Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Carburetion
Hochgeladen von
PravinSharmaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Carburetion
Hochgeladen von
PravinSharmaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1
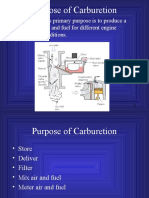
Purpose of Carburetion
A carburetors primary purpose is to produce a
mixture of air and fuel for different engine
operating conditions.
2
Purpose of Carburetion
Store
Deliver
Filter
Mix air and fuel
Meter air and fuel
3
Idle Mixture screw
Idle Speed Screw
Choke Plate Throttle Plate
Float
Float Bowl
Pilot Jet
Main Jet
Pedestal
4
5
Carburetion
Air-fuel
Requirements
Ratio of air to
fuel.
Stoichiometric
ratio of 14.7:1
Example 14.7
lbs of air to 1 lb
of fuel
Fuel ratios
Rich / lean
6
Carburetor Operating Conditions
Cold
Choke / prime
Low speed
Idle
Mid speed
Idle and high speed
Acceleration
Accelerator pump
High speed
Main discharge nozzle
7
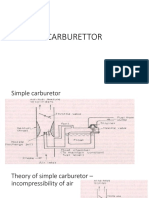
Carburetion Pressure Differences
Vacuum
Pressure less than atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure
Force of air on a surface at 14.7:1psi
Venturi principle
A restriction in an air passage which causes an
increase in air speed and a decrease in air pressure
8
Carburetion Pressure Differences
Air horn
Air enters at
Atmospheric
pressure
Venturi
High vacuum is
created
Engine side
Low vacuum
created on the
intake stroke
9
Carburetion
Atomization
Turning a liquid
into little droplets
Vaporization
Turning liquid
droplets into a
vapor or gaseous
state
10
Carburetion
Types of carburetors - air direction
Up Draft
11
Carburetion
Types of carburetors - air direction
Down draft
12
Carburetor Circuits
Float circuit
To maintain
proper fuel
level
13
Carburetor Circuits
Choke circuit
Provides a
rich air-fuel
mixture for
cold starts
14
Carburetor Circuits
Throttle
Regulates
air fuel
mixture
entering the
cylinders
15
Carburetor Circuits
Idle circuit
Supplies air-
fuel mixture
when the
throttle is
closed for
low speed
operation
16
Carburetor Circuits
High Speed
circuit
Full throttle
Maximum
air fuel
flow to
develop full
speed and
power
17
Carburetor Circuits
Accelerator
circuit
Provides
additional
fuel to
maintain the
air fuel ratio
when the
throttle is
quickly
opened.
18
Carburetion / Governors
Manual throttle controls
Governor throttle controls
Limit low speed
Limit high speed
Maintain constant speed
19
Running Conditions
Too Rich
Air-fuel mixture with excessive fuel
HC and CO pollution
Exhaust black soot
Too Lean
Air-fuel mixture lacking fuel
CO and NO
X
pollution
Engine overheating
Just Right
Smooth engine operation
Rapid Acceleration
Low pollution / Clean Exhaust
Normal operating temperature
20
Carburetion
The purpose of the fuel system is store,
deliver, mix and meter air and fuel for the
engine to function over a variety of
operating conditions.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- How To Design Roof Purlins - A Solved Example - StructvilleDokument16 SeitenHow To Design Roof Purlins - A Solved Example - StructvilleLavanyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mayan Calendar ExplainedDokument9 SeitenMayan Calendar Explainedbresail40% (1)
- Fuel Supply System in Petrol EnginesDokument54 SeitenFuel Supply System in Petrol EnginesKLUniveristy86% (14)
- IC Engine Notes Petrol Injection SystemDokument38 SeitenIC Engine Notes Petrol Injection SystemNithinvpNoch keine Bewertungen
- BlastingDokument138 SeitenBlastingcklconNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is 2974 Part 4 1979 Indian Standard Code of Practice For Design and Construction of Machine Foundations - Part 4 Foundations For Rotary Type Machines of Low Frequency PDFDokument23 SeitenIs 2974 Part 4 1979 Indian Standard Code of Practice For Design and Construction of Machine Foundations - Part 4 Foundations For Rotary Type Machines of Low Frequency PDFBibhu DattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report Vortex TubeDokument68 SeitenReport Vortex TubePravinSharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isolation and Purification of AlkaloidsDokument14 SeitenIsolation and Purification of AlkaloidsLuděk SpurnýNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Power PlantDokument14 SeitenGas Power Plantvenki249Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chul Park The Limits of Two-Temperature ModelDokument13 SeitenChul Park The Limits of Two-Temperature ModellazharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel Sistem JS31 JetstreamDokument75 SeitenFuel Sistem JS31 JetstreamCarlos Marquez100% (2)
- Production Planning and ControlDokument31 SeitenProduction Planning and ControlPradeep Kumar Mehta100% (2)
- Lesson 09 - Gas Turbines IDokument25 SeitenLesson 09 - Gas Turbines ISohaib Arshad100% (3)
- 07 Marine Diesel EnginesDokument26 Seiten07 Marine Diesel EnginesSurasan ThepsiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 APC ReductionDokument55 Seiten03 APC ReductionDevanshu SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- ValveTypesSelection - ControlsWikiDokument42 SeitenValveTypesSelection - ControlsWikiMayur PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- GT Gas Fuel and Air FlowDokument38 SeitenGT Gas Fuel and Air FlowhinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 9 - Fuel Systems PDFDokument73 SeitenModule 9 - Fuel Systems PDFOresteHernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.summary of Boiler PerfDokument46 Seiten7.summary of Boiler PerfRAJESH KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANSYS Stress LinearizationDokument15 SeitenANSYS Stress LinearizationTiago CandeiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbine Fuel SystemDokument66 SeitenTurbine Fuel SystemDamon Leong100% (1)
- Pertemuan 4 - Turbin Gas (2016)Dokument53 SeitenPertemuan 4 - Turbin Gas (2016)Prabowo WicaksonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saurabh Gas Turbine MEDokument41 SeitenSaurabh Gas Turbine MESubodh DuhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Efficiency Coalescers For Gas Processing OperationsDokument9 SeitenHigh Efficiency Coalescers For Gas Processing OperationsAndri SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 08 Carburetion LowDokument33 Seiten08 Carburetion LowMujtaba AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CARBURETOR Work System PDFDokument28 SeitenCARBURETOR Work System PDFH. Yusmira (Kang Otto)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Carburetor Work SystemDokument28 SeitenCarburetor Work SystemH. Yusmira (Kang Otto)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Carburettor PDFDokument20 SeitenCarburettor PDFDeepak MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AVIA122 Ch07Dokument56 SeitenAVIA122 Ch07이용일Noch keine Bewertungen
- sr22t Engine OperationsDokument102 Seitensr22t Engine OperationsPhilNoch keine Bewertungen
- IC Engine - 1Dokument17 SeitenIC Engine - 121-Syed Ihtasham Javaid ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cirrus Engine OperationsDokument120 SeitenCirrus Engine Operationscirrus.prjfrNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE - Unit III - Lect 1Dokument15 SeitenAE - Unit III - Lect 1Hh HhNoch keine Bewertungen
- SI Engine Carburation 2019 - 20Dokument18 SeitenSI Engine Carburation 2019 - 20Sagar BhargavNoch keine Bewertungen
- CARBURETION and Fuel InjectionDokument40 SeitenCARBURETION and Fuel Injectionravi100% (1)
- 3.the CarburetorDokument90 Seiten3.the CarburetorBikash sharrfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carburator Unit 2Dokument16 SeitenCarburator Unit 2Sapari VelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3Dokument75 SeitenModule 3Abhinav TusharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Om07 Pe KFDokument5 SeitenOm07 Pe KFghusunNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Fuel Metering in SI and CI Engines V01Dokument47 Seiten3 Fuel Metering in SI and CI Engines V01Dinesh ChowdaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engine Management 1: Cylinder: Charge and Air Fuel MixtureDokument48 SeitenEngine Management 1: Cylinder: Charge and Air Fuel MixtureCh'ng Jie HanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natural Heat Flow Increases Entropy - Converting Heat To Work Decreases EntropyDokument5 SeitenNatural Heat Flow Increases Entropy - Converting Heat To Work Decreases EntropyDuraimurugannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Mechatronics EnggDokument59 SeitenDepartment of Mechatronics EnggUsama EhsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Converting Energy To PowerDokument43 SeitenConverting Energy To PowerAunaunZaa'Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aircraft Fuel SystemDokument23 SeitenAircraft Fuel System210101034Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Fuel Feed System: - Gravity System - Pressure System - Vaccum System - Pump System - Fuel Injection SystemDokument59 SeitenTypes of Fuel Feed System: - Gravity System - Pressure System - Vaccum System - Pump System - Fuel Injection SystembantiebduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel SystemDokument19 SeitenFuel SystemIanArvinGaliciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel SystemDokument19 SeitenFuel Systemneeraj7.17Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Turbine EngineDokument22 SeitenGas Turbine EngineUday WankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Turbine: Saurabh PandeDokument41 SeitenGas Turbine: Saurabh PandeUpendra BajpaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 - 1 SI EnginesDokument28 Seiten7 - 1 SI EnginesArsalan AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Developments in Ic Engines: Lecture NotesDokument23 SeitenModern Developments in Ic Engines: Lecture NotesZEDI gamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Turbine and ConstructionDokument25 SeitenGas Turbine and ConstructionRamanujam SankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Combustion Engines ME 4142: Dr. Saif Ur Rahman Department of Mechanical EngineeringDokument23 SeitenInternal Combustion Engines ME 4142: Dr. Saif Ur Rahman Department of Mechanical EngineeringMuhammad AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On Gas TurbineDokument31 SeitenPresentation On Gas TurbineDhruvKandwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combustion ReportDokument13 SeitenCombustion ReportDeyn EstoqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boosting Engine Power: More Power - Four Possibilities With One Common ThreadDokument57 SeitenBoosting Engine Power: More Power - Four Possibilities With One Common Threadabdullah bin masoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aemr-Unit 1-Piston EngineDokument85 SeitenAemr-Unit 1-Piston Engineuthira100% (1)
- Lec No 10 & 11Dokument100 SeitenLec No 10 & 11FatimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carburetors ManualDokument21 SeitenCarburetors ManualHarold MangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diesel Engine PPDokument52 SeitenDiesel Engine PPSushanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air CompressorsDokument18 SeitenAir Compressorssaid ismailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Combustion Engines PresentationDokument23 SeitenInternal Combustion Engines PresentationNitesh BirlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aero Engine: Maintenance and RepairDokument94 SeitenAero Engine: Maintenance and RepairLogu SnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Compressor-1 PDFDokument10 SeitenAir Compressor-1 PDFAmeer HamzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Stroke EngineDokument38 Seiten2 Stroke EnginekirubamechNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Stroke EngineDokument38 Seiten2 Stroke EnginekirubamechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engine SystemsDokument87 SeitenEngine SystemsprabhjotbhangalNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME2041 Advanced Internal Combustion Engines: Unit IDokument21 SeitenME2041 Advanced Internal Combustion Engines: Unit IvijayNoch keine Bewertungen
- A BatchDokument71 SeitenA BatchVenkiteshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Countinous Variable TransmissionDokument11 SeitenCountinous Variable TransmissionPravinSharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vortex TubeDokument15 SeitenVortex TubePravinSharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sound Into Electrical ConversionDokument18 SeitenSound Into Electrical ConversionPravinSharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Finite Element Analysis - Hutton - (Mcgraw-Hill)Dokument3 SeitenFundamentals of Finite Element Analysis - Hutton - (Mcgraw-Hill)PravinSharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Heat Tratment ProcessDokument20 SeitenOn Heat Tratment ProcessPravinSharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Download FanProtectionDokument14 SeitenEnglish Download FanProtectionSubhankar UncertainityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stepper Motors VsServo MotorsDokument2 SeitenStepper Motors VsServo MotorsEhab MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculated MAWP MAPDokument4 SeitenCalculated MAWP MAPhataefendiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Build A Water Channel For A Fluid Dynamics LabDokument10 SeitenDesign and Build A Water Channel For A Fluid Dynamics Labsampath kumar K NNoch keine Bewertungen
- MTHS2007 Formula SheetwithtablescorrectedDokument3 SeitenMTHS2007 Formula SheetwithtablescorrectedBenjamin OpokuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gold Nanoparticles ColorDokument3 SeitenGold Nanoparticles ColorBrandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cohesive Energy 1Dokument5 SeitenCohesive Energy 1kalloliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boeing 747 Engine Research DR KanasaDokument5 SeitenBoeing 747 Engine Research DR Kanasaapi-435184538Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cve3008 Mid-Term Test (27.10.2022)Dokument4 SeitenCve3008 Mid-Term Test (27.10.2022)damell scottNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotalk 23Dokument16 SeitenRotalk 23Pramod AthiyarathuNoch keine Bewertungen
- (NagpurStudents - Org) Advanced PhysicsDokument4 Seiten(NagpurStudents - Org) Advanced PhysicsVaibhav NardangeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02-02 Dam FormworkDokument20 Seiten02-02 Dam FormworkJae Min HwangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Pdfsam - 51 - Pdfsam - Jane Bennett Vibrant Matter A Political Ecology of Things 2010 PDFDokument25 Seiten1 - Pdfsam - 51 - Pdfsam - Jane Bennett Vibrant Matter A Political Ecology of Things 2010 PDFAnna PrzytomskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frida Kunti Setiowati, Barlah Rumhayati: Seminar Nasional XI Pendidikan Biologi FKIP UNS 125Dokument6 SeitenFrida Kunti Setiowati, Barlah Rumhayati: Seminar Nasional XI Pendidikan Biologi FKIP UNS 125Ridwan PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earthquake AnalysisDokument11 SeitenEarthquake AnalysisSalauddinAnsariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Models - Rf.plasmonic Wire Grating PDFDokument26 SeitenModels - Rf.plasmonic Wire Grating PDFrak999Noch keine Bewertungen
- (19MT18302) Modeling and Analysis of Electrical Machines (Theory)Dokument3 Seiten(19MT18302) Modeling and Analysis of Electrical Machines (Theory)Prabhu MoorthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee 1002Dokument108 SeitenEe 1002Akhilesh Kumar MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 133123Dokument11 SeitenSection 133123Dian Aplimon JohannisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nortje Desiree 2002 PDFDokument328 SeitenNortje Desiree 2002 PDFAtul KulkarniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 3 For CHM 520: JK 92 S JK 67 SDokument15 SeitenQuiz 3 For CHM 520: JK 92 S JK 67 SnotmeNoch keine Bewertungen