Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
GSM Infrastructure
Hochgeladen von
MD Sahid0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
83 Ansichten19 SeitenMSC, BSC, BTS, VLR, HLR, GSGN, GSSN
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenMSC, BSC, BTS, VLR, HLR, GSGN, GSSN
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
83 Ansichten19 SeitenGSM Infrastructure
Hochgeladen von
MD SahidMSC, BSC, BTS, VLR, HLR, GSGN, GSSN
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 19
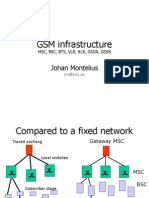
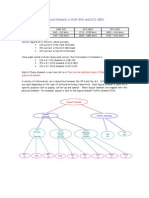
GSM infrastructure
MSC, BSC, BTS, VLR, HLR, GSGN, GSSN
Johan Montelius
jm@sics.se
Compared to a fixed network
Gateway MSC
MSC
BSC
MS
Local switches
Transit exchang
Subscriber stage
Fixed phone
Whats new?
Radio access network
Encryption
Voice coding
Locate a mobile station
Identify and authenticate
Handle mobility during a call
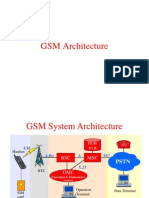
A bird eyes view
BTS
MS
BSC
MSC
BSC
BSC
BTS
BTS
GMSC
Access Network
databases
Typical Mobile operator
One to ten MSC per 1 M subscribers
Ten to one hundred BSC per MSC
Thousands of BTS per 1 M subscribers
Base Transceiver Station
Controls the radio link
encryption
error control
signal strength
1 - 6 duplex carriers, for
example:
two layers
120
o
sectors
(6+8)*3 = 42 voice calls
Cost ~ 100 200 k$
Base Station Controller
communication with the mobile
terminal
local hand-over
voice codecs
carrier allocation
paging to terminals
talks to the MSC
serves up to 40 BTSs
could be co-located with MSC
Mobile Swicthing Center
Mobility management
identifies and authenticates
locates
switches between BSCs
Handover to other MSCs
64 kbps regular voice channels
Radio Access network
A carrier is divided into logical channels
traffic channels TCH
control channels CCH
The first carrier holds 2 controll channels and
6 traffic channels. Additional carriers holds only
traffic channels.
Control Channels
Broadcast
Frequency correction: to synchronize (FCCH)
Broadcast control: this is me, these are my neighbours (BCCH)
Common control
Paging: to notify a mobile station (PCH)
Random access: for the mobile to request service (RACH)
Access grant: reply with assigned dedicated control channel (AGCH)
Dedicated control
Standalone dedicated control: used during call set-up, SMS etc (SDCCH)
Slow associated control: power, time etc (SACCH)
Fast associated control: handover etc, uses the TCH (FACCH)
Cell broadcast: cell broadcast
Traffic Channels
Duplex
Error control
Forward Error Correction (FEC)
retransmission (ARQ)
Full rate (TCH/F)
13 Kbps speech
9,6 or 14,4 Kpbs data
Half rate (TCH/H)
6,5 Kbps speech
7,2 or 4,8 Kbps data
Logical channels
8 time-slot TDMA frame 4.143 ms
Multiframe: 26 or 51 TDMA frames
Superframe: 26 or 51 multiframes 6.12 s
Hyperframe: 2048 superframes 3h28m
CCH
CCH CCH
TCH
One TDMA frame
Normal burst
57 b 57 b 26 b
tail
tail guard
user data user data
training
3 3
8.25
stealing flags
Frequency correction burst
Synchronization burst
Dummy burst
Access burst
148 b 0.577 ms
Keeping track of a mobile
station
VLR
visiting location register
Location area
Location area
update the VLR with new
location area
Moving to a new MSC
Location area
Location area
VLR
which LA which MSC ?
update the VLR with new
location area and new MSC
but also.
VLR
HLR
home location register
update the home location register!
Home Location Register
MSC
GMSC
PSTN
incomming call
where is the mobile?
HLR
How do we reach him?
VLR
Mobile station numbers
MSC
GMSC
PSTN
mobile subscriber ISDN number
(MSISDN) i.e. the phone number
HLR
Mobile Station Roaming
Number (MSRN).
VLR
Temporary Mobile
Subscriber Identity
International Mobile
Subscriber Identity
GPRS
BTS
MS
BSC
BTS
BTS
Access Network
Packet Control Unit
Gateway GPRS Support Node
GGSN
UDP/TCP tunnel
Serving GPRS Support Node
SGSN
Internet
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- GSM Infrastructure: Johan MonteliusDokument19 SeitenGSM Infrastructure: Johan MonteliuscarlosjohnsNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM InfrastructureDokument19 SeitenGSM InfrastructurekittisakddNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Mobile Communications and the TETRA SystemVon EverandDigital Mobile Communications and the TETRA SystemBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- GSM Infrastructure: MSC, BSC, BTS, VLR, HLR, GSGN, GSSNDokument19 SeitenGSM Infrastructure: MSC, BSC, BTS, VLR, HLR, GSGN, GSSNstephan-lNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final - GSM PMRDokument141 SeitenFinal - GSM PMRjaveria zafeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM PresentacionDokument81 SeitenGSM PresentacionRoberto RuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Systems for the Mobile Information SocietyVon EverandCommunication Systems for the Mobile Information SocietyNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM I NewDokument129 SeitenGSM I NewSanjana BoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pertemuan 7 GSM NetworkDokument38 SeitenPertemuan 7 GSM NetworkSTRMoch Hafizh AlfiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP Telephony: Deploying VoIP Protocols and IMS InfrastructureVon EverandIP Telephony: Deploying VoIP Protocols and IMS InfrastructureNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global System For MobileDokument26 SeitenGlobal System For MobileAditi AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTE Signaling: Troubleshooting and Performance MeasurementVon EverandLTE Signaling: Troubleshooting and Performance MeasurementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pertemuan 8 GSM-NetworkDokument38 SeitenPertemuan 8 GSM-NetworkYus MayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Channel-Adaptive Technologies and Cross-Layer Designs for Wireless Systems with Multiple Antennas: Theory and ApplicationsVon EverandChannel-Adaptive Technologies and Cross-Layer Designs for Wireless Systems with Multiple Antennas: Theory and ApplicationsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Presentation On GSM Network: BY:-Arun BeraDokument39 SeitenPresentation On GSM Network: BY:-Arun BeraAnwar SiddiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandVon EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS 9059 Mobile ComputingDokument107 SeitenCS 9059 Mobile Computingkarthi_gopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsVon EverandAdvances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsGabriele ManganaroBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- Lec1 (Channels)Dokument29 SeitenLec1 (Channels)Nazir AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : Anindita KunduDokument62 SeitenGlobal System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : Anindita KunduSuparno BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular System Infarstructure FHSSDokument79 SeitenCellular System Infarstructure FHSSUmayanga MadushanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Channel ConceptDokument35 SeitenGSM Channel ConceptShachi P GowdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Various Interfaces and Their Mapping: Skgochhayat RTTC, BhubaneswarDokument43 SeitenVarious Interfaces and Their Mapping: Skgochhayat RTTC, BhubaneswarKuldeep BishtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Some Important Questions For Interview Point of View-1Dokument23 SeitenSome Important Questions For Interview Point of View-1nileshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signalling and Control in GSMDokument22 SeitenSignalling and Control in GSMFebri DoangNoch keine Bewertungen
- M0dule-2 WCCDokument56 SeitenM0dule-2 WCCAkshathaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IR Nterface: By: W EDokument19 SeitenIR Nterface: By: W EabdallahNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF GSMDokument6 SeitenPDF GSMMahabub AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Call ProcessingDokument38 SeitenCall ProcessingPrakasam ArulappanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch3-airInterface GSMDokument22 SeitenCh3-airInterface GSMwassim_chinouiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concepts of Channels in GSMDokument13 SeitenConcepts of Channels in GSMSana DanyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 CDMA ConceptDokument53 Seiten01 CDMA ConceptSiraj SidhikNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Network Architecture: Masood HabibDokument46 SeitenGSM Network Architecture: Masood Habibdev12janNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Overview UpdatedDokument131 SeitenGSM Overview UpdatedSandip DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProjectDokument37 SeitenProjectSurina KondillyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Evelution Mod 2Dokument35 SeitenGSM Evelution Mod 2Nada GamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.GSM ChannelsDokument24 Seiten7.GSM Channelsmanthasaikarthik100% (1)
- Video Conferencing Online GamesDokument9 SeitenVideo Conferencing Online GamesamitsaharulzNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Logical ChannelsDokument5 SeitenGSM Logical ChannelsRahul SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd Generation Systems: - Review of Cellular Wireless Networks - UmtsDokument39 Seiten3rd Generation Systems: - Review of Cellular Wireless Networks - Umtsselvadpm5Noch keine Bewertungen
- GSM (Global System For Mobile Communications) and ExtensionsDokument33 SeitenGSM (Global System For Mobile Communications) and Extensionsਗੁਰਪਰੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਸੂਰਾਪੁਰੀNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture - GSMDokument102 SeitenLecture - GSMHusnainNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Channels & Air InterfaceDokument31 SeitenGSM Channels & Air InterfaceCabdallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT 601: Mobile Computing: GSM (Most of The Slides Stolen From Prof. Sridhar Iyer's Lectures)Dokument60 SeitenIT 601: Mobile Computing: GSM (Most of The Slides Stolen From Prof. Sridhar Iyer's Lectures)fearoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Présentation Sur GSMDokument60 SeitenPrésentation Sur GSMSarahHattanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logical Channels & Multi-Frame StructuresDokument20 SeitenLogical Channels & Multi-Frame Structuresfahadmalik89Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bandwidth ManagementDokument50 SeitenBandwidth ManagementOsama AbbassNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes Lecture7 GSMDokument32 SeitenNotes Lecture7 GSMAkhil DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT 601: Mobile Computing: GSM (Most of The Slides Stolen From Prof. Sridhar Iyer's Lectures)Dokument60 SeitenIT 601: Mobile Computing: GSM (Most of The Slides Stolen From Prof. Sridhar Iyer's Lectures)Spaf SrivenkateshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Channel ConceptDokument36 SeitenChannel ConceptNarender KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM)Dokument32 SeitenThe Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM)devajeet_nerist2840Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Telephony and CellularDokument38 SeitenBasic Telephony and CellularMuhammad TahirNoch keine Bewertungen
- The GSM and GPRS NetworkDokument19 SeitenThe GSM and GPRS NetworknityanarlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIR Interface Info of GSMDokument45 SeitenAIR Interface Info of GSMrajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OVERVIEWDokument79 SeitenOVERVIEWseth_awuah100% (1)
- NSN BTS Labeling FormatDokument2 SeitenNSN BTS Labeling FormatMD SahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abul Ammar PashaDokument3 SeitenAbul Ammar PashaMD SahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEC NEO CommissioningDokument19 SeitenNEC NEO CommissioningMD SahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEC NEO Commissioning ProcedureDokument24 SeitenNEC NEO Commissioning ProcedureMD SahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- WCCDokument1 SeiteWCCMD SahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working Principle of Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker ELCBDokument4 SeitenWorking Principle of Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker ELCBMD SahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ip Change ProcedureDokument9 SeitenIp Change ProcedureMD SahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEC NEO CommissioningDokument19 SeitenNEC NEO CommissioningMD SahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Radio ConceptsDokument3 SeitenGSM Radio ConceptsMD SahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEC NEO CommissioningDokument19 SeitenNEC NEO CommissioningMD SahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- E1 T1 CarrierDokument32 SeitenE1 T1 CarrierMD SahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flexi Multiradio BTS Commissioning and Integration - PPT NEWDokument24 SeitenFlexi Multiradio BTS Commissioning and Integration - PPT NEWMD Sahid78% (9)
- GSM InfrastructureDokument19 SeitenGSM InfrastructureMD SahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- FXC RRI CommissioningDokument21 SeitenFXC RRI CommissioningMD SahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- COLOR CODING OF NSN BTS Alarm and E1 CableDokument2 SeitenCOLOR CODING OF NSN BTS Alarm and E1 CableMD Sahid100% (2)
- Tems Parameters (Speech) : Gaurav Shivhare, Dinesh Rathor RF EngineerDokument15 SeitenTems Parameters (Speech) : Gaurav Shivhare, Dinesh Rathor RF EngineerMD SahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- DT Notes Part-2Dokument24 SeitenDT Notes Part-2Bhanu Gautam100% (1)
- AntenaDokument19 SeitenAntenaMD SahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excel FormulaDokument1 SeiteExcel FormulaMD SahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3G Call FlowDokument37 Seiten3G Call FlowMD SahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flexi Multiradio BTS Commissioning and Integration - PPT NEWDokument24 SeitenFlexi Multiradio BTS Commissioning and Integration - PPT NEWMD Sahid78% (9)
- COLOR CODING Seimens IDU & Flexi BTSDokument1 SeiteCOLOR CODING Seimens IDU & Flexi BTSMD SahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- COLOR CODING OF NSN BTS Alarm and E1 CableDokument2 SeitenCOLOR CODING OF NSN BTS Alarm and E1 CableMD Sahid100% (2)
- A-Panel Dual Polarization Half-Power Beam Width Adjust. Electr. DowntiltDokument2 SeitenA-Panel Dual Polarization Half-Power Beam Width Adjust. Electr. DowntiltUzair AkbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- San Francisco Chinese Christian Union, Et Al. v. City and County of San Francisco, Et Al. ComplaintDokument25 SeitenSan Francisco Chinese Christian Union, Et Al. v. City and County of San Francisco, Et Al. ComplaintFindLawNoch keine Bewertungen
- 671 - BP Well Control Tool Kit 2002Dokument19 Seiten671 - BP Well Control Tool Kit 2002Ibama MirillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paul S. Adler - Paul Du Gay - Glenn Morgan - Michael Reed (Eds.) - The Oxford Handbook of Sociology, Social Theory, and Organization Studies - Contemporary Currents-Oxford University Press, USA (2014)Dokument817 SeitenPaul S. Adler - Paul Du Gay - Glenn Morgan - Michael Reed (Eds.) - The Oxford Handbook of Sociology, Social Theory, and Organization Studies - Contemporary Currents-Oxford University Press, USA (2014)Andreea Dobrita67% (3)
- Panch ShilDokument118 SeitenPanch ShilSohel BangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Defination of ValuesDokument11 SeitenDefination of ValuesDipannita GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ibm v3700 Storeage PDFDokument694 SeitenIbm v3700 Storeage PDFJanakackvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems of Spun Concrete Piles Constructed in Soft Soil in HCMC and Mekong Delta - VietnamDokument6 SeitenProblems of Spun Concrete Piles Constructed in Soft Soil in HCMC and Mekong Delta - VietnamThaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hilti AnchorDokument5 SeitenHilti AnchorGopi KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cyber Law: Submitted byDokument8 SeitenCyber Law: Submitted bySonu MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mind Mapping BIOTEKDokument1 SeiteMind Mapping BIOTEKAdrian Muhammad RonalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13 - Conclusion and SuggestionsDokument4 Seiten13 - Conclusion and SuggestionsjothiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Document 20Dokument3 SeitenDocument 20api-586815209Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quality ManualDokument34 SeitenQuality Manualchao gao100% (9)
- Data MiningDokument721 SeitenData MiningAuly Natijatul AinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Letters To Apply For A Job - OdtDokument2 SeitenApplication Letters To Apply For A Job - OdtRita NourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of Performance of Container Terminals T PDFDokument10 SeitenEvaluation of Performance of Container Terminals T PDFjohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vivado Power Analysis OptimizationDokument120 SeitenVivado Power Analysis OptimizationBad BoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surface News - 20130704 - Low Res PDFDokument9 SeitenSurface News - 20130704 - Low Res PDFYoko GoldingNoch keine Bewertungen
- HyderabadDokument3 SeitenHyderabadChristoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nirma - Marketing PresentationDokument22 SeitenNirma - Marketing PresentationJayRavasa100% (2)
- Hardening'-Australian For Transformation: A Monograph by MAJ David J. Wainwright Australian Regular ArmyDokument89 SeitenHardening'-Australian For Transformation: A Monograph by MAJ David J. Wainwright Australian Regular ArmyJet VissanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kudla Vs PolandDokument4 SeitenKudla Vs PolandTony TopacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is EBSD ? Why Use EBSD ? Why Measure Microstructure ? What Does EBSD Do That Cannot Already Be Done ?Dokument5 SeitenWhat Is EBSD ? Why Use EBSD ? Why Measure Microstructure ? What Does EBSD Do That Cannot Already Be Done ?Zahir Rayhan JhonNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIami Beach City Attorney's DenialDokument7 SeitenMIami Beach City Attorney's DenialDavid Arthur WaltersNoch keine Bewertungen
- NumaConcert ManualDokument96 SeitenNumaConcert ManualPippo GuarneraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Netaji Subhas Open UniversityDokument4 SeitenNetaji Subhas Open UniversityraydipanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Electric/ Massachusetts State Records Request Response Part 3Dokument673 SeitenGeneral Electric/ Massachusetts State Records Request Response Part 3Gintautas DumciusNoch keine Bewertungen
- X606 PDFDokument1 SeiteX606 PDFDany OrioliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digitalisasi Alquran-1 PDFDokument40 SeitenDigitalisasi Alquran-1 PDFMohammad Zildan Pasyha MNoch keine Bewertungen