Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Human Reproduction System 2
Hochgeladen von
Conan Bagus EdogawaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Human Reproduction System 2
Hochgeladen von
Conan Bagus EdogawaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
HUMAN REPRODUCTION
Subject: Biology
What is the aim of reproduction ?
Introduction
Key Concepts
Human reproductive system consists of:
Primary reproductive organs (gonad)
Accessory glands
Ducts
Testes are male gonad, to produce sperm
Ovaries are female gonad, to produce egg
Gonads release sex hormones that control
reproductive function & development of secondary
sexual traits
The hormones are testosteron, LH, and FSH control
reproductive function
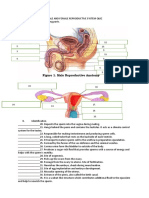
Male Reproduction
Consits:
1. Testis (gonad)
2. Ducts
3. Glands
4. Penis
Organs and accessory glands of
male reproductive tract
Reproductive organs:
Testis (2) : Production of sperm, sex hormone
Epididymis (2) : Sperm maturation site & sperm storage
Vas Deferens (2) : rapid transport of sperm
Ejaculatory duct (2) : Conduction of sperm to penis
Penis : organ of sexual intercourse
Accessory glans
Seminal vesicle (2) : secretion of large part of semen
Prostate gland : secretion of part of semen
Bulbourethral gland (2) : production of lubricating mucus
Testis
Function:
Produce spermatozoa
Produce sex hormone
Testis Structure
Shape: oval
Location: in scrotum
Complex tubular gland
Covered by a capsule
Devided into some lobules
each testis has 250 lobes
Each lobes has some
seminiferus tubules
Seminiferus tubules
Function:
Produce spermatozoa
Leydig cell:
Secrete testosteron (a steroid hormone)
Testosteron:
Central to the growth, form, and function of the
reproductive tract in males
Main role in sperm formation
Stimulates sexual & aggresive behavior
Control the development of secondary sexual
traits
Tubulus seminiferus
Leydig cells between tubules
Sperm Formation
Sperm formation. The process starts with a spermatogonium (a diploid germ cell)
Mitosis, meiosis, as well as incomplete cytoplasmic divisions result in a clone of
Immature haploid cells thet differentiate and develop into mature sperm)
SPERM structure
Consists:
head
neck
tail
Hormones Control
reproduction mechanism
LH: Luteinizing hormone
FSH: Folicle-stimulating hormone
Male reproductive function is
governed by coordinated secretion
of LH (lutenizing hormone), FSH
(follicle-stimulating hormone)
and testosterone. The region of
the brain called the hypothalamus
controls the secretion of these
hormones through a negative
feedback mechanism
Testosterone levels are maintained at
the proper levels for sperm production
by negative feedback loops to the
hypothalamus and pituitary gland from
the testes.
EPIDIDYMIS
PROSTAT
BULBOURETHRALIS
PENIS
consists 3 parts
skin/ cutis
corpus cavernosum
urethra
Penis Structure
Female Reproduction
Consists:
1. Ovary
2. Fallopian tube /
oviduct
1. Uterus
2. Vagina
3. Vulva
4. Mammae gland
Position of the female
reproductive organ
Female reproductive organ
Ovaries : Oocyte production and maturation, sex hormone
production
Oviducts : Ducts for conducting oocyte from ovary to uterus;
fertilization normally occurs here
Uterus : Chamber in which new individual develops
Cervix : Secretion of mucus that enhances sperm movement
into uterus and (after fertilization) reduces
embryos risk of bacterial infection
Vagina : Organ of sexual intercourse; birth canal
Female Reproduction System
1. OVARY
Structure
a paire
Shape: Ovale
Position : in the peritoneum
cavity
Supported by ligaments
Contains: follicle to produce
egg
Egg formation
Ovum formation
Secodary follicel
Tertier follicle
Feedback control of
hormonal secretion during a
menstrual cycle
A positive feedback loop from
An ovary to the hypothalamus
Causes a surge in LH secxretion.
The surge triggers ovulation.
The light micrograph shows
a secondary oocyte being
released from an ovary at this time.
Afterward, negative feedback
loops to the hypothalamus and
Pituitary inhibit FSH secretion.
They prevent another follicle from
maturing until the cycle is
completed
Menstrual cycle
Changes in the blood levels of hormones during the menstrual cycle. FSH and
LH are produced by the anterior pituitary; estrogen and progesterone are
produced by cells in the ovaries.
The menstrual cycle is governed by feedback loops between hypothalamus, anterior pituitary, and
ovaries. Early in the cycle, FSH and LH stimulate the growth of a folliclea primary oocyte and its
surrounding layer of cellsin an ovary. A mid-cycle surge of LH triggers ovulation. Early on,
estrogens call for endometrial repair and growth. Then, estrogens and progesterone prepare the
endometrium and other parts of the reproductive tract for pregnancy.
Menstrual cycle
A human females menstrual cycle lasts about twenty-eight days, on
average. The cycle is divided into three distinct phases.
Controling the
female
reproductiuon by
hormones system
Fertilization
Fertilization
Many sperm surround a secondary oocyte. The penetration of the zona
pellucida by one sperm stimulates the granules in the egg cortex to
release substances that prevent other sperm from entering. It also
stimulates meiosis II in the secondary oocyte and first polar body.
Fertization & zygote
development
Fertization & zygote
development
Featus
Mammae Gland
Milk Production Physiology
Reproduction control system
Quiz
Mention part of the reproductive organ below, and explain their
functions
b
a
c
d
e
f
g
h
i
j
k
l
Quiz
Mention part of the reproductive organ below, and explain their
functions
b
a
c
d
e
f
g
i j
k
l
k
l
m
n
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- DLP - Biology F4 - Answers - Chap 15 (Final)Dokument5 SeitenDLP - Biology F4 - Answers - Chap 15 (Final)JOSRIYN RATHNA A/P THAVARAJAN MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hormonal Control of GametogenesisDokument37 SeitenHormonal Control of GametogenesisZeneishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALWAYS REMEMBER GOD KNOWS YOUR THOUGHTSDokument35 SeitenALWAYS REMEMBER GOD KNOWS YOUR THOUGHTSDOUGLAS KIPRUTONoch keine Bewertungen
- Key to Understanding Reproductive SystemsDokument7 SeitenKey to Understanding Reproductive SystemsHAZEL JANE BAGUIONoch keine Bewertungen
- Pelvic Exam PDFDokument2 SeitenPelvic Exam PDFRosu GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Puberty/Reproductive Systems PowerpointDokument16 SeitenPuberty/Reproductive Systems Powerpointdnorton5437100% (1)
- The Female Reproductive SystemDokument16 SeitenThe Female Reproductive SystemLovie dovieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 Module 1 The Menstrual CycleDokument20 SeitenUnit 3 Module 1 The Menstrual CycleMARIANNE SORIANO100% (2)
- Different Forms of Infertility in MaleDokument36 SeitenDifferent Forms of Infertility in MaleSheikh QasimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Study Guide on Reproductive DevelopmentDokument5 SeitenStudent Study Guide on Reproductive DevelopmentKaye Zelen LautaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Male and Female Reproductive System QuizDokument2 SeitenMale and Female Reproductive System QuizMarife GuadalupeNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR Puppo Clin Anat 2014 Anatomy of SexDokument12 SeitenDR Puppo Clin Anat 2014 Anatomy of SexbrylanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Female Genital MutilationDokument14 SeitenFemale Genital MutilationNatukunda DianahNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Female Reproductive SystemDokument22 SeitenThe Female Reproductive SystemAnisatul Khabibah ZaenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For Basic Medical Language 6th Edition by BrooksDokument13 SeitenTest Bank For Basic Medical Language 6th Edition by BrooksLisaBowersfbzm100% (27)
- Squirting Orgasm SecretsDokument13 SeitenSquirting Orgasm SecretsUser UnknownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan 2020-2021Dokument7 SeitenLesson Plan 2020-2021MELIE BAGARESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theme Park PortfolioDokument10 SeitenTheme Park Portfolioapi-546170588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reproductive Cycles in MammalsDokument9 SeitenReproductive Cycles in MammalsSeemal shahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Sexuality: Mohammad FananiDokument54 SeitenHuman Sexuality: Mohammad FananiPutri AprilianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vaginismus A Review of The Literature On The Classification Diagnosis, Etiology and Treatment TranslateDokument14 SeitenVaginismus A Review of The Literature On The Classification Diagnosis, Etiology and Treatment TranslateErliana FaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCIENCE 10 - Quiz 1 - Male ReproductiveDokument1 SeiteSCIENCE 10 - Quiz 1 - Male ReproductiveJessa Tirambulo0% (1)
- Male GenitalsDokument29 SeitenMale Genitalssunielgowda100% (1)
- Sample ModuleDokument2 SeitenSample Modulerowena jumao-asNoch keine Bewertungen
- WORKSHEET 13.2 Formation of Male Gametes (Spermatogenesis)Dokument2 SeitenWORKSHEET 13.2 Formation of Male Gametes (Spermatogenesis)HUSNA 83100% (1)
- Efektivitas Berbagai Konsentrasi Laktosa Dalam Pengencer Tris Terhadap Viabilitas Semen Cair Kambing SaanenDokument8 SeitenEfektivitas Berbagai Konsentrasi Laktosa Dalam Pengencer Tris Terhadap Viabilitas Semen Cair Kambing Saanenachmad setiyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pubertal Development: Question FDokument19 SeitenPubertal Development: Question FHARPREETNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of Female Internal Genital OrganDokument18 SeitenAnatomy of Female Internal Genital OrganVandana Liju Dev VasudevanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Menstrual Cycle PhasesDokument2 SeitenMenstrual Cycle PhasesPatricia G ChiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rre Grade 5Dokument14 SeitenRre Grade 5Liezl Joy Eslao DudangNoch keine Bewertungen