Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
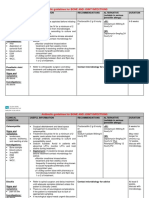
Tumour, Cysts Sinus and Fistula
Hochgeladen von
Afif Aizat0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
44 Ansichten51 SeitenDifferentiation
Originaltitel
Tumour,Cysts Sinus and Fistula
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenDifferentiation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
44 Ansichten51 SeitenTumour, Cysts Sinus and Fistula
Hochgeladen von
Afif AizatDifferentiation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 51
TUMOUR
New growth of cells
Independent growth
Atypically arranged
No function
TUMOUR
BENIGN
lipoma
fibroma
neuroma
papilloma
MALIGNANT
PAPILLOMA
SKIN PAPILLOMA
-Squamous papilloma..soft papilloma
..squamous papilloma
-Basal cell papilloma(seborrhoeic keratosis)
ARISING FROM MUCUOUS
MEMBRANE OF VISCERQAL ORGANS
-Transitional cell papilloma of bladder
-columnar cell papilloma of rectum
-Cuboidal cell papilloma of GB
-Sq papilloma of the larynx
-Papilloma of the breast
FIBROMA
Soft fibroma
Hard fibroma
-Neurofibroma
-Fibrolipoma
-Myofibroma
-Angiofibroma
LIPOMA
Benign tumor fm fat cells of adult type
Types
-Single subcut lipoma
-Multiple lipomatosis
-Uncapsulated lipoma
Histological types
Anatomical types
ANATOMICAL VARIETY OF
LIPOMA
Subcutaneous
Subfascial
Intermuscular
Subsynovial and intra-
articular
parosteal
Submucuous
Subserosal
Extradural
Interglandular
LIPOMA
Usually single
Painless
Slow growing
Soft
Cystic
Pseudofluctuation
Lobular surf
Slipping sign
Freely mobile
COMPLICATIONS OF
LIPOMA
Liposarcoma
-swelling grows rapidly
-painfulnerve infiltration
-red colour with dilated veins
-warm surface
-skin fungation or fixation
-mobility restricted
COMPLICATIONS OF
LIPOMA(cont)
Calcification
Myxomatous degeneration
Intussusception
NEUROMA
TRUE NEUROMA
ganglioneuromasympathetic chain
neuroblastomachildren
myelinic neuromaspinal cord
FALSE NEUROMA
End..cut end of nerve
Lateral.partial injury
NEUROFIBROMA
ARISING FROM CONNECTIVE TISSUE
OF NERVE SHEATH
TYPES OF NEUROFIBROMA
Single subcutaneous neurofibroma
Generalized neurofibromatosis (Von
Recklinghausen disease)
Plexiform neurofibromatosis(Trigeminal)
Elephantiasis neuromatosa
Pachydermatocele
Single subcutaneous
neurofibroma
Tingling and numbness,paraesthesia
Round to oval swelling in the direction of
the nerve
Smooth surface, round border
Consistency firm
Skin can be lifted
Generalized neurofibromatosis
(Von Recklinghausen disease)
Autosomal dominant
Coffee-au-lait spots
Soft and non-tender
NEURILEMMOMA
Arising from Schwann cells
Single or multiple
Fusiform shape
Soft,lobulated,well encapsulated tumours
MALIGNANT TUMORS
CARCINOMA
-ectodermal
-endodermal
-mesodermal
SARCOMA
-mesoblast
-mesenchymal
MALIGNANT TUMORS
AETIOLOGY
DIET
CHEMICALS
-benzanthrenes
-benzopyrenes
-B-naphthylamine
-nitrosamines and
amides
IONIZING RADIATION
ULTRAVIOLET
RADIATION
VIRAL FACTORS
DNAHPV,EB
RNAHTLV-1
HABITS
-Smoking
-Alcohol
CYSTIC SWELLINGS
IT IS A SWELLING LINED BY
EPITHELIUM OR ENDOTHELIUM
CONTAINING SEROUS FLUID,
MUCOID MATERIAL, PUS,
BLOOD,LYMPH OR PULTACEOUS
MATERIAL.
CLASSIFICATION OFCYSTIC
SWELLINGS
CONGENITAL
ACQUIRED
PARASITIC
CLASSIFICATION
CONGENITAL
-Sequestration
dermoid cyst
-Branchial cyst
-Thyroglossal cyst
-Lymphangioma
-Embryonic remnant
cyst
ACQUIRED
-Retension
-Exudation
-Distension
-Cystic tumors
-Traumatic
PARASITIC
-Hydatid
CLINICAL FEATURES
LOCATION
SHAPE
SURFACE
CONSISTENCY
FLUCTUATION
TRANSILLUMINATI
ON
MOBILITY
PLANE OF SWELLING
COMPRESSIBILITY
(Sign of refilling)
PULSATION
-expansile
-transmitted
PRESSURE EFFECT
-bone
-nerve
Compressible swelling
Haemangioma
Lymphangioma
Meningocoele
Salient features of aneurysm
Expansile pulsation
Proximal compression.size decrease
Distal compression.size increases
Thrill and Bruit
Distal pulses weak
COMPLICATION OF CYSTS
Infection
Calcification
Pressure effects
Malignant transformation
DERMOID CYST
Cyst containing desquamated cells lined by
squamous epithelium whose contents are
thick and viscid , appearing like toothpaste
which is a mixture of sweat, sebum,
desquamated cells and sometimes even hair.
CLASSIFICATION
Congenital/Sequestration Dermoid
Implantation Dermoid
Teratomatous Dermoid
Tubulo-embryonic dermoid
CONGENITAL
/SEQUESTRATION DERMOID
CYST
Occurs in the line of embryonic fusion
As the cyst grows it indents the mesoderm
(future bone)..explains the defect in the
bony structure
Occur any where in the midline of the body
CONGENITAL
/SEQUESTRATION DERMOID
CYST(cont)
External and internal angular dermoid
Median nasal dermoid
Sublingual dermoid
Suprasternal space of Burns
Pre/Post auricular dermoid
CONGENITAL
/SEQUESTRATION DERMOID
CYST(cont)
Manifest chilhood or adolescene
Painless ,slow growing swelling
Location of the cyst typically at the line of
fusion
Soft, cystic and fluctuant with negative
transillumination
Underlying bony defect
SEBACEOUS CYST
Also called as epidermoid cyst
Occurs due to blockage of the sebaceous
duct
SEBACEOUS CYST(cont)
Slow growing , early childhood
Does not occur in palm and sole
Punctumkeratin filled duct
Sign of moulding
Sign of indentation
Smooth surface, soft, non-tender,putty consistency
Pressure effect in the scalp loss of hair
COMPLICATIONS OF
SEBACEOUS CYST(cont)
Infection
Sebaceous hornslow drying of contents
after squeezing
Cocks peculiar tumorrefers to infected,
ulcerated cyst of the scalp with pouting
granulation tissue with everted edges
Calcification
BCC
GANGLION
Tensely cystic swelling due to myxomatous
degenerationof the synovial sheathllining
the joint /tendon sheath containing
gelatinous fluid
Location - scapholunate articulation
- flexor aspect of finger
GANGLION(cont)
Round to oval swelling, smooth surface well
defined borders
Tensely cystic, fluctuation and transillumination
negative
Mobility restricted when tendon put in contraction
Not connected to joint space
Becomes smallerdissapears between bones
GANGLION(cont)
Best left alone if asymptomatic
Aspiration and inj of sclerosant
Surgical excision but recurrance rate is high
GLOMUS TUMOUR
Glomangioma
Abundant AV anastomosis surrounded by
clear cells.glomus cellsand
non/medullated nerve fibresbetween the
cells
GLOMUS TUMOUR(cont)
Benign
Most painful either at rest or
movement.compression of nerve by dilated
blood vessels
5
th
decade
Location nail bed of hands and feet
Single, purple-red in colour, <1cm
D/D subungual haematoma
Surgical excision
BURSA
Sac or sac like cavity lined by endothelium
containing fluid
Function to reduce friction bet tendons &
bone
Inflammation.bursitis
Causes -constant pressure
-constant irritation
-minor trauma
EXAMPLES OF BURSITIS
Prepatellar bursa
Infrapatellar bursa
Olecranon bursa
Under insertion of
gracilis,sartorius,
semitendinosus
-housemaids knee
-clergymans knee
-students elbow
-Bursitis anserina
CLINICAL FEATURES OF
BURSITIS
A cystic swelling in an anatomical site of a
bursa is a chronic bursitis unless proven
otherwise
Soft,cystic circumscribed or oval swelling,
fluctuation positive but most often negative
due to inflammatory exudate
Signs of inflammation
SEMIMEMBRANOUS BURSA
VS BAKERS CYST
SM BURSA BAKERS CYST
AETIO Friction/pressure Rh/osteoarthritis
AGE Young Middle age
SEMIMEMBRANOUS BURSA
VS BAKERS CYST
LOCATION Higher&med Below&lat
FLEX KNEE Disappears Increases
EXT KNEE Appears Decreases
PATELLAR
TAP
_ +
COMPRESS. _ + (partially)
KNEE MOV Normal Restricted
TRANSILLUMINANT
SWELLING IN THE BODY
Ranula
Lymphangioma
Meningocele
Epididymal cyst
Hydrocele
RULES OF
TRANILLUMINATION TEST
DONE IN DARK SURROUNDING
AVOID SURFACE
TRANSILLUMINATION
MAYBE NEG.INFECTION,
HAEMORRHAGE/SCLEROTHERAPHY
FISTULA
An abnormal communication bet lumen of
one viscus and lumen of another (internal)
or communication of one hollow viscus and
with the exterior (body surface)
CLASSIFICATION OF
FISTULA
INTERNAL
Tracheo-oesophageal
fistula
Colovesical fistula
EXTERNAL
Thyroglossal fistula
Branchial fistula
Orocut fistula
SINUS
Blind track leading from the surface down
into the tissue lined by granulation tissue
CLASSIFICATION OF SINUS
CONGENITAL
Preauricular sinus
ACQUIRED
Median mental sinus
Tubercular sinus
Osteomylitis
Pilonidal sinus
PERSISTANCE OF SINUS
AND FISTULA
Foreign body
Infection
Epitheliasation of tract
Distal obstruction
Non-dependant drainage
Malignancy
Absence of rest
EXAMINATION OF SINUS
AND FISTULA
LOCATION
NUMBER
OPENING
-Sprouting granulation tissue
-Flush with skin
DISCHARGE
SURROUNDING SKIN
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- How To ForgiveDokument3 SeitenHow To ForgiveAnonymous 0PYZofvGSNoch keine Bewertungen
- 215 PDFDokument7 Seiten215 PDFlewamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Msif Atlas of Ms 2013 ReportDokument28 SeitenMsif Atlas of Ms 2013 ReporttomrehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stainless Steel Crown in Clinical Pedodontics - A ReviewDokument5 SeitenStainless Steel Crown in Clinical Pedodontics - A ReviewmztahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Benefit ListDokument221 SeitenDrug Benefit ListPharmaruthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACM812 Ventilator - ASCFDokument1 SeiteACM812 Ventilator - ASCFMoussa ToudjaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- SWS Bibliography1Dokument3 SeitenSWS Bibliography1Valaki MimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AbDokument5 SeitenAbapi-466413302Noch keine Bewertungen
- SMBS GradesDokument8 SeitenSMBS GradestinuvalsapaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health As Expanding ConsciousnessDokument8 SeitenHealth As Expanding ConsciousnessJun ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotic Guidelines For BONE AND JOINT INFECTIONSDokument3 SeitenAntibiotic Guidelines For BONE AND JOINT INFECTIONSKhurram NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- SchezophreniaDokument22 SeitenSchezophreniaxion_mew2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Presented By: Bhagyashree KaleDokument58 SeitenPresented By: Bhagyashree KaleSupriya JajnurkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCAI Shock Classification DeckDokument22 SeitenSCAI Shock Classification DeckJimmy JimmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MedsDokument2 SeitenMedsRuel MaddawinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 365 STRONG Eat Like A BodybuilderDokument10 Seiten365 STRONG Eat Like A BodybuilderSlevin_KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Vascular Disorders and Problems of Peripheral CirculationDokument45 SeitenAssessment and Management of Patients With Vascular Disorders and Problems of Peripheral CirculationCarlos RiosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam LecturesDokument329 SeitenFinal Exam LecturesBrettSkillettNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neem TreeDokument4 SeitenNeem Treedorzky22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Poster ISCP10 Final Daft CWCDokument1 SeitePoster ISCP10 Final Daft CWCVizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Etiopathogenesis & Staging of Cancer BreastDokument25 SeitenEtiopathogenesis & Staging of Cancer Breastapi-3701915Noch keine Bewertungen
- TCM Review SmallDokument57 SeitenTCM Review Smallpeter911cm100% (7)
- VAP in ChildrenDokument19 SeitenVAP in Childrensiekasmat upaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malunion Delayed Union and Nonunion FracturesDokument31 SeitenMalunion Delayed Union and Nonunion FracturesutisuryanjNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Japanese GMP Regulations 2003Dokument46 SeitenThe Japanese GMP Regulations 2003John LyallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaemia: by Swaathi R Final Year MbbsDokument33 SeitenAnaemia: by Swaathi R Final Year MbbsGopi NathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Byssinosis PDFDokument8 SeitenByssinosis PDFFaza AlhinduwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tesis vITAMIN C CONTENT IN FRUITSDokument24 SeitenTesis vITAMIN C CONTENT IN FRUITSHema JothyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijmrhs Vol 3 Issue 1Dokument228 SeitenIjmrhs Vol 3 Issue 1editorijmrhsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Asthma in Adults (Second Edition) : November 2017 Moh/P/Pak/Xxx (Gu)Dokument64 SeitenManagement of Asthma in Adults (Second Edition) : November 2017 Moh/P/Pak/Xxx (Gu)Shamsyul IqramNoch keine Bewertungen