Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Inertia
Hochgeladen von
rospazitaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Inertia
Hochgeladen von
rospazitaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
PHYSICS FORM 4
INERTIA
OBJECTIVES
To know the exactly definition of inertia.
To analyze the relationship between
inertia and mass.
To understand the effects of inertia in
daily life experience.
MENU
Definition of inertia
Relationship between mass inertia and mass.
Effect of inertia in our daily life
Quiz
Reference
When the cardboard covering the
glass is pulled out quickly, what will
happens to the coin?
ANSWER
When the cardboard covering the
glass is pulled out quickly, the coin
resting on the cardboard drops into
the glass
What will happen to the
rest of the coins when one
of the coin is moved out
quickly?
ANSWER
The inertia of the coins
maintains it in its original
position (at rest) even
when one of the coin is
moved out quickly
INERTIA
Inertia is the property of matter
that cause it to resist any
change in its motion or state of
rest
resistmenentang/ melawan
If an object is moving.
Initially :The car & driver are moving together
suddenly : car stops suddenly
driver continue moving forward
The inertia of the driver resists the change in
its motion-thus he was thrown forward
It tends to stay in that position
unless some force puts that
object into motion
If an object is at rest
Inertia is not physical quantity and
thus it does not have units
The property of inertia is found from
the Newtons first law of motion
Newtons First Law of Motion
"An object at rest tends to stay at rest and
an object in motion the same speed and
in the same direction tends to stay in
motion with unless acted upon by an
unbalanced force"
1
st
actv
The coin is in the state of rest
When the cardboard is pulled quickly,
the cardboard moving together with
the hand
But the inertia of the coin cause it to
remain at rest and thus it falls into
the cup
The inertia of the coin resists the
change in its motion
The tendency of an object to
remain at rest or, if moving, to
continue its uniform motion in a
straight line.
WHAT IS INERTIA
2
nd
actv
The bus & passengers are moving together
when the bus stops suddenly, the inertia
of each passenger maintain its motion
which is moving forward.
Thats why the passengers were
thrown forward
The inertia of the passengers
resists the change in its motion
Mass can influence
the effects of
inertia.
An object with a larger
mass has a larger
inertia.
mass
inertia
EXPERIMENT OF INERTIA
Inference : The Period of oscillation depends on
the mass of plasticine.
Hypothesis : the greater the mass of
plasticine,the longer the period of oscillation
Aim : To investigate the relationship between
the Period of oscillation and the mass of
plasticine
Variable :
-manipulated : Mass of plasticine
-responding : Period of oscillation
-constant : Angle of displacement/
length of saw blade
Experiment of Inertia
2. Plasticine of mass of 10 g was weighed using
electronic balance
1. The apparatus was set up as shown in the
diagram
3. The plasticine was fixed to the free end of
saw blade.
4. The plasticine was displaced horizontally and
released to make it oscillates.
METHOD OF CONTROLLING THE
MANIPULATED VARIABLE
Experiment of Inertia
6.Step 5 was repeated and the average time for
the same mass of plasticine was calculated.
5. The time taken for 10 complete oscillations
was measured using stopwatch and recorded.
REPEATING THE EXPERIMENT
7. The experiment was repeated for mass of
plasticine of 40 g, 60 g, 80 g and 100 g.
METHOD OF CONTROLLING THE
RESPONDING VARIABLE
Table for recording data
Mass of
plasticine
m (g)
Time taken for 10 complete
swings, t (s)
Period of
oscillation,
T = t
1
+t
2
10 (s)
2
T
2
/ s
2
t
1
t
2
t
1
+ t
2
2
10
20
30
40
50
Then plot graph of T
2
against m.
T
2
/ s
2
m / g
Graph of T2 against m
CONCLUSION :
From the graph, T
2
is directly proportional to m.
The hypothesis is accepted.
T
2
/ s
2
m / g
Graph of T2 against m
CONCLUSION :
From the graph, T
2
is increase linearly with m. The
hypothesis is accepted.
Interpreting data
Find the value of T when m = 45 g
T
2
/ s
2
m / g
45
0.33
*** intrapolation
If m = 45 g then T
2
= 0.33 s
2
YOU WANT TO KNOW
THE EXPLANATION
ABOUT THIS???
CLICK ON THE VIDEO
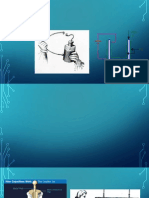
If the motorcycle were to abruptly stop, then the rider in
motion would continue in motion. The rider would likely
be propelled from the motorcycle and be hurled into the
air. Once they leave the motorcycle, the rider becomes a
projectile and continues in projectile-like motion. It is
because of inertia.
Applications of inertia
Some examples of using inertia in our daily life are :
1. To tighten the loose head of a hammer
To tighten the loose head of a hammer, knock one end of
the handle held vertically, on a hard surface.
The hammer head will continue on its downward motion
when the handle has been stopped, the top end of the
handle is slotted deeper into the hammer head.
2. Drying off the wet fur of cats and dogs.
Cats and dogs dry their wet fur by shaking their body
vigorously.
Water droplets on the fur tend to continue in motion when the
body has stopped shaking.
water droplets will be separated from the fur and fall away
3. To dislodge chili sauce from the bottle
Chili sauce in a bottle is poured out by a quick downward
movement of the bottle followed by a sudden stop.
The sauce in the bottle moves with the bottle during the
downward movement.
When bottle is stopped, the inertia of the sauce causes it to
continue on its downward movement and thus the sauce is
forced out of the bottle.
4. Passengers are thrown forward when a bus
moving bus stops suddenly
5. Passengers are hurled backward when a stationary
bus move suddenly.
When a student is riding a
bicycle and runs over a
stone, he is thrown forward.
Why does this happen?
ANSWER
THE INERTIA OF THE
STUDENT MAINTAINS HIS
FORWARD MOTION SO
THAT HE IS THROWN
FORWARD WHEN HIS
BICYCLE IS MOMENTARILY
STOPPED BY THE STONE
References
FOCUS SUPER HOT SPM PHYSICS- S.L
Chang, Koay Kheng Chuan, Yew Kok Leh.
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Newton - S Laws of MotionDokument64 SeitenNewton - S Laws of MotionRiss CalmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.3 InertiaDokument31 Seiten2.3 InertiaHannahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 8 Learning Enrichment Module (REVISED)Dokument53 SeitenScience 8 Learning Enrichment Module (REVISED)Ken Mitchell MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Laws of MotionDokument18 SeitenNewton's Laws of MotionCarah Jean Hurtado GillegaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acceleration DLPDokument3 SeitenAcceleration DLPMark Anthony BesinalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 8 LMDokument351 SeitenScience 8 LMHelma Jabello AriolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balanced and Unbalanced Forces and Net Force Notes PowerpointDokument27 SeitenBalanced and Unbalanced Forces and Net Force Notes PowerpointJeiril Divino100% (1)
- Day5 Group 6C (Newton's Laws of Motion)Dokument5 SeitenDay5 Group 6C (Newton's Laws of Motion)Charlie CanarejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 Science Q2 Wk4 GLAKDokument16 SeitenGrade 8 Science Q2 Wk4 GLAKANGEL MANGLICMOTNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLP Science Law of AccelerationDokument4 SeitenDLP Science Law of Accelerationezra mark arriesgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Law of MotionDokument35 SeitenNewton's Law of MotionJoryn Ramo100% (2)
- Regional Mass Training of Teachers on Newton's Second LawDokument3 SeitenRegional Mass Training of Teachers on Newton's Second LawGlenn QuibuyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCI8M1Dokument21 SeitenSCI8M1Marc Graham NacuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regional Training on Critical Content in Grade 8 ScienceDokument46 SeitenRegional Training on Critical Content in Grade 8 Sciencelie villoteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's First Law of Motion - Law of InertiaDokument18 SeitenNewton's First Law of Motion - Law of InertiaVicky Fortuna OliverosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regional Training of Teachers (RTOT) On Science Critical Content Grade 8 - Earth & Space (Earthquakes and Faults)Dokument75 SeitenRegional Training of Teachers (RTOT) On Science Critical Content Grade 8 - Earth & Space (Earthquakes and Faults)Ethyle Morales LingbawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work and EnergyDokument28 SeitenWork and EnergyMir'atun Nissa QuinalendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Laws ExplainedDokument8 SeitenNewton's Laws ExplainedJhoanna Elaine CuizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q2 Science8 Las W4Dokument24 SeitenQ2 Science8 Las W4Ronna Jean Sambitan100% (1)
- Law of InertiaDokument2 SeitenLaw of InertiaAimee HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- LP 3rd LawDokument5 SeitenLP 3rd LawRoan Joy BalbalosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Developmental Lesson Plan: Common Core/PA Standard(s)Dokument4 SeitenDevelopmental Lesson Plan: Common Core/PA Standard(s)api-542321775Noch keine Bewertungen
- Work and EnergyDokument30 SeitenWork and EnergyRamJiPandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newtons Law of Motion For Grade 8Dokument33 SeitenNewtons Law of Motion For Grade 8janice alquizar100% (1)
- Do Now:: What Is Motion? Describe The Motion of An ObjectDokument22 SeitenDo Now:: What Is Motion? Describe The Motion of An ObjectJoan Melendres100% (1)
- Understanding Potential EnergyDokument7 SeitenUnderstanding Potential EnergyCathy MoronioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Laws of Motion ExplainedDokument29 SeitenNewton's Laws of Motion ExplainedDonnette Commissiong JamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 SCIENCE 8Dokument24 SeitenModule 1 SCIENCE 8G-CASERES, Krisha Joyce A.100% (1)
- DLL Science 8 1st QuarterDokument95 SeitenDLL Science 8 1st QuarterRebecca Implica TuvillejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 Science OrientationDokument23 SeitenGrade 8 Science OrientationJONATHAN BRIAGASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 2Dokument16 SeitenScience 2RicalynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Science Lesson Plan 2Dokument2 SeitenDetailed Science Lesson Plan 2Lorraine Donio100% (1)
- Laws of Motion ExplainedDokument4 SeitenLaws of Motion ExplainedNellen BastismoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To Sound Lesson PlanDokument3 SeitenIntro To Sound Lesson Planapi-285015723Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science: Newton's Law of Motion-Law of InteractionDokument13 SeitenScience: Newton's Law of Motion-Law of InteractionFe Pakias GullodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan in Science 6 (Completed)Dokument14 SeitenLesson Plan in Science 6 (Completed)Brigette SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan - Momentum and ImpulseDokument16 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan - Momentum and ImpulsePeter Mortalia Salivio100% (1)
- Newtons Laws of MotionDokument35 SeitenNewtons Laws of Motionapi-262604908100% (4)
- Regional Training G8 - 1st Law of MotionDokument22 SeitenRegional Training G8 - 1st Law of MotionDaphnie Serate Nunez100% (1)
- Grade 8 Forces LessonDokument3 SeitenGrade 8 Forces LessonDerly Cirunay DatuinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's First LawDokument22 SeitenNewton's First LawJayPee BasiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final DemoDokument7 SeitenFinal DemoKiela ArizobalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demo Teaching ScienceDokument8 SeitenDemo Teaching ScienceKathy Claire Pecundo BallegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Physics Grade 8Dokument5 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan in Physics Grade 8Bon PatiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5b WorkEnergyPowerDokument20 Seiten5b WorkEnergyPowershallou sashimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Guide in Science 7 I. Objectives: Iiia-1)Dokument2 SeitenLesson Guide in Science 7 I. Objectives: Iiia-1)Jespher GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's 3rd Law of MotionDokument33 SeitenNewton's 3rd Law of MotionRamona EstevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sound WavesDokument91 SeitenSound WavesSarah Mae Lequin ManzanasNoch keine Bewertungen
- LP (Science 8)Dokument126 SeitenLP (Science 8)mark jay legoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 8 Quarter 1 - Module 1Dokument3 SeitenScience 8 Quarter 1 - Module 1emmjaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLP Application of Kinetic EnergyDokument7 SeitenDLP Application of Kinetic EnergyJULIE ANN PAJENoch keine Bewertungen
- VelocityDokument3 SeitenVelocityleizl MoncadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sci6 Q3 Module2Dokument28 SeitenSci6 Q3 Module2Jhon Kristoffer GabutNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHY 1 - Module 4Dokument25 SeitenPHY 1 - Module 4mtalquisola2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Velocity and Speed N Acceleration Word ProblemsDokument9 SeitenVelocity and Speed N Acceleration Word ProblemsLovieAlfonsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan in PhysicsDokument2 SeitenLesson Plan in PhysicsGen SinangoteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Sheets - Application DemoDokument3 SeitenActivity Sheets - Application DemoJa RedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Point Fizik Form 4Dokument26 SeitenPower Point Fizik Form 4Sasmuhd HamzahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Form 4Dokument31 SeitenPhysics Form 4evrex0% (2)
- General Physics 1.2b Moment of InertiaDokument42 SeitenGeneral Physics 1.2b Moment of InertiaLADY SUZETTE LANDICHONoch keine Bewertungen
- Idea of PressureDokument2 SeitenIdea of PressurerospazitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nota Latent HeatDokument1 SeiteNota Latent HeatrospazitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul Mara Heat-1Dokument7 SeitenModul Mara Heat-1rospazitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuideDokument32 SeitenChapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuiderospazitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MomentumDokument23 SeitenMomentumrospazitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- cikgusazali Blog Posts and ArticlesDokument14 Seitencikgusazali Blog Posts and ArticlesrospazitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kelantan Fiz K1 PDFDokument33 SeitenKelantan Fiz K1 PDFrospazitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Phy F5 Topical Test 3 (BI)Dokument10 SeitenIT Phy F5 Topical Test 3 (BI)rospazitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trial MRSM SPM 2014 Physics K1 No SkemaDokument48 SeitenTrial MRSM SPM 2014 Physics K1 No SkemaCikgu Faizal50% (2)
- MomentumDokument21 SeitenMomentumrospazitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Wind Turbines and How Their Aerodynamic Blades Harness Lift ForceDokument4 SeitenTypes of Wind Turbines and How Their Aerodynamic Blades Harness Lift Forcerospazita100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Physics StudentDokument18 SeitenChapter 1 Introduction To Physics StudentrospazitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hooke's LawDokument5 SeitenHooke's LawrospazitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Study of Natural Phenomena and Properties of Matter and EnergyDokument17 SeitenThe Study of Natural Phenomena and Properties of Matter and EnergyrospazitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Function of CapacitorDokument6 SeitenFunction of CapacitorrospazitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- About HovercraftDokument10 SeitenAbout HovercraftrospazitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maintaining Power Quality in Off-Grid Microgrids via Coordinated DG ControlDokument8 SeitenMaintaining Power Quality in Off-Grid Microgrids via Coordinated DG ControlSeekay Alais Karuppaiah CNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Paper-1 0 PDFDokument6 SeitenMath Paper-1 0 PDFHimanshu sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HT TransformerDokument6 SeitenHT TransformerMaintenance CircleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Two MarksDokument8 SeitenTwo MarkskrctmechNoch keine Bewertungen
- SIPROTEC 4 7UM62 multifunction generator protection relayDokument39 SeitenSIPROTEC 4 7UM62 multifunction generator protection relayJay Rameshbhai ParikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development of xEV Component Testing FacilityDokument46 SeitenDevelopment of xEV Component Testing FacilityArfie IkhsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Chemistry Calorimeter Problem AnswersDokument3 SeitenThermal Chemistry Calorimeter Problem AnswersrkvermNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC UPS Commissioning ProcedureDokument9 SeitenDC UPS Commissioning ProcedureManafNoch keine Bewertungen
- ResonanceDokument48 SeitenResonancePrakash Nik79% (92)
- Gas-Liquid Vertical Separator PDFDokument2 SeitenGas-Liquid Vertical Separator PDFRathish RagooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Us Earth Rite Plus Exd DatasheetDokument7 SeitenUs Earth Rite Plus Exd DatasheetwlyskrdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.5 Archimedes' Principle 2021Dokument15 Seiten2.5 Archimedes' Principle 2021Nurul shazwani100% (1)
- General Chemistry 2Dokument5 SeitenGeneral Chemistry 2Caf BlessedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Empanelled vendor list and cost details for rooftop solar power projectsDokument4 SeitenEmpanelled vendor list and cost details for rooftop solar power projectsAnkit JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AUX Air Conditioner Service ManualDokument60 SeitenAUX Air Conditioner Service Manualrock_music75% (4)
- Crush and RestitutionDokument77 SeitenCrush and RestitutionFabiano CardosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Residential Sevice Load Worksheet For Electrical Vehicle Charging System PDFDokument4 SeitenResidential Sevice Load Worksheet For Electrical Vehicle Charging System PDFandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retina Digest Che 2nd PDFDokument155 SeitenRetina Digest Che 2nd PDFSlytherinNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectrostaticsDokument16 SeitenElectrostaticsSuparnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nicd Battery Charger: Design: K. WalravenDokument1 SeiteNicd Battery Charger: Design: K. WalravenjaliltaghdarehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Problem Set - II PDFDokument3 SeitenPractice Problem Set - II PDFMukul ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- VTU-22-12-2018 08:29:13am: TG - TG - TG - TG - TG - TG - TG - TG - TGDokument9 SeitenVTU-22-12-2018 08:29:13am: TG - TG - TG - TG - TG - TG - TG - TG - TGPâvâñ NagarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment I - Spring 2021 - PHY101 - 03Dokument2 SeitenAssignment I - Spring 2021 - PHY101 - 03Nasif KamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model: THG1365YLS: Technical Data SheetDokument3 SeitenModel: THG1365YLS: Technical Data SheetAndres VargazNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3RN10131BW10 Datasheet enDokument3 Seiten3RN10131BW10 Datasheet enXuân Kiên VũNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Content of The Kawah Kamojang Geothermal ReservoirDokument10 SeitenWater Content of The Kawah Kamojang Geothermal ReservoirAswar Abu KhawlahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Actividad 4. Derivación de Funciones Algebraicas: Calculo DiferencialDokument8 SeitenActividad 4. Derivación de Funciones Algebraicas: Calculo Diferencialprimitivo58Noch keine Bewertungen
- Switching Impulse Flashover Performance of Different Types of Insulators at High Altitude Site of Above 2800 MDokument6 SeitenSwitching Impulse Flashover Performance of Different Types of Insulators at High Altitude Site of Above 2800 MdaaanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air-Conditioning Tutor COP ExperimentDokument4 SeitenAir-Conditioning Tutor COP ExperimentJady chess24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics AssignmentDokument4 SeitenPhysics Assignmentang_chang_1Noch keine Bewertungen