Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
1 Cell Structure
Hochgeladen von
Annisha IzzatieOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1 Cell Structure
Hochgeladen von
Annisha IzzatieCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Cell Structure and
Function
All living things are made up of basic units
called cells.
Cells vary in shape, sizes and content
depending on their function.
A light microscope is usually used to
help us observe microscopic cells.
The living component of a cell is called
protoplasm.
Protoplasm = cytoplasm + nucleus
Protoplasm surrounded by plasma
membrane.
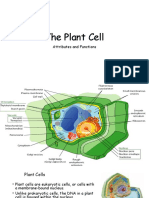
Plant cells have an outer boundary called
the cell wall.
Animal cell
Plant cell
Cell Parts and Structures
With electron microscopes, scientists are able to see
the cellular components of a cell in greater detail.
The cytoplasm contains structures called organelles.
Organelles perform specific function which enable the
cell to function as a unit of life.
A
n
i
m
a
l
c
e
l
l
P
l
a
n
t
c
e
l
l
Controls cellular
activities.
Nucleus membrane
controls inflow and
outflow of material to
and from nucleus
Nucleolus acts as site
of ribosome
construction.
Chromosome carries
hereditary information.
Acts as a medium
where biochemical
reactions and most
living processes
occur within the cell.
Provides the
organelles with
substances obtained
from external
environment.
Separates the content
of the cell from its
external environment.
Regulates the
movement of
substances entering
and leaving the cell.
Allows the exchange
of nutrients,
respiratory gases and
wastes products
between the cell and
its environment.
Chlorophyll captures the
energy of sunlight and
converts light energy into
chemical energy during
photosynthesis.
The green pigment of
chlorophyll gives plants
their colour.
Stores chemicals
such as organic
acids, sugar, amino
acids, mineral salts,
oxygen, carbon
dioxide and so on.
Regulates water
balance in plant
cells.
Maintains the shape of plant cells.
Provides mechanical strength and support to
plant cells.
Protects plants cells from rupturing due to the
movement of excess water into the cells.
Forms a network of
transportation within
the cell.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
(has ribosomes attached to its
surface)
Transports protein which is
synthesized in ribosomes.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
(does not have ribosome attach to
its surface)
Transports and
synthesized fat and
glyserol
Site of proteins synthesis.
They are either bound to the
endoplasmic reticulum or lie free in
the cytoplasm.
The sites of cellular
respiration.
Principle site of
energy production.
Energy generated or
released in the form
of ATP (adenosine
triphosphate).
Functions as a processing, packaging
and transport centre of carbohydrates,
proteins and glycoproteins.
These materials will be membrane-bound
and secrete through vesicles.
As a digestive
compartments.
In certain unicellular
organisms, lysosomes
fuse with food vacuoles
and dispense their
enzymes into these
vacuoles to digest the
contents of the vacuoles
Lysosomes
Comparison of
an Animal Cell
& a Plant Cell
Both has nucleus, cytoplasm,
mitochondrion, ribosome, cell
membrane, rough endoplasmic
reticulum, smooth endoplasmic
recticulum and Golgi apparatus
Similarities
Animal Cell
Plant Cell
Animal Cell Plant Cell
Differences
Do not have fixed shape
Shape
Have a fixed shape
Do not have cell walls
Cell walls
Have cell walls
Do not have vacuoles. If
present, vacuoles are usually
small and numerous
Vacuoles
Have a large central
vacuole
Do not have chloroplasts
Chloroplasts
All green plants have
chloroplast which contain
chlorophyll
Have centrioles
centrioles
Do not have centrioles
Carbohydrate is stored in the
form of glycogen
Food storage
Carbohydrate is stored in
the form of starch
The Density of
Organelles in
Spesific Cells
The number of organelles in each cell varies
according to type of organism and nature of the
cell.
For example,
more active cells will possess more
mitochondria than less active cells.
Abundant chloroplasts are found in the
palisade mesophyll cells than other parts of
the leaves.
Require energy to propel through the uterus
towards the Fallopian tubes, so that
fertilisation can take place.
Sperm cells
High density of ______
Contract and relax to
enable movement and
flight
Muscle cells
Require large amounts of energy
during active cell division to produce
new cells
Cells in meristems
High density of ______
Mesophyll palisade cells
Absorb sunlight during photosynthesis
High density of ______
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cell Structure and FunctionDokument41 SeitenCell Structure and FunctionSamuel LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Cell StructureDokument41 Seiten1 Cell StructureIra MunirahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure and FunctionDokument41 SeitenCell Structure and FunctionAhkyluzLaniazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Cells and Plant CellsDokument32 SeitenAnimal Cells and Plant CellsTheresa Filomena B BallesterosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure and Function GuideDokument5 SeitenCell Structure and Function GuideYunie KamarudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionDokument5 SeitenChapter 2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionsakurashahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Basic Unit of Life: Understanding Cells in 38 CharactersDokument38 SeitenThe Basic Unit of Life: Understanding Cells in 38 CharactersJENNILYN CASTILLONoch keine Bewertungen
- Note 2 Cell Structure PDFDokument5 SeitenNote 2 Cell Structure PDFRufaida TaahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3 Cell - Structure - FunctionDokument94 SeitenLecture 3 Cell - Structure - FunctionMuhammad Abbas WaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3-Cell Structure and TaxonomyDokument60 SeitenChapter 3-Cell Structure and TaxonomyMarcos AlbaridaNoch keine Bewertungen
- C2-Organisation and Maintenance of The OrganismDokument39 SeitenC2-Organisation and Maintenance of The OrganismyourmoNoch keine Bewertungen
- E18f338b CellsDokument42 SeitenE18f338b CellsMohammad Abdullah KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell and TransportDokument77 SeitenCell and TransportEugenie Francisco100% (1)
- Cell StructureDokument43 SeitenCell StructureKexinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells: The Building Blocks of LifeDokument40 SeitenCells: The Building Blocks of LifeSingh GurleenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 5.1 Cell The Basic Unit of LifeDokument39 SeitenLesson 5.1 Cell The Basic Unit of LifeMarjorie CaneteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure & FunctionDokument15 SeitenCell Structure & FunctionMilimo JingsawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell StructureDokument30 SeitenCell Structuremazura100% (1)
- Cells 1Dokument26 SeitenCells 1bruh bruh 68Noch keine Bewertungen
- CellsDokument38 SeitenCellsMaryam SabirNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPT - CellDokument75 SeitenPPT - CellTarun BisenNoch keine Bewertungen
- What is a CellDokument23 SeitenWhat is a CellCharm VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity: "Comparing Plant and Animal Cells"Dokument39 SeitenActivity: "Comparing Plant and Animal Cells"criselNoch keine Bewertungen
- CellDokument23 SeitenCellErdis MerepezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument44 SeitenChapter 3Altaf Hussain KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Lec.1 (w1) Overview and Plant StructureDokument32 Seiten1 Lec.1 (w1) Overview and Plant StructureRabiatul AdawiyyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quipper 1 - Earth and Life Science - CellDokument17 SeitenQuipper 1 - Earth and Life Science - CellPhil Christian MerinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Plant CellDokument30 SeitenThe Plant CellMichael GentilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells and Cell KineticsDokument59 SeitenCells and Cell KineticsKaycee ChirendaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of CellDokument42 SeitenStructure of CellJeevitha VanithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Energy: Earth and Life ScienceDokument48 SeitenCell Energy: Earth and Life ScienceCristina MaquintoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Biology BasicsDokument6 SeitenCell Biology BasicsEllyn De chavezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells: The Building Blocks of LifeDokument36 SeitenCells: The Building Blocks of LifeNoorSabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Medical Biology: Lecture 2: The World of CellDokument18 SeitenGeneral Medical Biology: Lecture 2: The World of CellRasan QadrNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOCHEMISTRY OF CELLS AND BIOMOLECULESDokument60 SeitenBIOCHEMISTRY OF CELLS AND BIOMOLECULESShaira Elyze Gabriel100% (1)
- Cell Structure & Function 2022Dokument43 SeitenCell Structure & Function 2022Kavita MahaseNoch keine Bewertungen
- What is a Cell? The Building Block of LifeDokument6 SeitenWhat is a Cell? The Building Block of LifeWaleed Bin KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell StructureDokument22 SeitenCell StructureAbdullah KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- IX Chapter 5 Fundamental Unit of LifeDokument69 SeitenIX Chapter 5 Fundamental Unit of LifeRamChandraChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDokument56 SeitenProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellKENT GARCIA100% (1)
- Cell Unit of Life Class NoteDokument36 SeitenCell Unit of Life Class NoteKavana SNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Cell?: Basics of CytologyDokument22 SeitenWhat Is A Cell?: Basics of Cytologyaybs solamoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell - Structure - Function Chapter 2Dokument42 SeitenCell - Structure - Function Chapter 2ErizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMA 11-1 CellsDokument111 SeitenSMA 11-1 Cellsnur aulia100% (1)
- 4 Cell and TissuesDokument44 Seiten4 Cell and TissuesAmbreen RiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure & Function: Basic Theor Y of LifeDokument34 SeitenCell Structure & Function: Basic Theor Y of LifeJhea DoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal CellsDokument17 SeitenAnimal CellsJhan SasisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure: By: Shemara PaulDokument44 SeitenCell Structure: By: Shemara PaulDequanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure and Function ExplainedDokument32 SeitenCell Structure and Function ExplainedHC GamerNoch keine Bewertungen
- World of CellDokument49 SeitenWorld of CellGil Vincent Tapit YaquitNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9IP - Biology Ch1Dokument68 Seiten9IP - Biology Ch1joudy rabbatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Parts and Its Function DLLDokument62 SeitenCell Parts and Its Function DLLRovelyn AlejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell - Structure and FunctionsDokument63 SeitenCell - Structure and FunctionsAdvayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal-cells-and-bacterial-cellsDokument40 SeitenAnimal-cells-and-bacterial-cellsClarence CaparasNoch keine Bewertungen
- LESSON 3 Parts of The Cell and Their FunctionsDokument27 SeitenLESSON 3 Parts of The Cell and Their FunctionsSophia CamachoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 8-2 Notes 2022-2023Dokument12 SeitenSection 8-2 Notes 2022-2023Verificar Ameijenda PratoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Plant CellsDokument48 SeitenChapter 1 Plant CellsAppy ZombaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksVon EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceVon EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNoch keine Bewertungen