Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Introduction MBA I (13 15) F
Hochgeladen von
manishkhandal88Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Introduction MBA I (13 15) F
Hochgeladen von
manishkhandal88Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Introduction
MBA-I (2013-15)
What is managerial Economics?
Mangerial economics is the application of
economic tools and techniques to business and
administrative decision making
The main objectives of Managerial economics
are:
To learn the usefulness of economics
in describing managerial behavior.
to improve managerial decisions.
to understand vital role of business in society.
Usefulness of managerial economics
(i)Evaluating the alternative choices
By linking the economic concepts to quantitavve
methods, the managers can evaluate various alternatives
and take the most appropriate decision. Since both the
human and material resources are scarce and limited one
has to take the decision for the use of the best
combinations.
Any problem in respect of production,pricing, labour,
rawmaterials, investmenant, organisational strategy etc
can be solved most efficiently for achiving the optimal
solution to the management decisions. All these can be
solved with the help of economic concepts and
quantitative methods.
Steps for such evaluation:
Identify ways to efficiently achieve goals.
Specify pricing and production strategies.
Spell out production and marketing rules to maximize profits.
Hence managerial economics has a singificant role in the managers
decision making process.
(ii) Making the Best Decision
In order to take appropriate decision, the managers are
required to understand the economic environment in which
they operate.
Managerial economics helps meet management objectives
efficiently by applying the economic theory and methodology to
decision making.
Managerial economics describes the logic of pricing practices for
maximising profits.
Mostly we will deal with the business applications.
For the successful business, the managers need to
adopt a set of principles which is popularly
known as busness ethics. They are are follows:
Above all else, keep your word. Say what you
mean and mean what you say.
Do the right thing. A handshake with an
honorable person is worth more than a ton of
legal documents from a corrupt individual.
Accept responsibility for your mistakes and fix
them. Be quick to share the credit for success.
Leave something on the table. Profit with your
customer not off your customer.
Stick by your principles. Pricniples are not for sale
at any price.
Role of Business in society:
The aim of business is not only to
maximise profit but also it aims at
fulfilling some social responsibility. These
are:
satisfying consumer wants.
contributing to social welfare
Serving the customers.
Providing employment opportunities.
Obeying laws and regulations of the
government.
On the one hand the main objectives of the business to
maximise profit and on the other hand it has to move
with the society in fulfilling the overall social welfare.
The firm has to operate in the context of economic
model to achieve this objective.
The business needs to be induced to move towards the
directions that society desires. For this it is necessary to
know the consumers demand, producers supply, market
environment, product quality, level of competition in the
market, pricing strategy, organisational strategy etc. Also
it has to deal with the political pressure or regulations of
the govt etc.
Hence the firm has to keep close relationship with the
society in respect to above issues to achive the social
objectives without foregoing the main goal of business.
How the firm serves the customers and
society?
Firm has to establish the realtionship with
suppliers, investors, workers, and
management jointly to serve the customers
and the society. This will be mainatained by
estimating the expected value maximisation in
terms of optimisation of profits keeping in
view the uncertainty and time value of money.
How is it done? It can be done by estimating the
present value of firms expected net cash flow
(future profits).
If is the profit, the present value of future
expected profits will be:
n
/(1+i)
t
t=1
t=time , i =discount rate, n= no. of years(time)
Profit is the total revenue minus the total cost: TR-TC.
Constraints of theory of firms:
Resource constraint: Human and material
Other constarints: legal, and such others
Limitations of the theory of firms:
Always it is not possible to optimise the
business profit. Hence it is untenable to
assume optimisation of profit under the
theory of firms.
Manytimes the cost of finding the best
solution is higher than its benefits. Hence the
mangers in this case seek for satisfactory
rather optimal results.
Measuring the profit of the firm/business
Business Versus Economic Profit
i. Business (accounting) profit reflects explicit
costs and revenues.
ii. Economic profit.
Reflects the implicit cost which Considers cash
and non-cash items.
Do profits vary among fims? There are wide variations in
profits of the firms.
Why do they vary?
It is on account of unexpected growth in revenue
and cost savings.
Profits vary among firms because of differences in
competions among different firms.
Throughout the managerial economics the
following main topics will be covered:
Demand and supply
Production and Cost concepts
Theory of the firm,its objectives,
constraints etc.
Marketing structure and its behaviour
Game theory and its application in
Business
Ecnomic Optimisation process
What is optimal decision? It is the best
decision of the mangers which is
consistent with the mangerial objectives
Maximizing the Value of the Firm by
fuilfilling the need of the customers most
efficiently
Managers need to be more cusomers
focused rather than involving with self
interest
Revenue Concepts
Price and quantity relation
P
Total Revenue = Price Quantity
Marginal Revenue:Change in total revenue associated with
a one-unit change in output.
Maximization of total Revenue : MR = 0.
Q
AR
MR
Cost Concepts
Total Cost= Fixed Cost + Variable Cost.
Marginal Cost is the change in total cost
associated with a one-unit change in
output.
Average Cost = Total Cost/Quantity
Average Cost is Minimum when: MC =
AC. It reflects efficient production of a
given output level.
Concepts of Profit
Total Profit : Total Revenue - Total Cost
Marginal Profit: change in total profit due to a one-
unit change in output: MR MC. It is the gain from
producing one more unit of output (Q).
Profit Maximization: MR MC = 0 or MR = MC
Incremental profits: It is the gain tied to a given
managerial decision, possibly involving multiple units
of Q.
The incremental revenue of a new productis
measured as the difference between the firms total
revenue before and after the new product is
introduced. So also the incremental cost. Accordingly
one can estimate the incremental profit.
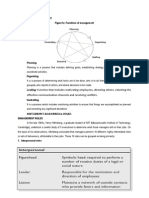
Decision making process
Establishing objective
Defining the problem
Identifying possible
alternative solutions
Evaluating alternative
courses of action
Legal and social
constraints
Of the alternative
courses of action,
choosing the best
Considering financial,
technological , infrastructure
and output constraints
Implementing and monitoring
the decision
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Key to Higher Profits: Pricing PowerVon EverandThe Key to Higher Profits: Pricing PowerBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- What Is Managerial Economics?Dokument24 SeitenWhat Is Managerial Economics?ChandanMatoliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial EconomicsDokument11 SeitenManagerial EconomicsAthena LouiseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Economics: Dr. Ashaq HussainDokument27 SeitenBusiness Economics: Dr. Ashaq HussainMaanvi RockzzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter OneDokument37 SeitenChapter Onehamdi abdrhmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scope of Managerial Economics CH 1Dokument13 SeitenScope of Managerial Economics CH 1hajra khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Managerial EconomicsDokument15 SeitenIntroduction To Managerial EconomicsMatthew Rogers100% (1)
- Managerial 01Dokument7 SeitenManagerial 01Shashikala WeerakoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Managerial EconomicsDokument24 Seiten01 Managerial EconomicsscribdwithyouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial Economics:: Theory, Applications, and CasesDokument50 SeitenManagerial Economics:: Theory, Applications, and CasesAbeer ShamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Chapter I Introduction of Business EconomicsDokument23 Seiten1 Chapter I Introduction of Business EconomicsIshan GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1Dokument101 SeitenUnit 1atulkumar.rise1Noch keine Bewertungen
- MG Eco Chapter 1Dokument25 SeitenMG Eco Chapter 1Fatima KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics Assignments Set-1 (WITH GRAPH)Dokument7 SeitenEconomics Assignments Set-1 (WITH GRAPH)Kamalakshya SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- I602 - 11 - Economics of The FirmDokument31 SeitenI602 - 11 - Economics of The FirmRohan SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me 1ST ChapDokument5 SeitenMe 1ST ChapAleem KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter2 Managerial-Economics P1Dokument15 SeitenChapter2 Managerial-Economics P1Yve LuelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS NOTES DC Without Market StructuresDokument160 SeitenMANAGERIAL ECONOMICS NOTES DC Without Market StructuressanelisofuturemoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial Economics: Definition, Nature, ScopeDokument45 SeitenManagerial Economics: Definition, Nature, ScopeEnergy GasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Profit MaximisationDokument42 SeitenProfit MaximisationIrfan Jamal100% (1)
- Unit 1Dokument35 SeitenUnit 1trapti191967Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Two - Goals, Constraints, CostsDokument30 SeitenLecture Two - Goals, Constraints, CostsClive NyowanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial Economics For ManagersDokument30 SeitenManagerial Economics For ManagersGautam BindlishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2Dokument17 SeitenLecture 2ackimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business (Managerial) EconomicsDokument47 SeitenBusiness (Managerial) Economicssankum7578Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pricing StrategyDokument17 SeitenPricing Strategycharlesmartial77Noch keine Bewertungen
- EconomicsDokument16 SeitenEconomicsShahab AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economic Unit 1Dokument43 SeitenEconomic Unit 123mco058Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ripose EntreprenuershipDokument18 SeitenRipose EntreprenuershipemronmavinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monti Maam Business EconomicsDokument193 SeitenMonti Maam Business Economicssjst0709Noch keine Bewertungen
- Roles and Responsibilities, Concepts of EconomicsDokument22 SeitenRoles and Responsibilities, Concepts of EconomicsUmamaheswari RajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Economics 2022Dokument12 SeitenBusiness Economics 2022PIYUSH GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is 'Economics?': EAB - Unit I NotesDokument10 SeitenWhat Is 'Economics?': EAB - Unit I NotesKumar KrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial EconomicsDokument27 SeitenManagerial Economicspagal pagliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Marketing Management HandoutsDokument14 SeitenStrategic Marketing Management HandoutsVeah Maynagcot BejarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nature and Scope of Managerial EconomicsDokument19 SeitenNature and Scope of Managerial EconomicsCasillar, Irish JoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SodapdfDokument40 SeitenSodapdfcommercewaale1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial EconomicsDokument20 SeitenManagerial EconomicsAnonymous kK5O7WFZ5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter One Introduction To Managerial EconomicsDokument20 SeitenChapter One Introduction To Managerial EconomicsAmar EliasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial Economics Chapter 1Dokument54 SeitenManagerial Economics Chapter 1Yve LuelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Marketing2018.Ch7.LENLMSDokument40 SeitenPrinciples of Marketing2018.Ch7.LENLMSHUONG NGUYEN VU QUYNHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Business EnvironmentDokument13 SeitenIntroduction To Business Environmentjahazi2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial Economics Meaning and Nature of M E Chief Characteristics Scope Role and Responsibilities Basic Concepts and PreceptsDokument34 SeitenManagerial Economics Meaning and Nature of M E Chief Characteristics Scope Role and Responsibilities Basic Concepts and PreceptsPulkit AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Not So Helpful Reviewer For Bam 040Dokument27 SeitenA Not So Helpful Reviewer For Bam 040rago.cachero.auNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Not So Helpful Reviewer For Bam 040Dokument34 SeitenA Not So Helpful Reviewer For Bam 040rago.cachero.au100% (1)
- Objectives of FirmDokument20 SeitenObjectives of Firmdranita@yahoo.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-4, Business ObjectivesDokument5 SeitenChapter-4, Business Objectivessaudejaz2020Noch keine Bewertungen
- Material No. 3Dokument9 SeitenMaterial No. 3rhbqztqbzyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial Eco1Dokument190 SeitenManagerial Eco1ManojNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics: Unlimited Wants ScarcityDokument27 SeitenEconomics: Unlimited Wants ScarcityKarma AkabaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Projections: Key Questions To Draft The Financial ProjectionDokument11 SeitenFinancial Projections: Key Questions To Draft The Financial ProjectionAmit MaisuriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of A FirmDokument25 SeitenTheory of A FirmShashi Tripathi100% (2)
- ECONOMIC ANALYSIS - For Business and Strategic DecisionsDokument295 SeitenECONOMIC ANALYSIS - For Business and Strategic DecisionsAlessandro Nájeraa100% (3)
- Normative and Positive. Normative Focuses On Prescriptive Statements, and Help Establish Rules AimedDokument3 SeitenNormative and Positive. Normative Focuses On Prescriptive Statements, and Help Establish Rules AimedSRS FirstGradeDegreeCollegeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Econ Analysis Introduction 201516 1Dokument42 SeitenEcon Analysis Introduction 201516 1Mohd Abidi NoranizahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marcom BudgetingDokument17 SeitenMarcom Budgetingsiddharth devnaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 2.1Dokument120 SeitenSession 2.1anuhya_katariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nature and Scope PDFDokument6 SeitenNature and Scope PDFSanchit MiglaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to Increase Sales Using Customer Value Optimization: Make Money OnlineVon EverandHow to Increase Sales Using Customer Value Optimization: Make Money OnlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relevance of Arbitration in IndiaDokument6 SeitenRelevance of Arbitration in Indiamanishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Research 2Dokument10 SeitenResearch 2manishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arbitration 1Dokument5 SeitenArbitration 1manishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- ResearchDokument8 SeitenResearchmanishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- My NotesDokument42 SeitenMy Notesmanishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- ResearchDokument8 SeitenResearchmanishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rural MarketingDokument10 SeitenRural Marketingmanishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Business GrammarDokument24 SeitenBusiness Grammarmanishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Session 18Dokument16 SeitenSession 18manishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Session 4Dokument3 SeitenSession 4manishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Session 4Dokument3 SeitenSession 4manishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Marginal Costing and CVPDokument24 SeitenMarginal Costing and CVPmanishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Slides On How Marketing Is Changing With The Time.Dokument6 SeitenSlides On How Marketing Is Changing With The Time.manishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Relevant Costs and Areas of Decision Making: 10/2/2014 1 Chandrakant@SOM, KIIT UniversityDokument24 SeitenRelevant Costs and Areas of Decision Making: 10/2/2014 1 Chandrakant@SOM, KIIT Universitymanishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Relevant Costs and Areas of Decision Making: 10/2/2014 1 Chandrakant@SOM, KIIT UniversityDokument24 SeitenRelevant Costs and Areas of Decision Making: 10/2/2014 1 Chandrakant@SOM, KIIT Universitymanishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial Economics Assignmnt-1Dokument2 SeitenManagerial Economics Assignmnt-1manishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Dokument15 SeitenSoftware Development Life Cycle (SDLC)manishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz Test 1 6th July.13Dokument3 SeitenQuiz Test 1 6th July.13manishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Process CostingDokument10 SeitenProcess Costingmanishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case StudyDokument4 SeitenCase Studymanishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Short Questions (Theory) of ABM (Financial Accounting)Dokument8 SeitenShort Questions (Theory) of ABM (Financial Accounting)manishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- StrategyDokument22 SeitenStrategymanishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative Technique NewDokument35 SeitenQuantitative Technique Newmanishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Session 3-4 Dimensions of StructureDokument24 SeitenSession 3-4 Dimensions of Structuremanishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Organizational DesignDokument9 SeitenOrganizational Designmanishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- RegressionDokument7 SeitenRegressionmanishkhandal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Plan Surf ExcelDokument22 SeitenMarketing Plan Surf ExcelM. Bilal Khan60% (5)
- Bwts Newsletter 657 771Dokument24 SeitenBwts Newsletter 657 771Humayun NawazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 13 Personal and Professional Development AssignmentDokument5 SeitenUnit 13 Personal and Professional Development AssignmentMohammadAhmad0% (1)
- Harvard HBS Casebook Consulting Case Interview Book哈佛商学院咨询案例面试Dokument115 SeitenHarvard HBS Casebook Consulting Case Interview Book哈佛商学院咨询案例面试issac li91% (11)
- TESCO Case StudyDokument7 SeitenTESCO Case StudyAustin Grace WeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing SBIDokument54 SeitenMarketing SBILakshmi PeramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nestle - Market Penetration - Manifested Marketing BlogDokument7 SeitenNestle - Market Penetration - Manifested Marketing BlogAdam DanialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Swot Strengths: OpportunitiesDokument11 SeitenSwot Strengths: Opportunitiesabir oueissNoch keine Bewertungen
- HebeiDokument24 SeitenHebeicool_stud_waliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dallas ISD Superintendent Mike Miles' "Destination 2020" Action PlanDokument32 SeitenDallas ISD Superintendent Mike Miles' "Destination 2020" Action PlanThe Dallas Morning News100% (1)
- The Ultimate Guide To Internal Communications StrategyDokument25 SeitenThe Ultimate Guide To Internal Communications Strategytsb9rhgmkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial Economics and Financial Analysis: Unit-IDokument24 SeitenManagerial Economics and Financial Analysis: Unit-IJanu JahnaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adoption of ISA-95 by Dow ChemicalDokument38 SeitenAdoption of ISA-95 by Dow ChemicalJosé Manuel FontaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 32 - Business StrategyDokument7 SeitenUnit 32 - Business StrategyAnushkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infotech Vendor Landscape Content and Email ArchivingDokument66 SeitenInfotech Vendor Landscape Content and Email Archivingcoolguy_auNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBA - OM Third Semester AssignmentsDokument2 SeitenMBA - OM Third Semester AssignmentsRitesh DeshmukhNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Oliver Wight IBPDokument2 SeitenThe Oliver Wight IBPAhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- People ResourcingDokument13 SeitenPeople ResourcingMehedi Masud100% (3)
- Ambient CommunicationsDokument19 SeitenAmbient CommunicationsMaria Anna M LegaspiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Towards - An PDFDokument33 SeitenTowards - An PDFlestari daswanNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Martketing Practice Questions: Keegan 8e Ch08Dokument7 SeitenInternational Martketing Practice Questions: Keegan 8e Ch08PandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employer BrandingDokument26 SeitenEmployer BrandingsujithasukumaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 1 2 and 3 Homework For Organizational ManagementDokument20 SeitenSession 1 2 and 3 Homework For Organizational ManagementSwapan Kumar SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEEK 2-The Organization Context Strategy, Structure and Culture (Compatibility Mode)Dokument39 SeitenWEEK 2-The Organization Context Strategy, Structure and Culture (Compatibility Mode)Chan HyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sales Management PlanningDokument30 SeitenSales Management PlanningJunaid Ahmed50% (2)
- Website Competency Dictionary 1Dokument50 SeitenWebsite Competency Dictionary 1Vahmi Brian Owen D'sullivansevenfoldimerzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supply Chain Manager in Cincinnati/Dayton OH Resume Jeffrey WolfeDokument1 SeiteSupply Chain Manager in Cincinnati/Dayton OH Resume Jeffrey WolfeJeffrey WolfeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Vision at Mentor GraphicsDokument3 SeitenRole of Vision at Mentor Graphicsziafat shehzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Management PresentationDokument35 SeitenStrategic Management Presentationrishuchaudhary100% (1)
- Strategic Business Model For Telecommunication Companies in The PhilippinesDokument25 SeitenStrategic Business Model For Telecommunication Companies in The PhilippinesgoerginamarquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Introduction To Strategic Management Notes @mission CA InterDokument11 Seiten1 Introduction To Strategic Management Notes @mission CA InterMehak KaushikkNoch keine Bewertungen