Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Holland Presentation
Hochgeladen von
frankling91Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Holland Presentation
Hochgeladen von
frankling91Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
THE NETHERLANDS
YOUR
GATEWAY TO EUROPE!
Outline
INTRODUCING
THE NETHERLANDS:
-Ideal geographical location
- Parliamentary democracy and constitutional monarchy
- Population
- Currency
- Area
- The Netherlands
- The United States
- Companies
NL
France
Germany
UK
Spain
Benefits of the Netherlands :
1. Cost Factors
2. Qualitative Factors
THE NETHERLANDS:
THE PERSONAL GATEWAY TO EUROPE
1.Cost Factors
A. Transportation costs
B. Facility costs
C. Labor costs
D. Taxation
AFFORDABILITY OF INTERNATIONAL SHIPMENTS
Source: World Bank, Connecting to Compete, 2007
Very Bad
Ease and affordability of arranging shipments
($)
Typical charge for a 40-foot export container or a semi-trailer (total cost to
transport and port services) based upon the Logistics Performance Survey
Very Good
1.A Transportation costs
Source: KPMG, Competitive Alternatives, 2008 Edition
Country*
Continental Intercontinental
Total annual
cost
(in US $)
Rank
Road freight
(per truck)
Sea freight
(per
container)
Air freight
(per kg)
Italy $1,485 $2,848 $2.70 $891 7
Netherlands $539 $2,364 $2.66 $424 1
The table above illustrates representative transportation costs for manufacturing operations, based on reasonable distribution pattern assumptions for each operation. These results
should be interpreted only as general indicators of transportation-cost relationships among countries, since they are based on typical product-distribution patterns for each operation
within each country. Operations with different product-distribution patterns may expect to have significantly different transportation costs.
* The five countries in this table were the only European countries included in the report
TRANSPORTATION COSTS
REAL ESTATE COSTS
1.B Facility costs
Source: Jones Lang LaSalle, Q3 2008
Warehouse costs /m2
$65
$60
1
5
25
125
Rotterdam Milan
COSTS OF STARTING BUSINESS CENTERS IN EUROPE
Monthly Cost in $ US per Workstation
LABOUR COSTS
$38,600.00
$38,800.00
$39,000.00
$39,200.00
$39,400.00
$39,600.00
$39,800.00
$40,000.00
Netherlands Italy
$39,118.00
$39,909.00
Para-professional (Staff) position salary
Source: Mercer employment costs 2008
Source: Mercer employment costs 2008
$1.00
$5.00
$25.00
$125.00
$625.00
$3,125.00
$15,625.00
$78,125.00
$390,625.00
Netherlands Italy
$103,143.00 $97,264.00
Management positions
EMPLOYMENT COSTS
100
66.4
92.6
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
New York Milan Amsterdam
MAIN TAX ADVANTAGES OF THE NETHERLANDS
Advanced Tax Rulings
The Participation Exemption
The 30% Ruling
1.D Taxation
CORPORATE TAX RATES IN EUROPE
33%
25.5%
0%
5%
10%
15%
20%
25%
30%
35%
Italy Netherlands
2.Qualitative Factors
A. Proximity to Customers
B. Infrastructure/LPI
C. Customs
D. Labor Quality
PROXIMITY TO CUSTOMERS
Germany, France and the United Kingdom.
Easily serve all major European markets with
minimum effort.
325 miles between Amsterdam and Paris, and
only 419 to Berlin..
Countries with GDP > $2 trillion
Countries with GDP $1 2 trillion
Countries with GDP < $1 trillion
Source: IMD, 2007
France
Germany
UK
NL
2 .A Proximity to
customers
170 Million Customers
within 300 Miles
244 Million Customers
within 600 Miles
PROXIMITY TO CUSTOMERS
Europe (60% of world trade).
INFRASTRUCTURE IN THE NETHERLANDS
Outstanding location.
Flat countryside and good river connections.
Maintained roads, railways, inland waterways,
airports and seaports.
(1) Port of Rotterdam
(2)Port of Amsterdam
(3)Amsterdam Airport Schiphol.
2.B Infrastructure
Express Road
24 Hours 48 Hours
24 Hours 72 Hours
24 Hours 96 Hours
24 Hours 120 Hours
48 Hours 144 Hours
Source: TMI Integrated Logistics; NDL/HIDC, 2007
TRANSPORTATION LEAD TIMES
Rest of Europe
16%
Netherlands
19%
France
14%
UK
17%
Germany
12%
Spain
5%
Belgium
11%
Italy
6%
Total Distribution center surface area per
country
Total Distribution Center Surface area per country
Two thirds of the total surface area of distribution centers in Europe.
Source: Cap Gemini 2007 report Europes most wanted Distribution Center Locations
Life Sciences and Pharmaceutical industry.
The Netherlands: 15% share.
Rest of Europe
43%
Netherlands
15%
France
6%
UK
6%
switzerland
9%
Spain
9%
Belgium
6%
Italy
6%
Share of Life Sciences and Pharmaceutical centers per
country
Source: Cap Gemini 2007. Europes most wanted distribution center Locations
Share of Pharmaceutical Distribution Centers per country
The Port of Rotterdam is one of the most important cargo junctions in the world
and it is Europes largest. 30,000 ships from all over the world arrive each year at
the port. The port relies on state-of-the-art technology to maintain a steady and
reliable distribution network.
Source: Port of Rotterdam, 2008
The strategic location within Europe, the open and fast connection with the
sea, the very deep access channel and the perfect hinterland connections:
these the main strengths of the port of Rotterdam.
PORT OF ROTTERDAM
Arrival
Departure
Rotterdam (NL) Felixstowe (UK) Antwerp (BE) LeHavre (FR) Hamburg (DE)
Yokahoma (Japan) - 8 18 - -
Singapore 44 - 6 9 12
Shanghai (China) 32 - 18 - 3
Kaohsiung (Korea) 14 - 19 1 -
Hong Kong (China) 36 5 21 6 -
Total 126 13 82 16 15
Overview First Port of Call
Time and time again, Amsterdam Airport Schiphol has been voted the best airport by
business travelers.
Fourth largest airport in Europe in terms of passengers; third largest in terms of cargo.
261 direct connections to 89 countries
Daily non-stop flights to Los Angeles
51 flights to London and 16 flights to Paris daily
Worlds Busiest Airports by International
Passenger Traffic
PASSENGER TRANSIT IN EUROPE
Source: Airports Council International, July 2007
Rank City Passengers in Millions
3 Amsterdam 45.9
20 Milan 18.7
QUALITY OF INFRASTRUCTURE
Source: World Bank, Connecting to Compete, 2007
CUSTOMS AUTHORITIES
Source: Opinion Survey IMD, 2007
2.C Customs
4.29
3.25
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
3.5
4
4.5
5
Netherlands (1) Italy (23)
Quality of Transport and IT infrastructure for
Logistics
(on a scale of 1-5)
7.72
5.53
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Netherlands Italy
Customs' authorities do facilitate the efficient transit of
goods
The most important long-term asset of any business is the
quality of its personnel. With its high-quality labor market,
the Netherlands meets this requirement of international
companies perhaps better than any other European
country. The Netherlands offers employers flexibility and
excellent working attitudes.
Since the early 1980s, growth in wage costs in the
Netherlands has been kept to moderate levels through
successful policies of wage restraint and productivity
improvements. Good labor relations and an efficient
regulatory framework allow the private sector to reap the
maximum benefits the Dutch labor force has to offer.
Source: IMD World Competitiveness 2008
LABOR QUALITY
Source: IMD World Competitiveness 2008
2.D Labor Quality
6.5
6.73
6.3
6.4
6.5
6.6
6.7
6.8
Italy Netherlands
Flexibilty and Adaptability of Employees
(Scale 1-10)
4.83
7.1
0 2 4 6 8
Italy
Netherlands
Productivity of Companies
(Scale 1-10)
Source: IMD World Competitiveness 2008.
MULTILINGUALISM & MOTIVATION
The Netherlands is one of the most multilingual countries in
Europe. Education and multilingualism generally have a
downward effect on labor costs. The Dutch are among the highest
skilled, service-oriented and remarkably productive workers in
the world, with a high degree of responsibility. The
multilingualism of the Dutch labor force is an important reason
for many American companies to set-up operations in the
Netherlands. Most of the Dutch speak English and many speak
German and/or French.
Source: IMD World Competitiveness 2008
8.12
3.83
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Netherlands Italy
Language Skills
Meeting the needs of Enterprises
6.71
4.94
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Netherlands
Italy
Workers Motivation 2008
EUROPEAN DISTRIBUTION CENTERS
MANUFACTURING AND ASSEMBLY
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- ISTAR Facilities (5e) PDFDokument12 SeitenISTAR Facilities (5e) PDFfrankling91Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- How Not To Host A Murder (5e)Dokument12 SeitenHow Not To Host A Murder (5e)Delfidus100% (2)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Dungeon Magazine Annual 2010Dokument161 SeitenDungeon Magazine Annual 2010frankling91100% (2)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- European Debt CrisisDokument12 SeitenEuropean Debt Crisisfrankling91Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Airline Alliance Legal WorkDokument46 SeitenAirline Alliance Legal WorksidjboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- American CompaniesDokument2 SeitenAmerican Companiesdouble_ell12205Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Case 1 Schipol International HubDokument2 SeitenCase 1 Schipol International HubibmayosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Schiphol International Hub Case StudyDokument4 SeitenSchiphol International Hub Case StudyDavid Adeabah Osafo100% (2)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- FWD Regarding Your Request C6130325Dokument2 SeitenFWD Regarding Your Request C6130325JoNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- 14-02-2022, WJVD6R Rio Prastiawan (CGK-PBM)Dokument5 Seiten14-02-2022, WJVD6R Rio Prastiawan (CGK-PBM)Rio PrastiawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accident Prevention: Crew Fails To Compute Crosswind Component, Boeing 757 Nosewheel Collapses On LandingDokument8 SeitenAccident Prevention: Crew Fails To Compute Crosswind Component, Boeing 757 Nosewheel Collapses On LandingRohit ChekuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Ehamlfpg PDF 1699181778Dokument38 SeitenEhamlfpg PDF 1699181778Namy NamygoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
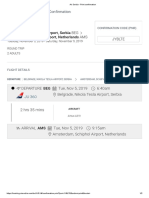
- Air Serbia - Print Confirmation2Dokument2 SeitenAir Serbia - Print Confirmation2VojislavNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Baggage at Schiphol ENGDokument4 SeitenBaggage at Schiphol ENGAsemMashrapovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPL Arrivals Plaza GuideDokument1 SeiteSPL Arrivals Plaza GuideSnežana PantelićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Fatigue and Fracture in An Aircraft Engine PylonDokument15 SeitenFatigue and Fracture in An Aircraft Engine PylonOSCARDELTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Emirates Ticket 1Dokument4 SeitenEmirates Ticket 1imigrasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESOL Literacies - TravelDokument87 SeitenESOL Literacies - TravelDebbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- WP Schipol Tesis 4411560 REPORTDokument308 SeitenWP Schipol Tesis 4411560 REPORTYugo PhurbojoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Gmail - Your Air France Booking Is Pending PaymentDokument9 SeitenGmail - Your Air France Booking Is Pending Paymentshawn alexNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Trip - CGK - AMSDokument2 SeitenMy Trip - CGK - AMSJefri PratamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- MR Petrov PDFDokument2 SeitenMR Petrov PDFMariusBelecciuNoch keine Bewertungen
- KLM 2020Dokument214 SeitenKLM 2020Fendy FendersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument23 SeitenUntitledapi-108818349Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ehamdgaa PDF 1705878197Dokument50 SeitenEhamdgaa PDF 1705878197chrisdantusevoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boarding Pass: Bucharest Amsterdam KL 1372Dokument4 SeitenBoarding Pass: Bucharest Amsterdam KL 1372Ana IordanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Airports 11 Nwe FDokument10 SeitenAirports 11 Nwe FMeedenken en Doen BV0% (1)
- Airport SchipolDokument12 SeitenAirport Schipolteuku riza syahrialNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Rotterdam Manual Travel Trade (English)Dokument85 SeitenRotterdam Manual Travel Trade (English)Rotterdam PartnersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limjeddv PDF 1678478447Dokument48 SeitenLimjeddv PDF 1678478447BarbarosTVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Starting Out in XPlaneDokument14 SeitenStarting Out in XPlaneGuo W. JackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Programming Interfaces PDFDokument3 SeitenApplication Programming Interfaces PDFLUIS GIRALDONoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study 7 Performance AppraisalDokument7 SeitenCase Study 7 Performance Appraisalsaba gul rehmatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Airport Cities - The Evolution-1Dokument17 SeitenAirport Cities - The Evolution-1IswatunHasanahSyatiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)