Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
CFX12 11 Cel
Hochgeladen von
virk_70Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CFX12 11 Cel
Hochgeladen von
virk_70Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
11-1
ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
April 28, 2009
Inventory #002598
Chapter 11
CFX Expression Language
(CEL)
Introduction to CFX
CFX Expression Language
11-2
ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
April 28, 2009
Inventory #002598
Training Manual
CEL - CFX Expression Language
Allows the user to create equations (can be functions of
solution/system variables) that can be used in CFX-Pre and CFD-Post
Example:
CEL
CFX Expression Language
11-3
ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
April 28, 2009
Inventory #002598
Training Manual
The syntax rules are the same as those for conventional arithmetic.
Operators are written as:
+ (addition) - (subtraction) * (multiplication)
/ (division) ^ (exponentiation)
Variables and expressions are case sensitive (example: t vs. T)
Expressions must be dimensionally consistent for addition and subtraction
operations (example: 1.0 [mm] +0.45 [yds] is OK)
You cannot add values with inconsistent dimensions
Fractional and decimal powers are allowed (example: a^(1/2) + 1.0^0.5)
Units of expressions are not declared they are the result of units in the
expression (example: a [kg m^-3] * b [m s^-1] has units of [kg m^-2 s^-1]
Some constants are also available in CEL for use in expressions:
e Constant: 2.7182818
g Acceleration due to gravity: 9.806 [m s^-2]
pi Constant: 3.1415927
R Universal Gas Constant: 8314.5 [m^2 s^-2 K^-1]
CEL Rules
CFX Expression Language
11-4
ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
April 28, 2009
Inventory #002598
Training Manual
Numerical functions and operators are also available in CEL
Right-click when creating expressions for a complete list
Custom functions with User Fortran can also be created
Function Operands Dimensions [x] Operands Values Results Dimensions
sin(x) Angle Any Dimensionless
cos(x) Angle Any Dimensionless
tan(x) *** Angle Any Dimensionless
asin(x) Dimensionless -1 x 1 Angle
acos(x) Dimensionless -1 x 1 Angle
atan(x) Dimensionless Any Angle
exp(x) Dimensionless Any Dimensionless
loge(x) Dimensionless 0 < x Dimensionless
log10(x) Dimensionless 0 < x Dimensionless
abs(x) Any Any [x]
sqrt(x) Any 0 x [x]^0.5
if(test, res1, res2)* Any Any Any (res1 and res2 must have the same dimensions)
min(x,y) **** Any Any [x]
max(x,y) **** Any Any [x]
step(x) * Dimensionless Any Dimensionless
*if functions contain a test, and two result outcomes. The first outcome, res1 will be returned if test evaluates to true. If test evaluates to false, res2 is
returned. Consider the following example, where we wish to set volume fraction to 1 when X is greater than 1 [m], and 0 if X is less than 1 [m]:
if (x>1[m], 1, 0)
In this case, if the result is precisely equal to 1[m], the result is (res1+res2)/2
**step(x) is 0 for negative x, 1 for positive x and 0.5 for x=0.
*** note that tan(x) is undefined for np/2 where n=1, 3, 5 .. .
**** both x and y must have the same dimensions.
Built In Functions
CFX Expression Language
11-5
ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
April 28, 2009
Inventory #002598
Training Manual
x Direction 1 in Reference Coordinate Frame
y Direction 2 in Reference Coordinate Frame
z Direction 3 in Reference Coordinate Frame
r Radial spatial location, r = (x^2+y^2)^0.5
theta Angle, arctan(y/x)
t Time
u Velocity in the x coordinate direction
v Velocity in the y coordinate direction
w Velocity in the z coordinate direction
p (absolute) Pressure
ke Turbulent kinetic energy
ed Turbulent eddy dissipation
T Temperature
sstrnr Shear strain rate
density Density
rNoDim Non-dimensional radius (rotating frame only)
viscosity Dynamic Viscosity
Cp Specific Heat Capacity at Constant Pressure
cond Thermal Conductivity
AV name Additional Variable name
mf Mass Fraction
Solver variables are available for use in any expression
Below is a partial list of the available system variables:
When creating expressions, right-click to access a full list
Depending on your
physics, some
variables will not be
valid e.g. you need
to solver heat transfer
to use T
Solver Variables
CFX Expression Language
11-6
ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
April 28, 2009
Inventory #002598
Training Manual
How To Create Expressions
CFX Expression Language
11-7
ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
April 28, 2009
Inventory #002598
Training Manual
To add more
expressions
(similar method in
CFD-Post)
How To Create Expressions
Right-click in the
Definition window
to access
Variables,
Constants,
Functions,
Locators and
existing
Expressions
CFX Expression Language
11-8
ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
April 28, 2009
Inventory #002598
Training Manual
where is the shear strain rate
Creating a variable viscosity
Viscosity of a shear thickening fluid:
1
n
K
Solver Variable and Expression Name are both
accessed via the right mouse button
CEL in CFX-Pre: Example 1
CFX Expression Language
11-9
ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
April 28, 2009
Inventory #002598
Training Manual
Alternatively, an expression can be entered directly into a field
CEL in CFX-Pre: Example 1
CFX Expression Language
11-10
ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
April 28, 2009
Inventory #002598
Training Manual
Using an if Function
Set inlet temperature to 300 K for the first 19 iterations then raise it to
320 K after 20 iterations
Solver variable
accessed with the right
mouse button
Note: On the 21
st
iteration
inlet temp = 310 K
CEL in CFX-Pre: Example 2
CFX Expression Language
11-11
ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
April 28, 2009
Inventory #002598
Training Manual
You can also define your own 1-D linear, or 3-D cloud of points
interpolation functions
Import
data
points or
add
manually
User Functions
CFX Expression Language
11-12
ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
April 28, 2009
Inventory #002598
Training Manual
Example: Having the timestep change
with iteration number as shown here
Timestep size is in seconds
Continued on next
slide...
User Functions: Example
Iteration Number is
dimensionless
CFX Expression Language
11-13
ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
April 28, 2009
Inventory #002598
Training Manual
Example: Having the timestep change
with iteration number as shown here
User Functions: Example
CFX Expression Language
11-14
ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
April 28, 2009
Inventory #002598
Training Manual
Integrated quantities can be used in expressions to evaluate variables over
some location
Examples:
Calculate the area average of Cp on an isosurface: areaAve(Cp)@iso1
Mass flow of particular fluid through a locator: oil.massFlow()@slice1
Available in CFX-Pre and CFD-Post
Usage is more strict in CFX-Pre
E.g. the argument supplied to the function must be a variable, not an expression
@<locator> syntax must always supply a named location used in the
physics definition
A boundary condition name, a domain name, a monitor point name, etc.
To reference general mesh regions use the syntax @REGION:<name>
Phases/components can be referenced using:
[<phase name>.][<component name>.]<function>@<locator>
E.g. Air.Nitrogen.massFlow()@outlet
Integrated Quantities
CFX Expression Language
11-15
ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
April 28, 2009
Inventory #002598
Training Manual
Integrated Quantities
Some functions allow an x, y or z operator:
area_x()@boundary gives the area projected in the x-direction
force_z()@wall gives the z component of the force on the wall
See documentation for a full list
These functions also allow an optional coordinate frame:
force_z_MyCoord()@wall gives the z component of the force on the wall using the
coordinate frame MyCoord
Each function requires either 0 or 1 arguments
areaAve requires 1 argument: areaAve(Temperature)@Wall
massFlow requires 0 arguments: massFlow()@Inlet
Return value units depend on the argument units
areaAve(Temperature)@Wall will return a value with units of Temperature
CFX Expression Language
11-16
ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
April 28, 2009
Inventory #002598
Training Manual
Below is a partial list of functions
See documentation for a complete list
Right-clicking when creating an expression will show most functions
Function Name and Syntax
<required> [<optional>]
area( )@<Location>
Area of a boundary or
interface.
Any 2D region (e.g., boundary
or interface)
area_x( )@<Location>
area_y( )@<Location>
area_z( )@<Location>
The (signed) component of the
normal area vector in the local
x, y or z direction. Any 2D region (e.g., a
boundary or interface)
areaAve(<var>)@<Location>
Area-weighted average of <var>
on a boundary.
Any 2D region (e.g., a
boundary or interface)
areaInt(<var>)@<Location>
Area-weighted integral of <var>
on a boundary.
Any 2D region (e.g., a
boundary or interface)
ave(<var>)@<Location>
Arithmetic average of <var>
within a domain or subdomain.
Any 3D region (e.g., domain or
subdomain)
[<Fluid>.]force( )@<Location>
The magnitude of the force
vector on a boundary. Any 2D region (e.g., a wall)
Operation Valid <Location>
Integrated Quantities
CFX Expression Language
11-17
ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
April 28, 2009
Inventory #002598
Training Manual
Function Name and Syntax
<required> [<optional>]
[<Fluid>.]force_x( )@<Location>
[<Fluid>.]force_y( )@<Location>
[<Fluid>.]force_z( )@<Location>
The (signed) component of the
force vector in the local x, y
or z direction. Any 2D region (e.g., a wall)
inside()@<Location>
Similar to the subdomain
variable, but allows a specific
2D or 3D location to be given.
Any 2D or 3D named sub-
region of the physical location
on which the expression is
evaluated.
mass()@<Location>
The total mass within a domain
or subdomain. This is fluid
dependent.
Any 3D region (e.g., domain or
subdomain)
massAve(<var>)@<Location>
Mass-weighted average of
<var> on a domain or
subdomain.
Any 3D region (e.g., domain or
subdomain)
massInt(<var>)@<Location>
The mass-weighted integration
of <var> within a domain or
subdomain
Any 3D region (e.g., domain or
subdomain)
[<Fluid>.]massFlow()@<Location> Mass flow through a boundary.
Any fluid surfaces (e.g., Inlets,
Outlets, Openings and fluid-
fluid interfaces)
[<Fluid>.]massFlowAve(<var>)
@<Location>
Mass flow weighted average of
<var> on a boundary.
Any fluid surfaces (e.g., Inlets,
Outlets, Openings and fluid-
fluid interfaces)
Operation Valid <Location>
Integrated Quantities
CFX Expression Language
11-18
ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
April 28, 2009
Inventory #002598
Training Manual
Function Name and Syntax
<required> [<optional>]
[<Fluid>.]massFlowAveAbs(<var>)
@<Location>
Absolute mass flow weighted
average of <var> on a
boundary.
Any fluid surfaces (e.g., Inlets,
Outlets, Openings and fluid-
fluid interfaces)
[<Fluid>.]massFlowInt(<var>)
@<Location>
Mass flow weighted integration
of <var> on a boundary.
Any fluid surfaces (e.g., Inlets,
Outlets, Openings and fluid-
fluid interfaces)
maxVal(<var>)@<Location>
Maximum Value of <var>
within a domain or subdomain.
Any 3D region (e.g., domain or
subdomain)
minVal(<var>)@<Location>
Minimum Value of <var> within
a domain or subdomain.
Any 3D region (e.g., domain or
subdomain)
probe(<var>)@<Location>
Returns the value of the
specified variable on the
specified Point locator.
Any point object (e.g., a
Source Point or Cartesian
Monitor Point)
rmsAve(<var>)@<Location>
RMS average of <var> within a
domain.
Any 3D region (e.g., domain or
subdomain)
sum(<var>)@<Location>
Sum of <var> over all domain
or subdomain vertices.
Any 3D region (e.g., domain or
subdomain)
Operation Valid <Location>
Integrated Quantities
CFX Expression Language
11-19
ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
April 28, 2009
Inventory #002598
Training Manual
Useful Functions
The inside() function returns 1 when inside the specified location and
0 when outside
Useful to limit the scope of a function to a subdomain or boundary
The step() function return 1 when the argument is positive and 0
when the argument is negative
Useful as an on-off switch
if() function can also be used as a switch
areaAve() and massFlowAve() are used to evaluate the average of a
quantity on a location
areaAve() is an area-weighted average. It is usually used on wall
boundaries and when the quantity is not carried with the flow, e.g.
Pressure at an outlet, Temperature on a wall
massFlowAve() is an average weighted by the local mass flow. It is
usually used to evaluate quantities that are carried with the flow, e.g.
Temperature at an outlet
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Diagnostic Test - AP CalculusDokument6 SeitenDiagnostic Test - AP CalculusShannon BurtonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bu I 7 - Dynamic Programming AlgorithmsDokument119 SeitenBu I 7 - Dynamic Programming AlgorithmsPhạm Gia DũngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Column Cover DetailsDokument10 SeitenColumn Cover Detailsvirk_70Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design Methods For AnchoragesDokument19 SeitenDesign Methods For Anchorageshitendra_gkNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Plymouth Module Record: MATS 320 Composites EngineeringDokument1 SeiteUniversity of Plymouth Module Record: MATS 320 Composites Engineeringvirk_70Noch keine Bewertungen
- London Drugs Compass Vending Machine LocationsDokument2 SeitenLondon Drugs Compass Vending Machine Locationsvirk_70Noch keine Bewertungen
- AAN003e Thermosets and Structural AdhesivesDokument5 SeitenAAN003e Thermosets and Structural Adhesivesvirk_70Noch keine Bewertungen
- Google MapsDokument4 SeitenGoogle Mapsvirk_70Noch keine Bewertungen
- 805 Reference SectionDokument16 Seiten805 Reference Sectionvirk_70Noch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 118 Guidelines For Prequalification and Design of Post-Installed and Cast-In Anchors in Australia - 2Dokument11 SeitenPaper 118 Guidelines For Prequalification and Design of Post-Installed and Cast-In Anchors in Australia - 2Tarek AbulailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pc. Tap and Die Set: Operator'S ManualDokument8 SeitenPc. Tap and Die Set: Operator'S Manualvirk_70Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Review of Bast Fibres and Their Composites - Part 1 Fibres As ReinforcementsDokument7 SeitenA Review of Bast Fibres and Their Composites - Part 1 Fibres As Reinforcementsvirk_70Noch keine Bewertungen
- Windows Liquid - US4561221Dokument6 SeitenWindows Liquid - US4561221virk_70Noch keine Bewertungen
- Blast Resistant Steel Door Overhead Door AssemblyDokument7 SeitenBlast Resistant Steel Door Overhead Door Assemblyvirk_70Noch keine Bewertungen
- s1 Screw Jacks PJLMPTDG 02Dokument130 Seitens1 Screw Jacks PJLMPTDG 02virk_70Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fa048 1407enDokument58 SeitenFa048 1407envirk_70Noch keine Bewertungen
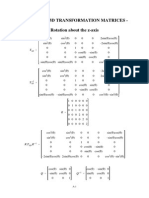
- 3d Transformation MatricesDokument3 Seiten3d Transformation Matricesvirk_70Noch keine Bewertungen
- Flip BoltDokument1 SeiteFlip Boltvirk_70Noch keine Bewertungen
- California Design CodesDokument260 SeitenCalifornia Design Codesvirk_70Noch keine Bewertungen
- NS26 1footingsDokument10 SeitenNS26 1footingszuzubettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- As Virk 2010Dokument133 SeitenAs Virk 2010virk_70Noch keine Bewertungen
- Inconel Alloy 718Dokument28 SeitenInconel Alloy 718hosseinidokht86Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dv05pub11 e ScriptDokument17 SeitenDv05pub11 e Scriptvirk_70Noch keine Bewertungen
- Seal mould cavity with O-ringDokument1 SeiteSeal mould cavity with O-ringvirk_70Noch keine Bewertungen
- TOPIC4 L ShortFibreCompositesDokument1 SeiteTOPIC4 L ShortFibreCompositesvirk_70Noch keine Bewertungen
- Novel Ultrasonic Dispersion of Carbon NanotubesDokument17 SeitenNovel Ultrasonic Dispersion of Carbon Nanotubesvirk_70Noch keine Bewertungen
- Planning & Building Fences On The FarmDokument20 SeitenPlanning & Building Fences On The FarmMarian StoicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IR TheoryDokument10 SeitenIR TheoryBenjamin Emenike Onyido JnrNoch keine Bewertungen
- PGI Opd at GlanceDokument18 SeitenPGI Opd at Glancevirk_70100% (2)
- Swaraj - by Arvind Kejriwal - EnglishDokument74 SeitenSwaraj - by Arvind Kejriwal - EnglishGaurav Bansal67% (3)
- A Review of Bast Fibres and Their Composites Part 3 - ModellingDokument8 SeitenA Review of Bast Fibres and Their Composites Part 3 - Modellingvirk_70Noch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Theory of Vibration Nonlinear Vibration ADokument3 SeitenAdvanced Theory of Vibration Nonlinear Vibration AranjithkrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE263 Homework 3 SolutionsDokument16 SeitenEE263 Homework 3 SolutionsLucky DeltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FEA Slab Analysis SolutionsDokument53 SeitenFEA Slab Analysis SolutionsZuhair NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discussion 3: AnswerDokument7 SeitenDiscussion 3: Answerحسن الفضيلNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ejercicios TL H. AntonDokument2 SeitenEjercicios TL H. AntonLuis ChipiturkinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 2packetDokument6 Seiten3 2packetapi-327561261Noch keine Bewertungen
- Integration Mcqs N AnsDokument6 SeitenIntegration Mcqs N AnsM. Shiraz HusnainNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3A1 Lecture 13Dokument46 Seiten3A1 Lecture 13apurvajahagirdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- S4 MathsDokument5 SeitenS4 Mathsbulemuibrahim6746Noch keine Bewertungen
- Strassen AlgorithmDokument2 SeitenStrassen AlgorithmNilayan AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSD Tutorial: Line Code Power SpectraDokument35 SeitenPSD Tutorial: Line Code Power Spectraasifmagsi415Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hansen, Nagy, OLeary - Deblurring Images. Matrices, Spectra and Filtering PDFDokument145 SeitenHansen, Nagy, OLeary - Deblurring Images. Matrices, Spectra and Filtering PDFأبو أسامهNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes Probability Theory (5thsem) 3Dokument9 SeitenLecture Notes Probability Theory (5thsem) 3MrigankaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3, Numerical Based On Population ForecastingDokument26 SeitenLecture 3, Numerical Based On Population ForecastingShivam SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 - The Limit of A Function - Theorems and ExamplesDokument65 SeitenLesson 1 - The Limit of A Function - Theorems and ExamplesLyca EstolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSP Manual - 2017 VTU 2015 Cbcs SchemeDokument99 SeitenDSP Manual - 2017 VTU 2015 Cbcs SchemeNikhil Miranda100% (1)
- Introduction To Finite Element Method (FEM)Dokument22 SeitenIntroduction To Finite Element Method (FEM)goldencomet100% (1)
- BCHD ProofDokument43 SeitenBCHD ProofIndranil MaitiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sum Sample EconDokument12 SeitenSum Sample EconMark Richard Hilbert (Rossetti)Noch keine Bewertungen
- MATH1081 Test 3 SolutionsDokument16 SeitenMATH1081 Test 3 SolutionsIsha DeshmukhNoch keine Bewertungen
- The FieldDokument36 SeitenThe FieldorionyiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rules of DifferentiationDokument26 SeitenRules of DifferentiationSnow CatNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Calculus Cheat SheetDokument2 SeitenAP Calculus Cheat Sheet3d5w2dNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-4 Contour IntegrationDokument58 SeitenUnit-4 Contour IntegrationJitender MeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Signal OperationsDokument12 SeitenBasic Signal OperationsFairouzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide to Coding with Mata in StataDokument16 SeitenGuide to Coding with Mata in Statache_wang_7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Business Statistics Key FormulasDokument5 SeitenBusiness Statistics Key FormulasMichal_Kramarz_619150% (4)
- An Introduction To Monte Carlo Simulations: Mattias JonssonDokument26 SeitenAn Introduction To Monte Carlo Simulations: Mattias JonssonAarohiShirkeNoch keine Bewertungen