Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
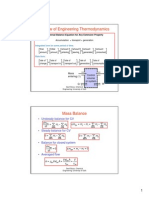
Thermodynamic Processes
Hochgeladen von
Karthick RamOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Thermodynamic Processes
Hochgeladen von
Karthick RamCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Thermodynamic Processes
States of a thermodynamic system can be changed by
interacting with its surrounding through work and heat. When
this change occurs in a system, it is said that the system is
undergoing a process.
A thermodynamic cycle is a sequence of different processes that
begins and ends at the same thermodynamic state.
Some sample processes:
Isothermal process: temperature is constant T=C
Isobaric process: pressure is constant, P=C
Isentropic process: entropy is constant, s=C
Constant-volume process, v=C
Adiabatic process: no heat transfer, Q=0
Process-1
Use ideal gas assumption (closed system):
2
1
2 1
1 2
Isothermal process: T=constant
Energy balance U=Q-W, for ideal gas U= H=0
since both are functions of temperature only
Q=W, W= P
ln ln
Isobaric process:
mRT dV
dV dV mRT
V V
V P
mRT mRT
V P
A A A
= =
| | | |
= =
| |
\ . \ .
} } }
2
2 1
1
2 1 2 1 2 1
2 2 1 1 2 1
P=constant
U=Q-W, W= PdV=P dV=P(V )
( ) ( ) ( )
( ) ( )
V
Q U P V V U U P V V
U PV U PV H H H
A
= A + = +
= + + = = A
} }
Process-2
v
v
Constant volume process: V=constant
Q-W= U, W= 0, no work done
Q= U=m u=m c
Adiabatic process: Q=0
Q-W= U, -W= U
- W=dU (infinitesimal increment of work and energy)
dU+PdV=0, mc 0
v
PdV
dT
mRT
dT dV
V
c
o
A =
A A
A A
| |
+ =
|
\ .
}
}
v
2 2 2 1 1
1 1 1 2 2
1
0, , integrate and assume
c =constant
ln ln ,
v
v
v
R
k
c
c RT dT dV
dT dV
V R T V
c T V T V V
R T V T V V
| |
+ = =
|
\ .
| | | | | | | |
= = =
| | | |
\ . \ . \ . \ .
Process-3
2 1
1 2
1 1 2
2 2 1
2 1 2 2
1 2 1 1
2 2 2 1
1 1 1
( 1)
1
1
1
, from ideal gas relation
PV=RT, , substitute
, multiply from both sides
,
k
k
k
k
k
T V
T V
V T P
V T P
T T P T
T T P T
T P P V
T P P
and
| |
=
|
\ .
| | | |
=
| |
\ . \ .
| |
| || | | |
=
|
| | |
\ .\ . \ .
\ .
| | | |
= =
| |
\ . \ . 2
1 1 2 2
k
Also and tan
For an ideal gas undergoing adiabatic process
k
k
k
V
PV PV pV cons t
| |
|
\ .
= =
Process-4
Polytropic Process: its P-V relation can be expressed as
PV
n
= constant, where n is a constant for a specific process
Isothermal, T=constant, if the gas is an ideal gas then
PV=RT=constant, n=1
Isobaric, P=constant, n=0 (for all substances)
Constant-volume, V=constant, V=constant(P)
(1/n)
, n=
(for all substances)
Adiabatic process, n=k for an ideal gas
1 1 2 2
2 2
1 1
1 1
2
1 1
1 1 2 2 1 1
1 1 2 1
1
( )
( )
( ) ( )
1 1
n n n
n n
n
n n n n
PV PV PV
W PdV PV V dV
PV PV PV
PV V dV V V
n n
= =
= =
= = =
} }
}
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Topic Assessment Integration PDFDokument5 SeitenTopic Assessment Integration PDFAdeyemi DorcasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volumetric Properties of Pure FluidsDokument21 SeitenVolumetric Properties of Pure FluidsIR Ika EtyEtyka Dora100% (1)
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsVon EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- PNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGVon EverandPNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working Guide to Vapor-Liquid Phase Equilibria CalculationsVon EverandWorking Guide to Vapor-Liquid Phase Equilibria CalculationsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Seminar Report On Artificial IntelligenceDokument24 SeitenSeminar Report On Artificial Intelligencenitheesh chandran r j64% (11)
- Second Law of Thermodynamics: T T Q QDokument10 SeitenSecond Law of Thermodynamics: T T Q Qnellai kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vlsi Physical DesignDokument26 SeitenVlsi Physical Designilias ahmed100% (1)
- Introduction To ThermodynamicsDokument130 SeitenIntroduction To ThermodynamicsJaimin Joshi0% (1)
- TER201 Lecture 6Dokument66 SeitenTER201 Lecture 6lnxxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Processes of Pure SubstancesDokument6 SeitenProcesses of Pure SubstancesOrley G FadriquelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 02Dokument32 SeitenChap 02echelon12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ch 4 上課教材 PDFDokument9 SeitenCh 4 上課教材 PDFTai-Yuan HsuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamic Processes: Analysis of Thermodynamic Processes by Applying 1 & 2 Law of ThermodynamicsDokument10 SeitenThermodynamic Processes: Analysis of Thermodynamic Processes by Applying 1 & 2 Law of Thermodynamicsmohdmehrajanwar1860Noch keine Bewertungen
- Polytropic Process of An Ideal GasDokument8 SeitenPolytropic Process of An Ideal GasChowdhury FatemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics 1 - Energy Analysis of Closed SystemsDokument26 SeitenThermodynamics 1 - Energy Analysis of Closed SystemsFlorasaurus17100% (2)
- Reversible and Irreversible ProcesesDokument12 SeitenReversible and Irreversible ProcesesFarouk BassaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Termodinamika, Entropy, Dan Energi Dalam 2014Dokument23 SeitenTermodinamika, Entropy, Dan Energi Dalam 2014Deriandra MuhyiddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThermodynamicsDokument9 SeitenThermodynamicssamir boseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Thermodynamics: Volumetric Properties of Pure FluidsDokument36 SeitenAdvanced Thermodynamics: Volumetric Properties of Pure FluidsArunodhayam NatarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Thermodynamic Process and 1 Law Application in It: - V) NR (T - T) (T - T)Dokument5 SeitenDifferent Thermodynamic Process and 1 Law Application in It: - V) NR (T - T) (T - T)priyam dasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamic CyclesDokument30 SeitenThermodynamic CyclesRudra PratapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stagnation PropertiesDokument25 SeitenStagnation PropertiesMSK6567% (3)
- Termodinamika LanjutDokument44 SeitenTermodinamika LanjutRyan Tw ChoumingNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITK-233-2 - PVT Behavior of FluidDokument57 SeitenITK-233-2 - PVT Behavior of FluidVinay GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1ST Law of ThermodynamicsDokument19 Seiten1ST Law of ThermodynamicsZamanoden D. UndaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Engineering Thermodynamics: Dr. Dharmendra Kumar Bal Assistant Professor (SR.) ScaleDokument50 SeitenProcess Engineering Thermodynamics: Dr. Dharmendra Kumar Bal Assistant Professor (SR.) ScaleAABID SHAIKNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThermodynamicsNotes PDFDokument41 SeitenThermodynamicsNotes PDFAsia CtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermo ReviewDokument4 SeitenThermo ReviewJeebee Logroño AloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics FormulasDokument6 SeitenPhysics FormulasRam PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamic PotentialsDokument22 SeitenThermodynamic PotentialsShubham BansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy: Sub Chapter CoveredDokument31 SeitenEnergy: Sub Chapter CoveredRenu SekaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- BTD-2. Work & HeatDokument13 SeitenBTD-2. Work & Heatmahammad kamaluddeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Law Worked ExamplesDokument4 Seiten1st Law Worked ExamplesMahir MahmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamic ProcessesDokument32 SeitenThermodynamic ProcessesAleem AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Power Cycles Study Guide in Powerpoint: To AccompanyDokument68 SeitenGas Power Cycles Study Guide in Powerpoint: To AccompanyManjunatha TnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Term Odin A MikaDokument27 SeitenTerm Odin A MikaAnonymous GTCOMvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volumetric PropertiesDokument36 SeitenVolumetric PropertiesRohan BhilkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 3 - Energy Balance Involving Gases PDFDokument15 SeitenPart 3 - Energy Balance Involving Gases PDFHarold SumagaysayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consider A Force, F, Acting On A Block Sliding On A Frictionless Surface X X XDokument17 SeitenConsider A Force, F, Acting On A Block Sliding On A Frictionless Surface X X XPrasad V. JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThermodynamicsDokument22 SeitenThermodynamicsatulsemiloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engine Cycles: - Thermodynamics SupplementDokument23 SeitenEngine Cycles: - Thermodynamics SupplementYoonjin HwangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics 2 E7Dokument41 SeitenThermodynamics 2 E7taya699Noch keine Bewertungen
- Prof. Dr. Ramli Ibrahim Dr. Norlaili Abu BakarDokument24 SeitenProf. Dr. Ramli Ibrahim Dr. Norlaili Abu BakarNurshuhada NordinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Transfer by Heat, Work, and Mass: LectureDokument48 SeitenEnergy Transfer by Heat, Work, and Mass: Lectureindustrial_47Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2-3 First Law of Thermodynamics - Session 3Dokument24 Seiten2-3 First Law of Thermodynamics - Session 3Baddam Jayasurya ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Engineering 2 - Compressors 1 The Perfect Gas ModelDokument12 SeitenPlant Engineering 2 - Compressors 1 The Perfect Gas ModelDee RajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 First Law-Closed System ProblemsDokument11 SeitenUnit 2 First Law-Closed System Problemspiravi66Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 15 Students PhysicsDokument53 SeitenChapter 15 Students PhysicsNur Farizah ZuhaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lect.4. Presentation (Processes)Dokument24 SeitenLect.4. Presentation (Processes)Ali aliraqiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Properties and State of A System.: Pressure, Volume, Velocity, Temperature and PositionDokument19 SeitenProperties and State of A System.: Pressure, Volume, Velocity, Temperature and PositionbenhasherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Ideal Gas Processes - Lecture 1Dokument7 SeitenChapter 4 Ideal Gas Processes - Lecture 1Juan KakakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE1104 Physics 1: List of EquationsDokument24 SeitenAE1104 Physics 1: List of EquationssmithastellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Five (Energy Analysis of Closed Systems)Dokument31 SeitenChapter Five (Energy Analysis of Closed Systems)ايات امجد امجدNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics Useful FormulasDokument2 SeitenThermodynamics Useful FormulasKristen KellerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.thermodynamic ProcessDokument5 Seiten2.thermodynamic ProcessDarklightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion PDFDokument49 SeitenGas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion PDFdass143143Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture - 10 - Second LawDokument10 SeitenLecture - 10 - Second LawMihai MirceaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 The 1st 2nd Laws of ThermodynamicsDokument135 Seiten2 The 1st 2nd Laws of ThermodynamicsPrince KevinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)Von EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Transformation Induced PlasticityDokument6 SeitenTransformation Induced PlasticityKarthick RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Legend of SleepyhollowDokument28 SeitenThe Legend of SleepyhollowKarthick RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Employment Today: Application For Placement ServiceDokument2 SeitenEngineering Employment Today: Application For Placement ServiceKarthick RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dimensioning and Tolerancing: Cad/Cam © Ir. Zambri HarunDokument26 SeitenDimensioning and Tolerancing: Cad/Cam © Ir. Zambri HarunKarthick RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- REC Shortlists For TCSDokument9 SeitenREC Shortlists For TCSKarthick RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Structural CeramicsDokument12 SeitenAdvanced Structural CeramicsKarthick RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crack Initiation and Propagation in Ductile and Brittle MaterialsDokument22 SeitenCrack Initiation and Propagation in Ductile and Brittle MaterialsKarthick RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Titanic EdaDokument14 SeitenTitanic EdaDeepak SemwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- AD3251 Data Structures Design Question Bank 1Dokument1 SeiteAD3251 Data Structures Design Question Bank 1bbook6930Noch keine Bewertungen
- MCAN201 Data Structure With Python Questions For 1st InternalDokument2 SeitenMCAN201 Data Structure With Python Questions For 1st InternalDr.Krishna BhowalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokument2 SeitenGujarat Technological UniversityRenieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit II Regular ExpressionDokument176 SeitenUnit II Regular Expressionjagdish750Noch keine Bewertungen
- DSP Question Bank 8-10-15Dokument14 SeitenDSP Question Bank 8-10-15raghav dhamaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 (PR)Dokument14 SeitenChapter 5 (PR)Shikha AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.2. Cryptographic Coding (Part 2)Dokument27 Seiten4.2. Cryptographic Coding (Part 2)ReachNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC 263 Signals and Systems Lab PDFDokument21 SeitenEC 263 Signals and Systems Lab PDFarundhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 00 IntroDokument10 Seiten00 IntrorunnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- DS100-2-Grp#4 Chapter 6 Advanced Analytical Theory and Methods Regression (CADAY, CASTOR, CRUZ, SANORIA, TAN)Dokument4 SeitenDS100-2-Grp#4 Chapter 6 Advanced Analytical Theory and Methods Regression (CADAY, CASTOR, CRUZ, SANORIA, TAN)Gelo CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1-3Dokument48 SeitenLesson 1-3T ENGANoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Structure Tree: DR Mourad RaafatDokument21 SeitenData Structure Tree: DR Mourad RaafatMomen abd ElrazekNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS 437 / CS 5317 Deep Learning: Murtaza TajDokument11 SeitenCS 437 / CS 5317 Deep Learning: Murtaza Tajhoshi hamzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IandF CT4 201509 ExamDokument10 SeitenIandF CT4 201509 ExamHaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intelligent Crop Recommendation SystemDokument4 SeitenIntelligent Crop Recommendation SystemBalasatyaappaji99 KurellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 20 CryptographyDokument5 SeitenModule 20 CryptographynikeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- M.tech. - Control SystemsDokument44 SeitenM.tech. - Control SystemsSandeep KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study For Data ScienceDokument3 SeitenCase Study For Data SciencethiruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear RegressionDokument29 SeitenLinear RegressionSreetam GangulyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measures of Central Tendency and Position (Ungrouped Data) : Lesson 3Dokument19 SeitenMeasures of Central Tendency and Position (Ungrouped Data) : Lesson 3Gemver Baula BalbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- BookSlides 5A Similarity Based LearningDokument40 SeitenBookSlides 5A Similarity Based LearningMba NaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- ET4060 Fundamentals of Data Communication Networks Lecture 06Dokument35 SeitenET4060 Fundamentals of Data Communication Networks Lecture 06Loc DoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lahore University of Management Sciences CS 202 - Data StructuresDokument2 SeitenLahore University of Management Sciences CS 202 - Data StructuresWaleed KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- OS Deadlock (Chapter 8)Dokument39 SeitenOS Deadlock (Chapter 8)ekiholoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Symbolic Pregression, Discovering Physical Laws From Raw Distorted Video, Udrescu, Tegmark, 2020Dokument13 SeitenSymbolic Pregression, Discovering Physical Laws From Raw Distorted Video, Udrescu, Tegmark, 2020Mario Leon GaticaNoch keine Bewertungen