Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Anti Tuberculosis Agents
Hochgeladen von
ejg26Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Anti Tuberculosis Agents
Hochgeladen von
ejg26Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
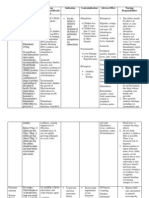
ANTI-TUBERCULOSIS
DRUGS
Action: appears to inhibit RNA synthesis,
thus
stops tubercle bacilli from multiplying
(first line) or functioning (second line)
LINES OF DEFENSE
First line Second line
Isoniazid (INH) Cycloserin
Rifampicin (Rifadin) Kanamycin
Ethambutol Ethonamide
Pyrazinamide Para-aminosalicylic acid
Streptomycin
Stuff to Remember:
active tuberculosis are treated
with drug combination for 6-9 mos.
multidrug-resistant strain
(MDRTB) are medicated for 1 year
up to2 years
given before meals
Isoniazide
should be given 1 hr before or 2 hrs
after meals because food may delay
absorption.
should be given at least 1 hr before antacids.
instruct to notify physician for signs of
hepatoxicity (jaundice), and neurotoxicity
numbness of extremities.
administer with Vitamin B6 to
counteract the neurotoxic side effects.
avoid alcohol.
Suppresses mycobacterial cell-wall synthesis
Rifampicin
given on an empty stomach with 8 0z. of
water, 1 hour before or 2hours after
meals and avoid taking antacids with
medications.
hepatotoxic thus avoid alcohol.
instruct the client that urine, feces,
sweat, and tears will be red
orange in color.
Pyrazinamide
given for 2 months.
increase serum uric acid and cause
photosensitivity.
Ethambutol
contraindicated in children under 13
years old.
obtain a baseline visual acuity because
it can cause optic neuritis.
Instruct the client to notify the physician
immediately if any visual problems
occurs.
Decreases mycobacterial RNA synthesis
Streptomycin
aminoglycoside antibiotic given IM.
nephrotoxic and ototoxic.
obtain baseline
audiometric test and repeat every 1-
2 months because the medications
impairs the CN VIII.
Adverse Effects
gastric irritation
CNS disturbances
liver disturbances
blood dyscrasias
Rifampicin Hepatotoxicity, Discoloration
of bodily fluids
Streptomycin - ototoxicity
Ethambutol - visual disturbances
Isoniazid - Liver Toxicity, Peripheral
Neuropathy due to suppressed absorption
of fat and vitamin B complex
Nursing Interventions
monitor client response to therapy
monitor blood work during therapy
if CNS disturbances are evident, take safety
precautions
teach client
to take medication as ordered
to eat foods rich in B-complex vitamins
avoid use of alcohol
report if become pregnant
ethambutol: report eye problems, have
regulareye exams
Just know your R.I.P.E.S!!!!
Antihypertensive Drugs
Action: dilates peripheral blood vessels
5 Major Types: ACE Inhibitor &
Angiotensin antagonists
Beta - blockers
Calcium channel blockers
Diuretics
Examples:
Hydralazine HCL (Apresoline)
Enalapril maleate (Vasotec)
Reserpine (Serpasil)
Prazosin HCL (Minipress)
Methyldopa (Aldomet)
Clonidine (Catapress)
Adverse Side Effects
orthostatic hypotension
dizziness
bradycardia
tachycardia
sexual dysfunction
deterioration in renal function
agranulosis
Nursing Interventions
monitor vital signs and blood pressure, sitting
and standing
monitor for hearing changes, renal functioning
if hypotension, closely monitor client
encourage intake of foods high in vitamin B
Teach client:
- low sodium diet
- change positions slowly
- take medication as instructed
- avoid hazardous activities
- protect medication from heat and light
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Anti-Tuberculosis AgentsDokument15 SeitenAnti-Tuberculosis AgentsNick van ExelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug 25Dokument17 SeitenDrug 25carol_gigliotti24100% (1)
- Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]Von EverandBasic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Drug Study (GBS)Dokument16 SeitenDrug Study (GBS)Mary Rose Verzosa LuisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument9 SeitenDrug StudyShane Arroyo100% (1)
- DrugsDokument13 SeitenDrugsJune DumdumayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesVon EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisDokument19 SeitenDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alert Medical Series: Emergency Medicine Alert I, II, IIIVon EverandAlert Medical Series: Emergency Medicine Alert I, II, IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology Review For NursesDokument11 SeitenPharmacology Review For Nursesisabel_avancena100% (4)
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Von EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- DRUg StudyDokument11 SeitenDRUg StudyKathNoch keine Bewertungen
- IsoniazidDokument2 SeitenIsoniazidMichael Kuzbyt100% (1)
- Drug RationaleDokument77 SeitenDrug RationaleYolanda WilliamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs NclexDokument30 SeitenDrugs Nclexawuahboh100% (1)
- Topic 2.1: Antibiotics: Unit 2: Anti-Infective MedicationsDokument50 SeitenTopic 2.1: Antibiotics: Unit 2: Anti-Infective MedicationsNirali ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEEK2 Course Task (ALFEREZ, DINIELA)Dokument4 SeitenWEEK2 Course Task (ALFEREZ, DINIELA)DINIELA ALLAINE ALFEREZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument7 SeitenDrug StudyDiana Laura LeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pedia Ward Drug Study...Dokument12 SeitenPedia Ward Drug Study...Sheena Arnoco ToraynoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenDrug StudyGail SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dosage: Route:: Mycobacterium TuberculosisDokument21 SeitenDosage: Route:: Mycobacterium TuberculosisLyn ConsingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology HESI ReviewDokument13 SeitenPharmacology HESI Reviewhkw0006164% (11)
- Course Task 2Dokument2 SeitenCourse Task 2John Elton TangpuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Case PresentationDokument5 SeitenDrug Study Case PresentationRobert MedinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotics.: Prepared by L.Mbise OCTOBER 2012Dokument40 SeitenAntibiotics.: Prepared by L.Mbise OCTOBER 2012Moses MberwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Comprehensive Resource For Physicians, Drug and IllnessinformationDokument6 SeitenThe Comprehensive Resource For Physicians, Drug and IllnessinformationEdward ElricNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Study, Nursing, PreoperativeDokument9 SeitenDrugs Study, Nursing, PreoperativeKevin Sam AguirreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument7 SeitenDrug StudyKynaWeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Pharmacology Handouts For ZamboDokument7 SeitenNursing Pharmacology Handouts For ZamboAlexa Abidin Oldenborg100% (8)
- Nursing Drug CardsDokument32 SeitenNursing Drug CardsJenna Rasmussen100% (3)
- Drug StudyDokument6 SeitenDrug StudyChickz HunterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Drugs StudyDokument13 SeitenComplete Drugs StudyPeace Andong PerochoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHARMA BulletsDokument6 SeitenPHARMA BulletsRhea Anne VeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study HydralazineDokument10 SeitenDrug Study HydralazineLuige AvilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineDokument8 SeitenDrug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineAiryn CanonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument10 SeitenDrug StudyRye IbarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETHAMBUTOLDokument2 SeitenETHAMBUTOLXerxes DejitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology CaptoprilDokument14 SeitenPharmacology Captoprildalilaarshad31Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nclex NotesDokument67 SeitenNclex Notesjanet roosevelt94% (65)
- Drug Name Classification and Mechanism of Action Indication/ Dosage/ Route Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing InterventionsDokument6 SeitenDrug Name Classification and Mechanism of Action Indication/ Dosage/ Route Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing InterventionsVin LandichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RX - Citicoline, Kalium, Ketosteril, Methycobal, Myonal, Lipolin GelDokument6 SeitenRX - Citicoline, Kalium, Ketosteril, Methycobal, Myonal, Lipolin GelntootNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study ArvinDokument6 SeitenDrug Study ArvinArvin BeltranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aubrey Rose A. Vidon September 20, 2020 BSN 3Y1 - 2 Unit Task #4Dokument12 SeitenAubrey Rose A. Vidon September 20, 2020 BSN 3Y1 - 2 Unit Task #4AriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDokument15 SeitenDrug Study On Emergency DrugsDennise Juayang100% (1)
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDokument15 SeitenDrug Study On Emergency DrugsJAy TootNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument9 SeitenDrug StudyEzshkha OngueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular SystemDokument4 SeitenCardiovascular SystemRegineCuasSulibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency DrugsDokument15 SeitenEmergency Drugsjheverly123100% (1)
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDokument16 SeitenDrug Study On Emergency DrugsJosepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Albendazole Information From DrugsDokument4 SeitenComplete Albendazole Information From DrugselephantynoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teachng DemoDokument32 SeitenTeachng DemoNom NomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lisinopril PDFDokument3 SeitenLisinopril PDFHannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antineoplastic Agents ReportDokument3 SeitenAntineoplastic Agents ReportMegan Rose MontillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name of Drug Route/Dose Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects/Adverse Reactions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokument9 SeitenName of Drug Route/Dose Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects/Adverse Reactions Nursing ResponsibilitiespauchanmnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ranitidine Tramadol Ketorolac Ampicillin Paracetamol Drug StudyDokument10 SeitenRanitidine Tramadol Ketorolac Ampicillin Paracetamol Drug StudyMarco MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Honda Accord 95Dokument2 SeitenHonda Accord 95ejg26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case StudyDokument2 SeitenCase Studyejg26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Facebook or Facing Your BookDokument2 SeitenFacebook or Facing Your Bookejg26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chain of InfectionDokument2 SeitenChain of Infectionejg26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Theresa J. Llanes: ObjectiveDokument2 SeitenTheresa J. Llanes: Objectiveejg26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Health Center: Organizational Chart Ampid 1 San Mateo, RizalDokument1 SeiteHealth Center: Organizational Chart Ampid 1 San Mateo, Rizalejg26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Freuds Psychosexual Stages of Development Oral StageDokument8 SeitenFreuds Psychosexual Stages of Development Oral Stageejg26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Empire of The Sun Soc 18Dokument3 SeitenEmpire of The Sun Soc 18ejg26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dopa DobuDokument2 SeitenDopa Dobuejg26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Movie Reports DutyVLDokument9 SeitenMovie Reports DutyVLejg26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Purposes of SurgeryDokument2 SeitenPurposes of Surgeryejg26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aaron Learning InsightsDokument1 SeiteAaron Learning Insightsejg26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Intake and Output Monitoring Sheet: Date TimeDokument3 SeitenIntake and Output Monitoring Sheet: Date Timeejg26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Report Sa Informatics!Dokument13 SeitenReport Sa Informatics!ejg26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rarejob Endorsement Letter For BpiDokument1 SeiteRarejob Endorsement Letter For Bpiejg26100% (2)
- Ketorolac Drug StudyDokument1 SeiteKetorolac Drug Studyejg26Noch keine Bewertungen
- QuizDokument2 SeitenQuizejg26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Informatics in CanadaDokument25 SeitenNursing Informatics in Canadaejg26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Roosevelt College System Institute of Nursing and Health Education Sumulong Highway Cainta, RizalDokument2 SeitenRoosevelt College System Institute of Nursing and Health Education Sumulong Highway Cainta, Rizalejg26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Roosevelt College System Institute of Nursing and Health Education Sumulong Highway Cainta, RizalDokument1 SeiteRoosevelt College System Institute of Nursing and Health Education Sumulong Highway Cainta, Rizalejg26Noch keine Bewertungen
- FNCP Health Center ChartDokument1 SeiteFNCP Health Center Chartejg26Noch keine Bewertungen
- FNCP Barangay ChartDokument1 SeiteFNCP Barangay Chartejg26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tuberculosis DrugsDokument136 SeitenTuberculosis DrugsSyed Gulshan NaqviNoch keine Bewertungen
- DERMA SPMC LeprosyDokument9 SeitenDERMA SPMC LeprosyNicole Alexandra KhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotics - Classification & Mode of Action PDFDokument8 SeitenAntibiotics - Classification & Mode of Action PDFtarun paulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teachng DemoDokument32 SeitenTeachng DemoNom NomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tuberculosis of The Urogenital TractDokument3 SeitenTuberculosis of The Urogenital TractIan HuangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Report-2016-17 Novartis India LimitedDokument139 SeitenAnnual Report-2016-17 Novartis India LimitedNitin JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rifamycin - General InformationDokument4 SeitenRifamycin - General InformationRachelle Anne LetranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology MidtermDokument27 SeitenPharmacology Midtermnaomie manaliliNoch keine Bewertungen
- WHO - WHO To Publish First Official Guidelines On Leprosy Diagnosis, Treatment and PreventionDokument5 SeitenWHO - WHO To Publish First Official Guidelines On Leprosy Diagnosis, Treatment and PreventionSari RiastiningsihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Complex in ChildrenDokument1 SeitePrimary Complex in ChildrenMae Novelle EspinosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pretomanid Treatment For TuberculosisDokument7 SeitenPretomanid Treatment For TuberculosisHeryanti PusparisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Interactions Checker - Medscape Drug Reference DatabaseDokument9 SeitenDrug Interactions Checker - Medscape Drug Reference DatabaseDewi AryaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety and Side Effects of RifampinDokument10 SeitenSafety and Side Effects of RifampinbagusNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.5 PHARMA ANTI MYCOBACTERIAL AGENTSpdfDokument18 Seiten3.5 PHARMA ANTI MYCOBACTERIAL AGENTSpdfJanet SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- SNC TuberculosisDokument19 SeitenSNC TuberculosisFabricio NuñezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dermatologic PharmacologyDokument88 SeitenDermatologic PharmacologyAlunaficha Melody KiraniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atmaja Sirupang-Journal Reading MHDokument9 SeitenAtmaja Sirupang-Journal Reading MHAtmaja R. SirupangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti TB DrugsDokument23 SeitenAnti TB DrugsAbiHa YousaufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology Antimycobacterial DrugsDokument9 SeitenPharmacology Antimycobacterial Drugsroyce charlieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On RNTCP GuidelinesDokument35 SeitenPresentation On RNTCP Guidelinesvarshasharma05Noch keine Bewertungen
- TuberculosisDokument16 SeitenTuberculosiswiwonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Report: Supevisor: Dr. Irma Tarida Listiawati, SP - KK By: Alif Ramadhan, S.KedDokument22 SeitenCase Report: Supevisor: Dr. Irma Tarida Listiawati, SP - KK By: Alif Ramadhan, S.Kedpang_paangNoch keine Bewertungen
- O/dr - Ririn FK UnilaDokument29 SeitenO/dr - Ririn FK UnilaNyimas Annissa Mutiara Andini100% (1)
- AttbDokument6 SeitenAttbmuiz_travxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antituberculous Drugs - An Overview - UpToDateDokument21 SeitenAntituberculous Drugs - An Overview - UpToDateBryan Tam ArevaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Antibiotics in Orthopedic InfectionsDokument31 SeitenRole of Antibiotics in Orthopedic InfectionsRakesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti TBDokument68 SeitenAnti TBGunjan YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument7 SeitenDrug StudysarahtotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pott's DiseaseDokument8 SeitenPott's DiseaseBij HilarioNoch keine Bewertungen




![Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/475660044/149x198/2c7fc45015/1691161640?v=1)