Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Biliary Pathology
Hochgeladen von
Eva Hadaniah0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
62 Ansichten39 SeitenThe document discusses various biliary pathologies including acute cholecystitis, cholangitis, and recurrent pyogenic cholangitis. It covers clinical assessment of patients including history, symptoms, and diagnostic imaging. Treatment options are explained such as cholecystostomy, percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage, ERCP, and definitive surgical management. Close monitoring of patients is emphasized along with administering appropriate antibiotics and timing of biliary decompression.
Originalbeschreibung:
kesehatan
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe document discusses various biliary pathologies including acute cholecystitis, cholangitis, and recurrent pyogenic cholangitis. It covers clinical assessment of patients including history, symptoms, and diagnostic imaging. Treatment options are explained such as cholecystostomy, percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage, ERCP, and definitive surgical management. Close monitoring of patients is emphasized along with administering appropriate antibiotics and timing of biliary decompression.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
62 Ansichten39 SeitenBiliary Pathology
Hochgeladen von
Eva HadaniahThe document discusses various biliary pathologies including acute cholecystitis, cholangitis, and recurrent pyogenic cholangitis. It covers clinical assessment of patients including history, symptoms, and diagnostic imaging. Treatment options are explained such as cholecystostomy, percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage, ERCP, and definitive surgical management. Close monitoring of patients is emphasized along with administering appropriate antibiotics and timing of biliary decompression.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 39
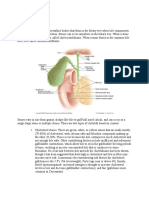
Liver
Gallbladder Biliary tree
Acute cholecystitis
Empyema of gallbladder
Mucoceal of gallbladder
Cholangitis
RPC
Pancreatitis
Biliary Patholgy
History and Examination
Previous biliary surgery
Previous history of biliary pathology
Epigastic / RUQ pain
Duration of pain
Associate symptoms / signs
E.g. Tea color urine, jaundice, stool color
Vital signs
Pulse, resp rate, blood pressure, temperature
Toxic or not ??
X rays
Abdominal supine x ray
Gallstone
Aerobilia
CXR --- right side pleural effusion
Blood test
WCC, LFT, amylase
ECG
Aerobilia
Acute cholecystitis
Acute cholecystitis
Blockage of cystic duct
Tissue oedema . Ischaemia infection
Ultrasound abdomen
Thickened gallbladder wall
Sonographic murphys sign
Pericholecystic fluid
Gallstone
Conservative Vs Early Lap +/- open
cholecystectomy Vs Cholecystostomy
Medical / GA risk of the patient
Acute Cholecystitis
Ultrasound abdomen
Thickened gallbladder wall
Pericholecystic Fluid
Sonographic murphy sign
Also look at:
Free fluid
CBD size / CBD stone
Gallstones
Acute Cholecystitis
Early Vs Delay Cholecystectomy
Medical risk too high for GA operation
Precutaneous Cholecystostomy
Decompress the gallbladder
Drain infected bile / pus
Still require antibiotic
Precutaneous Transhepatic Cholecystostomy
Cholecystostomy
Decompress the gallbladder
Observe for improvement
Continue deterioration
? Perforated gallbladder urgent operation
Tube blocked
Drain content and amount
Bile production approx 500mls per day
Mucous only blocked cystic duct
Lots of bile (500mls or above) CBD stone
Check cholecystogram
Tube position
Position of stone in gallbladder (cystic duct still obstructed ?)
Cholangiogram (any CBD stone drop stone)
Definitive Rx plan
Lap cholecystectomy
Conservative Rx / Removal of tube
Cholecystogram
Cholangitis
Cholangitis
Cholangitis
Fever
RUQ pain
Jaundice
+/- Confusion
Biliary Decompression
Need to check clotting profile
Vit K IV 10mg daily
Antibiotics
Definitive Mx
Aim to remove causative
factors
Assess patient clinical status
Vital parameters
Resuscitation
Biliary decompression
Ultra-urgent Vs urgent/early
Charcots triad
Biliary decompression
ERCP
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatogram
PTBD
Percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage
ECBD
Exploration of common bile duct
ERCP
Internal stent
ERCP not suitable
ERCP with previous B1 gastrectomy
ERCP with previous B2 gastrectomy
Definitely higher risk of perforation
Cholangitis
What if ERCP failed ??
Anatomical problem
Technical difficulties
Patient condition poor
Respiratory problem
Severe sepsis / MOF
External PTBD
Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage
External PTBD Right side system
Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage
Under LA, interventional radiological procedure
Risks
Contrast allergies, Local anaesthetic agents allergies
Liver laceration, bleeding, traumatic tapping
NOT suitable in patient with marked ascites
Tube complications
Kinking, blockage, dislodgement
Patient usually spike high fever after procedure
Need injection of contrast into biliary tree ---
bacteraemia
External PTBD
Right or left system ?
Usually communicable except in case of tumour
Usually external PTBD at initial stage
Short procedure time, less manipulation
Aim is to decompress the biliary system
Internal external PTBD
Aim to direct bile into duodenum
Need better cholangiogram first (therefore wait till 1 wk after
inflammation settle and edema subside)
Lost of fluid, electrolytes
Able to disconnect the bed side bag
Allow future ERCP (two hand technique) if initial ERCP
failed due to difficult cannulation
Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage
eksternal PTBD
Sistem kanan atau kiri?
Biasanya menular kecuali dalam kasus
tumor
PTBD Biasanya eksternal pada tahap
awal
Waktu prosedur yang singkat, kurang
manipulasi
Tujuannya adalah untuk dekompresi
sistem bilier
PTBD eksternal - internal
Bertujuan untuk empedu langsung ke usus
dua belas jari
Perlu cholangiogram lebih baik pertama
(karena menunggu sampai 1 minggu
setelah peradangan menetap dan edema
mereda)
Kehilangan cairan, elektrolit
Mampu melepas tas samping tempat tidur
Biarkan ERCP masa depan (dua teknik
hand) jika ERCP awal gagal karena
kanulasi sulit
Internal external PTBD
Internal-external PTBD
ERCP two hand technique
Internal external PTBD
ERCP
Monitor patient progress
Vital signs
Clinical signs
Drainage amount and content
Suspect blockage revision ?
Definitive Management Plan
Surgery
Trans PTBD dilatation and removal of CBD
stone
Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage
Remember to use correct antibiotic
Send for
Cholangitis can be quickly lethal especially in elderly
Need accurate clinical assessment and appropriate treatment
Timing of biliary decompression is crucial
Recurrent Pyogenic Cholangitis
L
R
ERCP of a case of RPC
Stones
RPC
Appropriate antibiotic
According to previous bile culture
Depends on the disease distribution
Peripheral and / or Central
Decompression of biliary system
Definitive Treatment
Exploration of common bile duct +/- drainage
procedure
Choledochoduodenostomy
Choledochojejunostomy
Liver segmentectomy
RPC
Before definitive procedure
Need to correctly assess
Biliary drainage and function of the liver
Accurate assessment of the distribution of the
disease
CT abdomen
EHIDA scan
RPC Right Lobe CT
RPC Left lobe
RPC
Definitive treatments Vs conservative Plan
Need to BALANCE the risk of OT and the
problems of disease process
Disease process
Recurrent attack
Liver abscess formation
Cholangiocarcinoma
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- B MJ AppendicitisDokument6 SeitenB MJ AppendicitisXavier QuinteroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Angiomyolipoma of The Kidney - WWW - Urology-TextbookDokument4 SeitenAngiomyolipoma of The Kidney - WWW - Urology-TextbookEva HadaniahNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- HerbalifeDokument27 SeitenHerbalifeEva HadaniahNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Cardiac ValvesDokument9 SeitenCardiac ValvesEva HadaniahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Adult Intussusception: A Radiological Approach: Case ReportDokument4 SeitenAdult Intussusception: A Radiological Approach: Case ReportEva HadaniahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Cue and Clue PL Idx PDX PTX Pmo&EdDokument3 SeitenCue and Clue PL Idx PDX PTX Pmo&EdIka AyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Operating Room Nursing: Vergel G. Leonardo Rn. ManDokument72 SeitenOperating Room Nursing: Vergel G. Leonardo Rn. ManRalph Lorenz Avila AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Case PresentationDokument22 SeitenCase PresentationBharathbushan V MandiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Cholangiography (T Tube)Dokument1 SeiteCholangiography (T Tube)jojolilimomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Soal Ujian Bedah Digestif Dr. Errawan RDokument4 SeitenSoal Ujian Bedah Digestif Dr. Errawan RZulfikar ChaeruddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cholecystitis Repaired)Dokument38 SeitenCholecystitis Repaired)Keicy DazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Cholecystectomy PPT FixDokument16 SeitenCholecystectomy PPT Fixmutmainnah_kamil100% (1)
- Open Cholecystectomy: By: Santoyo, Sarah Jane R. BSN 3-B Group 6-Operating RoomDokument6 SeitenOpen Cholecystectomy: By: Santoyo, Sarah Jane R. BSN 3-B Group 6-Operating RoomJullie Anne SantoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- CholelithiasisDokument6 SeitenCholelithiasisLara GatbontonNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Tokyo Guidelines 2018Dokument115 SeitenTokyo Guidelines 2018Alik Razi100% (1)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Assessing Abdominal Pain in Adults A Rational Cost Effective and Evidence-Based StrategyDokument20 SeitenAssessing Abdominal Pain in Adults A Rational Cost Effective and Evidence-Based StrategyaicitelleticiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cholecystitis PresentationDokument12 SeitenCholecystitis PresentationShivangi KulbhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- SURGERY MedicalDokument15 SeitenSURGERY MedicalSNoch keine Bewertungen
- RADIO Liver and GallbladderDokument6 SeitenRADIO Liver and GallbladderJeffrey RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legend: Cholecystitis NCLEX Questions: GreenDokument19 SeitenLegend: Cholecystitis NCLEX Questions: GreenSheril100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Safe Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy An Illustrated AtlasDokument171 SeitenSafe Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy An Illustrated AtlasText OK100% (2)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Cholelithiasis: Introduction: General Illness InformationDokument9 SeitenCholelithiasis: Introduction: General Illness InformationJhangot Abad GabucoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master The Ward Surgery (PreBook Version) PDFDokument80 SeitenMaster The Ward Surgery (PreBook Version) PDFWalpad100% (4)
- July 2019 - Glory Group (Classified)Dokument361 SeitenJuly 2019 - Glory Group (Classified)Ido EgaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam MCQs ID 5 SemesterDokument38 SeitenExam MCQs ID 5 SemesterMani MozhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute PancreatitisDokument8 SeitenAcute PancreatitisAthan AntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methodist Hospital of Southern California, Arcadia, Los Angeles CountyDokument6 SeitenMethodist Hospital of Southern California, Arcadia, Los Angeles CountySouthern California Public RadioNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Obstructive JaundiceDokument13 SeitenObstructive JaundiceJeevan VijayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cholecystitis: A Case Presentation of Group 1&2Dokument73 SeitenCholecystitis: A Case Presentation of Group 1&2MARIA STEPHANY DELA CRUZ100% (1)
- Acute Calculous Cholecystitis Strasberg 2008 NEJMDokument8 SeitenAcute Calculous Cholecystitis Strasberg 2008 NEJMFrancisco Castro100% (1)
- Causes of Abdominal Pain in AdultsDokument41 SeitenCauses of Abdominal Pain in AdultsAmjaSaud100% (1)
- Acute Cholecystitis:: Etiological TypesDokument5 SeitenAcute Cholecystitis:: Etiological Typesvivek yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 A PDFDokument51 Seiten1 A PDFMysheb SSNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Surgery KNMU Acute Cholecystitis LectureDokument4 SeitenGeneral Surgery KNMU Acute Cholecystitis LectureslyfoxkittyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medicine Colloquium Exam - 2015 ADokument41 SeitenMedicine Colloquium Exam - 2015 ArachaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)