Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Strategy Analysis & Choice: Strategic Management: Concepts & Cases 12 Edition Fred David Nov: 2009
Hochgeladen von
Talha Khan SherwaniOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Strategy Analysis & Choice: Strategic Management: Concepts & Cases 12 Edition Fred David Nov: 2009
Hochgeladen von
Talha Khan SherwaniCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ch 6 -1
Chapter 6
Strategy Analysis & Choice
Strategic Management:
Concepts & Cases
12
th
Edition
Fred David
Nov: 2009
Perform
External
Audit
Chapter 3
Perform
Internal
Audit
Chapter 4
Establish
Long-Term
Objectives
Chapter 5
Generate,
Evaluate,
Select
Strategies
Chapter 6
Implement
Strategies:
Mgmt Issues
Chapter 7
Implement
Strategies:
Marketing,
Fin/Acct,
R&D, CIS
Chapter 8
Measure &
Evaluate
Performance
Chapter 9
Vision
&
Mission
Chapter 2
Types of Strategies
Strategy
Formulation
Strategy
Implementation
Strategy
Evaluation
The Process of Generating, Evaluating
and Selecting Strategies
What course of action (strategy) to pursue
to achieve mission, goals and objectives
Current strategies + Mission goals, objects +
External environment basis for generating
and evaluating strategies.
Looking at the present position desired position
Ch 6 -3
The Process of Generating, Evaluating
and Selecting Strategies
Find all flexible alternatives
Involve as many different managers &
employees
Give every one all internal & external audit
information
Creativity is the key
All alternatives should be discussed
List proposed strategies
Prioritize &rank them (1 least implementable4 Most
likely)
Ch 6 -4
Ch 6 -5
Comprehensive Strategy-Formulation
Framework
Stage 1:
The Input Stage
Stage 2:
The Matching Stage
Stage 3:
The Decision Stage
Ch 6 -6
Stage 1: The Input Stage
Basic input information for the matching &
decision stage
Requires strategists to quantify subjectivity
early in the process w.r.t:
External and Internal Analysis
Good intuitive judgment always needed
Cite information from EFE, CPM and IFE
The Strategy-Formulation Analytical
Framework
STAGE 1: THE INPUT STAGE
EFE MATRIX CPM IFE
STAGE 2: THE MATCHING STAGE
SWOT
MATRIX
SPACE
MATRIX
BCG
MATRIX
Internal-External
(IE) Matrix
Grand Strategy
Matrix
STAGE 3: THE DECISION STAGE
Quantitative Strategic Planning Matrix
(QSPM)
Ch 6 -7
Ch 6 -8
Strategy-Formulation Analytical
Framework
SWOT Matrix
SPACE Matrix
BCG Matrix
IE Matrix
Grand Strategy Matrix
Stage 2:
The Matching Stage
Ch 6 -9
SWOT Matrix
Strengths-Opportunities (SO)
Weaknesses-Opportunities (WO)
Strengths-Threats (ST)
Weaknesses-Threats (WT)
Four Types of Strategies
Be Quantitative
Use Notions (S1-O3, W3-O2, W2-T5)
Here just generate alternatives, dont select
them
Not all strategies generated in SWOT Matrix will be
considered for implementation
Ch 6 -10
SWOT Matrix
Leave Blank
Strengths S
List Strengths
S1
S2
S3
S4
Weaknesses W
List Weaknesses
W1
W2
W3
W4
Opportunities O
List Opportunities
O1
O2
O3
O4
SO Strategies
Use strengths to take
advantage of
opportunities
WO Strategies
Overcoming weaknesses
to exploit opportunities
Threats T
List Threats
T1
T2
T3
T4
ST Strategies
Use strengths to avoid
threats
WT Strategies
Minimize weaknesses and
avoid threats
Very precarious position
(Defensive tactics)
Matching Key External and Internal Factors to formulate
Alternative Strategies
Key Internal Factors Key External Factors Resultant Strategy
Excess working capital
(Strg)
20% annual growth in
Cell phone industry (OP)
Acquire Company XYZ
Insufficient capacity (WK) Exit of two major foreign
companies (OP)
Pursue horizontal
integration by buying
competitors facilities
Strong R & D (Strg) Number of young
adults(TH)
NPD for older adults
Poor employees morale
(WK)
Strong Union activity (TH) Develop new
employee benefit
Package (overcome
Wk-Avoid TH)
Ch 6 -11
Ch 6 -12
Strategy-Formulation Analytical
Framework
SWOT Matrix
SPACE Matrix
BCG Matrix
IE Matrix
Grand Strategy Matrix
Stage 2:
The Matching Stage
Ch 6 -13
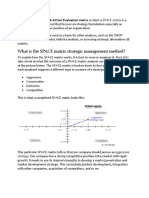
SPACE Matrix
Strategic Position & Action Evaluation Matrix
Four Quadrants:
Aggressive
Conservative
Defensive
Competitive
Two Internal Dimensions
Financial Strength (FS)
Competitive Advantage (CA)
Two External Dimensions
Environmental Stability (ES)
Industry Strength (IS)
Ch 6 -14
SPACE Factors
Environmental Stability (ES)
Technological changes
Rate of inflation
Demand variability
Price range of competing products
Barriers to entry
Competitive pressure
Ease of exit from market
Price elasticity of demand
Risk involved in business
Financial Strength (FS)
Return on investment
Leverage
Liquidity
Working capital
Cash flow from Operations
Inventory Turnover
Price Earnings Ratio
External Strategic Position Internal Strategic Position
Ch 6 -15
SPACE Factors
Industry Strength (IS)
Growth potential
Profit potential
Financial stability
Technological know how
Resource utilization
Ease of entry into market
Productivity
Competitive Advantage CA
Market share
Product quality
Product life cycle
Customer loyalty
Competitions capacity utilization
Technological know-how
Control over suppliers & distributors
External Strategic Position Internal Strategic Position
SPACE Matrix
FS
+6
+1
+5
+4
+3
+2
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
-6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 +1 +2 +3 +4 +5 +6
ES
CA IS
(+ 6) FS = BEST
(+ 6) IS = BEST
(+1) FS = WORST
(+ 1) IS = WORST
(-1) CA= BEST
(-6) ES= WORST
(-6) CA= WORST
(-1) ES= BEST
Assign numerical rating:
For FS and IS
+6 = Best
+1 = Worst
For ES and CA
-1 = Best
-6 = Worst
Compute an Average Score
INTERNAL STRATEGIC POSITION EXTERNAL STRATEGIC POSITION
A
X
I
S
X
Competitive (CA) Industry (IS)
(-6 Worst, -1 best)
-1 Product Quality
-1 Market Share
-3 Brand & image
-2 Product life Cycle
Average: -1.75
(+1 Worst, +6 Best)
+6 Barriers to entry
+4 Growth potential
+4 Access to financing
+5 Consolidation
Average: +4.75
A
X
I
S
Y
Financial Strength (FS) Environmental (ES)
(+1 Worst, +6 Best)
+5 ROA
+4 Leverage
+6 Liquidity
+5 Cash Flow
Average: +5.00
(-6 Worst, -1 best)
-2 Inflation
-1 Technology
-2 Demand elasticity
-4 Taxation
Average: -2.25
Compute an Average Score
INTERNAL STRATEGIC POSITION EXTERNAL STRATEGIC POSITION
A
X
I
S
X
Competitive (CA) Industry (IS)
(-6 Worst, -1 best)
-1 Product Quality
-1 Market Share
-3 Brand & image
-2 Product life Cycle
Average: -1.75
(+1 Worst, +6 Best)
+6 Barriers to entry
+4 Growth potential
+4 Access to financing
+5 Consolidation
Average: +4.75
A
X
I
S
Y
Financial Strength (FS) Environmental (ES)
(+1 Worst, +6 Best)
+5 ROA
+4 Leverage
+6 Liquidity
+5 Cash Flow
Average: +5.00
(-6 Worst, -1 best)
-2 Inflation
-1 Technology
-2 Demand elasticity
-4 Taxation
Average: -2.25
Total Axis X Score: CA+IS = +4.75 + (-1.25)
=3.00
Total Axis Y Score: FS + ES = +5.00 + (-2.25)
= 2.75
SPACE Matrix
FS
+6
+1
+5
+4
+3
+2
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
-6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 +1 +2 +3 +4 +5 +6
ES
CA IS
Total Axis X Score:
3.00
Total Axis Y Score:
2.75
Suggested
Strategy type
Conservative Aggressive
Defensive Competitive
Ch 6 -20
SPACE Matrix
FS
+6
+1
+5
+4
+3
+2
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
-6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 +1 +2 +3 +4 +5 +6
ES
CA IS
Conservative Aggressive
Defensive Competitive
Market Penetration
Market Development
Product Development
Related Diversification
Backward, forward, horizontal
integration
Market Penetration
Market Development
Product Development
Diversification (Related or Unrelated)
Retrenchment
Divestiture
Liquidation
Backward, forward, horizontal
integration
Market Penetration
Market Development
Product Development
Ch 6 -21
Strategy-Formulation Analytical
Framework
SWOT Matrix
SPACE Matrix
BCG Matrix
IE Matrix
Grand Strategy Matrix
Stage 2:
The Matching Stage
Ch 6 -22
BCG Matrix
Boston Consulting Group Matrix
Autonomous divisions = business portfolio (Profit
centers)
Divisions may compete in different industries
Focus is on relative market-share position & industry
growth rate
X Axis: Relative Market Share Position
Y Axis: Industry Sales Growth Rate
Ch 6 -23
BCG Matrix
Relative Market Share Position
High
1.0
Medium
.50
Low
0.0
I
n
d
u
s
t
r
y
S
a
l
e
s
G
r
o
w
t
h
R
a
t
e
High
+20
Low
-20
Medium
0
Question Marks
I
Stars
II
Cash Cows
III
Dogs
IV
31
20
8
39
2
X Axis: Relative Market Share Position
Y Axis: Industry Sales Growth Rate
Ch 6 -24
BCG Matrix
Relative Market Share Position
High
1.0
Medium
.50
Low
0.0
I
n
d
u
s
t
r
y
S
a
l
e
s
G
r
o
w
t
h
R
a
t
e
High
+20
Low
-20
Medium
0
Question Marks
Stars
Cash Cows Dogs
Backward, forward, horizontal
integration
Market Penetration
Market Development
Product Development
Market Penetration
Market Development
Product Development
Divesture
Product Development
Diversification
Retrenchment
Divestiture
Retrenchment
Divestiture
Liquidation
Ch 6 -25
Strategy-Formulation Analytical
Framework
SWOT Matrix
SPACE Matrix
BCG Matrix
IE Matrix
Grand Strategy Matrix
Stage 2:
The Matching Stage
The Internal-External (IE) Matrix
9 Cell Display
Also a portfolio matrix
The Size of the Circles represents the percentage
of sales contribution of each division
The slice of the pie reveals the percentage profit
contribution of each division
Generates input from IFE and EFE Scores
Ch 6 -26
Ch 6 -27
I
II III
IV
V
VI
IX VIII VII
1.0 3.0 2.0 4.0
1.0
3.0
2.0
The IFE Total Weighted Scores
Strong
3.0-4.0
Average
2.0-2.99
Weak
1.0-1.99
High
3.0-4.0
Medium
2.0-2.99
Low
1.0-1.99
The
EFE
Total
Weighted
Scores
Hold and Maintain
Market Penetration
Product Development
Harvest or Divest
Retrenchment
Divesture
Forward, Backward, horizontal
integration
Market Penetration
Market Development
Product Development
Grow and Build
Ch 6 -28
Strategy-Formulation Analytical
Framework
SWOT Matrix
SPACE Matrix
BCG Matrix
IE Matrix
Grand Strategy Matrix
Stage 2:
The Matching Stage
Ch 6 -29
Grand Strategy Matrix
Tool for formulating alternative strategies
Based on two dimensions
Competitive position
Market (Industry) growth > 5% Rapid
Ch 6 -30
Quadrant IV
1. Concentric diversification
2. Horizontal diversification
3. Conglomerate
diversification
4. Joint ventures
Quadrant III
1. Retrenchment
2. Concentric diversification
3. Horizontal diversification
4. Conglomerate
diversification
5. Liquidation
Quadrant I
1. Market development
2. Market penetration
3. Product development
4. Forward integration
5. Backward integration
6. Horizontal integration
7. Concentric diversification
Quadrant II
1. Market development
2. Market penetration
3. Product development
4. Horizontal integration
5. Divestiture
6. Liquidation
RAPID MARKET GROWTH
SLOW MARKET GROWTH
WEAK
COMPETITIVE
POSITION
STRONG
COMPETITIVE
POSITION
Ch 6 -31
Quadrant I
RAPID MARKET GROWTH
SLOW MARKET GROWTH
WEAK
COMPETITIVE
POSITION
STRONG
COMPETITIVE
POSITION
Excellent strategic position
Take advantage of Ext-Envt
Take risks aggressively when
necessary
Concentration on current
markets/products
1. Market development
2. Market penetration
3. Product development
4. Forward integration
5. Backward integration
6. Horizontal integration
7. Concentric diversification
Adopt these if you have
surplus resources
Use this if the organization is
concentrating on single
product Diversify into more
related businesses
Ch 6 -32
Quadrant II
RAPID MARKET GROWTH
SLOW MARKET GROWTH
WEAK
COMPETITIVE
POSITION
STRONG
COMPETITIVE
POSITION
Industry is growing but weak
competitive position
Evaluate present position
How to improve competitiveness
1. Market development
2. Market penetration
3. Product development
4. Horizontal integration
5. Divestiture
6. Liquidation
Option I:
Intensive Growth
Option II:
Horizontal Integration
Last Option:
Defensive
Ch 6 -33
Quadrant III
RAPID MARKET GROWTH
SLOW MARKET GROWTH
WEAK
COMPETITIVE
POSITION
STRONG
COMPETITIVE
POSITION
1. Retrenchment
2. Concentric diversification
3. Unrelated diversification
4. Divesture
5. Liquidation
Compete in slow-growth industries
Weak competitive position
Drastic changes are required
quickly
Cost & asset reduction
Shift Resources away from current
Business to different areas
Sell off
Ch 6 -34
Quadrant IV
RAPID MARKET GROWTH
SLOW MARKET GROWTH
WEAK
COMPETITIVE
POSITION
STRONG
COMPETITIVE
POSITION
Strong competitive position
Slow-growth industry
Diversification to more
promising growth areas
1. Concentric diversification
2. Conglomerate diversification
3. Joint ventures
Strong competitive position Is used
by moving in other markets
Or Pursue
Ch 6 -35
Strategy-Formulation Analytical
Framework
Stage 3:
The Decision Stage
Quantitative Strategic
Planning Matrix
(QSPM)
QSPM: Quantitative Strategic
Planning Matrix
Determines relative attractiveness of feasible
alternative actions
Which alternative strategies are best
Tool to evaluate alternatives strategies objectively
Use good intuitive judgment in selecting strategies
Determines the relative attractiveness of different
strategies
Ch 6 -36
Important
Any number of set of alternative strategies
can be included
Any number of strategies can make up a
given set, BUT only strategies within a given
set are evaluated relative to each other e.g.
one set of strategies may include diversification.
another set may include issuing stock & selling a
division to raise needed capital.
These two sets of strategies are totally different
and the QSPM evaluates strategies only within a
given set.
Ch 6 -37
Outcomes of Techniques in Matching Stage
Alternative Strategies SWOT SPACE BCG IE GRAND TOTAL
X X 2
X X 2
X 1
X X X X 4
X X X X 4
X 1
0
0
X X X X 4
X X X X 4
X X 2
Ch 6 -38
6 steps to QSPM
1. Make a list of the firms key external
opportunities/threats and Internal Strengths/
weaknesses in the left Column.
10 minimum for each
2. Assign weights to each key external and
internal factor
same as EFE and IFE
3. Examine the stage 2 (matching) matrices and
identify alternative strategies that the
organization should consider implementing
Group them into mutually exclusive sets
Open Turkish Airlines Document
Ch 6 -39
6 steps to QSPM
4. Determine the Attractiveness scores (AS)
Ask does this factor affect the choice of strategies benign
made? If yes assign scores:
1 = Not attractive
2= Somewhat attractive
3 = Reasonably attractive
4 = Highly attractive
All strategies should be assigned a weight. If one factor does
not effect the 2
nd
or 3
rd
alternative, it will not be included and
a dash will be applied to all three alternatives 1, 2, 3, even if
it were effecting the 1
st
alternative.
Important: Never rate duplicate scores( 1s, 2s, 3s
or 4s) in a row
Only work row by row.
Rates assigned and their difference should have a rationale
to do so.
Ch 6 -40
5. Compute the total attractiveness scores (TAS)
Multiply the weights by the attractiveness
These will indicate the relative attractiveness of each
alternative strategy
6. Compute the Sum Total Attractiveness Scores.
Add TAS in each strategy column .
The Sum Total Attractiveness Scores (STAS) reveals which
strategy is most attractive
Magnitude of STAS amongst strategies will give desirability
of one strategy over another.
Table 6-6
Ch 6 -41
Ch 6 -42
QSPM
Key Internal Factors
Management
Marketing
Finance/Accounting
Production/Operations
Research and Development
Computer Information
Systems
Strategy 3 Strategy 2 Strategy 1 Weight Key External Factors
Economy
Political/Legal/Governmental
Social/Cultural/Demographic/
Environmental
Technological
Competitive
Strategic Alternatives
Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall
Ch 6 -43
QSPM (for a Retail Computer Store)
Key External Factors
Buy New Land and
Build New Larger Store
Fully Renovate
Existing Store
Opportunities Weight AS TAS AS TAS
1. Population of City Growing 10% 0.10 4 0.40 2 0.2
2. Rival Computer Store opening one mile away 0.10 2 0.20 4 0.40
3. Vehicle Traffic passing store up 12% 0.08 1 0.80 4 0.32
4. Vendors average six new products per year 0.05 --- --- --- ---
5. Senior citizen use of computers up 8% 0.05 --- --- --- ---
6. Small business growth I area up 10% 0.10 --- --- --- ---
7. Desire for Websites up 18% by Realtors 0.06 --- --- --- ---
8. Desire for Websites up 18% by Small Firms 0.06 --- --- --- ---
1
Contd
Threats
1.Best Buy opening new store nearby in 1 year 0.15 4 0.60 3 0.45
2. Local University offers computer repair 0.08 --- --- --- ---
3. New bypass for HWY 34 in 1 year will divert traffic 0.12 4 --- 1 ---
4. New Mall being built nearby 0.08 2 --- 4 ---
5. Gas prices up by 14% 0.04 --- --- --- ---
6. Vendors raising prices by 8% 0.03 --- --- --- ---
1.00
Key Internal Factors
Buy New Land and
Build New Larger Store
Fully Renovate
Existing Store
Strengths Weight AS TAS AS TAS
1. Inventory turnover increased from 5.8 to 6.7 0.05 --- --- --- ---
2. Average customer purchase increased from $97 to $128 0.07 2 0.14 4 0.28
3. Employee morale is excellent 0.10 --- --- --- ---
4. In-store promotions resulted in 20% increase in sales 0.05 --- --- --- ---
5. Revenues from repair/service segment of store up 16% 0.15 4 0.60 3 0.45
6. In-store technical support personnel have MIS college degree 0.05 --- --- --- ---
7. Stores debt-to-total assets ratio declined to 34% 0.03 4 0.12 2 0.06
3
Weaknesses
1. Revenue from Software segment of store down 12% 0.10 --- --- --- ---
2. Location of store negatively impacted by new Highway 34 0.15 4 0.60 1 0.15
3. Carpet and paint in store somewhat in disrepair 0.02 1 0.02 4 0.08
4. Bathroom in store needs refurbishing 0.02 1 0.02 4 0.08
5. Revenues from businesses down 8% 0.04 3 0.12 4 0.16
6. Store has no website 0.05 --- --- --- ---
7. Often customers have to wait to check-Out 0.05 2 0.10 4 0.20
TOTAL 1.00 3.72 2.83
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Self-Service Data Analytics and Governance for ManagersVon EverandSelf-Service Data Analytics and Governance for ManagersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of StrategyDokument50 SeitenAnalysis of StrategyVignesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6Dokument34 SeitenChapter 6Azam MacchiatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Space & QSPMDokument41 SeitenSpace & QSPMRadhik Kalra50% (2)
- cdf58sm Mod 3.1Dokument68 Seitencdf58sm Mod 3.1vibhuti goelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategy Analysis and SelectingDokument26 SeitenStrategy Analysis and SelectingNyadroh Clement MchammondsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 6 Strategic Analysis and Choice ImportantDokument34 SeitenLecture 6 Strategic Analysis and Choice ImportantSarsal6067Noch keine Bewertungen
- Strategy Formulation. Strategy Analysis & Choice (8-10M)Dokument45 SeitenStrategy Formulation. Strategy Analysis & Choice (8-10M)Muhammad FaisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategy Analysis and ChoiceDokument32 SeitenStrategy Analysis and ChoicerajendrakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - Strategy Analysis and Management Decision - SVDokument76 SeitenChapter 3 - Strategy Analysis and Management Decision - SV8.Nguyễn Việt HoàngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Analysis ToolsDokument30 SeitenStrategic Analysis Toolsmostafa elshehabyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Askri Final 1Dokument10 SeitenAskri Final 1fahadsiddiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 6-StramaaDokument61 SeitenLesson 6-Stramaaishinoya keishiNoch keine Bewertungen
- WK 8Dokument55 SeitenWK 8Muhammad AmryNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Strategic Position and Action EvaluationDokument6 SeitenThe Strategic Position and Action Evaluationraju_su143Noch keine Bewertungen
- Space and BCG MatrrixDokument16 SeitenSpace and BCG Matrrixnewa944Noch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic ChoiceDokument31 SeitenStrategic ChoiceRajesh TandonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Aquino Ronquillo Tapia Mondia Parada Origen Guadalupe Geronimo Arcay NarizDokument53 Seiten3 Aquino Ronquillo Tapia Mondia Parada Origen Guadalupe Geronimo Arcay NarizrcdcaviteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Triarko Nurlambang: PT Daya Makara UIDokument30 SeitenTriarko Nurlambang: PT Daya Makara UIAnonymous B6yEOYINoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 - Strategy Generation and Selection 2Dokument74 SeitenChapter 8 - Strategy Generation and Selection 2safira dindaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MGT603 - Strategic Management Solved MCQ and Subjective Lecture Wise For Final Term Exam PreparationDokument76 SeitenMGT603 - Strategic Management Solved MCQ and Subjective Lecture Wise For Final Term Exam Preparationmuhammad shahbazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Management - Chapter 6Dokument56 SeitenStrategic Management - Chapter 6juan faustian siregarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 5 Strategy Formulation 3 (Strategy Generation Selection)Dokument49 SeitenTopic 5 Strategy Formulation 3 (Strategy Generation Selection)黄洁宣Noch keine Bewertungen
- Strategy Analysis & Choice: Strategic Management: Concepts & Cases 11 Edition Fred DavidDokument50 SeitenStrategy Analysis & Choice: Strategic Management: Concepts & Cases 11 Edition Fred Davidliza shahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5Dokument54 SeitenChapter 5JulianNoch keine Bewertungen
- EFE MatrixDokument9 SeitenEFE MatrixMuhammad Asad Bin FaruqNoch keine Bewertungen
- David 6 Rev 1Dokument73 SeitenDavid 6 Rev 1Alvin DimasacatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valuing Growth Managing RiskDokument35 SeitenValuing Growth Managing RiskJohn Aldridge Chew67% (3)
- SPACE Matrix Strategic Management MethodDokument15 SeitenSPACE Matrix Strategic Management MethodAloja ValienteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter2 (2 1 1)Dokument50 SeitenChapter2 (2 1 1)Xander MaxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategy Analysis and ChoiceDokument32 SeitenStrategy Analysis and ChoiceManjari MundanadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 - HandoutDokument21 SeitenChapter 5 - HandoutNhật HoàngNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Strategy Module 2 2012Dokument12 Seiten2 Strategy Module 2 2012anashussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matching StageDokument3 SeitenMatching StageSittie Islah Hadji FaisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 HandoutDokument21 SeitenChapter 5 HandoutDuc Trieu MinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Input Tools Require Strategists To Quantify Subjectivity During Early Stages of The Strategy-Formulation ProcessDokument24 SeitenThe Input Tools Require Strategists To Quantify Subjectivity During Early Stages of The Strategy-Formulation ProcessHannah Ruth M. GarpaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Strategy Analysis and ChoiceDokument13 SeitenChapter 4 Strategy Analysis and Choicemelvin cunananNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPACE StarbucksDokument3 SeitenSPACE StarbucksAzfar NoordinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 - HandoutDokument21 SeitenChapter 5 - HandoutNinh NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Managment TotalDokument49 SeitenStrategic Managment TotalkailashdhirwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategy Generation and Selection: Chapter EightDokument53 SeitenStrategy Generation and Selection: Chapter EightAwesomely FairNoch keine Bewertungen
- MGT603 FinalTerm 2008 S01Dokument57 SeitenMGT603 FinalTerm 2008 S01NadirAbidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Strategy Analysis and Choice Summary 17132120-002Dokument6 SeitenChapter 6 Strategy Analysis and Choice Summary 17132120-002NOORI KhanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Space MTRXDokument4 SeitenSpace MTRXakkuliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 - Strategy Generation and Selection (For Sharing)Dokument30 Seiten06 - Strategy Generation and Selection (For Sharing)Andrew AndersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 6. Strategy Analysis and ChoiceDokument45 SeitenCH 6. Strategy Analysis and ChoiceMaham GillaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Space Matrix BMWDokument4 SeitenSpace Matrix BMWmadalus123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sixteenth Edition: Strategy Analysis and ChoiceDokument56 SeitenSixteenth Edition: Strategy Analysis and ChoiceMinh Trang NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- AssignmentDokument10 SeitenAssignmentWaqar AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- StrategiesDokument17 SeitenStrategiesLiaqat AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 - Strategy Analysis & ChoiceDokument10 SeitenChapter 6 - Strategy Analysis & ChoiceHimangee Gupta0% (1)
- MGT603 Final Term Solved Papers 08 Papers SolvedDokument83 SeitenMGT603 Final Term Solved Papers 08 Papers SolvedMurad Khan100% (1)
- Strat Reviewer Chapter 6Dokument20 SeitenStrat Reviewer Chapter 6Ross John JimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- David PPT Exp Ch06Dokument64 SeitenDavid PPT Exp Ch06Gracia PrimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is The SPACE Matrix Strategic Management Method?Dokument4 SeitenWhat Is The SPACE Matrix Strategic Management Method?Subhadeep PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nhóm 5 Nguyễn Quốc Huy SWOT AND SPACE MATRIX 1Dokument6 SeitenNhóm 5 Nguyễn Quốc Huy SWOT AND SPACE MATRIX 1Gamer và Âm nhạcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic ManagementDokument16 SeitenStrategic ManagementM. E. C.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hamill Bassue Owen Hendershot Goran NagradicDokument47 SeitenHamill Bassue Owen Hendershot Goran NagradicIrfan SaleemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strama Mod 6Dokument13 SeitenStrama Mod 6Jaysah BaniagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chargezoom Achieves PCI-DSS ComplianceDokument2 SeitenChargezoom Achieves PCI-DSS CompliancePR.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Newton-Leibniz Book Research - Gate - 06!12!2023Dokument17 SeitenThe Newton-Leibniz Book Research - Gate - 06!12!2023Constantine KirichesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Linear Equations A Through HDokument20 SeitenSimple Linear Equations A Through HFresgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Education Division of Cebu ProvinceDokument5 SeitenDepartment of Education Division of Cebu ProvinceNelsie FernanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Hand Out Comm. Skill BSC AgDokument2 SeitenCourse Hand Out Comm. Skill BSC Agfarid khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MK Slide PDFDokument26 SeitenMK Slide PDFPrabakaran NrdNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Formulary of Unani Medicine Part Ia-O PDFDokument336 SeitenNational Formulary of Unani Medicine Part Ia-O PDFMuhammad Sharif Janjua0% (1)
- Contoh Pidato Bahasa Inggris Dan Terjemahannya Untuk SMPDokument15 SeitenContoh Pidato Bahasa Inggris Dan Terjemahannya Untuk SMPAli Husein SiregarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pemphigus Subtypes Clinical Features Diagnosis andDokument23 SeitenPemphigus Subtypes Clinical Features Diagnosis andAnonymous bdFllrgorzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 39 - Riyadhah Wasyamsi Waduhaha RevDokument13 Seiten39 - Riyadhah Wasyamsi Waduhaha RevZulkarnain Agung100% (18)
- Cambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/31Dokument20 SeitenCambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/31Balachandran PalaniandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ms Cell Theory TestDokument6 SeitenMs Cell Theory Testapi-375761980Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gian Lorenzo BerniniDokument12 SeitenGian Lorenzo BerniniGiulia Galli LavigneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weekly Learning Plan: Department of EducationDokument2 SeitenWeekly Learning Plan: Department of EducationJim SulitNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Does The Scripture Say - ' - Studies in The Function of Scripture in Early Judaism and Christianity, Volume 1 - The Synoptic GospelsDokument149 SeitenWhat Does The Scripture Say - ' - Studies in The Function of Scripture in Early Judaism and Christianity, Volume 1 - The Synoptic GospelsCometa Halley100% (1)
- Baccarat StrategyDokument7 SeitenBaccarat StrategyRenz Mervin Rivera100% (3)
- LabDokument11 SeitenLableonora KrasniqiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Earth and Life Science: Exogenic ProcessesDokument2 SeitenLesson Plan Earth and Life Science: Exogenic ProcessesNuevalyn Quijano FernandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group Process in The Philippine SettingDokument3 SeitenGroup Process in The Philippine Settingthelark50% (2)
- Massage Format..Dokument2 SeitenMassage Format..Anahita Malhan100% (2)
- Simple Linear Regression Analysis: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDokument16 SeitenSimple Linear Regression Analysis: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinNaeem AyazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Catholic Prayer 1Dokument88 SeitenBasic Catholic Prayer 1Josephine PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Read Chapter 4 Minicase: Fondren Publishing, Inc. From The Sales Force Management Textbook by Mark W. Johnston & Greg W. MarshallDokument1 SeiteRead Chapter 4 Minicase: Fondren Publishing, Inc. From The Sales Force Management Textbook by Mark W. Johnston & Greg W. MarshallKJRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virtual Verde Release Plan Emails: Email 1Dokument4 SeitenVirtual Verde Release Plan Emails: Email 1Violet StarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuromarketing EssayDokument3 SeitenNeuromarketing Essayjorge jmzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Michael Parenti - The Demonization of Slobodan MilosevicDokument9 SeitenMichael Parenti - The Demonization of Slobodan MilosevicRicardo Castro Camba100% (1)
- Mod B - HSC EssayDokument11 SeitenMod B - HSC EssayAryan GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRM Project (Oyo)Dokument16 SeitenCRM Project (Oyo)Meenakshi AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Secant Method - Derivation: A. Bracketing MethodsDokument5 SeitenSecant Method - Derivation: A. Bracketing MethodsStephen Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen