Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
2012-11-13 Editing 3rd Iberoamerican Syposium of Marine Insurance DH
Hochgeladen von
elchancletaOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
2012-11-13 Editing 3rd Iberoamerican Syposium of Marine Insurance DH
Hochgeladen von
elchancletaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Determinants of Risk Administration in the
Global Net of Cargo Transportation:
Speaker: Zeyan Zhang
Institute of Transport and ogisti!s Studies
The "ni#ersity of Sydney
$usiness S!hool
The Third IberoAmeri!an Symposium of %arine
Insuran!e
China&s 'oint of (ie)
OUTLINE
2
Introduction
The Causes of Supply Chain Disruptions
The Vulnerabilities in Maritime Transport Chains
The Impacts of Supply Chain Disruptions
Chinese Shippers Perceptions for Maritime Related SCDs
Mitigation Strategies for Supply Chain Disruptions
Chinas Logistics Industry
uantifying Supply Chain Disruptions Costs
Conclusions
The Causes of Supply Chain Disruptions
3
Supply chains !SCs" are comple# systems of net$or%s
&lobal SCs could be further subdi'ided into three layers( o'ersight layer)
transaction layer and logistics layer !*illis and +rti,) -../"
The Causes of Supply Chain Disruptions
4
The Vulnerabilities in Maritime Transport Chains
5
Sources of Maritime Transportation Related SCDs
The Impacts of Supply Chain Disruptions
6
The cost impact $ould be bet$een 0SD 12. million and 0SD 13..
million for each day a supply net$or% is disrupted4
Shareholder 'alue $ould decrease by 3.5-674 The a'erage abnormal
stoc% returns of the firms sampled $as about 8/.7 o'er a time period
that begins one year before and e#tends to t$o years after the
disruption announcement date4
9 port closure could cause a loss ranging from millions to trillions of
dollars for shippers) carriers) and consignees) and e'en damage a
nations economy4
Schedule unreliability in liner shipping operations affects se'eral
actors $ithin the maritime transport chain(
The threat of piracy is multifaceted4
The conse:uences of terrorist attac%s on maritime transport chain
systems include human) economic) and intangible conse:uences5
Chinese Shippers& 'er!eptions for %aritime
Related SCDs
7
Sur'ey Screen
Chinese Shippers& 'er!eptions for %aritime
Related SCDs
8
Sample Description
Chinese Respondents Shen*hen Shanghai
Sample Si*e /; -2
Importers
-;7 /67
+,porters
<37 2-7
Chinese Shippers& 'er!eptions for %aritime
Related SCDs
9
Chinese shippers perceptions for maritime related SCDs costs
Supply chain disruption=related costs Sum !7"
Lost sales>profit 22
Damage reputation /-
Increase administration $or%load and costs ?@
Increase transport costs ?-
Damage customer relationship -6
9ccount recei'able and cash flo$ 3/
Lead time increased 6
Chinese Shippers& 'er!eptions for %aritime
Related SCDs
10
Chinese shippers contingency plans for maritime related SCDs
Detail of !ontingen!y plans Sum !7"
-perational le#el
Change shipping schedule>route ?253/
Communication to all parties to reschedule deli'ery time -65?6
9lternati'e sourcing>substitute product 3<52<
Aegotiate price discount>rebate to customers>apply penalty to suppliers 6533
Strategi! le#el
Lengthen estimated lead time 35?2
Increase safety stoc% 35?2
Di'ersify carriers>suppliers base 3.563
Build ris% management team 3?523
In'est on IT system impro'e trac%ing>de'elop ne$ product
Mitigation Strategies for SCDs
11
Getting it Right from the Start
Proacti'e strategy !eg5 selecting CsafeD locations) robust suppliers"
$uilding a Se!ure and .le,ible Company Culture
Collaboration
Collaborati'e Transportation Management !CTM"
$uilding Redundan!ies
9 short=term SCD and In'entory carrying>managing costs are lo$
o
Eolding safety stoc%
o
Strategic stoc%
9 longer period of time SCD) and in'entory managing costs>the
ris%s of product obsolescence are high
o
Redundant capacities
o
Feeping a redundant IT system
Mitigation Strategies for SCDs
12
!Continuing"
$uilding .le,ibilities
Standardi,ation
Postponement
9 fle#ible supply base strategy
Gle#ible transportation strategy
Dynamic pricing>promotion>substitutable products strategies
!Dell successfully na'igated a SCD caused by the 3;;; Tai$an earth:ua%e by steering its
customers to buy particular products"
Chinas Logistics Industry
13
China&s ogisti!s Industry atest De#elopment
9n a'erage annual gro$th rate of -?74
In -.33) Chinas e#ternal logistic cost totalled RMB65/ trillion)
accounting for 3<567 of the &DP4
The structure of China logistics costs (
Chinas Logistics Industry
14
China ogisti!s Infrastru!ture De#elopment
Road transport
o
9ccounting for <@527 of the total freight carried internally in -..;4
o
To$ns $ith high$ays account for ;;5-/7 of all to$ns) and ;-56@7
of total 'illages country$ide ha'e access to high$ays5
Rail transport
o
Rail freight only accounts for 335;7 of the total freight shipped4
o
The third largest rail net$or% in the $orld $ith ;;)...%m of trac%4
o
9 proHect is under$ay to connect containeri,ed bo# shipments from
China to Iurope 'ia rail5
Chinas Logistics Industry
15
!Continuing"
Inland waterway
o
9ccounts for 33527 of the total freight in -..;4
o
Chinas 33.)... %m of na'igable distances pro'ides the $orlds
largest inland $ater$ay net$or%4
o
Ae$ Jangt,e Ri'er Port utilisation ma%es it an economically and
en'ironmentally sound alternati'e to road haulage5
Maritime
o
By the end of -..6) there $ere /3? ports in China) ?@ of $hich
ha'e an annual handling capacity of or abo'e3. million tons4
o
The port of Shanghai became the largest container port in the
$orld in terms of its throughput in -.3.5
Chinas Logistics Industry
16
!Continuing"
Air freight
o
9ccounts for only a small proportion of Chinas freight
transport mi#4
o
China has 2.- airports of $hich 667 ha'e pa'ed run$ays5
Chinas forwarding, brokerage and warehousing services
o
Increasing $arehouse efficiencies and capacities in China are
strongly needed4
o
Lo$ efficiency of $arehousing operations is a maHor
$ea%ness in Chinese SC systems5
Chinas Logistics Industry
17
China ogisti!s Industry Challenges
Lo$ efficiency and higher logistics costs4
Lac% of national integrated transportation net$or%4
Poor IT infrastructure and inability to use ad'ance technology4
0nderde'eloped $arehousing ser'ice4
Local protectionism4
9 scarcity of :ualified logistics personnel4
Inconsistency in policies and regulations4 and
Gragmented domestic freight5
Chinas Logistics Industry
18
Eigh$ays became par%ing lots in -.3- Chinas national day
holidays
Chinas Logistics Industry
19
R%$/01/ billion sales and more than 23 million pa!kages on //4//453/56 7single day8
Chinas Logistics Industry
20
Re!ommendations for Colombian Importers
Choose robust suppliers4
Choose robust ?PLs in China4
!better $ith lobbying and bargaining po$er $ith local go'ernment)
eg5 G+KC+AA5 &uan#i is indispensable in China"
9d'anced $arning strategies4
!lengthen lead=time) particularly) Labour day) Aational day) festi'als) etc5
+r bring for$ard to a'oid the Chinese festi'als"
Inhance information 'isibility4 and
Inhance collaboration $ith SC parties5
uantifying Supply Chain Disruptions Costs
21
Methodology
The Latent Class Models !LCM"= a probabilistic modelling
Seemingly 0nrelated Regression Models !S0RI"
C C
X1 X2
X3
Xn X1 X2 X3
Xn
% / % 5
= =
C c
q c
q c
C c
qc
qc
qc
h
h
V
V
p
" e#p!
" e#p!
" e#p!
" e#p!
=
=
= =
i
K
k
qsik qsk
K
k
qsjk qsk
i
c qsi
c qsj
c qsj
x
x
V
V
p
" e#p!
" e#p!
" e#p!
" e#p!
3
3
)
5 ) C
P P y
P P y
P
C
C c
qc c qsi qsi
qc c qsj qsi
c qs
uantifying Supply Chain Disruptions Costs
22
.indings
The LCMs re'ealed that respondents latent preference heterogeneity
created t$o segments !lo$ and high" under normal operation and three
segments !lo$) medium) and high" $ith a disruption 5
uantifying Supply Chain Disruptions Costs
23
!Continuing"
Shippers *TP are different under normal and disruption operations4
Shippers VTTS could increase more than / times if there is a disruption5
uantifying Supply Chain Disruptions Costs
24
!Continuing"
The S0RI model results re'eal that production) company>supply chain
characteristics) and shipment specific characteristics ha'e significant
influence on shippers preference for maritime ser'ice attributes $ith and
$ithout a disruption5
o
Gor e#ample( geographical locations
uantifying Supply Chain Disruptions Costs
25
!Continuing"
o
Gor e#ample( geographical locations
iq i Shenzhen iq Sydney iq k k
k
U Shenzhen Sydney x = + + +
Conclusions
26
The findings !ould be helpful for industry stakeholders(
Shippers
Ser'ice pro'iders
Insurers
&o'ernments and policy ma%ers
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Supply Chain Management of Major Courier Companies in IndiaDokument15 SeitenSupply Chain Management of Major Courier Companies in IndiaNilabjo Kanti PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics of Logistics Transportation, Warehousing and Distribution SystemDokument114 SeitenDynamics of Logistics Transportation, Warehousing and Distribution Systemanon_528179379100% (1)
- Model Test 33Dokument12 SeitenModel Test 33MaheshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dry Ports and The Extended Gateway Concept Porthinterland ContaiDokument26 SeitenDry Ports and The Extended Gateway Concept Porthinterland ContaiSaid BasalimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature Review Shipping IndustryDokument6 SeitenLiterature Review Shipping Industryea1yd6vn100% (1)
- Supply Chain Management (MAL)Dokument2 SeitenSupply Chain Management (MAL)Hasib AhsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis Title Related To Marine TransportationDokument8 SeitenThesis Title Related To Marine Transportationbser9zca100% (2)
- Logistics and Transportation Industry in IndiaDokument79 SeitenLogistics and Transportation Industry in Indiaabdulkhaderjeelani14Noch keine Bewertungen
- INVESTASI & LOGISTIK Sri RahardjoDokument66 SeitenINVESTASI & LOGISTIK Sri RahardjoWendra NovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decongesting Delhi A Creative Problem Solving ApproachDokument16 SeitenDecongesting Delhi A Creative Problem Solving ApproachMuktesh Chander IPSNoch keine Bewertungen
- World Cruise IndustryDokument43 SeitenWorld Cruise IndustryCherie OrpiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 6 Reverse Logistics PresentationDokument27 SeitenCH 6 Reverse Logistics PresentationSiddhesh KolgaonkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report Analysing Port and Shipping Operations Using Big Data June2018Dokument50 SeitenReport Analysing Port and Shipping Operations Using Big Data June2018Shreyansh tripathi100% (1)
- Connectivity Analysis of The Global Shipping Network by Eigenvalue DecompositionDokument11 SeitenConnectivity Analysis of The Global Shipping Network by Eigenvalue DecompositionNatee PanomchokpisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSHIP101 DISL Course OutlineDokument5 SeitenCSHIP101 DISL Course OutlineChristinaMurrayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marine Transportation Thesis TitleDokument8 SeitenMarine Transportation Thesis Titletracyberrycary100% (1)
- Modul 11 Prediksi Demand TrafficDokument26 SeitenModul 11 Prediksi Demand TrafficErwin SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Distribution Logistics: College of Dunaújváros Dunaújváros Táncsics M. U. 1/A. F/118/EDokument15 SeitenDistribution Logistics: College of Dunaújváros Dunaújváros Táncsics M. U. 1/A. F/118/EEric AmoakoNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Content Downloaded From 146.50.98.82 On Sun, 13 Nov 2022 01:22:16 UTCDokument25 SeitenThis Content Downloaded From 146.50.98.82 On Sun, 13 Nov 2022 01:22:16 UTCQIAN HUANGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logistics and Transportation Industry in IndiaDokument59 SeitenLogistics and Transportation Industry in Indiadk6666Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case Innovative Distribuiton CompanyDokument11 SeitenCase Innovative Distribuiton Companyf1370671Noch keine Bewertungen
- Finals Chapter 7 - Introduction To Transport ServicesDokument22 SeitenFinals Chapter 7 - Introduction To Transport ServicesAlexis EusebioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Container Industry Value ChainDokument14 SeitenContainer Industry Value ChainRasmus ArentsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determinants of Port Performance - Case Study of FDokument9 SeitenDeterminants of Port Performance - Case Study of FWai PhyopaingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 1Dokument16 SeitenPaper 1sivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crainic - Laporte - IJPRTransportation in Supply Chain ManagementDokument5 SeitenCrainic - Laporte - IJPRTransportation in Supply Chain Managementtwinkle girlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Koje Su Osnovne Karakteristike Postojećeg Stanja Zaštite Životne Sredine I Transporta?Dokument3 SeitenKoje Su Osnovne Karakteristike Postojećeg Stanja Zaštite Životne Sredine I Transporta?Abdul Kerim AlihodzicNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Evaluation of Container Ports in China and Korea With The Analytic Hierarchy ProcessDokument16 SeitenAn Evaluation of Container Ports in China and Korea With The Analytic Hierarchy ProcessrasthoenNoch keine Bewertungen
- m4 TranspoDokument101 Seitenm4 TranspomarcusluismacusiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 WestvacoDokument4 Seiten04 Westvacoelvarg09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Port Engineering Planning, Design and Analysis: Prepared By: Jeremy MolayemDokument15 SeitenPort Engineering Planning, Design and Analysis: Prepared By: Jeremy MolayemJeremy MolayemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waste Management in The Public Transport Systems in India, China and The Uk A Comparative AnalysisDokument5 SeitenWaste Management in The Public Transport Systems in India, China and The Uk A Comparative AnalysisShaquille Jordan DagdagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 6: Supply Chain Management: OutlineDokument65 SeitenLesson 6: Supply Chain Management: OutlineUlyviatrisnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imt 69Dokument4 SeitenImt 69arun1974Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ch7 Port Hinterlands LogisticsDokument37 SeitenCh7 Port Hinterlands LogisticsAswinanderst Twilight-Forever TbcKuadratNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logistics ConceptsDokument34 SeitenLogistics ConceptsprekshiashuNoch keine Bewertungen
- NTC2014 SU R 06 - ListDokument57 SeitenNTC2014 SU R 06 - Listmutton moonswamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Increased Funds To Ensure Passenger Amenities and CleanlinessDokument3 SeitenIncreased Funds To Ensure Passenger Amenities and CleanlinessSunilKumarGuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Design DBMDokument35 SeitenNetwork Design DBMNareshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Describe The Five Modes of Transportation, Identifying The Most Significant Characteristic of Each - Supply Chain Management - W3mentorDokument4 SeitenDescribe The Five Modes of Transportation, Identifying The Most Significant Characteristic of Each - Supply Chain Management - W3mentorKawaljitSinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject Code:: C C CCDokument23 SeitenSubject Code:: C C CCMithesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Globalisation Vitro, Ahmet, Prashant, BJ, WaqasDokument25 SeitenGlobalisation Vitro, Ahmet, Prashant, BJ, WaqasShri Prashant JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation1 (VPA) Supply Chain Management FinalDokument241 SeitenPresentation1 (VPA) Supply Chain Management FinalRohit Batra100% (1)
- Nirmitee 2003: Maharashtra Institute of Technology, PuneDokument10 SeitenNirmitee 2003: Maharashtra Institute of Technology, PunePradeepLokhandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inland Waterways and The Global Supply ChainDokument24 SeitenInland Waterways and The Global Supply ChainBambang Setiawan MNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Case Study On:: Utilisation of Container Movement-IRC: Import To ExportDokument22 SeitenA Case Study On:: Utilisation of Container Movement-IRC: Import To ExportCHAHATNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal Latihan IECOMDokument24 SeitenSoal Latihan IECOMBernard SinartaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HO 5 Sampling DistributionDokument4 SeitenHO 5 Sampling Distributionakash bamankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Globalization and LogisticsDokument25 SeitenGlobalization and LogisticsMyunghee LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tracking Medicine - John E. WennbergDokument340 SeitenTracking Medicine - John E. WennbergurbanincultureNoch keine Bewertungen
- SISLOG-1. Introduction To Logistics Management and StrategyDokument35 SeitenSISLOG-1. Introduction To Logistics Management and StrategyGhani RizkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supply Chain Management Quiz PDFDokument7 SeitenSupply Chain Management Quiz PDFbhartia100% (2)
- Est May 2022Dokument3 SeitenEst May 2022MarvinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Queuing Analysis: Chapter OutlineDokument22 SeitenQueuing Analysis: Chapter OutlineMike SerquinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For Improving Airport Services For International Customers (2016)Dokument55 SeitenGuidelines For Improving Airport Services For International Customers (2016)Iqbal Khan MohammadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1231231231231231231231231231231lecture 1Dokument52 Seiten1231231231231231231231231231231lecture 1lfobillyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ROAD & Rail TransportationDokument8 SeitenROAD & Rail TransportationSatnam SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson - 06 - Highway Safety & Traffic Flow - S2016Dokument27 SeitenLesson - 06 - Highway Safety & Traffic Flow - S2016Sharanya IyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Keukainv OriginalDokument296 SeitenKeukainv Originalrtyy100% (1)
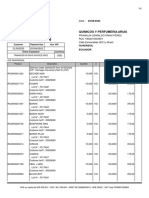
- Factura ComercialDokument6 SeitenFactura ComercialKaren MezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estatement 2020021828 PDFDokument1 SeiteEstatement 2020021828 PDFALL IN ONE. BOOLIWOOd SONGNoch keine Bewertungen
- MGV Form (FORM ABC)Dokument32 SeitenMGV Form (FORM ABC)Muhammad MujibNoch keine Bewertungen
- IDFC FIRST Bank Statement As of 31 MAR 2019 PDFDokument9 SeitenIDFC FIRST Bank Statement As of 31 MAR 2019 PDFchandrakant bansode50% (2)
- Two Collection Recceipt 66067547Dokument1 SeiteTwo Collection Recceipt 66067547Kumar BinoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuizDokument5 SeitenQuizRomaica Ella AmbidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReturnDokument1 SeiteReturnFaisal Islam ButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- State Bank of India2 PDFDokument2 SeitenState Bank of India2 PDFibicengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Ticket Receipt, April 05 For MR JEMUEL LABRADORDokument2 SeitenElectronic Ticket Receipt, April 05 For MR JEMUEL LABRADORJemuel LabradorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jep 24 000712157Dokument1 SeiteJep 24 000712157ivo mandantesNoch keine Bewertungen
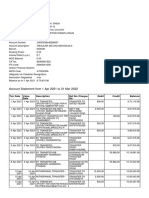
- Account Statement From 1 Apr 2021 To 31 Mar 2022: TXN Date Value Date Description Ref No./Cheque No. Debit Credit BalanceDokument12 SeitenAccount Statement From 1 Apr 2021 To 31 Mar 2022: TXN Date Value Date Description Ref No./Cheque No. Debit Credit BalanceNiwadi PremiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Payment Slip: Summary of Charges / Payments Current Bill AnalysisDokument8 SeitenPayment Slip: Summary of Charges / Payments Current Bill AnalysisMelanie Kelly NeilsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- INDIAN ISPAT REPLY Letter PERSONAL HEARINGDokument3 SeitenINDIAN ISPAT REPLY Letter PERSONAL HEARINGSURANA1973100% (1)
- Income-Tax Banggawan2019 CR7Dokument10 SeitenIncome-Tax Banggawan2019 CR7Noreen Ledda11% (9)
- Motor - Assist - Booklet (Done Excel, Done CC)Dokument52 SeitenMotor - Assist - Booklet (Done Excel, Done CC)CK AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Staedler Vs CIRDokument58 SeitenStaedler Vs CIRJerome Delos ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesco - Web BillDokument1 SeiteLesco - Web Billnawaab saaabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teresita Buenaflor ShoesDokument19 SeitenTeresita Buenaflor ShoesGiselle Martinez87% (30)
- Maintain - Financial - Standards - & - Records - Refined Pak YunDokument107 SeitenMaintain - Financial - Standards - & - Records - Refined Pak YunJohn EpraimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Payroll in GermanyDokument8 SeitenPayroll in GermanyofdujcgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Incoterms and Chartering TermsDokument30 SeitenIncoterms and Chartering TermsThaisBrandãoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Freight Forwarder in The Execution of ExportDokument28 SeitenRole of Freight Forwarder in The Execution of ExportMohd Fahad80% (10)
- Stat 3Dokument9 SeitenStat 3Madan RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ereceipt PDFDokument1 SeiteEreceipt PDFAnonymous ap9S5dwPigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Travel Agents DatabaseDokument216 SeitenTravel Agents DatabaseNeshchint Mendon100% (1)
- Wire Transfer NotificationDokument1 SeiteWire Transfer NotificationElias AguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Protect Essential Insurance 2Dokument9 SeitenSmart Protect Essential Insurance 2nusthe2745100% (1)
- Details of Statement: Name Kavitha Paripelly D/O Raghu Ram, Plot No: 204, Bhargav HomesDokument10 SeitenDetails of Statement: Name Kavitha Paripelly D/O Raghu Ram, Plot No: 204, Bhargav HomesAashishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kotler - Chapter 9.marketing ChannelsDokument37 SeitenKotler - Chapter 9.marketing Channelsamirahzaiyad100% (2)