Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Type of Corrosion
Hochgeladen von
Nur Afiqah100%(2)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (2 Abstimmungen)
61 Ansichten12 SeitenAs an a / P technician, you must be familiar with the different types of corrosion. Simplest form of corrosion is "dry corrosion" or by its common name rust. Surface corrosion can also lead to pitting corrosion if it continue to spread and left untreated.
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenAs an a / P technician, you must be familiar with the different types of corrosion. Simplest form of corrosion is "dry corrosion" or by its common name rust. Surface corrosion can also lead to pitting corrosion if it continue to spread and left untreated.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(2)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (2 Abstimmungen)
61 Ansichten12 SeitenType of Corrosion
Hochgeladen von
Nur AfiqahAs an a / P technician, you must be familiar with the different types of corrosion. Simplest form of corrosion is "dry corrosion" or by its common name rust. Surface corrosion can also lead to pitting corrosion if it continue to spread and left untreated.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 12
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
Subject Code: GAV 1451
Malaysian Institute of Aviation Technology
Issue No :
ORIGINAL
II. Types Of Corrosion
As an A/P technician, you must be familiar with the
different types of corrosion as well as how to identify
them. Below are the types of corrosion:
1. Oxidation
2. Uniform Surface corrosion
3. Pitting corrosion
4. Galvanic corrosion
5. Concentration cell corrosion
6. Oxygen concentration cell corrosion
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
Subject Code: GAV 1451
Malaysian Institute of Aviation Technology
Issue No :
ORIGINAL
7. Metal Ion Concentration Cell Corrosion
8. Active Passive Cell
9. Filiform Corrosion
10. Intergranular Corrosion
11. Exfoliation Corrosion
12. Stress Corrosion
13. Fretting Corrosion
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
Subject Code: GAV 1451
Malaysian Institute of Aviation Technology
Issue No :
ORIGINAL
1.Oxidation
One of the simplest forms of corrosion is dry
corrosion or by its common name rust.
Chemical action in which a metallic element is united
with oxygen
Aluminum alloy may be protected from oxidation by
electrolytically or chemically forming a hard oxide film
on its surface. e.g. ALCLAD
This airtight film prevents any air or moisture
reaching the metal and oxide itself will not continue to
react with the oxygen in the air.
The best way to protect iron is by temporarily cover it
with oil or grease or permanently coat it with paint.
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
Subject Code: GAV 1451
Malaysian Institute of Aviation Technology
Issue No :
ORIGINAL
2. Uniform Surface Corrosion
Occur on the surface of metal
Dull surface caused by contaminants in the air react
with the metal and change microscopic amounts of it
into corrosion salts.
These contaminants includes airborne chlorine or
sulphur compounds, exhaust gases, battery fumes
and moisture.
Surface corrosion can also leads to pitting corrosion if
it continue to spread and left untreated.
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
Subject Code: GAV 1451
Malaysian Institute of Aviation Technology
Issue No :
ORIGINAL
3. Pitting Corrosion
Result of Uniform Surface Corrosion let
untreated.
a localized corrosion which starts at a surface
and progresses into metal.
Usually detected by the appearance of
clumps of white powder on the surface .
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
Subject Code: GAV 1451
Malaysian Institute of Aviation Technology
Issue No :
ORIGINAL
4. Galvanic Corrosion
Occurs any time two dissimilar metals make electrical
contact in the present at an electrolyte.
It can take place where two dissimilar metal skins are
riveted together.
or where aluminum inspection plates are attached to
the structure with steel screws.
The further apart the groups (electrochemical series
for metal), the more active the corrosion
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
Subject Code: GAV 1451
Malaysian Institute of Aviation Technology
Issue No :
ORIGINAL
5. Concentration Cell Corrosion
A type of corrosion in which the electrode potential
difference is caused by a difference in ion
concentration of the electrolyte instead of a
difference in galvanic composition within the metal.
Three types of corrosion:
1. Oxygen Concentration Cell Corrosion
2. Metal Ion Concentration Cell Corrosion
3. Active Passive Cells
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
Subject Code: GAV 1451
Malaysian Institute of Aviation Technology
Issue No :
ORIGINAL
6. Filiform Corrosion
Consists of threadlike filaments of corrosion that
form on the surface of metals coated with organic
substances such as paint films.
It occur when the wash primer used on a metal has
not been properly cured.
It shows itself as a puffiness under the paint film
and is first noticed around rivet heads and along the
lap joints of skins.
It can be prevented by storing aircraft in an
environment with relative humidity below 70%.
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
Subject Code: GAV 1451
Malaysian Institute of Aviation Technology
Issue No :
ORIGINAL
7. Intergranular Corrosion
Attacks metal along the grain boundaries.
It occur when the metal is not properly heat treated.
Most types of corrosion on aluminum alloys are
intergranular.
Spot welds and seam welds can also leads to this
type of corrosion.
Hard to detect because it is inside the metal.
Ultrasonic and X-ray is needed for this corrosion.
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
Subject Code: GAV 1451
Malaysian Institute of Aviation Technology
Issue No :
ORIGINAL
8. Exfoliation Corrosion
An extreme case of intergranular corrosion
in an extruded metal part such as channels
where the grain structure is laminar (layer-
like).
The corrosion causes the metal to separate
in layers or delaminate.
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
Subject Code: GAV 1451
Malaysian Institute of Aviation Technology
Issue No :
ORIGINAL
9. Stress Corrosion
Is a form of intergranular corrosion that forms in a
metal when it is subject to continuous tensile
stress.
Results from improper quenching after heat
treatment or from interference fit of a fasteners.
Common location are at stressed skin around
pressed and bushings and tapered pipe fittings.
NDT test such as dye penetrant, eddy current or
ultrasonic inspection is used to find the actual extent
of the damage.
FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
Subject Code: GAV 1451
Malaysian Institute of Aviation Technology
Issue No :
ORIGINAL
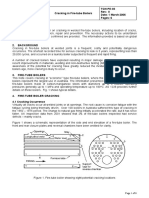
10. Fretting Corrosion
Corrosion that forms between two surfaces which fit
tightly together, but move slightly relative to one
another.
The wear breaks down the protective surface film
and allows corrosion to occur.
Occur around rivets in a skin indicated by dark
deposits streaming out behind the rivet heads (rivet
smoking).
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Metal Corrosion Mechanisms and TypesDokument42 SeitenMetal Corrosion Mechanisms and Typesmujeebmehar100% (2)
- Mooring, Towing, TaxingDokument4 SeitenMooring, Towing, TaxingRodriguez ArthursNoch keine Bewertungen
- Honda International ManagementDokument29 SeitenHonda International ManagementTanumoy Sengupta100% (1)
- MIC in Heat Exchanger TubingDokument6 SeitenMIC in Heat Exchanger TubingdutuconstantinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weld Cladding Overlay - Topics by ScienceDokument73 SeitenWeld Cladding Overlay - Topics by ScienceMichael TayactacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1Dokument30 SeitenModule 1mahmoud aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 8 Forms of Corrosion: A Guide to Identifying TypesDokument21 SeitenThe 8 Forms of Corrosion: A Guide to Identifying TypesJunaldi75% (4)
- Whirlpool Washing Machine Repair Manual 4GWTW4740YQ1 4GWTW4800YQ1 4GWTW4800YQ2 4GWTW4740YQ2Dokument64 SeitenWhirlpool Washing Machine Repair Manual 4GWTW4740YQ1 4GWTW4800YQ1 4GWTW4800YQ2 4GWTW4740YQ2fugaperuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Silos: Technical SheetDokument31 SeitenIndustrial Silos: Technical Sheetred patriotNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.the Basics of Ferrous MetallurgyDokument83 Seiten1.the Basics of Ferrous MetallurgyfenasikerimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrogen Induced Cracking PDFDokument254 SeitenHydrogen Induced Cracking PDFAnas PratamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alloy Steels: Dr. Indika de SilvaDokument25 SeitenAlloy Steels: Dr. Indika de SilvaChandima K PriyamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cracking in Fire Tube BoilersDokument8 SeitenCracking in Fire Tube BoilersRui AlexandreNoch keine Bewertungen
- MetallurgyDokument190 SeitenMetallurgyJose J. Nuñez100% (2)
- Corrosion PDFDokument51 SeitenCorrosion PDFSuryansh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cast IronDokument43 SeitenCast IronThulasi Ram100% (1)
- Types of CorrosionDokument53 SeitenTypes of CorrosionFelix Julio Céspedes Soto100% (3)
- Metallurgy For Non Metallurgist - Module-1Dokument61 SeitenMetallurgy For Non Metallurgist - Module-1ajaysharma_1009Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lectut MT 307 PPT MT 307 04 Weld Metallurgy - WYlLE5JDokument25 SeitenLectut MT 307 PPT MT 307 04 Weld Metallurgy - WYlLE5Jsachingir100% (1)
- Welding MetallurgyDokument30 SeitenWelding MetallurgySamanthaPereraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Weld Strength CalnsDokument3 SeitenFinal Weld Strength CalnsSajal KulshresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pitting CorrosionDokument19 SeitenPitting CorrosionAbdul Moeed Kalson100% (2)
- 1-Forms of CorrosionDokument59 Seiten1-Forms of Corrosion이선엽100% (1)
- Astm C490Dokument5 SeitenAstm C490Horacio ApolayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CorrosionDokument65 SeitenCorrosionSurendra Kamal100% (9)
- Segregation and Banding in SteelDokument2 SeitenSegregation and Banding in SteelskluxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Welding JointsDokument20 SeitenTypes of Welding Jointssuresh rajendranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embrittlement of Engineering AlloysVon EverandEmbrittlement of Engineering AlloysC.L. BriantNoch keine Bewertungen
- MicrostructuresDokument10 SeitenMicrostructuresErin BarryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10-Low Alloy Steel PDFDokument32 Seiten10-Low Alloy Steel PDFIdes Trian100% (1)
- Corrosion Quiz AnswersDokument5 SeitenCorrosion Quiz AnswersErik Alfiandy100% (1)
- Cracking of Alloy 800H Reformer RiserDokument14 SeitenCracking of Alloy 800H Reformer RiserTiah Nam Kuan100% (1)
- Corrosion and Materials in Hydrocarbon Production: A Compendium of Operational and Engineering AspectsVon EverandCorrosion and Materials in Hydrocarbon Production: A Compendium of Operational and Engineering AspectsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form of Corrosion Illustration Form of Corrosion IllustrationDokument2 SeitenForm of Corrosion Illustration Form of Corrosion IllustrationkhalesnabilNoch keine Bewertungen
- SuspensionDokument43 SeitenSuspensionyash1239100% (1)
- Corrosion: Metal/Environment ReactionsVon EverandCorrosion: Metal/Environment ReactionsL L ShreirBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (7)
- Sap MM TicketsDokument9 SeitenSap MM TicketsSatyajit Sahoo100% (1)
- CLSCC LiteratureDokument62 SeitenCLSCC LiteratureNakarin PotidokmaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Treatment of Welded Joints GuideDokument26 SeitenHeat Treatment of Welded Joints Guidelinhcdt3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atmospheric Corrosion Mechanisms and MonitoringDokument27 SeitenAtmospheric Corrosion Mechanisms and MonitoringmghgolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weldability PDFDokument60 SeitenWeldability PDFS GoudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 - Factors Promote Corrosion in Steam PlantDokument16 Seiten4 - Factors Promote Corrosion in Steam PlantMohammed AlSaleh100% (4)
- How To Weld S Duplex SsDokument47 SeitenHow To Weld S Duplex Sszebra9368Noch keine Bewertungen
- Weldability of Materials - Carbon Manganese and Low Alloy SteelsDokument6 SeitenWeldability of Materials - Carbon Manganese and Low Alloy SteelsmanimaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graphitization, temper embrittlement and other forms of damageDokument12 SeitenGraphitization, temper embrittlement and other forms of damagemajid100% (1)
- Biological Treatment of Microbial Corrosion: Opportunities and ChallengesVon EverandBiological Treatment of Microbial Corrosion: Opportunities and ChallengesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ferrous Alloys Classification and Types GuideDokument36 SeitenFerrous Alloys Classification and Types GuideNipun HarshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIC CorrosionDokument28 SeitenMIC Corrosionsuperdick14100% (2)
- Sterile Operations Quality Risk AssessmentDokument29 SeitenSterile Operations Quality Risk Assessmentgbra80100% (1)
- Master Thesis FinalDokument125 SeitenMaster Thesis FinalShailesh K SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dissimilar Metal WeldingDokument37 SeitenDissimilar Metal WeldingAlbar33% (3)
- Case Study On Corrosion Water Tube BoilersDokument3 SeitenCase Study On Corrosion Water Tube BoilersSalem Garrab100% (2)
- Boiler Water Systems OptimizationDokument30 SeitenBoiler Water Systems OptimizationkishoregskNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dissimilar WeldingDokument42 SeitenDissimilar WeldingMan MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metallic CoatingDokument14 SeitenMetallic CoatingJOSEPH HERBERT MABELNoch keine Bewertungen
- AWS Electrode classifications explainedDokument3 SeitenAWS Electrode classifications explainedUsamaIjazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liquid Metal EmbrittlementDokument1 SeiteLiquid Metal EmbrittlementalphadingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For Hard Facing Onto SteelsDokument7 SeitenGuidelines For Hard Facing Onto SteelsmohamedfirozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Alloying Elements On Steel Properties (SubsTech)Dokument2 SeitenEffect of Alloying Elements On Steel Properties (SubsTech)hguptabhel100% (1)
- Fundamentalsof CorrosionNov2012Dokument39 SeitenFundamentalsof CorrosionNov2012diaccessltd_17172961Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics of Welding Better VersionDokument3 SeitenPhysics of Welding Better VersionKhurram RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Forms of Corrosion - Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion MIC - Microbial CorrosionDokument2 SeitenDifferent Forms of Corrosion - Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion MIC - Microbial CorrosionHarry NuryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM Welding Tips A410 To A643Dokument20 SeitenASTM Welding Tips A410 To A643MARIO HUAMANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Steels-1Dokument85 SeitenClassification of Steels-1Saptarshi SenguptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Killed and Capped Steel IngotsDokument5 SeitenKilled and Capped Steel IngotsalacalleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asset Integrity Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandAsset Integrity Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 AVT Assignment July 2014Dokument2 Seiten3 AVT Assignment July 2014Nur AfiqahNoch keine Bewertungen
- BenjaminDokument1 SeiteBenjaminNur AfiqahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report EnglishDokument4 SeitenReport EnglishNur AfiqahNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEBLDokument1 SeiteBEBLNur AfiqahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical and Tribological Performance of Aluminium Metal Matrix CompositesDokument27 SeitenMechanical and Tribological Performance of Aluminium Metal Matrix CompositesPradeepkumar SamanthulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSRMDokument2 SeitenBSRMAbul Kalam AzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- X Ce Series Catalog PagesDokument15 SeitenX Ce Series Catalog PagessourcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 28 DFD and Er DiagramDokument10 SeitenLesson 28 DFD and Er DiagramSelect dsouzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyd AdvantageDokument4 SeitenHyd AdvantageVictorDjChiqueCastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leica AT960 Brochure - en PDFDokument9 SeitenLeica AT960 Brochure - en PDFJDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Honda Petcock Recall RCRIT-08V141-7216Dokument6 SeitenHonda Petcock Recall RCRIT-08V141-7216Gheorghe DanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Toyota Achieved Success Through Its Unique Management PhilosophyDokument66 SeitenHow Toyota Achieved Success Through Its Unique Management PhilosophyKakon AnmonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designing Tall Buildings Structure As Architecture-103-134Dokument32 SeitenDesigning Tall Buildings Structure As Architecture-103-134Milka VincentiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- China Vaseline White Petroleum Jelly - Snow White Vaseline - China Vaseline White, Petroleum Jelly PDFDokument3 SeitenChina Vaseline White Petroleum Jelly - Snow White Vaseline - China Vaseline White, Petroleum Jelly PDFIstianah Achy HaeruddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- SS 671Dokument9 SeitenSS 671OwNoch keine Bewertungen
- What is the importance of base line in chain surveyingDokument17 SeitenWhat is the importance of base line in chain surveyingFahadmeyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- d59687gc10 Toc GLMFDokument14 Seitend59687gc10 Toc GLMFmahmoud_elassaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certified CMMI Associate Exam ResultsDokument8 SeitenCertified CMMI Associate Exam ResultsDaniel Softjoy MontjoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- November 2016Dokument20 SeitenNovember 2016Deepak JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2009 UAV Project DescriptionDokument2 Seiten2009 UAV Project Descriptionjohnyb111Noch keine Bewertungen
- VI Semester Airport and Railway EngineeringDokument2 SeitenVI Semester Airport and Railway EngineeringdineshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improve company operations with a functional ISM projectDokument10 SeitenImprove company operations with a functional ISM projectSachin BorkkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- SQM Lecture3 Org Structure Roles&RespDokument19 SeitenSQM Lecture3 Org Structure Roles&Respjayanto_mayankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case StudyDokument17 SeitenCase StudyAbdo ChalawitNoch keine Bewertungen