Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
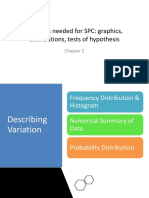
Quality Control
Hochgeladen von
AydaLeeCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Quality Control
Hochgeladen von
AydaLeeCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
PREPARED BY :
PN NOR MAHANI MD RASIDI
ITEM DESCRIPTION
DEFINITION The science that deals with the collection,
tabulation, analysis, interpretation, and
presentation of quantitative data.
PURPOSE variation in processes and populations
interactions among the variables in processes
and populations
operational definitions
INVOLVES Collecting
Classifying
Summarizing
Organizing
Analyzing
Interpreting
DATA
VARIABLES
Quality characteristic that are
measurable and countable
CONTINUOUS
Measurable
(meter,pascal)
DISCRETE
Countable
(1,2,3.)
ATTRIBUTES
Quality characteristics that are classified as
either conforming or nonconforming and
comparison.
ORDINAL
Comparison
(poor, average, good)
NOMINAL
Conforming or
nonconforming
(on or off, yes or no).
POPULATION
The whole collection
of measurements
SAMPLE
A small portion is
selected from
population to
represent population.
POPULATION
A population
frequency
distribution
can be
represented by
a smooth curve
(NORMAL
CURVE)
SAMPLE
A sample
frequency
distribution
can be
represented by
HISTOGRAM.
GRAPHICAL TECHNIQUE
(Picture of frequency distribution)
ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUE
To plot or picture of a frequency
distribution.
1) Histogram
2) Relative Frequency Histogram
3) Cumulative Frequency Histogram
4) Relative Cumulative Frequency
Histogram
Summarize data by computing a
measure of central tendency and
a measure of the dispersion.
A summarization of how the data
points (observations) occur
within each subdivision of
observed values or groups of
observed values.
Less space compared to
graphical technique.
Allow for additional calculations
& inferences.
MEASURES OF CENTRAL
TENDENCY
MEASURE OF DISPERSION
How the data to build up
in the centre:
1) Average
2) Median
3) Mode
How data are spread out or
scattered on each side of the
central value.
1) Range R
2) Standard Deviation S
3) Variance S
2
ITEM DEFINITION FORMULA
UNGROUPED DATA GROUPED DATA
AVERAGE The sum of
observations
divided by the
no. of
observation
n= number of observed
values
X
1
, X
2
.X
n
= observed
value
f
i
= frequency
X
i
= midpoint
MODE A set of numbers
is the value that
occurs with the
greatest
frequency.
3, 3, 4, 5, 5, 5, and 7
Mode is 5 (unimodal)
105, 105, 105, 107, 108,
109, 109, 109,110 and 112
Mode is 105 and 109
(bimodal)
Midpoint of the cell with the
highest frequency is the
mode.
ITEM DEFINITION FORMULA
UNGROUPED DATA GROUPED DATA
MEDIAN The number of items
above it is equal to the
number below it.
3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 8 ,10
Median is the fourth
item (6), 3 items above
and 3 items
- Arrange in ordered
-If number in series is
odd, the median is
the mid point of the
values.
3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 8 , 10
Median is 6
M
d
= median
L
m
= lower boundary of
the cell with the median
n = total no. of
observation
C
fm
= cumulative
frequency of all cells
below L
m
f
m
= frequency of median
cell
I = cell interval
2
fm
d m
m
n
C
M L i
f
| |
|
= +
|
|
\ .
Symmetrical (Average=median=mode)
Positively Skewed (mode<median<average)
Negatively Skewed (average<median<mode)
ITEM DEFINITION FORMULA
UNGROUPED DATA GROUPED DATA
RANGE The different
between the
largest and
smallest value.
R = range
X
h
= highest observation in a series
X
l
= lowest observation in a series
STANDARD
DEVIATION
Numerical value
in the units of the
observed values
that measures the
spreading
tendency of the
data
OR
X
i
= observed value
X = average
n = number of observed
values
X
i
= midpoint
f
i
= frequency
h l R X X =
2
R
midrange =
2
n n
2
i i
i i
n x ( x )
s=
n(n-1)
1
Solve problem
2
Determine the process capability
3
Compare with specifications
4
Suggest the shape of the population
5
Indicate discrepancies in data such as gaps
DEFINITION
Symmetrical, unimodal, bell-shaped distribution with mean,
median and mode having the same value).
A population curve or distribution is developed from a frequency
histogram.
The normal curve is such a good description of the variations that
occurs to most quallity characteristics in industry.
A normal curve is symmetrical about
The mean, mode, and median are equal
The curve is uni-modal and bell-shaped
Data values concentrate around the mean
Area under the normal curve equals 1
ITEM DESCRIPTION
FORMULA
Where:
z = stadard normal value
X = individual value
o= population standard deviation
= mean
GRAPH
o
=
X
z
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Fundamentals of StatisticsDokument33 SeitenFundamentals of StatisticsAydaLeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Organize DataDokument4 SeitenHow To Organize DataMichael YuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Probability and StatisticsDokument42 SeitenEngineering Probability and StatisticsKevin RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- StatisticsDokument12 SeitenStatisticsRaymond ArifiantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Istanbul Aydin University: Describing, Exploring, and Comparing DataDokument21 SeitenIstanbul Aydin University: Describing, Exploring, and Comparing Dataxxnameless 97Noch keine Bewertungen
- STATS and PROBABILITYDokument7 SeitenSTATS and PROBABILITYJaykuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading - Exploratory Data AnalysisDokument33 SeitenReading - Exploratory Data Analysisvaibhavpardeshi55Noch keine Bewertungen
- AP Statistics Chapter 1 & 2 Notes - Exploring Data and Describing LocationDokument25 SeitenAP Statistics Chapter 1 & 2 Notes - Exploring Data and Describing LocationNguyen Phan Hoang AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAT 152 - P2 ReviewerDokument9 SeitenMAT 152 - P2 Reviewerfernandezmaekyla1330Noch keine Bewertungen
- Math Majorship StatisticsDokument9 SeitenMath Majorship StatisticsMark ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Majorship Statistics PDFDokument9 SeitenMath Majorship Statistics PDFRoberto Esteller Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Descriptive Statistics Summary (Session 1-5) : Types of Data - Two TypesDokument4 SeitenDescriptive Statistics Summary (Session 1-5) : Types of Data - Two TypesDipak Kumar PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPC Statistics: Histograms, Distributions & Hypothesis TestsDokument158 SeitenSPC Statistics: Histograms, Distributions & Hypothesis Testsgeletaw mitawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prelim Lec 2017Dokument49 SeitenPrelim Lec 2017Marc AlamoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day 01-Basic StatisticsDokument36 SeitenDay 01-Basic StatisticsRashid ali khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research 3: Inferential StatisticsDokument39 SeitenResearch 3: Inferential StatisticsHanna nicole JapsayNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChandruDokument27 SeitenChandruSidhant BhayanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day 01-Basic Statistics - Part (I)Dokument29 SeitenDay 01-Basic Statistics - Part (I)Sparsh VijayvargiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RSU - Statistics - Lecture 3 - Final - myRSUDokument34 SeitenRSU - Statistics - Lecture 3 - Final - myRSUirina.mozajevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measusres of LocationsDokument52 SeitenMeasusres of LocationsSubashDahalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measures of Central Tendency and VariationDokument13 SeitenMeasures of Central Tendency and VariationAshley DestrizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics For Data ScienceDokument93 SeitenStatistics For Data ScienceCesar LobatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Descriptive Statistics Explained: Measures of Central Tendency, Spread and ShapeDokument34 SeitenDescriptive Statistics Explained: Measures of Central Tendency, Spread and ShapeNAVANEETHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes - Module 2Dokument22 SeitenNotes - Module 2LARINGO IanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic 1Dokument60 SeitenBasic 1Rajesh DwivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Introduction The Teaching of Theory (3 Hours) ObjectiveDokument32 SeitenChapter 1 Introduction The Teaching of Theory (3 Hours) Objectiveapi-3728690100% (1)
- Statistics: A Branch of Mathematics That Deals With: Planning Collecting Organizing Presenting Analyzing InterpretingDokument43 SeitenStatistics: A Branch of Mathematics That Deals With: Planning Collecting Organizing Presenting Analyzing InterpretingVan DuranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Statistics 3Dokument13 SeitenBio Statistics 3Moos LightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notas EstadisticaDokument20 SeitenNotas EstadisticaCristian CanazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Basic StatisticsDokument12 Seiten2-Basic StatisticsLab KliteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic StatisticsDokument52 SeitenBasic StatisticsKrishna Veni GnanasekaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter1 StatisticDokument33 SeitenChapter1 StatisticKelvin YipNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDA 3E Chapter 2Dokument40 SeitenSDA 3E Chapter 2xinearpingerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mean Median ModeDokument56 SeitenMean Median ModeJenneth Cabinto DalisanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measures Central Tendency Mean Mode MedianDokument26 SeitenMeasures Central Tendency Mean Mode MedianHetal Koringa patelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Probability and Statistics For Computer Scientists Second Edition, By: Michael BaronDokument63 SeitenProbability and Statistics For Computer Scientists Second Edition, By: Michael BaronVall GyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module-1 2Dokument32 SeitenModule-1 2Ctrl-Alt-DelNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGLISH IN STATISTICS AND COMBINATORICS Kelompok 4Dokument28 SeitenENGLISH IN STATISTICS AND COMBINATORICS Kelompok 4Nova IvtihalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Central Tendency, Measures of Dispersion, NormalDokument31 SeitenCentral Tendency, Measures of Dispersion, NormalShad RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 2 Central Tendency and VariabilityDokument28 SeitenWeek 2 Central Tendency and VariabilityMuhaimin Abdu AzizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Mining Descriptive SummarizationDokument32 SeitenData Mining Descriptive SummarizationAnkush LaybarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doc. AP Stat~ Supplemental Ch. 1 – Exploring DataDokument3 SeitenDoc. AP Stat~ Supplemental Ch. 1 – Exploring Datailiketrees282Noch keine Bewertungen
- NITKclass 1Dokument50 SeitenNITKclass 1'-MubashirBaigNoch keine Bewertungen
- SINGLE VARIABLE Notes 5.3 Year 10Dokument9 SeitenSINGLE VARIABLE Notes 5.3 Year 10primalp6105Noch keine Bewertungen
- Central TendencyDokument26 SeitenCentral TendencyAlok MittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exploring Data: AP Statistics Unit 1: Chapters 1-4Dokument83 SeitenExploring Data: AP Statistics Unit 1: Chapters 1-4Jacob PegherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 - Business Statistics & AnalyticsDokument25 SeitenUnit 1 - Business Statistics & Analyticsk89794Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Basic StatisticsDokument12 Seiten2-Basic StatisticsLab KliteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiological StatisticsDokument12 SeitenPhysiological StatisticsGerlyn MortegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sit 212 Lecture NoteDokument99 SeitenSit 212 Lecture NoteTracy JaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMS 504-Week 4&5 NewDokument40 SeitenIMS 504-Week 4&5 NewAhmad ShahirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Descriptive Statistics PDFDokument130 SeitenDescriptive Statistics PDFShaheed MorweNoch keine Bewertungen
- DM 02 01 Data UndrestandingDokument35 SeitenDM 02 01 Data UndrestandingPallavi BhartiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH - 4Dokument71 SeitenCH - 4PIYUSH MANGILAL SONINoch keine Bewertungen
- Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Mode, MedianDokument30 SeitenMeasures of Central Tendency: Mean, Mode, Medianafnan nabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RMBS BPT402Dokument103 SeitenRMBS BPT402Atul DahiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2.2 - Statistics - Desc Stat and DistribDokument48 SeitenLecture 2.2 - Statistics - Desc Stat and Distribnguyenaiquynh150801Noch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics Helps Numerical Evidence ProblemDokument7 SeitenStatistics Helps Numerical Evidence ProblemsureshNoch keine Bewertungen
- PlumberDokument31 SeitenPlumberAydaLeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Flow Velocity in DuctsDokument2 SeitenAir Flow Velocity in DuctsKarthikeyan SankarrajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- M'sia STDRD 1780-2005 Smoke ControlDokument9 SeitenM'sia STDRD 1780-2005 Smoke ControlAydaLeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business PlanDokument24 SeitenBusiness PlanAydaLeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fire Protection SystemDokument4 SeitenFire Protection SystemAydaLeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conversion Factors Chart for Common UnitsDokument17 SeitenConversion Factors Chart for Common Unitskaushaldesai88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kara&Suoglu ProjectreportDokument4 SeitenKara&Suoglu ProjectreportRicard Comas xacnóNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are Universities ForDokument19 SeitenWhat Are Universities ForBikash Ranjan MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- RA For Installation & Dismantling of Loading Platform A69Dokument15 SeitenRA For Installation & Dismantling of Loading Platform A69Sajid ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digitrip 520Dokument40 SeitenDigitrip 520HACNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strata KT Office OpportunityDokument41 SeitenStrata KT Office OpportunitySanskar SurekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PA2 Value and PD2 ValueDokument4 SeitenPA2 Value and PD2 Valueguddu1680Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kanavos Pharmaceutical Distribution Chain 2007 PDFDokument121 SeitenKanavos Pharmaceutical Distribution Chain 2007 PDFJoao N Da SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Install Windows XP From Pen Drive Step by Step GuideDokument3 SeitenHow To Install Windows XP From Pen Drive Step by Step GuideJithendra Kumar MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal 082013Dokument100 SeitenJournal 082013Javier Farias Vera100% (1)
- Active Disturbance Rejection Control For Nonlinear SystemsDokument8 SeitenActive Disturbance Rejection Control For Nonlinear SystemsTrần Việt CườngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gregory University Library Assignment on Qualities of a Reader Service LibrarianDokument7 SeitenGregory University Library Assignment on Qualities of a Reader Service LibrarianEnyiogu AbrahamNoch keine Bewertungen
- War, Rivalry An State Building in Latin AmericaDokument16 SeitenWar, Rivalry An State Building in Latin AmericaPablo Andrés Garrido GonzálezNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSMA Moile Money Philippines Case Study V X21 21Dokument23 SeitenGSMA Moile Money Philippines Case Study V X21 21davidcloud99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mini Centre CatalogDokument26 SeitenMini Centre CatalogJohn EarleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- T Cells & Autoimmunity, s3Dokument21 SeitenT Cells & Autoimmunity, s3LiaAriestaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Services : An OverviewDokument15 SeitenFinancial Services : An OverviewAnirudh JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- SIM7020 Series - HTTP (S) - Application Note - V1.04Dokument15 SeitenSIM7020 Series - HTTP (S) - Application Note - V1.04Vinicius BarozziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jeremy Hughes ReviewDokument5 SeitenJeremy Hughes ReviewgracecavNoch keine Bewertungen
- EINC ChecklistDokument3 SeitenEINC ChecklistMARK JEFTE BRIONESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unitisation of Legal Methodsalsdkgh GHNJFKL A SDFG LKJH Asdfgf Lkjhasdfg LKKJ Asdfg LKJH A Slkjfs Aaaaaaaaaaaaslkdfj Asldkjf SLDKFJDokument3 SeitenUnitisation of Legal Methodsalsdkgh GHNJFKL A SDFG LKJH Asdfgf Lkjhasdfg LKKJ Asdfg LKJH A Slkjfs Aaaaaaaaaaaaslkdfj Asldkjf SLDKFJKailashnath Reddy AjjuguttuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rock Type Identification Flow Chart: Sedimentary SedimentaryDokument8 SeitenRock Type Identification Flow Chart: Sedimentary Sedimentarymeletiou stamatiosNoch keine Bewertungen
- MF-QA-001 PDIR ReportDokument2 SeitenMF-QA-001 PDIR ReportBHUSHAN BAGULNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intraoperative Nursing Care GuideDokument12 SeitenIntraoperative Nursing Care GuideDarlyn AmplayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graphic Organizers for Organizing IdeasDokument11 SeitenGraphic Organizers for Organizing IdeasMargie Tirado JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Secret Language of AttractionDokument278 SeitenThe Secret Language of Attractionsandrojairdhonre89% (93)
- Template - Time in ManufacturingDokument2 SeitenTemplate - Time in ManufacturingVero RoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philip Larkin: The Art of Poetry 30Dokument32 SeitenPhilip Larkin: The Art of Poetry 30Telmo RodriguesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutritional support through feeding tubesDokument76 SeitenNutritional support through feeding tubesKryzza LeizellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vonovia 9M2021 Presentation 20211118Dokument76 SeitenVonovia 9M2021 Presentation 20211118LorenzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bolt Jul 201598704967704 PDFDokument136 SeitenBolt Jul 201598704967704 PDFaaryangargNoch keine Bewertungen