC Ii: Daniel David L. TalaveraDokument5 SeitenCarpentry NC Ii: Daniel David L. TalaveraKhael Angelo Zheus JaclaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MICRF230Dokument20 SeitenMICRF230Amador Garcia IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- TVL-SMAW 12 - Week 4 - Lesson 1 - Concept of Welding Codes and StandardsDokument9 SeitenTVL-SMAW 12 - Week 4 - Lesson 1 - Concept of Welding Codes and StandardsNelPalalonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tablet Time - Student GuideDokument5 SeitenTablet Time - Student GuideAyesha BaigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development and Growth of Teeth: Dr. Madhusudhan ReddyDokument48 SeitenDevelopment and Growth of Teeth: Dr. Madhusudhan ReddysiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Splices LAS 3rd Quarter Week 1Dokument6 SeitenSplices LAS 3rd Quarter Week 1Winnielyn Quarteros BarreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Overview of Marketing - Week 1Dokument7 SeitenAn Overview of Marketing - Week 1Jowjie TVNoch keine Bewertungen
- MVC Training Course Prerequisite: WWW - Focustech.InDokument2 SeitenMVC Training Course Prerequisite: WWW - Focustech.InLakshman Samanth ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hamza Akbar: 0308-8616996 House No#531A-5 O/S Dehli Gate MultanDokument3 SeitenHamza Akbar: 0308-8616996 House No#531A-5 O/S Dehli Gate MultanTalalNoch keine Bewertungen
- GMDSSDokument1 SeiteGMDSSRahul rajeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classroom Activty Rubrics Classroom Activty Rubrics: Total TotalDokument1 SeiteClassroom Activty Rubrics Classroom Activty Rubrics: Total TotalMay Almerez- WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Life Cycle of Brent FieldDokument21 SeitenThe Life Cycle of Brent FieldMalayan AjumovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pep 2Dokument54 SeitenPep 2vasubandi8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Claudia Maienborn, Semantics, 381Dokument34 SeitenClaudia Maienborn, Semantics, 381robert guimaraesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Btech CertificatesDokument6 SeitenBtech CertificatesSuresh VadlamudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alexander Fraser TytlerDokument4 SeitenAlexander Fraser Tytlersbr9guyNoch keine Bewertungen