Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
BMS
Hochgeladen von
bilal almelegy100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
2K Ansichten70 SeitenBuilding management system (bms) basics, functions and future trends agenda. A proper environment is described with four variables: temperature, humidity, pressure and ventilation. The comfort zone for temperature is between 68degF (20degC) and 75degF (25degC).
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
BMS.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenBuilding management system (bms) basics, functions and future trends agenda. A proper environment is described with four variables: temperature, humidity, pressure and ventilation. The comfort zone for temperature is between 68degF (20degC) and 75degF (25degC).
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
2K Ansichten70 SeitenBMS
Hochgeladen von
bilal almelegyBuilding management system (bms) basics, functions and future trends agenda. A proper environment is described with four variables: temperature, humidity, pressure and ventilation. The comfort zone for temperature is between 68degF (20degC) and 75degF (25degC).
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 70
Building Management System
Basics, Functions and Future Trends
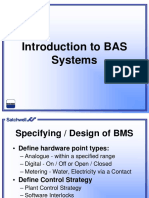
Agenda
BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM
Pneumatic, Electric, Electronic and Direct
Digital Control.
Direct Digital Controller Structure,
Functions and Features
Energy saving programs within the BMS
BMS Network and Open Protocols
Facility Management and Integration
Integration with Maintenance Manager
New Trends
Albert M. Butz invents the
thermostat
HVAC CONTROL History
HVAC CONTROL History
Function of HVAC controls
A Heating, Ventilating, and Air-Conditioning (HVAC)
Control system operates the mechanical equipment
(boilers, chillers, pumps, fans, etc.) to maintain the
proper environment in a cost-effective manner. A
proper environment is described with four variables:
temperature, humidity, pressure and ventilation.
Temperature
Function of HVAC controls
The comfort zone for temperature is between 68F
(20C) and 75F (25C).
Humidity The comfort zone for humidity is between
20% relative humidity (RH) and 60% RH
Pressure . The rooms and buildings typically have a
slightly positive pressure to reduce outside air
infiltration.
Ventilation . Rooms typically have several complete air
changes per hour. Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) is an
important issue.
BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM
Sensor
A sensor monitors and measures a variable. The HVAC variables are temperature,
humidity, and pressure. Different types of signals are produced by different types of
sensors.
BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM
Controller
The controller receives the signal from the sensor and produces an output signal
with setpoint, sensitivity (differential or throttling range), and action. Types of signals from
these devices are as follows:
Electric Controls The majority of electric controls contain the sensor and controller
as one piece. Electric controls use ON / OFF signals.
Pneumatic Controls Controller outputs are 3 to 15 psi (21 to 105 kPa).
Electronic Controls There are basically two types of electronic signals.
Voltage outputs may be 0 to 10 Vdc, 2 to 15 Vdc, or other ranges depending on the
controller. Voltage outputs have the disadvantage, when compared to current signals,
that voltage signals are more susceptible to distortion over long wire distances.
Current outputs modulate from 4 to 20 mA. They have the advantage of producing
little signal distortion over long wire distances.
BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM
Controller
The controller receives the signal from the sensor and produces an output signal
with setpoint, sensitivity (differential or throttling range), and action. Types of signals from
these devices are as follows:
Electric Controls The majority of electric controls contain the sensor and controller
as one piece. Electric controls use ON / OFF signals.
Pneumatic Controls Controller outputs are 3 to 15 psi (21 to 105 kPa).
Electronic Controls There are basically two types of electronic signals.
Voltage outputs may be 0 to 10 Vdc, 2 to 15 Vdc, or other ranges depending on the
controller. Voltage outputs have the disadvantage, when compared to current signals,
that voltage signals are more susceptible to distortion over long wire distances.
Current outputs modulate from 4 to 20 mA. They have the advantage of producing
little signal distortion over long wire distances.
BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM
BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM
Compressed air from compressor is used to as a source of energy for Pneumatic
Controllers. E ach Pneumatic controller support one control Loop. Currently is Used
for specific applications and service cost is expensive.
BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM
Electric Controller handles one control function, usually support ON/OFF Control
Mode (Fully open or fully closed final control element). Also is slow and rarely used
now.
Electronic Controller handles one control function, and support either modulating or
ON/OFF Control Mode. Used for small jobs as economic solution.
Centralizing Control With
Mimic Panel
Direct Digital Controllers
(DDCs)
Direct Digital Controllers is a microprocessor based device, and has a battery backed
memory to hold control programs and operating system, and also Input / Output
connectors to deal with sensors and final control elements.
Direct Digital Controllers are the core product for the Building Management System.
Direct Digital Controllers
(DDCs)
Some Direct Digital Controllers already have built in program and called Unitary
controllers and handle the control of specific equipment (Simple AHU, Fan Coil,
VAV,..ect). Programmable controllers support multiple applications and equipment.
Direct digital controllers can handle more than control loop at a time.
slide 16
maths
logic
PID
Direct Digital Controllers
(DDCs)
Graphical programming tool is usually used to program and configure DDC
controllers.
Each manufacturer implement the proper programming language for his own
product.
slide 17
Direct Digital Controllers
Input/ Outputs
Different Type of inputs and outputs are connected to the DDC controller.
slide 18
Analogue
Temp
Pressure
Humidity
Digital
Run
Fault
Trip
Analogue
Modulated
Digital
On On
On/Off
Pulse
Meters
maths
logic
PID
Direct Digital Controllers
Input/ Outputs Example
slide 19
Digital Inputs Examples:-
Differential Pressure Switch is an example of Digital Input.
Usually installed across a fan or a filter. If the contact is
closed the DDC can detect either the fan is running or the
filter is clogged.
Smoke Detector installed in the duct to allow the controller
to stop the Air Handling Unit in case of Fire.
Auxiliary contact from contactor to indicate if the contactor is
energized or NOT.
Direct Digital Controllers
Input/ Outputs Example
slide 20
Analog Inputs Example:-
Temperature Sensors/ Setpoint Modules for Rooms.
Temperature Sensors for Ducts.
Immersion temperature Sensors for water Pipes.
Humidity Transmitters for Rooms and Ducts.
Differential Pressure Transmitters for Clean
Rooms.
Direct Digital Controllers
Input/ Outputs Example
slide 21
Analog Output Examples:-
DDC produce a voltage signal ranged from 0 to 10 Volt.
According to the value the controlled device respond.
To Control the Fan Speed via inverter (Speed Drive).
To Modulate water Valve .
To Modulate Damper Motor and control Air
Flow.
Direct Digital Controllers
Input/ Outputs Example
slide 22
Digital Output Examples:-
Digital output is a relay output controlled by DDC
To Energize contactor in the motor control center in order to
start Fan or Pump.
To Start a condensing unit when using DX Air
Handling Units.
To energize Heater Battery Stages via
contactors
slide 23
DP
T
DP
T
DP
T
T
DP T
T
T
DP
boilers
DP
T
DP
T
DP
T
T
DP T
T
T
DP
chillers
FS
T T
T
air handling units
Application Programs
After connecting Field devices via Input/
outputs module, the application programs can
be downloaded to the controller memory
(Usually by using Laptop computer).
Commissioning and testing stage will start
slide 24
DP
T
DP
T
DP
T
T
DP T
T
T
DP
boilers
DP
T
DP
T
DP
T
T
DP T
T
T
DP
chillers
FS
T T
T
air handling units
Application Programs
After connecting Field devices via Input/
outputs module, the application programs can
be downloaded to the controller memory
(Usually by using Laptop computer).
Commissioning and testing stage will start
slide 25
Programming Tool
Programming Tool consists of mathematical and Boolean modules that
are connected to the inputs and outputs and also to each other in order
to produce the HVAC control Applications
slide 26
Application Program
After Finalizing the application program, It is tested off line and then
download to the controller.
slide 27
PID Module
The most important module is the PID that is usually used to drive an
analog signal for the final control element (Motorized Valve or Damper
actuator) in order to get the controlled medium to setpoint
PID Control
The PID Module calculates the error
between setpoint and measured value and
apply a control algorithm that is based on a
proportional gain, an integration action and
a derivative action.
Proportional Action Proportional Plus
Integral Actions
Proportional Plus
Integral Plus
Derivative Actions
PID Control
With proportional control, the output is a function of the
deviation of the controlled variable from the setpoint. As
the control point stabilizes, offset occurs.
Proportional
Action
PID Control
With the addition of integral control, the
control point returns to setpoint over a
period of time with some degree of
overshoot.
Proportional Plus
Integral Actions
PID Control
The significant difference is the elimination
of offset after the system has stabilized.
The adding the derivative
element reduces overshoot and decreases
response time.
Proportional Plus
Integral Plus
Derivative Actions
Energy Management
Hemisphere)
Energy Management Programs are Built in the
Direct Digital Controllers memory and help in
saving power in case of the proper Field
Devices are installed.
Energy Management
Comfort Costs
Energy Management is a compromise
between comfort and cost. It works between
the extreme boundaries of temperature and
RH.
Hemisphere)
Night cycle
Optimum Start/Stop
Zero energy band
Load reset
Night cooling
Enthalpy control
CO
2
control
Peak shaving
Duty cycling
Presence detection
Lighting control
Energy Management
The Most Applicable Energy Saving
Programs.
Night cycle
TT
TC
TT
Time
W
a
t
e
r
t
e
m
p
e
r
a
t
u
r
e
Applicable in Europe and some
areas in USA to invest .
Optimum Start / Stop with cooling
Optimum period to start and stop
HVAC Equipment while comfort
weather is reached during
occupancy.
Occupancy
Optimum
Start
Optimum
Stop
R
o
o
m
t
e
m
p
e
r
a
t
u
r
e
s
e
t
p
o
i
n
t
Night Night
Time
Zero energy band
Night offset
Zero energy band
R
o
o
m
t
e
m
p
e
r
a
t
u
r
e
Room temperature
setpoint
When space temperature located
within comfort range, No cooling or
heating will be used.
Night cooling
T
i
RH
i
T
a
RH
a
If
T
a
< T
i
&
RH
a
< RH
i
&
Time between 04:00 and 08:00
Then
Night cooling
End
Enthalpy control
T
M
M
M
+
M
-
M M
RH T RH
T RH
Comparing outside and return
Enthalpy
CO
2
control
+
M
x
y
CO
2
w
DSPL
Time
E
l
e
c
t
r
i
c
a
l
l
o
a
d
Peak
limit
Schedded loads
Applicable when Electrical cost is
higher at peak time
Presence detection
Night offset
Standby offset
Zero energy band
R
o
o
m
t
e
m
p
e
r
a
t
u
r
e
Room temperature
setpoint
Needs Occupancy Detector
Building Management System
Direct Digital Controller can work in
standalone bases. Readings can be
collected in the field by using
handheld operator terminal.
Building Management System
C
o
%RH
T
C
Effective Setpoint
% %
C C
If the direct digital controllers are connected together and
to a central computer, then the building management
system is established.
Building Management System
The building management system software in
the computer does not perform any control
functions, as all the control routines are
executed in the DDCs.
The Building Management system function is
as follows:-.
Centralized the operation of the HVAC system
instead to pass by every machine to operate
and get the readings or change the setpoint
Receive and record Alarms, Logs and reports.
Low Level Integration with other systems.
Graphic Display for equipment and readings.
Sample of Building Management
Graphical Presentation
Air Handling Display
Sample of Building Management
Graphical Presentation
Chillier Plant Display
Sample of Building Management
Graphical Presentation
CHARTS
Sample of Building Management
Graphical Presentation
Alarm Logs
Language of Communication
(Protocol)
Language of Communication
(Protocol)
Open Protocol
Years after, the implementation of a common
communication language Protocol started and
the most common protocols now are the Bacnet and
Lonworks.
Open Protocol
The BACnet History
1987
The ASHRAE (American Society of Heating Refrigeration and
Air-Conditioning Engineering) Standard Project Committee SPC
135P was founded. The committee was challenged to define a
communication protocol for building control and energy
management.
January 1989
The ASHRAE journal publishes a first article about the idea of a
new protocol and the philosophy behind it.
Open Protocol
The BACnet History
August 1991
The BACnet protocol has been sent out for a first review
March 1994
The BACnet protocol has been published for a second review
cycle
Spring 1995
The BACnet protocol received a third public review.
Each of the reviews lasted for 3 - 6 month. More than 790
review comments had been collected during the three public
review cycles.
Open Protocol
The BACnet History
September 1995
The ASHRAE Board of directors voted to ratify the BACnet
standard and published ASHRAE 135-1995.
December 1995
BACnet was adopted by the ANSI (American National Standards
Institute) as the ASHRAE/ANSI Standard 135-1995.
February 1996
BACnet debuted at the occasion of the International Air-
Conditioning, Heating and Refrigerating Exposition.
Open Protocol
The BACnet History
Spring 1997
The CEN Technical Committee (TC) 247 Working Group (WG) 4
adopted and published BACnet as European Prenorm ENV
1805-1 (Management Level) and
prENV 13321 (Automation Level).
In the meantime BACnet also had been ratified as
DIN V ENV 1805-1.
December 1998
The ENV 13321 "Data communication for HVAC application:
automation net" became approved.
BACnet is a communication protocol to exchange data
in Multi-Vendor Building Management
Systems/Networks
It fits to the requirements of heating, cooling,
ventilation control but ...
may also be the basis for integration of applications
like lighting, security and fire control
Whats BACnet good for?
Whats BACnet good for?
The sophistication of a specific device, in terms of its
ability to carry out particular service requests is
reflected by the device's conformance class.
Each conformance class specifies a minimum set of services,
objects, and properties which the device must support in
order to claim membership in a particular class.
The terms initiate and execute are used to describe a
device's capability to perform the application services
defined in the standard.
Whats BACnet good for?
Functional groups: collections of BACnet standard
object types and application services that collectively
meet the communication requirements of a single
building function.
The idea is to support specifiers as they specify specific
functionality like Event Initiation or Clock for particular
devices.
BACnet is compliant to the OSI Communication
Model.There are various options for the physical and
the datalink layer.
What is the BTL?
BACnet Testing Laboratory was established by BACnet
International to support compliance testing and interoperability
testing activities.
General activities of the BTL
The general activities of the BTL are to publish an Implementation
Guidelines document for users of BACnet with the help of the
working group, to organize and run the annual Interoperability
Workshop, and to test products for certification.
LONWORK BY
Founded By Mike Markkula (Intel,Apple)
Over 450 Products in product range
Head Office: Palo Alto, California, USA.
Over $100m and 500 man-years invested in bringing
LONWORKS Technology to the market place
LONWORK BY
Device Interoperability
Intelligent Devices
Standard Point Types (SNVTs)
Manufacturer Independent
Open Communication Protocol (LNS)
Lonmark
Independent Organisation
The LonMark logo is an indication that a
product completed the LonMark conformance
tests and has been designed to interoperate across
an open multi-vendor LONWORKS control network
More than 200 members
Neuron Chip
Most LonMark devices have this micro chip inside
Designed by Echelon
Made by Motorola, Toshiba & Cypress Semiconductor
Every chip has a unique 48 bit ID
There are different Neuron chips for different uses
with the same design but different memory size, CPU
speed etc...
This keeps the price down for smaller devices but the
processing power for complex devices
Neuron Chip
I/O (Counters
Resources
Drivers, etc..)
Application
CPU
RAM/ROM/EPROM
Media
Access CPU
RAM/ROM/EPROM
Network
CPU
RAM/ROM/EPROM
Protocol Firmware
(Layers 1-2)
Protocol Firmware
(Layers 3-6)
Transceiver
Optional
External
Memory
I/O
Conditioning
Power
Regulator
Node Specific
Program
Neuron Chip
ID #65673882930482726987...
Network
Comm
Port
Neuron ID
Every device has a unique Neuron ID stored in the chip
at manufacture, this cannot be changed.
When a device is commissioned the Neuron ID is
required to make sure the correct device is programmed.
There are Three methods of acquiring the Neuron ID
1. Manual Entry- Type the ID into the tool or Use a bar
code reader.
2. Discovery- the network tool can discover unconfigured
devices
4. Service PIN- press the devices service pin
Protocol Differences on Products
and Services
LON Bacnet
Future Trends
Customer Expectations
Reduction of initial investments
Building Control System uses existing IT infrastructure
A single user interface for all building disciplines (HVAC, Lighting, Lifts,
Fire, )
Customers want supplier independence in case of later system
enhancement
Reduction of operating, energy and maintenance costs
Mobile operators want to operate the building at any time, from
everywhere, immediately
Less trained operator needs intuitive" operating interfaces
Central Help Desk serves many buildings in a geographical region
Growing expectations for comfort and service
Reduced energy consumption
Future Trends
Customer Expectations
Global connectivity
Global companies need global BMS
information
Easy to operate
Access at any time, from everywhere,
immediately
Use mainstream technology
IT-world compliance
Slim, inexpensive clients
Future Trends
Customer Expectations
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Hvac BasicsDokument20 SeitenHvac BasicsRommy Romanza100% (3)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- HVAC Chilled Water Distribution SchemesDokument56 SeitenHVAC Chilled Water Distribution SchemesJenson Joy100% (5)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Large Chilled Water SystemDokument314 SeitenLarge Chilled Water SystemEsteban Lopez Arboleda100% (3)
- Durgasoft Core Java Latest1111Dokument440 SeitenDurgasoft Core Java Latest1111Swapnil Erande71% (7)
- Chapter 8 Duct Design and SealingDokument14 SeitenChapter 8 Duct Design and SealingMiguel FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 Duct Design and SealingDokument14 SeitenChapter 8 Duct Design and SealingMiguel FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cooling Tower Pumping and PipingDokument40 SeitenCooling Tower Pumping and Pipingthenshan100% (3)
- Electrical Design Guide WWTPDokument158 SeitenElectrical Design Guide WWTPKent RenemberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commercial HVAC Systems and Energy Code RequirementsDokument63 SeitenCommercial HVAC Systems and Energy Code Requirementsambuenaflor100% (1)
- Commercial HVAC Systems and Energy Code RequirementsDokument63 SeitenCommercial HVAC Systems and Energy Code Requirementsambuenaflor100% (1)
- 02 Chilled Water Piping Pumps PDFDokument64 Seiten02 Chilled Water Piping Pumps PDFbilal almelegyNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Cooling Tower Handbook - FINAL PDFDokument33 SeitenCooling Tower Handbook - FINAL PDFOscarJimenez19870% (1)
- Python PostgreSQL Tutorial Using Psycopg2 (Complete Guide)Dokument9 SeitenPython PostgreSQL Tutorial Using Psycopg2 (Complete Guide)ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bms DesignDokument22 SeitenBms Designbilal almelegyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training Catalog 2017: Johnson Controls Training InstituteDokument77 SeitenTraining Catalog 2017: Johnson Controls Training Institutebilal almelegyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MR11 GRIR Clearing Account MaintenanceDokument9 SeitenMR11 GRIR Clearing Account MaintenanceJayanth MaydipalleNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1200 Buildings Program BMS Seminar 1Dokument37 Seiten1200 Buildings Program BMS Seminar 1HayanJanakatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Considerations For Hot Water Plumbing PDFDokument105 SeitenDesign Considerations For Hot Water Plumbing PDFdanateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Efficiency: Practice GuideDokument56 SeitenWater Efficiency: Practice Guidebilal almelegyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enervent PegasosTwinTropicDokument21 SeitenEnervent PegasosTwinTropicbilal almelegyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enervent PegasosTwinTropicDokument21 SeitenEnervent PegasosTwinTropicbilal almelegyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stainless Steel Pipe To American StandardsDokument7 SeitenStainless Steel Pipe To American StandardsAnonymous dziHEjc7YNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study PDFDokument17 SeitenCase Study PDFWaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enervent PegasosTwinTropicDokument21 SeitenEnervent PegasosTwinTropicbilal almelegyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Bms FeaturesDokument17 Seiten2-Bms FeaturesMostafa AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMSOverview PDFDokument15 SeitenBMSOverview PDFHafizah EzaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- RLD MMM Deppmann Hydronic Chilled Condenser Water Pipe Sizing Michigan Energy Code PDFDokument4 SeitenRLD MMM Deppmann Hydronic Chilled Condenser Water Pipe Sizing Michigan Energy Code PDFbilal almelegyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prediction of pressure drop in chilled water piping using CFD analysisDokument6 SeitenPrediction of pressure drop in chilled water piping using CFD analysisforevertay2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- ISO-8859-1 - Principles of Management Sem 1 SlidesDokument52 SeitenISO-8859-1 - Principles of Management Sem 1 Slidesdipti30Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cooling TowersDokument35 SeitenCooling Towersedbaka100% (1)
- Chilled Water Dist I But I OnDokument44 SeitenChilled Water Dist I But I OnVineeth MuraleedharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 23 21 13 Hydronic Piping PDFDokument8 Seiten23 21 13 Hydronic Piping PDFbilal almelegyNoch keine Bewertungen
- HVACManl PDFDokument166 SeitenHVACManl PDFErvinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Year Project Proposal: IOT Based Energy MeterDokument8 SeitenFinal Year Project Proposal: IOT Based Energy MeterDaniyal ShahzaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- E40019 01Dokument250 SeitenE40019 01André CunhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Android Based Object Detection Application For Food ItemsDokument6 SeitenAndroid Based Object Detection Application For Food ItemsHafza GhafoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Note CODESYS OPC DA ServerDokument11 SeitenApplication Note CODESYS OPC DA Servermauricio borgesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Configuring VRF LiteDokument12 SeitenConfiguring VRF Litetudocris100% (1)
- Discovering Computers 2012: Your Interactive Guide To The Digital WorldDokument37 SeitenDiscovering Computers 2012: Your Interactive Guide To The Digital WorldMaha IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manager IT Infrastructure in ST Louis MO Resume Kent WilkeDokument2 SeitenManager IT Infrastructure in ST Louis MO Resume Kent WilkeKentWilkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Guide: Created by DR Yan MofoloDokument6 SeitenUser Guide: Created by DR Yan Mofolonathaniel ekaikoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matrimonial Project ReportDokument27 SeitenMatrimonial Project Reportrajputamitd100% (2)
- Linux Interview Questions and AnswersDokument46 SeitenLinux Interview Questions and AnswersBalamurugan Swaminathan100% (1)
- Chapter: 4.5 Types of Network Topic: 4.5.1 Peer To Peer NetworkDokument5 SeitenChapter: 4.5 Types of Network Topic: 4.5.1 Peer To Peer NetworkETL LABSNoch keine Bewertungen
- RadiusManager User Manual 4.1Dokument83 SeitenRadiusManager User Manual 4.1tutakhaluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Design: Register-Transfer Level (RTL) DesignDokument88 SeitenDigital Design: Register-Transfer Level (RTL) DesignmasrinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Socket Programming: Connecting ProcessesDokument10 SeitenSocket Programming: Connecting ProcessesAlok GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MX TL MXMC 1-8 en 20180703Dokument142 SeitenMX TL MXMC 1-8 en 20180703aleksandar petrovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explore Langkawi's Cultural Heritage with Our Mobile AppDokument7 SeitenExplore Langkawi's Cultural Heritage with Our Mobile Appfieqaradzi0% (1)
- Ebk Incident ManagementDokument20 SeitenEbk Incident Managementswapnil_nikamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tori Tidswell: Work ExperienceDokument2 SeitenTori Tidswell: Work Experienceapi-557437673Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anna University NotesDokument92 SeitenAnna University NotesVignesh RamachandranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuzzy Keyword Search Over Encrypted Data in Cloud ComputingDokument2 SeitenFuzzy Keyword Search Over Encrypted Data in Cloud ComputingJubaira SamsudeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Software Engineer Cover LetterDokument3 SeitenSoftware Engineer Cover Letternur syahkinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teltonika FM1120 User Manual v4.2Dokument87 SeitenTeltonika FM1120 User Manual v4.2Javier PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nico Assignment SADDokument16 SeitenNico Assignment SADNicolas Lich MatuenyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1to25 MergedDokument36 Seiten1to25 Mergedreshmi.avkNoch keine Bewertungen
- IDEMIA CompanyDokument13 SeitenIDEMIA CompanyAlex JamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- M 0 NkrusDokument2 SeitenM 0 NkrusnutchaponkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily System Monitoring: SM51 SAP ServersDokument3 SeitenDaily System Monitoring: SM51 SAP ServersurpalvijayNoch keine Bewertungen