Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Object Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 02
Hochgeladen von
Thiago BecharaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Object Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 02
Hochgeladen von
Thiago BecharaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Object-Oriented Programming
(OOP)
Lecture No. 2
Information Hiding
Information is stored within the object
It is hidden from the outside world
It can only be manipulated by the object
itself
Example Information Hiding
Alis name is stored within his brain
We cant access his name directly
Rather we can ask him to tell his name
Example Information Hiding
A phone stores several phone numbers
We cant read the numbers directly from the
SIM card
Rather phone-set reads this information for
us
Information Hiding
Advantages
Simplifies the model by hiding
implementation details
It is a barrier against change propagation
Encapsulation
Data and behaviour are tightly coupled
inside an object
Both the information structure and
implementation details of its operations are
hidden from the outer world
Example Encapsulation
Ali stores his personal information and
knows how to translate it to the desired
language
We dont know
How the data is stored
How Ali translates this information
Example Encapsulation
A Phone stores phone numbers in digital
format and knows how to convert it into
human-readable characters
We dont know
How the data is stored
How it is converted to human-readable
characters
Encapsulation Advantages
Simplicity and clarity
Low complexity
Better understanding
Object has an Interface
An object encapsulates data and behaviour
So how objects interact with each other?
Each object provides an interface
(operations)
Other objects communicate through this
interface
Example Interface of a Car
Steer Wheels
Accelerate
Change Gear
Apply Brakes
Turn Lights On/Off
Example Interface of a Phone
Input Number
Place Call
Disconnect Call
Add number to address book
Remove number
Update number
Implementation
Provides services offered by the object
interface
This includes
Data structures to hold object state
Functionality that provides required services
Example Implementation of
Gear Box
Data Structure
Mechanical structure of gear box
Functionality
Mechanism to change gear
Example Implementation of
Address Book in a Phone
Data Structure
SIM card
Functionality
Read/write circuitry
Separation of Interface &
Implementation
Means change in implementation does not
effect object interface
This is achieved via principles of information
hiding and encapsulation
Example Separation of
Interface & Implementation
A driver can drive a car independent of
engine type (petrol, diesel)
Because interface does not change with the
implementation
Example Separation of
Interface & Implementation
A driver can apply brakes independent of
brakes type (simple, disk)
Again, reason is the same interface
Advantages of Separation
Users need not to worry about a change
until the interface is same
Low Complexity
Direct access to information structure of an
object can produce errors
Messages
Objects communicate through messages
They send messages (stimuli) by invoking
appropriate operations on the target object
The number and kind of messages that can
be sent to an object depends upon its
interface
Examples Messages
A Person sends message (stimulus) stop
to a Car by applying brakes
A Person sends message place call to a
Phone by pressing appropriate button
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Supermarket Final Project PDFDokument38 SeitenSupermarket Final Project PDFPrakash SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ex - No:1a: Student Database Using Class: #Include #Include Const Size 25Dokument27 SeitenEx - No:1a: Student Database Using Class: #Include #Include Const Size 25Arul_Selva_Mar_7285Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cvpresentation 190812154654Dokument25 SeitenCvpresentation 190812154654PyariMohan JenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument51 SeitenUntitledOmkar RaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- OOPs Complete FilepdfDokument52 SeitenOOPs Complete FilepdfMayank SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual - TYL - C++ TrainingDokument63 SeitenManual - TYL - C++ TrainingMANGESH KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- C++ ConceptDokument82 SeitenC++ ConceptRaju KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pedestrian Detection - Kristina PicklDokument45 SeitenPedestrian Detection - Kristina PicklZulkarnain ZainudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Object Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 27Dokument29 SeitenObject Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 27Sameer HaneNoch keine Bewertungen
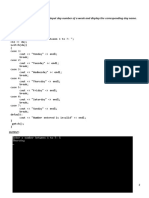
- Program - 1: Write A Program To Input Day Number of A Week and Display The Corresponding Day NameDokument46 SeitenProgram - 1: Write A Program To Input Day Number of A Week and Display The Corresponding Day NameDharnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPP Project (Zodiac)Dokument15 SeitenCPP Project (Zodiac)Rakesh ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPP BSC Lab Program 2020 21Dokument21 SeitenCPP BSC Lab Program 2020 21irfanahmed.dbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT5409 Ch7 Part1 Object Detection v2Dokument97 SeitenIT5409 Ch7 Part1 Object Detection v2Bui Minh DucNoch keine Bewertungen
- Object Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 37Dokument33 SeitenObject Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 37Sameer HaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical FileDokument85 SeitenPractical FileRahul Shivroop100% (1)
- Object Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 12Dokument35 SeitenObject Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 12Sameer HaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT5409 Ch5 Segmentation v2Dokument64 SeitenIT5409 Ch5 Segmentation v2nguyễn ĐứcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Face Detection: Many Slides Adapted From P. ViolaDokument37 SeitenFace Detection: Many Slides Adapted From P. ViolamailmekaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) Lecture No. 1Dokument18 SeitenObject-Oriented Programming (OOP) Lecture No. 1razianisarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Object Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 22Dokument34 SeitenObject Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 22Sameer HaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- C++ Unit 2Dokument69 SeitenC++ Unit 2OrlinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Object Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 36Dokument25 SeitenObject Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 36Sameer HaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Object Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 23Dokument25 SeitenObject Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 23Sameer HaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Object Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 34Dokument22 SeitenObject Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 34Sameer HaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Object Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 33Dokument27 SeitenObject Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 33Sameer HaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Object Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 45Dokument35 SeitenObject Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 45Sameer HaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Object Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 04Dokument26 SeitenObject Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 04Sameer HaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- C++ Programs and My SQL: Roll No:-39 Class - XII A Submitted By: - Vipul KharwarDokument38 SeitenC++ Programs and My SQL: Roll No:-39 Class - XII A Submitted By: - Vipul KharwarVipul KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- IndustryalDokument187 SeitenIndustryalMikiyas GetasewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Object Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 21Dokument49 SeitenObject Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 21Sameer HaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Object Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 16Dokument32 SeitenObject Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 16Sameer HaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Structures Using C++ by DR Varsha Patil: Oxford University Press © 2012Dokument49 SeitenData Structures Using C++ by DR Varsha Patil: Oxford University Press © 2012Maria LavanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT5409 - Ch7 - Part3 - DL For CV-v2 - 4pagesDokument42 SeitenIT5409 - Ch7 - Part3 - DL For CV-v2 - 4pagesngocnguyentheNoch keine Bewertungen
- C++ Complete NotesDokument163 SeitenC++ Complete NotesSaurav NarukaNoch keine Bewertungen
- C++ MaterialDokument109 SeitenC++ MaterialNiranjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Web TechnologiesDokument379 SeitenWeb Technologiesonesoundmind100% (1)
- JM International School: C++ Practical FileDokument39 SeitenJM International School: C++ Practical FileSolankiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Object Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 31Dokument35 SeitenObject Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 31Sameer HaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical AssignmentDokument86 SeitenPractical AssignmentOvidiu_PurcelNoch keine Bewertungen
- C++ Practical FileDokument48 SeitenC++ Practical Filehappybhogpur100% (1)
- Unit-2 C++ Basics - Edited PDFDokument59 SeitenUnit-2 C++ Basics - Edited PDFMark junnel NorberteNoch keine Bewertungen
- OOP Program AnswersDokument47 SeitenOOP Program AnswersAayan MullaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Object Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 40Dokument31 SeitenObject Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 40Sameer HaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical File of C++Dokument242 SeitenPractical File of C++oak tooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Object Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 41Dokument38 SeitenObject Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 41DewanImdadNoch keine Bewertungen
- UML - LectureDokument37 SeitenUML - LectureShabanizamana100% (1)
- PROGRAM1Dokument119 SeitenPROGRAM1Rahul DeswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- SQL 1Dokument25 SeitenSQL 1AtthulaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Object Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 42Dokument43 SeitenObject Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 42Sameer HaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- C++ 4th Sem PgmsDokument24 SeitenC++ 4th Sem PgmsJose KurianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Object Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 25Dokument28 SeitenObject Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 25Sameer HaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- CO1 Python OOPs ConceptsDokument37 SeitenCO1 Python OOPs Conceptsanilkumar06Noch keine Bewertungen
- Q1.Write A Program Using Multiple Inheritance For The Classes Student, Game and PersonDokument55 SeitenQ1.Write A Program Using Multiple Inheritance For The Classes Student, Game and PersoncehodeNoch keine Bewertungen
- #Include Void MainDokument29 Seiten#Include Void MainDeepak GourNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASSIGNMENT-1 (20 Files Merged) PDFDokument70 SeitenASSIGNMENT-1 (20 Files Merged) PDFPrakhar PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oop Practical ManualDokument34 SeitenOop Practical ManualShivamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) Lecture No. 2Dokument21 SeitenObject-Oriented Programming (OOP) Lecture No. 2Muhammad ZeeshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture To HeavenDokument20 SeitenLecture To HeavenMaliha Maqsood AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISP-QnA - ANSWERSDokument26 SeitenISP-QnA - ANSWERSwander boyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PLUTO: Cloud Assist Parallel Encryption For Data in Mobile Cloud ComputingDokument12 SeitenPLUTO: Cloud Assist Parallel Encryption For Data in Mobile Cloud ComputingasfNoch keine Bewertungen
- TextDokument2 SeitenTextThiago BecharaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TextoDokument1 SeiteTextoThiago BecharaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnglishDokument2 SeitenEnglishThiago BecharaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Object Oriented Programming - CS304 VU Lectures Power Point Slides PDFDokument2 SeitenObject Oriented Programming - CS304 VU Lectures Power Point Slides PDFThiago Bechara100% (1)
- Bepauche International LLC - Teacher Application FormDokument4 SeitenBepauche International LLC - Teacher Application FormNamja Ileum Ozara GaabucayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Management Case Study 2Dokument3 SeitenMarketing Management Case Study 2phuc phanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRML RescuebootDokument4 SeitenGRML RescuebootcoldironNoch keine Bewertungen
- ROMOSS 2016 Best Charging Solution ProviderDokument12 SeitenROMOSS 2016 Best Charging Solution Providerruth lopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Install DNS Server at Ubuntu 8Dokument2 SeitenInstall DNS Server at Ubuntu 8ngadoel2308Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 7Dokument2 SeitenLab 7Life PubgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Date Field FunctionsDokument21 SeitenDate Field FunctionsChavala SatishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: Introduction: (Computer System Structure and Interrupts)Dokument20 SeitenChapter 1: Introduction: (Computer System Structure and Interrupts)Ayush DusejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AU6850 Datasheet: USB Host MP3 Decoder SOCDokument20 SeitenAU6850 Datasheet: USB Host MP3 Decoder SOCOswaldo Rengifo MuozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Action Multimedia Feb Price ListDokument21 SeitenAction Multimedia Feb Price ListRafeeq AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Avr 2807Dokument130 SeitenAvr 2807bechaseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gfk1305B - CIMPLICITY HMI Basic Control Engine Program Editor Operation ManualDokument127 SeitenGfk1305B - CIMPLICITY HMI Basic Control Engine Program Editor Operation ManualEduardo NascimentoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hi-Pe: High Performance Walk-Through Multi-Zone Metal DetectorDokument6 SeitenHi-Pe: High Performance Walk-Through Multi-Zone Metal DetectorKhaled ElSaeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment / Lab Sheet / Project / Case Study No. 2Dokument9 SeitenAssignment / Lab Sheet / Project / Case Study No. 2Rakshya NepaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Python - Rapid Pro To Typing of Applications On The Mobile PlatformDokument349 SeitenMobile Python - Rapid Pro To Typing of Applications On The Mobile PlatformMohit Garg100% (2)
- Computer Science, 9618 Home Assignment (35 Marks)Dokument5 SeitenComputer Science, 9618 Home Assignment (35 Marks)Saurya PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MR Guide 81110 Rev B PDFDokument196 SeitenMR Guide 81110 Rev B PDFlinkranjitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 12: Software DevelopmentDokument17 SeitenUnit 12: Software Developmentapi-485038711Noch keine Bewertungen
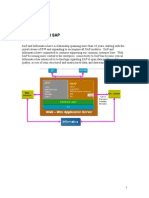
- PowerExchange - SAP Functionality OverviewDokument13 SeitenPowerExchange - SAP Functionality OverviewMahesh SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- L22 InterfaceDokument35 SeitenL22 Interfaceadarsh rajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diafix Troubleshooting NovoDokument242 SeitenDiafix Troubleshooting NovoInfo e TecNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yealink SIP-T2 Series T19 (P) E2 T4 Series IP Phones Administrator Guide V81 20Dokument1.042 SeitenYealink SIP-T2 Series T19 (P) E2 T4 Series IP Phones Administrator Guide V81 20groovyonlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Java AppletsDokument16 SeitenJava AppletsSachin ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of GOOSE Messages On IED Protection Schemes: Executive SummaryDokument5 SeitenImpact of GOOSE Messages On IED Protection Schemes: Executive SummaryNesma BOUDAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Drive An Led Display MatrixDokument8 SeitenHow To Drive An Led Display MatrixMark Anthony Sabio Lucero100% (1)
- 5 Artificial Intelligence Aided Innovation Education Based On Multiple IntelligenceDokument4 Seiten5 Artificial Intelligence Aided Innovation Education Based On Multiple IntelligenceFelix BarahonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computational Science - ICCS 2023Dokument751 SeitenComputational Science - ICCS 2023Vehpi YILDIRIMNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF CycloneII DatasheetDokument110 SeitenPDF CycloneII DatasheetSatvik HardatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccnpv7.1 Switch Lab3-1 Vlan-trunk-Vtp StudentDokument20 SeitenCcnpv7.1 Switch Lab3-1 Vlan-trunk-Vtp StudentItamar Zimmerman0% (1)
- p424 KowalskiDokument13 Seitenp424 KowalskiMaya Ria AgustinNoch keine Bewertungen