Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Replication and Transciption of Dna
Hochgeladen von
Tri Hiu Amborowati0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
94 Ansichten29 SeitenDNA polymerases catalyze the step-by-step addition. Each strand of double-helical DNA is used as a template for the replication of complementary daughter strands. The RNA genome of a retrovirus is converted into DNA by reverse transcriptase.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Exploring Genes
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenDNA polymerases catalyze the step-by-step addition. Each strand of double-helical DNA is used as a template for the replication of complementary daughter strands. The RNA genome of a retrovirus is converted into DNA by reverse transcriptase.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
94 Ansichten29 SeitenReplication and Transciption of Dna
Hochgeladen von
Tri Hiu AmborowatiDNA polymerases catalyze the step-by-step addition. Each strand of double-helical DNA is used as a template for the replication of complementary daughter strands. The RNA genome of a retrovirus is converted into DNA by reverse transcriptase.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 29
tion and transciption
ted by Polymerases that Take Instructions
DNA Polymerase Catalyzes Phosphodiester-Bond
Formation
DNA polymerases catalyze the step-by-step
addition
The new DNAof chain
deoxyribonucleotide units toona aDNA
is assembled directly
chain (FigureDNA
preexisting 5.21
template
). . The reaction
catalyzed, in its simplest form, is:
(DNA)n+ dNTP
(DNA)n+1 + PPi
where dNTP stands for any deoxyribonucleotide
and PPi is a pyrophosphate molecule.
Polymerization Reaction Catalyzed by DNA
Polymerases.
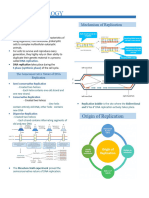
DNA Replication . The formation of a phosphodiester bridge
is catalyzed by DNA polymerases .
DNA Undergoes
Semiconservative Replication
• The Watson-Crick hypothesis
proposed that each strand of
double-helical DNA is used as a
template for the replication of
complementary daughter strands.
• In this way two daughter duplex DNA
molecules identical to the parent
DNA would be formed, each
containing one intact strand from
the parental DNA
Diagram of Semiconservative
Replication.
Parental DNA is shown in blue
and newly synthesized DNA in
red.
Flow of Information from RNA to DNA in Retroviruses . The RNA
genome of a retrovirus is converted into DNA by reverse
transcriptase, an enzyme brought into the cell by the infecting virus
particle. Reverse transcriptase catalyzes the synthesis of a
complementary DNA strand, the digestion of the RNA, and the subsequent
synthesis of the DNA strand.
A Complete Genome . The diagram depicts the genome of
Haemophilus influenzae , the first complete genome of a free-
living organism to be sequenced. The genome encodes more than 1700
proteins and 70 RNA molecules. The likely function of approximately
one-half of the proteins was determined by comparisons with sequences
from proteins previously characterized in other species. [From R. D.
Fleischmann et al., Science 269(1995):496; scan courtesy of TIGR.]
Gene Expression Is the Transformation of
Structural genesInto
DNA Information are segments
FunctionalofMolecules
DNA that
DNA
codealso
for contains other
polypeptide segments
chains that
and RNAs
Thus
have chromosomes contain structural
a purely regulatory function. genes
There are many genes
and regulatory in a. single
sequences
chromosome
Gene Expression Is the Transformation of
The
DNA information
Information stored as DNA becomes
Into Functional
First
useful, an
Molecules RNAitcopy
when is made. in the
is expressed
Second , the of
production information in messenger
RNA and proteins . RNA
is translated into a functional protein.
Several Kinds of RNA Play Key Roles in
1Gene
. Messenger RNA is the template for protein
Expression
synthesis
2. TransferorRNAtranslation
carries amino. An mRNA
acidsmolecule
in an may
be producedform
3activated
. Ribosomal for
RNAtoeachthegene
(rRNA ,theormajor
) ribosome group of genes
forcomponent
peptide- of
bond formation
ribosomes , plays, inboth
a sequence
a catalyticdictated
and aby the
mRNA template
structural . There
role is at least
in protein one .kind of
synthesis
tRNA for each of the 20 amino acids.
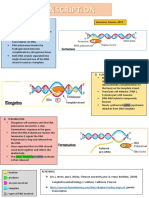
All Cellular RNA Is Synthesized by RNA
Polymerases
The synthesis of RNA from a DNA template is
called transcription
RNA polymerase andthe
requires is catalyzed
following by the
enzyme RNA: polymerase.
1components
. A template . The preferred template is double-
2stranded DNA.precursors. All four ribonucleoside
. Activated
triphosphates ATP, GTP
3. A divalent metal ion, .UTP
Mg2, +and
or CTP
Mn2+are
are
required
effective
(RNA
. . )n+ NTP (RNA)n+1 +
PPi
RNA Polymerases Take Instructions from DNA
Transcription
Templates Begins near Promoter Sites
RNA
and polymerase proceedsSites.
Ends at Terminator along DNA
the templates
DNA
template , transcribing
contain regions called one of itssites
promoter strands
that
until it reaches
specifically bindaRNA
terminator sequence
polymerase and .
determine where transcription begins.
(Figure 5.27A).
Transcription Mechanism of the Chain - Elongation Reaction
Catalyzed by RNA Polymerase .
Complementarity between mRNA and DNA .
DNA Sequence Yields the Amino
Acid Sequence .
Promoter Sites for Transcription ..
Promoter Sites for
Transcription
• Promoter sites are required for the
initiation of transcription in both
(A) prokaryotes and (B) eukaryotes.
• The first nucleotide to be
transcribed is numbered +1.
• The adjacent nucleotide on the 5 side
is numbered -1. The sequences shown
are those of the coding strand of
DNA
Transfer RNA Is the Adaptor Molecule in
tRNA
Proteincontains an amino acid attachment
Synthesis
Asite
tRNAandmolecule carries
a template a specific
-recognition siteamino
.
acid in an activated form to the site of
protein synthesis.
Base Sequence of the 3
end of an mRNA transcript
in E . coli . A stable
hairpin structure is
followed by a sequence of
uridine (U) residues.
Symbolic Diagram of
an Aminoacyl-tRNA. The
amino acid is
attached at the 3 end
of the RNA. The
anticodon is the
template-recognition
site.
Attachment of an Amino Acid to a tRNA
Molecule . The amino acid (shown in blue) is
esterified to the 3 - hydroxyl group of the terminal
adenosine of tRNA.
The genetic code is the relation between
Three nucleotides
the sequence of basesencode
in an
DNAamino
(or itsacid
RNA
.
Genetic experiments
transcripts ) and the showed that
sequence of an amino
amino
Some
acidsamino
acid acids
isininproteins are
fact encoded
. encoded
by a by moreof
group
than
threeone codon
bases , or, there
codon. are 64 possible
base triplets and only 20 amino acids.
In fact, 61 of the 64 possible triplets
Thus , forparticular
specify most aminoamino
acidsacids
, thereandis3
more than(called
triplets one code word
stop codons
. ) designate
the termination of translation.
Major Features of the Genetic Code
All 64 codons have been deciphered.
Because the code is highly degenerate,
The
onlyother 18 amino
tryptophan andacids are each encoded
methionine
The
by number
aretwo
encoded ofbycodons
or more Indeed
. just for a particular
, leucine
one triplet , arginine
each. ,
amino acid correlates
and serine are specified withbyits
sixfrequency
codons
of
eachoccurrence
. in proteins.
Summary
A Nucleic Acid Consists of Four Kinds of Bases Linked
Ato aPair of NucleicBackbone
Sugar-Phosphate Acid Chains with
Complementary
DNA Sequences
Is Replicated Can Form That
by Polymerases a
Double
Take
Gene Instructions
Expression
- Is from
the Templates
Transformation of
Helical
Amino Structure
DNA Information
Acids into Functional
Are Encoded by Groups of
Molecules
Three Bases Starting from a Fixed Point
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Protein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaDokument29 SeitenProtein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaHritik KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protein SynthesisDokument54 SeitenProtein SynthesisYousef WardatNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Diploma Biology: Essential Idea: Transcription and Translation Allow The GeneticDokument37 SeitenIB Diploma Biology: Essential Idea: Transcription and Translation Allow The GeneticClàudia VicenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritanceDokument10 SeitenNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritanceSneha HipparkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription and TranslationDokument24 SeitenTranscription and TranslationGenesis FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05b. Part 2 of Nucleic Acids For BSRadTechDokument26 Seiten05b. Part 2 of Nucleic Acids For BSRadTechBea Abigail BrocalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Lesson 1.1Dokument16 SeitenBiology Lesson 1.1Crystal Joy BondadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dna Rna Protsin 2020Dokument48 SeitenDna Rna Protsin 2020RaragloriaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- L18 Polypeptide SynthesisDokument18 SeitenL18 Polypeptide Synthesisareejhussaini26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gene ExpressionDokument29 SeitenGene ExpressionZainab Jamal SiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription and TranslationDokument58 SeitenTranscription and Translationkevin_ramos007Noch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Replication and Protein SynthesisDokument2 SeitenDNA Replication and Protein SynthesislibbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 12 NotesDokument2 SeitenCH 12 NotesCJNoch keine Bewertungen
- TranscriptionDokument31 SeitenTranscriptionDeeptanshu PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- TranslationDokument51 SeitenTranslationAleena MustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetic Code, DNA, RNA, Protein SynthesisDokument46 SeitenGenetic Code, DNA, RNA, Protein SynthesisdeepakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 17 - Transcription and TranslationDokument14 SeitenChapter 17 - Transcription and TranslationAdonias NiyurukundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dna Replication and Protein SynthesisDokument9 SeitenDna Replication and Protein Synthesisbravebrave2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription Translation - Types of RNA 2022Dokument20 SeitenTranscription Translation - Types of RNA 2022Merey ZiyabekNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.10 Protein-SynthesisDokument20 Seiten3.10 Protein-SynthesisPratika MNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNADokument64 SeitenDNAsapphireriego01Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 17 KEYDokument5 SeitenCH 17 KEYJohnathan BeversNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription and TranslationDokument35 SeitenTranscription and TranslationMing mingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription and Translation NarrativeDokument3 SeitenTranscription and Translation NarrativeBridget Anne BenitezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polypeptide Synthesis: TranscriptionDokument3 SeitenPolypeptide Synthesis: TranscriptionliklyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription and RNA ProcessingDokument38 SeitenTranscription and RNA ProcessingRishi Kumar100% (1)
- Transcription & TranslationDokument8 SeitenTranscription & TranslationDr DapperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Central DogmaDokument35 SeitenCentral Dogmatariqul13017Noch keine Bewertungen
- COMPETANCE BASED QUESTION Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritanceDokument9 SeitenCOMPETANCE BASED QUESTION Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritanceKarthika UmashankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 17 From Gene To Protein FixDokument30 SeitenChap 17 From Gene To Protein FixRizaldi Al FauzanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio AssessmentDokument5 SeitenBio Assessmentxx nataliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RNA Protein SynthesisDokument14 SeitenRNA Protein SynthesisLAL BUKHSHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protien Synth 11thDokument3 SeitenProtien Synth 11thtewoldeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protein SynthesisDokument135 SeitenProtein SynthesisCarlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ritobrata Goswami: TranslationDokument20 SeitenRitobrata Goswami: TranslationAshmit RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 12Dokument69 SeitenCH 12ᄋᄂᄋᄂNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Proteins: EP2 Protein SynthesisDokument38 SeitenEngineering Proteins: EP2 Protein SynthesisOCRChemistrySaltersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5Dokument27 SeitenLecture 5Animikh RayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription & TranslationDokument5 SeitenTranscription & TranslationJerico NaveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Usanee Anukool (PH.D.) Clinical Microbiology Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences Chiang Mai University 2 July 2009Dokument60 SeitenUsanee Anukool (PH.D.) Clinical Microbiology Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences Chiang Mai University 2 July 2009Suruk UdomsomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protein SynthesisDokument18 SeitenProtein SynthesisRussel OtillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.9 Chapter 4 - Protein Synthesis - TranscriptionDokument19 Seiten4.9 Chapter 4 - Protein Synthesis - Transcriptionlilpidas54Noch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription and RNA ProcessingDokument37 SeitenTranscription and RNA ProcessingEarl ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2006 CHM6108 L9L10 SlidesDokument40 Seiten2006 CHM6108 L9L10 Slidesaidar.seralinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Miniature Protein BIologyDokument83 SeitenMiniature Protein BIologyPREET KANOOGANoch keine Bewertungen
- M.I.T LessonsDokument12 SeitenM.I.T LessonsChassy KammyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Biology PPT 05Dokument56 SeitenMolecular Biology PPT 05Mirage LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- RNAProtein Synthesis VocabDokument2 SeitenRNAProtein Synthesis VocabdherSZN ツNoch keine Bewertungen
- De La Proteina La GenaDokument67 SeitenDe La Proteina La GenaiuventasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Genetic Code: Translation ProcessDokument93 SeitenThe Genetic Code: Translation ProcessErics EfranyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription and TranslationDokument16 SeitenTranscription and TranslationParth MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12 - Genetics NotesDokument1 SeiteClass 12 - Genetics NotesDimas HernadyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 11transcription-2013Dokument30 Seiten5 11transcription-2013jernsssNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3A - RNA Types and StructuresDokument3 SeitenLesson 3A - RNA Types and Structureshannah CorpuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 9Dokument66 SeitenLesson 9Irica Mae CiervoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription WorkingDokument51 SeitenTranscription Workingapi-3858544Noch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Overview Central DogmaDokument56 SeitenDNA Overview Central DogmaBukhari DiangkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gene ExpressionDokument46 SeitenGene Expressionmohammed mahmoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Draft Assigment Bio 2Dokument2 SeitenDraft Assigment Bio 2puteri hanisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Trigonometry Using Empirical Modelling: 2.1 Visual Over Verbal LearningDokument5 SeitenTeaching Trigonometry Using Empirical Modelling: 2.1 Visual Over Verbal LearningJeffrey Cariaga Reclamado IINoch keine Bewertungen
- SCERT Kerala State Syllabus 9th Standard English Textbooks Part 1-1Dokument104 SeitenSCERT Kerala State Syllabus 9th Standard English Textbooks Part 1-1Athulya ThondangattilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 444323735-Chem-Matters-Workbook-2E-Teacher-s-Edn-pdf 16-16Dokument1 Seite444323735-Chem-Matters-Workbook-2E-Teacher-s-Edn-pdf 16-16whatisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genil v. Rivera DigestDokument3 SeitenGenil v. Rivera DigestCharmila SiplonNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Linguistic Colonialism of EnglishDokument4 SeitenThe Linguistic Colonialism of EnglishAdriana MirandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3400 MD IomDokument52 Seiten3400 MD IomIhabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quotation of Suny PDFDokument5 SeitenQuotation of Suny PDFHaider KingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch-10 Human Eye Notes FinalDokument27 SeitenCh-10 Human Eye Notes Finalkilemas494Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ej. 1 Fin CorpDokument3 SeitenEj. 1 Fin CorpChantal AvilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- LP32HS User Manual v1Dokument52 SeitenLP32HS User Manual v1tonizx7rrNoch keine Bewertungen
- D25KS Sanvick PDFDokument4 SeitenD25KS Sanvick PDFJiménez Manuel100% (1)
- The Turning Circle of VehiclesDokument2 SeitenThe Turning Circle of Vehiclesanon_170098985Noch keine Bewertungen
- Session 1Dokument18 SeitenSession 1Akash GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circular ConvolutionDokument3 SeitenCircular Convolutionseeksudhanshu1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Borges, The SouthDokument4 SeitenBorges, The Southdanielg233100% (1)
- Test Physics Chapter# 12,13,14 (2 Year) NameDokument1 SeiteTest Physics Chapter# 12,13,14 (2 Year) NameStay FocusedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Galgotias University Uttar Pradesh School of Computing Science & Engineering B.Tech. (CSE) 2018-19 Semester Wise Breakup of CoursesDokument2 SeitenGalgotias University Uttar Pradesh School of Computing Science & Engineering B.Tech. (CSE) 2018-19 Semester Wise Breakup of CoursesRohit Singh BhatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIIMS 2015 Solved PaperDokument436 SeitenAIIMS 2015 Solved PaperSurya TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Mutual Funds For 2023 & BeyondDokument17 SeitenBest Mutual Funds For 2023 & BeyondPrateekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Problems - Electrochemical CellDokument5 SeitenPractice Problems - Electrochemical CellYehia IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- John DrydenDokument3 SeitenJohn DrydenDunas SvetlanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Precursor Effects of Citric Acid and Citrates On Zno Crystal FormationDokument7 SeitenPrecursor Effects of Citric Acid and Citrates On Zno Crystal FormationAlv R GraciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information Systems and Supply Chain ManagementDokument2 SeitenInformation Systems and Supply Chain Managementvipinkandpal86Noch keine Bewertungen
- Johnson & Johnson Equity Research ReportDokument13 SeitenJohnson & Johnson Equity Research ReportPraveen R V100% (3)
- Grammar and Vocabulary TestDokument5 SeitenGrammar and Vocabulary TestLeonora ConejosNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReadingDokument205 SeitenReadingHiền ThuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saiva Dharma ShastrasDokument379 SeitenSaiva Dharma ShastrasfunnybizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detail Design Drawings: OCTOBER., 2017 Date Span Carriage WayDokument26 SeitenDetail Design Drawings: OCTOBER., 2017 Date Span Carriage WayManvendra NigamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mueller Hinton Agar (M-H Agar) : CompositionDokument2 SeitenMueller Hinton Agar (M-H Agar) : CompositionRizkaaulyaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- APA Vs Harvard Referencing - PDFDokument4 SeitenAPA Vs Harvard Referencing - PDFTalo Contajazz Chileshe50% (2)