Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Neo Bladder
Hochgeladen von
believeme0305890 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
130 Ansichten32 SeitenNeobladder
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenNeobladder
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
130 Ansichten32 SeitenNeo Bladder
Hochgeladen von
believeme030589Neobladder
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 32
Urinary Diversions:
1851- Ureteroproctostomy (Simon)
1878- Ureterosigmoidostomy (Smith)
1950s- Ileal loop (Bricker)
1959- Ileal neobladder (Camay)
1970s to early 80s- Koch and Indiana
Late 80s- Orthotopic diversion
History of Diversion Surgery
What Necessitates Urinary
Diversions?
Invasive bladder cancer
Hostile neurogenic bladder
Interstitial or radiation cystitis
Congenital abnormalities
Intractable incontinence
6th most common cancer in U.S.
New cases: 73,510
Deaths: 14,880
3x more common in men
Bladder Cancer Facts
National Cancer Institute, 2012
Urostomy (ileal conduit)
Continent Cutaneous Urostomy
Orthotopic Neobladder
Urinary Diversion Options
Non-continent
Ureterostomy
Ileal Conduit
Continent
Indiana Pouch (continent cutaneous)
Orthotopic Neobladder
Non-continent vs. Continent
Surgical Selection Factors
Availability of surgeon and O.R.
Age of patient
Comorbidities
Renal function
Location of tumor
Sphincter competence
Hx of pelvic radiation
Hx of bowel disease
Surgical Selection Factors
Manual dexterity
Mental status
Weight
Patient preference
Surgical Selection Factors
Duke: 60% ileal conduits, 40% internal
continent pouches (2012)
Prevalence of Continent
Diversions
Ileal pouch in native anatomical
location
AKA
Studer diversion
Orthotopic Neobladder
Cons
Delayed continence
Urinary retention
Metabolic acidosis
Catheterize
Pros
Cosmesis
No stoma
Independently
void
Cost effective
Orthotopic Neobladder
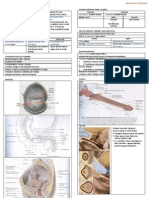
Orthotopic Neobladder Pouchogram
Symptoms: Prevention:
Fever Irrigation
Bacteriuria Fluid intake
Pouch pain
Treatment:
Antibiotics (Flagyl)
Pouchitis
Voiding
Q2hr day and Q3hr at night
Ultimately Q 4hr day & Q 8hr night
Valsalva, Cred method, sit on toilet
Measure and record output
Activation Teaching: NB
Crede Maneuver
Kaufman DS, Shipley WU, & Feldman AS. Bladder Cancer.
Lancet. 2009;374(9685):239-247.
Hautmann RE, Abol-Enein H, Hafez K, et al. Urinary diversion.
Urology . 2007; 69(suppl):1749, 2007.
Somani BK, Gimlin D, Fayers P, et.al. Quality of life and body
image for bladder cancer patients undergoing radical
cystectomy and urinary diversion. Urology. 2009; 74(5):1138-43.
Nabil G, Cody JD, Dublin N, et.al. Urinary diversion and bladder
reconstruction/replacement using intestinal segments for
intractable incontinence or following cystectomy. 2009 The
Cochrane Collaboration/JohnWiley & Sons, Ltd.
References
Gray M & Beitz JM. Counseling patients undergoing urinary
diversion: does the type of diversion influence quality of life?
JWOCN.2005. Jan-Feb;32(1):7-15.
Gemmill R et al. Going with the flow: quality of life outcomes of
cancer survivors with urinary diversion. JWOCN 2010. Jan-
Feb;37(1):65-72.
Dutta SC et al. HRQOL assessment after radical cystectomy:
comparison of IC and ON. J Urol 2002;168(1):164-167
Gerharz EW et al. QOL in patients with bladder cancer. Urol
Oncol 2005;23(3):201-207.
References
Kikuchi E et al. Assessment of Long-Term Quality of Life Using
the FACT-BL Questionnaire in Patients with an IC, CR, or ON.
JJCO2006; 36(11)712716
References
http://www.uoaa.org/ostomy_info/
http://www.uoaa.org/ostomy_info/
http://bcan.org
http://www.wocn.org
http://www.ostomysecrets.com
http://www.options-ostomy.com
http://www.trianglebcs.org
Patient Resources
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Blandy's UrologyVon EverandBlandy's UrologyOmar M. AboumarzoukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cotton and Williams' Practical Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: The FundamentalsVon EverandCotton and Williams' Practical Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: The FundamentalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Faculty of Medicine NR - Ii Department of Surgery NR - Ii: Diseases of The Biliary TractDokument40 SeitenFaculty of Medicine NR - Ii Department of Surgery NR - Ii: Diseases of The Biliary TractGalina LozovanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bladder Substitution and Urinary DiversionDokument58 SeitenBladder Substitution and Urinary DiversionlifespotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary CatheterDokument19 SeitenUrinary CatheterNur HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Anomalies of Urinary BladderDokument102 SeitenCongenital Anomalies of Urinary Bladdernancy voraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benign Prostate Hyperplasia: Div. of Urology, Dept. Surgery Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera UtaraDokument56 SeitenBenign Prostate Hyperplasia: Div. of Urology, Dept. Surgery Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera UtaraJessica PurbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- POP June 10,2021 1Dokument48 SeitenPOP June 10,2021 1Kerod AbebeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xanthogranulomatous PyelonephritisDokument14 SeitenXanthogranulomatous PyelonephritisalaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Urinary RetentionDokument26 SeitenAcute Urinary Retentionlukmankyubi100% (1)
- Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)Dokument68 SeitenAcute Kidney Injury (AKI)Alex beharuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urology Lectures: Undergraduate StudentsDokument107 SeitenUrology Lectures: Undergraduate StudentsLana Loco100% (1)
- Benign Prostatic HypertrophyDokument111 SeitenBenign Prostatic HypertrophyOnkar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suprapubic Catheter Bladder TrainingDokument17 SeitenSuprapubic Catheter Bladder TrainingOrmias PratamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HematuriaDokument15 SeitenHematurianisaw_2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Billiary SystemDokument60 SeitenBilliary SystemDONALD UNASHENoch keine Bewertungen
- Urological EmergencyDokument83 SeitenUrological EmergencyIrwan SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiology in UrologyDokument39 SeitenRadiology in UrologyUgan SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approach To Patients With Inguinoscrotal Masses: Section of Urology Department of Surgery The Medical CityDokument43 SeitenApproach To Patients With Inguinoscrotal Masses: Section of Urology Department of Surgery The Medical CityKevin Eric SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Acute and Chronic Retention in MenDokument52 SeitenManagement of Acute and Chronic Retention in MenSri HariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Total Pelvic ExenterationDokument13 SeitenTotal Pelvic ExenterationRirin Wahyuni100% (1)
- Testicular TorsionDokument12 SeitenTesticular TorsionlicutNoch keine Bewertungen
- 54.the Gallbladder and Bile DuctsDokument19 Seiten54.the Gallbladder and Bile DuctsAdenegan Adesola RaymondNoch keine Bewertungen
- HematuriaDokument51 SeitenHematuriaRam ManoharNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCNDokument3 SeitenPCNAzirah TawangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Presentation and Literature Review of Adrenal MassesDokument50 SeitenCase Presentation and Literature Review of Adrenal MassesAnas Mk HindawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pemeriksaan IVPDokument41 SeitenPemeriksaan IVPChandra Noor SatriyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uro2008, Vol.35, Issues 3, Minimally Invasive Genitourinary ProceduresDokument180 SeitenUro2008, Vol.35, Issues 3, Minimally Invasive Genitourinary ProcedureschuvanlaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HematuriaDokument31 SeitenHematuriaSiti Zainab Bani PurwanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retractile Testis PDFDokument6 SeitenRetractile Testis PDFDella Elvina RoeslandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Pyelonephritis Treatment & Management: Approach ConsiderationsDokument4 SeitenAcute Pyelonephritis Treatment & Management: Approach ConsiderationsPeter InocandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carcinoma Penis Management: Dr. Lilamani Rajthala MS Resident Moderator: Dr. Samir ShresthaDokument63 SeitenCarcinoma Penis Management: Dr. Lilamani Rajthala MS Resident Moderator: Dr. Samir ShresthaBibek GhimireNoch keine Bewertungen
- LiverDokument27 SeitenLiverAndi Arwan AgusnawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extrahepatic CholestasisDokument31 SeitenExtrahepatic CholestasismackieccNoch keine Bewertungen
- CathaterDokument34 SeitenCathaterBirhanu Ayenew100% (1)
- Pujo / UpjoDokument39 SeitenPujo / UpjoHafizur RashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Early Detection and Management Colorectal CancerDokument59 SeitenEarly Detection and Management Colorectal CancerAbduh BIKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary System: Cytology, Histology, Cystoscopy, and RadiologyVon EverandUrinary System: Cytology, Histology, Cystoscopy, and RadiologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antireflux Surgery Lich-GregoirDokument16 SeitenAntireflux Surgery Lich-GregoircristiangelsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Testicular Cancer Fact Sheet PDFDokument2 SeitenTesticular Cancer Fact Sheet PDFRandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Portal Hypertension SurgeryDokument6 SeitenPortal Hypertension SurgeryjackSNMMCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breast Cancer: Katherine Macgillivray & Melissa PoirierDokument62 SeitenBreast Cancer: Katherine Macgillivray & Melissa PoirierJonathan Darell WijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanism of MicturitionDokument4 SeitenMechanism of MicturitionGerardLum100% (2)
- Compilation Pocket Guidelines 2021Dokument525 SeitenCompilation Pocket Guidelines 2021Radu-Constantin Vrinceanu100% (1)
- PriapismDokument14 SeitenPriapismNana Virtuoso EsselNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differential Diagnosis Pain Right HypochondriumDokument35 SeitenDifferential Diagnosis Pain Right HypochondriumDrArish Mahmood100% (1)
- Current Concepts of UrethroplastyDokument226 SeitenCurrent Concepts of Urethroplastywasis0% (1)
- Omphalocele Omphalocele: Perceptor: DR. AMRAN SINAGA, SP.B AUTHOR: Ida Ayu Ratna W, S.Ked (G1A214018)Dokument17 SeitenOmphalocele Omphalocele: Perceptor: DR. AMRAN SINAGA, SP.B AUTHOR: Ida Ayu Ratna W, S.Ked (G1A214018)Rully Riyan DikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bladder Outlet Obstruction in Children PDFDokument64 SeitenBladder Outlet Obstruction in Children PDFalaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urological Emergency CasesDokument6 SeitenUrological Emergency CasesjamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2017 Bone Modifying Agents in Met BC Slides - PpsDokument14 Seiten2017 Bone Modifying Agents in Met BC Slides - Ppsthanh tinh BuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genito-Urinary Tract 37Dokument6 SeitenGenito-Urinary Tract 37Hasan A AsFourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hernia: Inguinal - Surgical Anatomy, Presentation, Treatment, ComplicationsDokument43 SeitenHernia: Inguinal - Surgical Anatomy, Presentation, Treatment, ComplicationsFobin VargheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.urinary LithiasisDokument22 Seiten1.urinary LithiasisMohamed AbduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Per Rectal Bleeding CompiledDokument33 SeitenPer Rectal Bleeding CompiledRajhmuniran Kandasamy100% (1)
- Rectal Cancer PPT 2.1Dokument131 SeitenRectal Cancer PPT 2.1Usmle GuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- UROLOGYDokument26 SeitenUROLOGYgan choon huiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProstactomyDokument18 SeitenProstactomyBharat BhushanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colonoscopy: Dr. Aries Budianto, SPB (K) BDDokument52 SeitenColonoscopy: Dr. Aries Budianto, SPB (K) BDRisal WintokoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urology OralDokument2 SeitenUrology OralCorina TeteleaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 2 ITI Consensus Report: Prosthodontics and Implant DentistryDokument9 SeitenGroup 2 ITI Consensus Report: Prosthodontics and Implant DentistryEsme ValenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Size PilotDokument5 SeitenSample Size PilotmsriramcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Nyoman - Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (NPSLE) .Dokument41 SeitenDr. Nyoman - Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (NPSLE) .hum2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar PustakaDokument2 SeitenDaftar PustakaSyaifulBahriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perioperative NursingDokument12 SeitenPerioperative Nursingtheglobalnursing100% (12)
- Life History of Dr.J.T. KentDokument13 SeitenLife History of Dr.J.T. KentPrathibha MadikiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PolycythemiaDokument22 SeitenPolycythemiaIrman DinejadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foods That Can Purify Blood Naturally - PositiveMedffDokument7 SeitenFoods That Can Purify Blood Naturally - PositiveMedfftmk1989Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Alzheimer's - Alzheimer's AssociationDokument6 SeitenWhat Is Alzheimer's - Alzheimer's AssociationRatnaPrasadNalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- IAF MD 8 2011 Application of ISO 17011 in MDQMS (ISO 13485) Issue 1 2011Dokument17 SeitenIAF MD 8 2011 Application of ISO 17011 in MDQMS (ISO 13485) Issue 1 2011carlosprieto36Noch keine Bewertungen
- Emu HusbandryDokument126 SeitenEmu HusbandrySHANMUGAPRIYAN100% (2)
- Panic StationsDokument9 SeitenPanic Stationsdaneen naqviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schistosomes Parasite in HumanDokument27 SeitenSchistosomes Parasite in HumanAnonymous HXLczq3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pembrolizumab MonographDokument8 SeitenPembrolizumab MonographpmuftiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insulin Flargine (Lantus)Dokument1 SeiteInsulin Flargine (Lantus)ENoch keine Bewertungen
- Disturbed Sleep PatternDokument2 SeitenDisturbed Sleep PatternNiel Dela Cruz86% (7)
- Speech and Language Therapies To Improve Pragmatics and Discourse Skills in Patients With SchizophreniaDokument9 SeitenSpeech and Language Therapies To Improve Pragmatics and Discourse Skills in Patients With SchizophreniaDayannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Occupational TherapyDokument50 SeitenIntroduction To Occupational TherapyDevy CaruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomimetic Dentistry: Review ArticleDokument5 SeitenBiomimetic Dentistry: Review ArticleMatias Soto ParraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neal Sal Z Testimonials OnDokument6 SeitenNeal Sal Z Testimonials OnCarlos LiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSYCHOLOGICAL EVALUATION REPORT - Movie Review - BLACK SWANDokument8 SeitenPSYCHOLOGICAL EVALUATION REPORT - Movie Review - BLACK SWANJayson TamposNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bladder Diverticulum and SepsisDokument4 SeitenBladder Diverticulum and SepsisInternational Medical PublisherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre Analytical Clot EdDokument12 SeitenPre Analytical Clot EdAnonymous w4qodCJNoch keine Bewertungen
- FlipCutter A Pin That Changes Arthroscopic Tunnel Drilling Forever...Dokument12 SeitenFlipCutter A Pin That Changes Arthroscopic Tunnel Drilling Forever...andrelbportoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Freud - Fetishism (1927e)Dokument6 SeitenFreud - Fetishism (1927e)I Smith100% (1)
- Narcotics PreventionDokument3 SeitenNarcotics PreventionAnonymous y6SCMnNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXSA - Gold Award Recipients 2009Dokument1 SeiteEXSA - Gold Award Recipients 2009applebarrelNoch keine Bewertungen
- GowthamiDokument35 SeitenGowthamiDR VENKATARAMANA MurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Partial MastectomyDokument17 SeitenPartial MastectomyJill Rae Lloren ConsolacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Batiquin v. Court of AppealsDokument9 SeitenBatiquin v. Court of AppealsEnzo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen