Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
REFERAT Pendekatan Klinis Pansitopenia
Hochgeladen von
Yudhistira AdiOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
REFERAT Pendekatan Klinis Pansitopenia
Hochgeladen von
Yudhistira AdiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
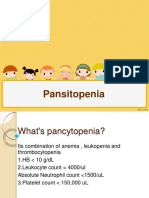
Pendekatan Diagnostik
Pansitopenia
Dian Riani 2009730132
Pembimbing : Dr. Tuti Sri Hastuti Sp.PD
M-Kes
jumlah 3 komponen darah:
Eritrosit, Leukosit dan Trombosit.
Anemia, leukopenia,
dan trombositopenia.
produksi darah di
sumsum tulang
Bone marrow faillure
syndrome
Immune mediated
destruction
Non immune mediated
sequestration in
peripher
Table of etiologies for pancytopenia. Abbreviation: GVHD, graft-versus-host disease
From the collection of Jeff K. Davies
Primer
Idiopatik
Kongenital
Fanconi anemia
Dyskeratosis congenital
Diamond blacfan anemia
Shwachman diamond syndrome
Severe congenital neutropenia
Kostman syndrome
Amegakaryotic thrombocytopenia
Sekunder
Obat-obatan
Sitotoksik
Chloramphenicol
Respon idiosinkrasi (immune mediated) :
NSAIDS
Colchicine
Chlorampenicol
Sulfonamid
Phenothiazine
Thiazid
Anti thyroid
Anti epileptik
Anti diabetik
Infeksi virus
Sering : hepatitis B dan C
Jarang : cytomegalo virus, epstein Barr Virus,
HIV, Hepatitis A, rubella, influenza, measles,
mumps
Infeksi mycobacterium
Penyakit autoimmune
Kimiawi (benzene, arsenik)
Infiltrasi keganasan
Hematologi: limfoma, leukimia, myeloma
Tumor solid
Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria
Spplenomegali
Radiasi
Ringan Hemoglobin <8 gr/dL, sel PMN > 2000/mm
3
, trombosit
>20.000/mm
3
Sedang Hemoglobin <7 gr/dL, sel PMN < 500/mm
3
, trombosit
<20.000/mm
3
Berat Leukosit <200 /mm
3
, trombosit <10.000/mm
3
Derajat pansitopenia
Anamnesis
Pemeriksaan fisik
Pemeriksaan Hitung darah lengkap
Analisis darah tepi
Aspirasi dan biopsi sumsung tulang
Anemia aplastik
Sindrom gagal sumsum tulang
turunan
Riwayat keguguran
Riwayat menderita keganasan
Gangguan metabolik
Riwayat penyakit hati
Riwayat penggunaan obat
sitotoksik dan radio terapi
Pemeriksaan Fisik
Oral :
Ptekie/ Perdarahan di rongga mulut
(trombositopenia)
Stomatitis/chelitis (neutropenia, def.
Vit B12)
Hiperplasia gusi (leukimia )
Kandidiasis oral/ eksudat faring
(neutropenia, infeksi herpes virus)
Mata :
Perdarahan retina (trombositopenia)
Infiltrasi lekemik (leukimia akut)
Sklera ikhterik (Paroxysmal nocturna
hemoglobinuria, hepatitis, sirosis)
Epiphora (dyskeratosis congenital)
Respiratori :
Clubbing (ca. paru)
Takipnea
Kardiovaskular:
Takikardi, edema,
CHF
Bekas pembedahan
jantung (sindrom
kongenital).
Abdomen :
Nyeri perut kakan atas (
hepatitis )
Limfadenopati (infeksi,
penyakit limfoproliferatif,
HIV)
Tanda penyakit hati
kronis
Splenomegali (infeksi,
penyakit
myeloproliferatif,
limfoproliferatif)
Kulit :
Malar rash (SLE)
Purpura
(trombositopenia)
Pigmentasi retikular,
kuku displastik
(dyskeratosis
congenital)
Area hipopigmentasi
Hiperpigmentasi, caf
au lait (anemia fanconi
Muskuloskeletal :
Short stature ( fanconi
anemia, kelainan
congenital lain)
Artritis, sinovitis (SLE)
Jari-jari abnormal
(anemia fanconi)
Sign assosiated with HIV
:
Morbiliform rash
Sarkoma kaposi,
nodul ulseratif
Laboratorium
Pemeriksaan standar
Hitung darah lengkap
Apusan darah tepi
Hitung retikulosit darah
Fungsi hati dan serologi hepatitis
Tes koagulasi, bleeding time, fibrinogen, D-dimer
Tes direct antiglobulin
Serum B12 dan folat
Seru HIV
TES anti nucleid acid
Biopsi sumsum tulang
Selularitas:
: gangguan produksi darah: pasca kemoterapi, sepsis/infeksi
akut, HIV Stadium lanjut, syndrom myelodisplasi hipoplastik,
IBMFS,anemia aplastik idiopatik, SLE, PNH
N/: produksi yang tidak efektif/destruksi/sekuestrasi sel-sel
darah: myelodisplasia, leukimia akut/kronik,myeloma dengan
plasma selnya, infiltrasi keganasan, HIV stadium dini/akut,
anemia megaloblastik.
Histologi :
Infiltrasi sel
Blast
Gambaran myelodispplasia
Aspirasi Sumsum Tulang
Sitologi (perubahan megaloblastik, perubahan
displastik, infiltrasi sel abnormal dan infeksi)
Imunofenotif (leukimia akut dan kronik,
penyakit limfoproliferatif)
Sitogenik (myelodisplasi, leukimia akut dan
kronik, penyakit limpoproliferatif).
Temuan laboratorium
Common
Differential 1st Tests Other Tests
Chemotherapy peripheral blood: anisocytosis, poikilocytosis,
basophilic stippling
bone marrow aspirate: variable hypoplasia
bone marrow biopsy: hypoplasia, megaloblastosis
Radiotherapy peripheral blood: anisocytosis, poikilocytosis,
basophilic stippling
bone marrow aspirate: variable hypoplasia
bone marrow biopsy: hypoplasia, megaloblastosis
Vitamin B12 deficiency peripheral blood film: oval macrocytic RBCs, irregular
size and shape of RBCs (anisocytosis and
poikilocytosis), hypersegmented granulocytes (>5
lobes)
serum reticulocyte count: usually low
serum B12: low in B12 deficiency
bone marrow aspirate: hypercellular, megaloblastic
erythroblasts, giant metamyelocytes
serum LDH: moderately raised
serum bilirubin: moderately raised, mostly indirect
Folic acid deficiency peripheral blood film: oval macrocytic RBCs,
irregular size and shape of RBCs (anisocytosis and
poikilocytosis), hypersegmented granulocytes (>5
lobes)
serum reticulocyte count: usually low
serum RBC folate: low in folate deficiency
bone marrow aspirate: hypercellular,
megaloblastic erythroblasts, giant metamyelocytes
serum LDH: moderately raised
serum bilirubin: moderately raised, mostly
indirect
Bone marrow infiltration by
nonhematologic malignancy
peripheral blood film: leuko-erythroblastic cell
forms
bone marrow aspirate: clumps of tumor cells
CXR: mass (lung cancer)
serum LFTs: elevated ALT and AST ( hepatic
metastases)
serum coagulation profile: prolonged PT and PTT
serum fibrinogen and D-dimer: diminished
fibrinogen and elevated D-dimer (indicative of
chronic disseminated intravascular coagulation)
CT of abdomen: may reveal
abdominal or renal mass
serum prostatic-specific
antigen: elevated in prostate cancer
thyroid ultrasound: irregular mass or
nodule
breast imaging: mass or calcifications
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma peripheral blood film: variable; may show
circulating lymphoma cells
bone marrow aspirate: increased proportion of
lymphoid cells
immunophenotyping (of peripheral blood or bone
marrow): clonal population of lymphoid cells
lymph node biopsy: lymphoproliferative disorder
Hairy cell leukemia peripheral blood film: circulating
lymphoma cells
bone marrow aspirate: increased
proportion of lymphoid cells
immunophenotyping (of peripheral blood
or bone marrow): clonal population of
lymphoid cells
Chronic lymphocytic
leukemia
peripheral blood film: circulating leukemia
cells cells
bone marrow aspirate: increased
proportion of lymphoid cells
immunophenotyping (of peripheral blood
or bone marrow): clonal population of
lymphoid cells
lymph node
biopsy: lymphoproliferative
disorder
Myelodysplasia peripheral blood film: may have irregular
or macrocytic RBCs, dysplastic granulocytes,
platelets may be large and hypogranular
serum reticulocyte count: usually low, may
be normal or raised
bone marrow aspirate: usually
hypercellular, rarely, hypocellular
(hypocellular myelodysplasia), dysplastic
changes
cytogenetics: may be abnormal
Cirrhosis peripheral blood film: macrocytes, target
cells, stomatocytes, acanthocytes
reticulocyte count: elevated or normal
serum LFTs: elevated
bone marrow
aspirate: hypercellular, erythroid
hyperplasia
Hepatitis B peripheral blood film: macrocytes, target cells,
stomatocytes, acanthocytes
reticulocyte count: elevated or normal
serum LFTs: elevated
serum HBsAg: positive
bone marrow
aspirate: hypercellular,
erythroid hyperplasia
Hepatitis C peripheral blood film: macrocytes, target cells,
stomatocytes, acanthocytes
reticulocyte count: elevated or normal
serum LFTs: elevated
serum antihepatitis C virus (HCV): presence of
HCV antibodies
bone marrow
aspirate: hypercellular,
erythroid hyperplasia
Autoimmune hepatitis peripheral blood film: macrocytes, target cells,
stomatocytes, acanthocytes
reticulocyte count: elevated or normal
serum LFTs: elevated
autoantibody screen: positive
bone marrow
aspirate: hypercellular,
erythroid hyperplasia
HIV peripheral blood film: atypical lymphocytes
(acute seroconversion), rouleaux, dysplastic
neutrophils
reticulocyte count: reduced
HIV serology: positive
bone marrow aspirate: hypercellular (acute
seroconversion), hypocellular,
dyserythropoiesis
protein
electrophoresis: polyclo
nal
hypergammaglobulinem
ia
Cytomegalovirus infection peripheral blood film: atypical lymphocytes, spherocytes if coexisting
hemolysis
CMV-specific IgM and IgG: positive
bone marrow aspirate: cellularity usually increased, hemophagocytosis
may be prominent
bone marrow trephine biopsy: cellularity usually increased
Mycobacterial infection peripheral blood film: rouleaux
reticulocyte count: reduced
bone marrow aspirate: reduced cellularity, hemophagocytosis
bone marrow trephine biopsy: reduced cellularity, granulomas, fibrosis
bone marrow culture: positive for organism
Uncommon
Differential 1st Tests Other Tests
Acute myeloid leukemia peripheral blood film: blasts on blood film,
presence of Auer rods
serum PT, PTT, fibrinogen, D-dimer: may be
abnormal, suspect DIC
bone marrow aspiration: usually hypercellular
with blasts, rarely hypocellular
bone marrow biopsy: presence of blasts,
infiltration, Auer rods
immunophenotyping: detection of clonal
population of blasts
cytogenetics: identification or nonrandom
chromosomal abnormalities
serum PT, PTT, fibrinogen, D-dimer:prolonged PT,
PTT; diminished fibrinogen, elevated D-dimer
Acute lymphocytic leukemia peripheral blood film: blasts may or may not be
present
bone marrow aspirate: hypercellular with blasts;
occasionally hypocellular (childhood ALL)
immunophenotyping (of peripheral blood
or bone marrow): detection of clonal
population of blasts
cytogenetics: identification of nonrandom
chromosomal abnormalities
Multiple myeloma peripheral blood film: rouleaux, circulating
plasma cells may rarely be present
bone marrow aspirate: plasma cell infiltrate,
abnormal plasma cells, plasmablasts
immunophenotyping (of peripheral blood or
bone marrow): plasma cells exhibit restriction of
kappa or lambda light chain expression
serum and urine electrophoresis:monoclonal
serum protein and urinary Bence-Jones proteins
(light chains) detected
radiologic skeletal survey: lytic lesions
and/or osteopenia
Myelofibrosis peripheral blood film: leuko-erythroblastic, tear drop RBCs
bone marrow aspirate: hypercellular and fibrotic, often dry
tap and nondiagnostic
serum and RBC
folate: usually diminished
serum B12: usually
elevated
Lysosomal storage
disorders
leukocyte glucocerebroside activity:reduced or absent
peripheral blood film: pancytopenia
reticulocyte count: may be high, normal, or reduced
bone marrow aspirate: may reveal Gaucher cells
bleeding time: prolonged
Anorexia nervosa peripheral blood film: red cell acanthocytes, poikilocytosis
and basophilic stippling
reticulocyte count: low
bone marrow aspirate: hypocellular, reduced hematopoietic
cells, may show gelatinous transformation
bone marrow trephine biopsy: hypocellular without
infiltration or fibrosis
diepoxybutane test: normal
Graft-versus-host
disease
peripheral blood film: no specific features
reticulocyte count: low
bone marrow aspirate: hypocellular, reduced hematopoietic
cells, increased macrophages, erythrophagocytosis
bone marrow trephine biopsy: hypocellular without
infiltration or fibrosis, increased macrophages
skin, liver, upper GI biopsy: characteristic appearances of
acute GVHD
HLA typing of peripheral blood lymphocytes: chimerism
Heavy metal
(arsenic) poisoning
peripheral blood film: basophilic stippling
bone marrow aspirate: hypocellular without infiltrate
or fibrosis, decreased hematopoietic cells,
dyserythropoiesis
bone marrow trephine biopsy: hypocellular without
infiltration or fibrosis dyserythropoiesis
diepoxybutane test: normal
screening for PNH clone: negative
arsenic level (serum, urine, hair, nails):elevated
Parvovirus infection
in sickle cell anemia
CBC: drop in hemoglobin concentration of >30 percent
secondary to complete arrest of erythropoiesis
reticulocyte count: decrease or absence of
measurable reticulocytes
bone marrow biopsy: remarkable for severe aplasia
Dyskeratosis
congenita
peripheral blood film: red cells usually macrocytic
reticulocyte count: low or absent
bone marrow aspirate: hypocellular, reduced
hematopoietic cells, dyserythropoiesis common
bone marrow trephine biopsy: hypocellular without
infiltration or fibrosis
diepoxybutane test: normal (peripheral blood
lymphocytes)
screening for PNH clone: may be present
peripheral blood and/or bone marrow
immunophenotyping: normal
blood and/or bone marrow cytogenetics:clonal
abnormalities present in some patients
genetic studies: may identify
1 of several genetic mutations
telomere length: abnormally
short; length in lymphocytes
and granulocytes <1 percentile
for age
Paroxysmal nocturnal
hemoglobinuria
peripheral blood film: polychromasia
reticulocyte count: relative reticulocytosis
bone marrow aspirate: hypocellular, reduced hematopoietic
cells, mast cells may be increased
diepoxybutane test: normal
screening for PNH
clone: positive
Idiopathic aplastic anemia peripheral blood film: normocytic or mildly macrocytic
RBCs, no immature precursors present
serum reticulocyte count: low or absent
bone marrow aspirate: hypocellular, mild dyserythropoiesis
common
bone marrow trephine biopsy: hypocellular without fibrosis
or infiltrate
diepoxybutane test (peripheral blood
lymphocytes): normal
screening for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria clone
(peripheral blood, bone marrow): detectable in up to 30% of
patients
peripheral blood, bone marrow
immunophenotyping: normal
peripheral blood, bone marrow cytogenetics: abnormal
clones present in a minority of patients
Fanconi anemia peripheral blood film: RBCs usually macrocytic
reticulocyte count: low or absent
bone marrow aspirate: hypocellular dyserythropoiesis
diepoxybutane test (peripheral blood
lymphocytes): increased chromosomal breakage
Idiopathic portal
hypertension
peripheral blood film: no specific features
reticulocyte count: elevated or normal
serum LFTs: normal or mildly elevated
bone marrow
aspirate: hypercellular, erythroid
hyperplasia
bone marrow trephine
biopsy:hypercellular, erythroid
hyperplasia
Chronic myeloid
leukemia
peripheral blood film: myeloid maturing cells,
elevated basophils, eosinophils
cytogenetics: Philadelphia chromosome
positive
bone marrow biopsy: granulocytic hyperplasia
Brucellosis peripheral blood film: no specific features
bone marrow aspirate: trilineage
hypercellularity, hematophagocytosis
blood and bone marrow cultures: positive for
organism
Leishmaniasis peripheral blood film: rouleaux; organisms
rarely seen in peripheral blood film
bone marrow aspirate: trilineage
hypercellularity; organisms may be seen within
macrophages (Leishman-Donovan bodies)
bone marrow trephine biopsy: trilineage
hypercellularity, hematophagocytosis, small
granulomata
immunochromatographic or PCR-based tests
on peripheral blood or bone marrow
aspirate: positive for organism
Hemophagocytosis
syndromes
peripheral blood film: no specific features
bone marrow aspirate: trilineage
hypercellularity, hematophagocytosis
blood and bone marrow cultures: positive for
organism
autoimmune screen: positive ANA
and anti-ds DNA
serum ferritin: >10,000 mcg/L
molecular genetic testing: specific
karyotype present
Drug-induced immune
pancytopenia
platelet-specific antibodies: positive
peripheral blood film: no specific features
reticulocyte count: elevated
bone marrow aspirate: hypercellular
bone marrow trephine biopsy: hypercellular
Evans syndrome with
associated neutropenia
peripheral blood film: polychromasia, spherocytes
reticulocyte count: elevated
direct antiglobulin test: positive
platelet, neutrophil-specific antibodies:positive
bone marrow aspirate: normal or trilineage hypercellularity
bone marrow trephine biopsy: normal or trilineage hypercellularity
Systemic lupus
erythematosus
peripheral blood film: rouleaux
autoimmune screen: positive ANA and anti-DNA
ultrasound of the abdomen: splenomegaly
bone marrow aspirate: hypocellular, Adysplastic changes, hematophagocytosis
bone marrow trephine biopsy: hypocellular, benign lymphoid aggregates
Rheumatoid arthritis peripheral blood film: rouleaux
autoimmune screen: positive rheumatoid factor
bone marrow aspirate: hypocellular, dysplastic changes, hematophagocytosis
bone marrow trephine biopsy: hypocellular, benign lymphoid aggregates
ultrasound of the abdomen: splenomegaly
Infectious mononucleosis serum monospot: positive
peripheral blood film: atypical lymphocytes
Epstein-Barr nuclear antibody: present
blood serology (specific IgM and IgG titers) for viral capsid antigen: positive
Felty syndrome bone marrow biopsy: myeloid hyperplasia with excess of immature forms
autoimmune screen: positive rheumatoid factor
ultrasound of the abdomen: splenomegal
Pansitopenia bukanlah suatu gejala melainkan
suatu triad yang di sebabkan suatu proses
penyakit yang melibatkan sumsum tulang baik
primer maupun sekunder
Pansitopenia masalah sering di temui sehari-
hari
Perlu pemeriksaan yang lebih spesifik untuk
mengetahui penyebabnya.
Tinjauan Pustaka
1. Evaluation of pancytopenia Diagnostic
approach-Eppocrates online
hhtps://online.epocrates.com/u/29211024/
evaluation+of+pancytopenia.
2. Makalah lenkap Bandung hematologi
oncology meeting 2013, page 7-15
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Physiology Question BankDokument9 SeitenPhysiology Question BankShriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Biology Notes ch22 Chemical Coordination and Integration PDFDokument6 Seiten11 Biology Notes ch22 Chemical Coordination and Integration PDFAarav VarshneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Rebuild Hair Program Ebook Jared Gates Free Download PDFDokument12 SeitenThe Rebuild Hair Program Ebook Jared Gates Free Download PDFBhimesh50% (4)
- 1000 MCQS - PAEDODONTICS, COMMUNITIY & PUBLIC HEALTH Plus September 2014 MCQsDokument22 Seiten1000 MCQS - PAEDODONTICS, COMMUNITIY & PUBLIC HEALTH Plus September 2014 MCQsHarjotBrar100% (2)
- Trauma OkuliDokument50 SeitenTrauma Okuliaditya brahmantio sujakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Messages From The Body Index: by Michael J. Lincoln, PH.DDokument29 SeitenMessages From The Body Index: by Michael J. Lincoln, PH.DNico Panadiou41% (17)
- Primary HeadacheDokument46 SeitenPrimary HeadacheRosaldy Muhamad100% (1)
- Emergency in OncologiDokument70 SeitenEmergency in OncologiAzwin KamarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Terapi Cairan: Pembimbing: Dr. Dr. Bobby Setiadi Dharmawan, SpaDokument45 SeitenTerapi Cairan: Pembimbing: Dr. Dr. Bobby Setiadi Dharmawan, SpaAdamilzaryFikryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chest Radiological AnatomyDokument70 SeitenChest Radiological AnatomyNykole Nyx100% (2)
- Aspek Medikolegal Abortus Flo22 BaruDokument21 SeitenAspek Medikolegal Abortus Flo22 BaruPusparasmi Mas Ayu SuprabhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Index Wayne N New Castle (Thyroid)Dokument1 SeiteIndex Wayne N New Castle (Thyroid)asyiqinramdan100% (1)
- Kapandji TrunkDokument245 SeitenKapandji TrunkVTZIOTZIAS90% (10)
- Kanker Kolorektal - Azril Okta ArdhiansyahDokument106 SeitenKanker Kolorektal - Azril Okta Ardhiansyahbrianto adhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gga Anak PDFDokument27 SeitenGga Anak PDFAlexandro HomalessyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tatalaksana Pasien Dispepsia Pada LansiaDokument14 SeitenTatalaksana Pasien Dispepsia Pada LansiaWiwing MarisyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Terapi Cairan PD AnakDokument62 SeitenTerapi Cairan PD AnakadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- UrinalysisDokument32 SeitenUrinalysiskholoud220Noch keine Bewertungen
- Scanare Zyto PDFDokument23 SeitenScanare Zyto PDFSintimbrean RamoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Akut Abdomen: Divisi Bedah Digestif Bagian Ilmu Bedah Fk. Unair - SurabayaDokument24 SeitenAkut Abdomen: Divisi Bedah Digestif Bagian Ilmu Bedah Fk. Unair - SurabayaYasdika ImamNoch keine Bewertungen
- HipertiroidDokument31 SeitenHipertiroidEdo Pramana PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- TiroidDokument26 SeitenTiroidJoni Riana MustaqimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sindrom Dispepsia: Kepanitraan Klinik Ilmu Penyakit Dalam Rsud DR Chasbullah AbdulmadjidDokument21 SeitenSindrom Dispepsia: Kepanitraan Klinik Ilmu Penyakit Dalam Rsud DR Chasbullah Abdulmadjidladyfame100% (1)
- KONSTIPASIDokument33 SeitenKONSTIPASIalhidayahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosis Aki Dan CKDDokument39 SeitenDiagnosis Aki Dan CKDEly Kartika100% (1)
- PansitopeniaDokument33 SeitenPansitopeniaBrad WrightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pembahasan UKDI CLINIC 1 Batch Mei 2016Dokument535 SeitenPembahasan UKDI CLINIC 1 Batch Mei 2016William Hartanto RusliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gagal Ginjal Akut Dan Kronik: Divisi Ginjal & Hipertensi SMF/Lab - Ilmu Penyakit Dalam FK - UNS / RSUD DR - MoewardiDokument29 SeitenGagal Ginjal Akut Dan Kronik: Divisi Ginjal & Hipertensi SMF/Lab - Ilmu Penyakit Dalam FK - UNS / RSUD DR - MoewardiHabiby Habibaty QolbiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TELAAH KRITIS JURNAL Kel 2 - RCTDokument20 SeitenTELAAH KRITIS JURNAL Kel 2 - RCTNama ManaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Print RapiDokument32 SeitenPrint RapiNiedlichta TamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HERNIORRAPHY (Hernioplasty)Dokument37 SeitenHERNIORRAPHY (Hernioplasty)Aldo AtjehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kegawatan Respirasi May2016-FkumyDokument62 SeitenKegawatan Respirasi May2016-FkumyAgustina Tri P. DNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdominal Pain in Children - Dr. Hermanto SP - BaDokument41 SeitenAbdominal Pain in Children - Dr. Hermanto SP - Bajimmy_junNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar SKDI THT PDFDokument5 SeitenDaftar SKDI THT PDFYohanes Daniel Dwiwirya BadawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tindakan TorakosentesisDokument15 SeitenTindakan TorakosentesisAyu Ayu AyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skdi GehDokument30 SeitenSkdi GehviandamayantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kolestasis Intrahepatal Vs EkstrahepatalDokument4 SeitenKolestasis Intrahepatal Vs EkstrahepatalrikarikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ensefalopati Uremikum Bu YantiDokument16 SeitenEnsefalopati Uremikum Bu YantiAnggi SetyariniNoch keine Bewertungen
- n378.008 Iris Website Staging of CKD PDFDokument8 Seitenn378.008 Iris Website Staging of CKD PDFrutebeufNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 DHF InternaDokument59 Seiten2 DHF Internasaladass 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hemorragic Post PartumDokument35 SeitenHemorragic Post PartumMuhammad AsrizalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid and Electrolyte Problems in Renal DysfunctionDokument5 SeitenFluid and Electrolyte Problems in Renal Dysfunctionfachrudin arNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Ago Harlim - MikosisDokument50 SeitenDr. Ago Harlim - MikosisBrian Pasa NababanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medsense Diagnosis - Treatment of Menstrual Problems (Peserta)Dokument83 SeitenMedsense Diagnosis - Treatment of Menstrual Problems (Peserta)James BudiantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refreshing DHFDokument13 SeitenRefreshing DHFNia Nurhayati ZakiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Referat SepsisDokument18 SeitenReferat SepsisImelva GirsangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) / Decompensation Cordis Functional Class (DCFCDokument25 SeitenCongestive Heart Failure (CHF) / Decompensation Cordis Functional Class (DCFCYUSRIL ZUMADINSYAHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosis Banding Kejang DemamDokument7 SeitenDiagnosis Banding Kejang DemamCesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interpretasi Thorax FotoDokument38 SeitenInterpretasi Thorax FotoSinta SintaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- THT Bimbel Ukdi Mantap 2015 - NorestrictionDokument227 SeitenTHT Bimbel Ukdi Mantap 2015 - NorestrictionpanduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interpretasi Hasil Analisa Gas Darah: (Formula Anderson-Hasselbach)Dokument28 SeitenInterpretasi Hasil Analisa Gas Darah: (Formula Anderson-Hasselbach)mafoel39Noch keine Bewertungen
- TUGAS IPD 1-50 + DapusDokument17 SeitenTUGAS IPD 1-50 + DapusM. RamazaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug EruptionDokument46 SeitenDrug EruptionSisca ChearzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rangkuman IPDDokument8 SeitenRangkuman IPDMuhammad Iqbal Purwana100% (1)
- Obat Dan Kehamilan, Drugs, Aman Untuk Ibu Hamil, FarmasiDokument13 SeitenObat Dan Kehamilan, Drugs, Aman Untuk Ibu Hamil, FarmasifrankysukwendyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gangguan Involuntary MovementDokument54 SeitenGangguan Involuntary MovementMuammar RizkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Akut SkrotumDokument26 SeitenAkut SkrotumToni PinemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tatalaksana Terkini Cedera Ginjal AkutDokument25 SeitenTatalaksana Terkini Cedera Ginjal AkutSulistyawati WrimunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laporan KasusDokument22 SeitenLaporan KasusMahek MunawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Referat AppendicitisDokument21 SeitenReferat Appendicitisyaspie100% (2)
- KDIGO AKI Guideline PDFDokument141 SeitenKDIGO AKI Guideline PDFAbigail LucasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anemia Hemolitik Et Causa ThalasemiaDokument47 SeitenAnemia Hemolitik Et Causa ThalasemiaAnusha PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ranking Unas SmakDokument14 SeitenRanking Unas Smakl0stsga123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Laporan Pendahuluan Hernia Pada AnakDokument16 SeitenLaporan Pendahuluan Hernia Pada AnakrinawahyuniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Patcharee Komvilaisak - Approaching To Pancytopenia 24112017Dokument43 Seiten5 Patcharee Komvilaisak - Approaching To Pancytopenia 24112017Satvik BansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR Vishu P Bhasin DCP Resident, Santosh Medical CollegeDokument30 SeitenDR Vishu P Bhasin DCP Resident, Santosh Medical CollegeDabogski FranceNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR Vishu P Bhasin DCP Resident, Santosh Medical CollegeDokument30 SeitenDR Vishu P Bhasin DCP Resident, Santosh Medical CollegeDabogski FranceNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Patcharee Komvilaisak - Approaching To PancytopeniaDokument36 Seiten5 Patcharee Komvilaisak - Approaching To PancytopeniaMardiyah PratiwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnostic Laboratoric To Anemia: Prof. Dr. Adi Koesoema Aman SPPK (KH) - Dr. Malayana Nasution Mked. Clin - Path. SPPKDokument41 SeitenDiagnostic Laboratoric To Anemia: Prof. Dr. Adi Koesoema Aman SPPK (KH) - Dr. Malayana Nasution Mked. Clin - Path. SPPKrubyniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reba Worksheet B WDokument1 SeiteReba Worksheet B WYudhistira AdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rosenbaum Near Card InstructionsDokument1 SeiteRosenbaum Near Card InstructionsYudhistira AdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial "Sepsis": Rossy Efridanis Ballona Pembimbing: Dr. Toton Suryotono, SP - PDDokument12 SeitenTutorial "Sepsis": Rossy Efridanis Ballona Pembimbing: Dr. Toton Suryotono, SP - PDYudhistira AdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ery MaitatorumDokument10 SeitenEry MaitatorumYudhistira AdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bleeding Causes in The First Trimester PregnancyDokument32 SeitenBleeding Causes in The First Trimester PregnancyYudhistira AdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nej Mo A 1305889Dokument9 SeitenNej Mo A 1305889Yudhistira AdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hysterectomy: Eric Cui Bio 199 Spring 2009Dokument12 SeitenHysterectomy: Eric Cui Bio 199 Spring 2009Yudhistira AdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Change in Hba1C (%) (A) and TBW (KG) (B) During The 52-Week Double-Blind Treatment PeriodDokument9 SeitenChange in Hba1C (%) (A) and TBW (KG) (B) During The 52-Week Double-Blind Treatment PeriodYudhistira AdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HysterectomyDokument70 SeitenHysterectomyYudhistira AdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dapagliflozin Vs GlipizideDokument8 SeitenDapagliflozin Vs GlipizideYudhistira AdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson PlanDokument13 SeitenLesson Planapi-276183071100% (1)
- Aesthetic Crown LengtheningDokument9 SeitenAesthetic Crown Lengtheningeduardosala13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Innate Immunity (DrWahyuni)Dokument42 SeitenInnate Immunity (DrWahyuni)Nurfadilah Zahratul WahidahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument2 SeitenAnatomy and PhysiologyKamille Jeane Stice CavalidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Notes Class 11 - Biology Chapter 19 - Excretory Product and Their EliminationDokument9 SeitenRevision Notes Class 11 - Biology Chapter 19 - Excretory Product and Their EliminationHarpreetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pages From GMP001 - Module01 - Course04Dokument10 SeitenPages From GMP001 - Module01 - Course04Mangesh RautNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safe Zones'' For Miniscrew Implant PlacementDokument7 SeitenSafe Zones'' For Miniscrew Implant PlacementTeodora OpreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem-Based Learning ReportDokument24 SeitenProblem-Based Learning Reporterdayu86Noch keine Bewertungen
- MicturitionDokument29 SeitenMicturitionHifza Anjum KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Chimpanzee BrainDokument21 SeitenA Chimpanzee BrainKevin ChenNoch keine Bewertungen
- KokichDokument6 SeitenKokichJoy ChangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of PCAPDokument8 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of PCAPMads0% (1)
- Blood TestsDokument3 SeitenBlood TestsMarycharinelle Antolin MolinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transfusion Related Immunomodulation (Trim) : By/ Aymen OmerDokument14 SeitenTransfusion Related Immunomodulation (Trim) : By/ Aymen OmeraymenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction and Epithelial TissueDokument66 SeitenIntroduction and Epithelial Tissueapi-294162496100% (1)
- Questions and Their Ideal AnswersDokument17 SeitenQuestions and Their Ideal AnswersHamzaShabaka100% (2)
- Cleavage Formation and Blastulation: Lesson 2.3: Animal DevelopmentDokument8 SeitenCleavage Formation and Blastulation: Lesson 2.3: Animal DevelopmentWestminster AbbeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 20 Urinary System NotesDokument45 SeitenUnit 20 Urinary System NotesRyann SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy-and-Pathophysiology-of-Anemia LEVEL 2Dokument8 SeitenAnatomy-and-Pathophysiology-of-Anemia LEVEL 2Briana Louise HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Lobster Lumpur 1 PDFDokument38 SeitenJurnal Lobster Lumpur 1 PDFI1C118001 MUH.ARJUNASAKTINoch keine Bewertungen
- The EyesDokument9 SeitenThe EyesEmmanuel JohnsonNoch keine Bewertungen