Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
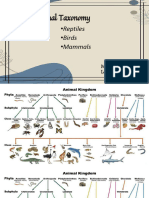
Amphibians: Class Amphibia
Hochgeladen von
Sakalus WepeOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Amphibians: Class Amphibia
Hochgeladen von
Sakalus WepeCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Amphibians
Class Amphibia
Amphibians
Animals that can live on land and in water
Chinese Giant Salamander
Amphibians
First animals with four limbs
Tetrapods: vertebrates that have four
limbs.
Acanthostega
Found in 360 million year-old rocks in
Greenland
Had lungs and eight-toed legs, but also
had gills and a lateral line system.
Fish to Amphibian Transition
Adaptations
help amphibians live on land
Large shoulder and
hip bones help
support more weight.
Adaptations
Interlocking projections on the vertebrae
help keep the backbone from twisting and
sagging.
Adaptations
Mobile, muscular tongue allows
amphibians to capture and manipulate
food.
Adaptations
Development of a
middle ear help some
amphibians hear out
of water.
Adaptations
Breathe through the
skin or with the use of
gills or lungs
Adaptations
Amphibians have a three-chambered heart
Amphibians return to the water to
reproduce
Eggs do not have
shells
Strategies to keep eggs wet:
Laying eggs directly in water
Laying eggs on moist ground
Wrapping eggs in leaves
Brooding eggs in pockets on the females
back
Pygmy Marsupial Frog
Flectonotus pygmaeus
Tadpoles
Some frogs start as tadpoles
Have gills and a broad-finned tail
Amphibian Metamorphosis
Change in form and habits of an animal
It affects nearly every organ in the
tadpoles body
Tadpole into Adult Frog
Gills are reabsorbed and lungs develop
Circulatory system is reorganized to send
blood to the lungs
Tail fin is reabsorbed
Tadpole into Adult Frog
Body grows limbs and completely
reorganizes its skeleton, muscles, and
parts of the nervous system.
Digestive system is rebuilt to handle a
carnivorous diet.
Three Groups of Modern
Amphibians
Salamanders
Frogs
Caecilians
Salamanders
More than 300
species
Long body
Four walking limbs
tail
Salamanders
Walk with a side-to-side movement that
may be similar to ancient tetrapods
The largest family of salamanders do not
have lungs, so they exchange gases
through the lining of their skin and mouth.
Family Plethodontidae
Lungless salamanders
Most common kind
Salamanders
Larvae and adults are carnivores
Invertebrates Vertebrates
Insects Fish
Worms Frogs
Snails
Frogs
Over 3000 species
Largest group of living amphibians
Adult Frogs
Tailless bodies
Long, muscular hind limbs
Webbed feet
Exposed eardrums
Bulging eyes
Adult Frogs
Bodies adapted for jumping
Elongated bones in their hips, legs and feet
for increased speed and power
Hind legs have fused bones that absorb the
shock of landing
Toads
One family of frogs
Rougher, bumpier
skin
Shorter legs- not
good jumpers
Glands make toxins
that protect them from
predators also in
tropical frogs
Frogs
Live in every
environment on Earth
except at the poles
and the driest
deserts.
Caecilians
Legless, burrowing amphibians
Live in the tropics, such as South America
Caecilians
160 species
Range from 4 inches
to 5 feet
Banded bodies that
make them look like
giant earthworms
Caecilians
Are predators
Search for earthworms
and grubs
Have no arms or legs for
burrowing, so have to
move like an earthworm.
Use hydrostatic skeleton
to stiffen its body and
drive its head forward like
a battering ram.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Amphibians: Class AmphibiaDokument33 SeitenAmphibians: Class Amphibiaisfi farihaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AmphibiansDokument34 SeitenAmphibiansMuhammad Fuad MuhsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolutiontoDokument25 SeitenSolutiontoJJ RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata-2Dokument68 SeitenKingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata-2api-285078865Noch keine Bewertungen
- ReptilesDokument34 SeitenReptilesZevannayasmineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 32: Reptiles and BirdsDokument69 SeitenChapter 32: Reptiles and BirdsRaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- REPTILESDokument52 SeitenREPTILESBerces BelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amphibians - E-LearningDokument83 SeitenAmphibians - E-LearningJustyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class ReptiliaDokument49 SeitenClass ReptiliaManuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biol 106 L Kingdom Animalia Chordata VertebratesDokument28 SeitenBiol 106 L Kingdom Animalia Chordata VertebrateswhybioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Btc. Herpetology-1-1-1-1Dokument73 SeitenBtc. Herpetology-1-1-1-1Saimons VictorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-23-Animals SummaryDokument28 SeitenChapter-23-Animals SummaryJan Marlon GoritNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pertemuan 7 ArthropodaDokument50 SeitenPertemuan 7 ArthropodaNicole de BellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal KingdomDokument103 SeitenAnimal KingdomAlexander Yeung100% (1)
- Kingdo M Animali ADokument29 SeitenKingdo M Animali ABaltazar EmmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vertebrates and InvertebratesDokument3 SeitenVertebrates and InvertebratesShar Nur JeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCIENCE 6 Q2 InvertebratesDokument59 SeitenSCIENCE 6 Q2 InvertebratesGlenda Abogadie PinguelNoch keine Bewertungen
- VERTEBRATEDokument64 SeitenVERTEBRATEMaulana Reizqy AnugrahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic-12 - Arthropods 13Dokument51 SeitenTopic-12 - Arthropods 13Inaya ImranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Kingdom: by Allen Wilhelm and Zach AffolterDokument34 SeitenAnimal Kingdom: by Allen Wilhelm and Zach AffolterZachNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Animals AutosavedDokument35 SeitenClassification of Animals AutosavedjuliankobieplaysNoch keine Bewertungen
- VertebratesDokument56 SeitenVertebratesPinaka ShungaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9: Marine Reptiles, Birds, and MammalsDokument71 SeitenChapter 9: Marine Reptiles, Birds, and MammalsLUTHFIA PRATIWINoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Week2Dokument37 Seiten2nd Week2Kegie SulpotNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 InvertebrateDokument47 Seiten12 InvertebrateAmelia Puji LestariNoch keine Bewertungen
- TetrapodDokument83 SeitenTetrapodyafetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 31, Section 1Dokument18 SeitenChapter 31, Section 1XxClarityAftonxXNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kingdom AnimliaDokument20 SeitenKingdom AnimliaALISHBA TANOLINoch keine Bewertungen
- AmphibianDokument13 SeitenAmphibianAllison LeCoqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phylum Mollusca 5 - 001Dokument16 SeitenPhylum Mollusca 5 - 001JeemCarloFagelaPulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AmphibiansDokument13 SeitenAmphibiansjujuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phylum Arthropoda: by DwiDokument40 SeitenPhylum Arthropoda: by DwiNisa RNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3a - Module 3 Biodiversity Animalia Part 3b 2020Dokument66 Seiten3a - Module 3 Biodiversity Animalia Part 3b 2020Hailey McLeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amphibians and Reptiles Animal and Environmental BiologyDokument43 SeitenAmphibians and Reptiles Animal and Environmental Biologymisakisuki7Noch keine Bewertungen
- 19 Chap 23 ChordataDokument41 Seiten19 Chap 23 ChordataFarman khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Animals 2016Dokument29 SeitenClassification of Animals 2016BALQIS NURAZIZAHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vertebrates 2020Dokument62 SeitenVertebrates 2020Julia MeirellesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 Chapter 25 PPTDokument37 Seiten2014 Chapter 25 PPTAgus WahyudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evolution of ElephantsDokument19 SeitenEvolution of Elephantstehreem iftikharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arthropods: Armored Achievers Crabs, Lobster, Shrimp, BarnaclesDokument23 SeitenArthropods: Armored Achievers Crabs, Lobster, Shrimp, BarnaclesAilyn DecenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01.presentation U6Dokument8 Seiten01.presentation U6Lidia BaratasNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReptilesDokument23 SeitenReptilesReylen MaderazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReptilesDokument23 SeitenReptilesReylen MaderazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 11. Phylum Echinodermata PDFDokument37 SeitenLesson 11. Phylum Echinodermata PDFJonard PedrosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Classification of AnimalsDokument33 SeitenList of Classification of AnimalsOtenciano MautganonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urochordata & Cephalochordata NotesDokument4 SeitenUrochordata & Cephalochordata NotesInsnyur Fandy PilardinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aves - Phylogeny FinDokument40 SeitenAves - Phylogeny Fin23mzg004Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 30 Notes FishDokument48 SeitenCH 30 Notes Fishapi-244168124Noch keine Bewertungen
- Classificationofanimals 5 9 2014 5 21 48 PMDokument33 SeitenClassificationofanimals 5 9 2014 5 21 48 PMCJ TuldaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of AnimalsDokument33 SeitenClassification of Animalsrajeshmmahajan100% (1)
- Animal Kingdom ComplexDokument62 SeitenAnimal Kingdom Complexbobbie66Noch keine Bewertungen
- Characteristics of ReptilesDokument18 SeitenCharacteristics of ReptilesNihal YildrimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molluscs New Revised Ppt-1Dokument41 SeitenMolluscs New Revised Ppt-1Issa Avena100% (2)
- Classificationofanimals 5 9 2014 5 21 48 PMDokument33 SeitenClassificationofanimals 5 9 2014 5 21 48 PMJanice Tañedo PancipaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arthropods GR7 BioDokument36 SeitenArthropods GR7 Biosara ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Bear: University of Zakho Faculty of Science Dep. of Biology (2019-2020)Dokument12 SeitenWater Bear: University of Zakho Faculty of Science Dep. of Biology (2019-2020)Ahmed Amir100% (1)
- Animal Taxonomy of Reptiles, Birds, and MammalsDokument50 SeitenAnimal Taxonomy of Reptiles, Birds, and MammalsPldtangge hilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation: Invertebrate Zoology Phylum Arthropoda: Group 2Dokument30 SeitenPresentation: Invertebrate Zoology Phylum Arthropoda: Group 2Jonathan JohnnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kindom AnimaliaDokument39 SeitenKindom AnimaliaJohnrey CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Is An OPEN BOOK Examination: WASM: Minerals, Energy and Chemical Engineering ExaminationDokument11 SeitenThis Is An OPEN BOOK Examination: WASM: Minerals, Energy and Chemical Engineering ExaminationGrant HosieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biodiversity and Earth HistoryDokument410 SeitenBiodiversity and Earth HistoryFelipe Andres Morales Vicencio75% (4)
- Ivan Sanderson Ultrapramitive HumanoidsDokument37 SeitenIvan Sanderson Ultrapramitive Humanoidsdwl3858100% (1)
- Theories of Endogenic by Neetu SinghDokument43 SeitenTheories of Endogenic by Neetu SinghNeetu SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- SkeletonDokument3 SeitenSkeletonAngieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paleozoic Early PDFDokument219 SeitenPaleozoic Early PDFmarcos15121986100% (2)
- 2010 3D Symposium-Murray Roth US Shale ComparisonDokument68 Seiten2010 3D Symposium-Murray Roth US Shale Comparisongschlachter2Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Geological Evolution of Africa - EolssDokument15 SeitenThe Geological Evolution of Africa - EolssstephenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hunting HumansDokument161 SeitenHunting HumansLukas TaiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geology and Mineralization of The Eocene Tuscarora Volcanic Field, Elko County, NevadaDokument12 SeitenGeology and Mineralization of The Eocene Tuscarora Volcanic Field, Elko County, NevadaJulio Miranda AlarconNoch keine Bewertungen
- ForaminiferaDokument10 SeitenForaminiferaKei MlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dhmthy111516 - Lesson dfhdfh8Dokument5 SeitenDhmthy111516 - Lesson dfhdfh8srsyNoch keine Bewertungen
- b2201 B PDFDokument29 Seitenb2201 B PDFRaj_SheetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flowering PlantDokument18 SeitenFlowering Plantx456456456xNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contoh Soal Report TextDokument5 SeitenContoh Soal Report TextfarisariNoch keine Bewertungen
- BENNETT, M. y S. MORSE. 2014. Human Footprints. Fossilised Locomotion PDFDokument226 SeitenBENNETT, M. y S. MORSE. 2014. Human Footprints. Fossilised Locomotion PDFjorge castilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- View of Godzilla: Kenneth Carpenter PH DDokument5 SeitenView of Godzilla: Kenneth Carpenter PH DJust JakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological ProgrammingDokument2 SeitenBiological ProgrammingBrian100% (4)
- Echinoderm at ADokument9 SeitenEchinoderm at ARiyah Zuhriyah TokappaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1964 Geology of The Himalayas by Gansser SDokument308 Seiten1964 Geology of The Himalayas by Gansser Szeeshan ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrocarbon Potential Scotian SlopeDokument111 SeitenHydrocarbon Potential Scotian SlopeOkewole Olayemi SamuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geologic Time ScaleDokument2 SeitenGeologic Time ScaleAngela Pearl AngelesNoch keine Bewertungen
- OffshoreDokument82 SeitenOffshorepaufrio0% (1)
- CORE-UA 312 Earth, Life and Time Fall 2017 RampinoDokument4 SeitenCORE-UA 312 Earth, Life and Time Fall 2017 RampinoSofiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sam Boggs Jr. Principles of Sedimentology and Stratigraphy 4th Edition 2005Dokument185 SeitenSam Boggs Jr. Principles of Sedimentology and Stratigraphy 4th Edition 2005JonathanVladimirGiraldoCalcinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnkylosaurusDokument15 SeitenAnkylosaurusShanmukha RongaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- PURSUIT Newsletter No. 52, Fall 1980 - Ivan T. SandersonDokument60 SeitenPURSUIT Newsletter No. 52, Fall 1980 - Ivan T. Sandersonufortean100% (1)
- Gondwana MapDokument1 SeiteGondwana MapAnonymous zHra6Pv100% (1)
- Geology ProjectDokument13 SeitenGeology ProjectMONISHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geology of Vancouver IslandDokument53 SeitenGeology of Vancouver Islandel4ctronNoch keine Bewertungen