Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Uric Acid
Hochgeladen von
Sintong SianturiOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Uric Acid
Hochgeladen von
Sintong SianturiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
GOUT AND URIC ACID
METABOLISM
Definition of Gout
Inflammatory arthritis induced by microscopic
crystals of monosodium urate monohydrate
(MSU) and to pathognomic deposition of
aggregated MSU crystals (tophi) in various
tissues and some organs
Chronic hyperuricemia
Urolithiasis
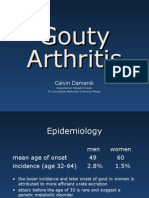
INCIDENCE
0,5-0,7% on men > 0,1% on woman
Serum urate values increase with age
HYPERURICEMIA
MEN : > 5,1 mg/dl
Woman : > 4,0 mg/dl
Uric acid
10-59 years 2,5-9,0 mg/dl
Female 2,0-8,0 mg/dl
ETIOLOGI
PRIMER
- langsung pembentukan asam urat (alkohol,
obesitas, diet tinggi purin) atau penurunan
ekskresinya dalam tubuh (gagal ginjal,
diuretik).
SEKUNDER
- pembentukan asam urat yang berlebih atau
penurunan ekskresi asam urat yang berkurang
akibat proses penyakit lain/ pemakaian obat
tertentu
URIC ACID PRODUCTION AND
ELIMINATION
Glomerular filtration
- Complete
- by diuretics, renal diuretics
Tubular reabsorption
- Active, linked to Na reabsorption
- Inhibited by uricosuric drugs: probenecid, Sulfinpyrazone,
benzobromarone, high dose aspirin
Tubular secretion
- Active process
- Inhibited by agents that cause hyperuricemia: pirazinamid, low dose
aspirin, B-hydroxybutyrate, branched-chain ketoasidosis
Postsecretory reabsorbtion
Tubular
reabsorption
98-100
Glomerular
filtration
100
Tubular
secretion
50
Postscretory
reabsorption
40-44 6-10
x.o
x.o
BIOSYNTHETIC PATHAWAYS
De novo
Salvage
Tahap Perjalanan Klinis
Hiperurisemia asimtomatik
- terjadi peningkatan asam urat serum
- tidak ada gejala yg timbul
Artritis gout akut
- pembengkakan dan nyeri mendadak
- tanda peradangan lokal
- demam dan peningkatan leukosit
Tahap interkritis
- tidak ada gejala pada masa ini
- serangan berulang pada waktu kurang dari 1 tahun
(jk tidak diobati)
Tahap gout kronik
- peradangan kronik nyeri, sakit, kaku, penonjolan
dan pembesaran sendi
- terbentuk tofi (bursa olekranon, tendon achilles,
heliks telinga)
Tubular
reabsorption
98-100
Glomerular
filtration
100
Tubular
secretion
50
Postscretory
reabsorption
40-44 6-10
Penurunan
krn diuretik,
Gagal ginjal
Diinhibisi oleh
uricosuric drugs
(probenecid,
sulfinpyrazone,
benzobromarone,
high dose aspirin)
Inhibited by agents that cause
hyperuricemia: pirazinamid, low
dose aspirin, B-hydroxybutyrate,
branched-chain ketoasidosis
x.o
x.o
ACUTE GOUT INTERVAL GOUT LONG TERM
Therapeutic goal:
terminate acute
inflammatory attack
Therapeutic goal:
Prevent recurent attacks
Therapeutic goal:
Prevent attacks; resolve
tophi; maintain serum
urate at < 6mg/dl
NSAIDS Colchicine oral Colchicine oral
Colchicine oral Start hypouricemic agent if
indicated by frequent
attacks, severe
hyperuricemia, presence of
tophi, urolithiasis, or urate
overexcretion
Allopurinol
Colchicine IV Uricosuric agent
Steroids High fluid intake to
promote uric acid excretion
in a dilute urine. Diet-
moderate protein, low fat;
avoid excessive alcohol
High fluid intake,
particularly at night, to
promote uric acid excretion
in a dilute urine. Diet-
moderate protein, low fat;
avoid excessive alcohol
Hypouricemic agents Acetazolamide 250 mg at
bedtime (may be used to
keep urine pH > 6)
TERIMA KASIH
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Acute Renal Failure SymptomsDokument10 SeitenAcute Renal Failure SymptomsEdwin Delos Reyes AbuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Perfect Pancreatitis Diet Cookbook; The Complete Nutrition Guide To Managing And Healing Pancreatitis With Delectable And Nourishing Recipes;Von EverandThe Perfect Pancreatitis Diet Cookbook; The Complete Nutrition Guide To Managing And Healing Pancreatitis With Delectable And Nourishing Recipes;Noch keine Bewertungen
- NSAIDs for Acute Gout AttacksDokument26 SeitenNSAIDs for Acute Gout AttacksReny Rony BersaudaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 6 NotesDokument17 SeitenExam 6 NotesWhitney WilliamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gouthy Arthritis: Lita Diah Rheumatology, Internal Med. Dr. Soetomo Hospital Airlangga Med SchoolDokument73 SeitenGouthy Arthritis: Lita Diah Rheumatology, Internal Med. Dr. Soetomo Hospital Airlangga Med SchoolMuhammad DaviqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gout Edited by MeDokument52 SeitenGout Edited by MeHikma PrajawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal MedsurgDokument14 SeitenRenal MedsurgCliff Lois ╭∩╮⎷⎛⎝⎲⏝⏝⎲⎠⎷⎛╭∩╮ Ouano100% (1)
- GoutDokument32 SeitenGoutChristin Feliana Sitanggang100% (4)
- CPG: Management of GoutDokument25 SeitenCPG: Management of Goutadi_asrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 3 Renal DisorderDokument74 SeitenWeek 3 Renal DisorderManal jNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manage Chronic Kidney Injury in ChildrenDokument29 SeitenManage Chronic Kidney Injury in ChildrenPriya GKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pancreas and SpleenDokument106 SeitenPancreas and SpleenJorge De Vera100% (1)
- Acute PancreatitisDokument36 SeitenAcute PancreatitisURo KkuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8013 7 Obat Hiperuricemia - PPTX WWWDokument31 Seiten8013 7 Obat Hiperuricemia - PPTX WWWKaroniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urine Analysis FinalDokument112 SeitenUrine Analysis FinalNischita JayarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing & Managing Urinary Tract DisordersDokument5 SeitenAssessing & Managing Urinary Tract DisordersAlyssa Nicole CajayonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal NursingDokument11 SeitenRenal NursingFreeNursingNotes100% (10)
- 5 - Drugs Used For Treatment of Gout EditedDokument35 Seiten5 - Drugs Used For Treatment of Gout EditedSakariye hasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arif K S Presentation Final 2Dokument94 SeitenArif K S Presentation Final 2Rajan BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyper Ure Semi ADokument44 SeitenHyper Ure Semi Abagusputrabali13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biliary&Pancreas DisordersDokument34 SeitenBiliary&Pancreas DisordersLarry De LaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peptic Ulcer Disease: by Aniedu, UgochukwuDokument32 SeitenPeptic Ulcer Disease: by Aniedu, UgochukwuManish Sapkota100% (1)
- Week3 PancreasDokument74 SeitenWeek3 PancreasriverabeanicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Askep PankreatitisDokument48 SeitenAskep PankreatitisYeni DwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Uric Acid: Biochemistry, Physiology, and Clinical SignificanceDokument28 SeitenUnderstanding Uric Acid: Biochemistry, Physiology, and Clinical SignificanceAya100% (1)
- Uric Acid UnderexcreterDokument1 SeiteUric Acid UnderexcretermcwnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- GoutDokument26 SeitenGoutRifki AlfikriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrointestinal and HepatobiliaryDokument54 SeitenGastrointestinal and Hepatobiliaryjeshema100% (1)
- Renal CalculiDokument5 SeitenRenal CalculiRufus Raj100% (1)
- Urinary Tract Infection Clinical Case by SlidesgoDokument23 SeitenUrinary Tract Infection Clinical Case by Slidesgomichel britoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis: by Adrija Ghosal Intern of Malda Medical College and HospitalDokument30 SeitenInfantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis: by Adrija Ghosal Intern of Malda Medical College and HospitalApurvdeep SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Disorders 1Dokument73 SeitenRenal Disorders 1Kyla PamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANTI-GOUT DRUGS New11Dokument31 SeitenANTI-GOUT DRUGS New11Ghina RizwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NASRUHAN ARIFIANTO, S.Farm., M.Farm - Klin., Apt. Stifar Sunan Giri - PonorogoDokument50 SeitenNASRUHAN ARIFIANTO, S.Farm., M.Farm - Klin., Apt. Stifar Sunan Giri - Ponorogoandyra betanamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agents Used To Treat Hyperuricemia and GoutDokument19 SeitenAgents Used To Treat Hyperuricemia and GoutQuolette Constante100% (1)
- Acute Pancreatitis: Presenter:Luqman Arif Bin Ahmad Hazri Supervisor: DR DarrenDokument25 SeitenAcute Pancreatitis: Presenter:Luqman Arif Bin Ahmad Hazri Supervisor: DR DarrenLuqman Arif Ahmad HazriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs For Gout 2020Dokument49 SeitenDrugs For Gout 2020Mohammad EnnabNoch keine Bewertungen
- C5. Renal Disorders FileDokument38 SeitenC5. Renal Disorders Filecoco brillqnteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute PancreatitisDokument31 SeitenAcute PancreatitisAmoroso, Marian Corneth D.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Share GENITO-URINARYDokument69 SeitenShare GENITO-URINARYRomer RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCMB 316 Cu11 Liver, Pancreas, & GallbladderDokument74 SeitenNCMB 316 Cu11 Liver, Pancreas, & GallbladderJanine Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPC Edit RMDokument39 SeitenCPC Edit RMSoumya GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pancreatitis: Dr. Dr. Shahrul Rahman, SP - PD, FINASIMDokument64 SeitenPancreatitis: Dr. Dr. Shahrul Rahman, SP - PD, FINASIMAqilah HanifahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding 2007Dokument43 SeitenUpper Gastrointestinal Bleeding 2007Matthew ThompsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacotherapy of DiarhheaDokument29 SeitenPharmacotherapy of DiarhheaFahril LabuduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sesión GotaDokument37 SeitenSesión GotaMapi GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4 - Spasmodic Colic HorseDokument20 SeitenLecture 4 - Spasmodic Colic HorseUNICORN TIMENoch keine Bewertungen
- Gis156 Slide Prolaps RektumDokument24 SeitenGis156 Slide Prolaps RektumRahadiyan HadinataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Bile DuctDokument28 SeitenCommon Bile DuctAmanda ScarletNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Renal FailureDokument30 SeitenAcute Renal FailureJerinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosis and Management of GoutDokument43 SeitenDiagnosis and Management of GoutrrcalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pancreatitis: Causes, Symptoms, and TreatmentDokument5 SeitenPancreatitis: Causes, Symptoms, and TreatmentSanthu Su100% (2)
- Renal FailureDokument48 SeitenRenal FailureCindy MamalangkasNoch keine Bewertungen
- NephrolithiasisDokument2 SeitenNephrolithiasisMichalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEPHROSISDokument31 SeitenNEPHROSISvinnu kalyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GOUT AND PSEUDOGOUT: CRYSTAL-ASSOCIATED ARTHRITISDokument56 SeitenGOUT AND PSEUDOGOUT: CRYSTAL-ASSOCIATED ARTHRITISSindhu BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Pancreati-Wps Office 100Dokument45 SeitenAcute Pancreati-Wps Office 100Mariam AntonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Gout and Hyperuricemia: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentDokument23 SeitenUnderstanding Gout and Hyperuricemia: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatmentعلي الطياريNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prof. Dr. W. H. Sibuea, SPPD.: Clinic Medical Science, FK Uki 30 September 2013Dokument53 SeitenProf. Dr. W. H. Sibuea, SPPD.: Clinic Medical Science, FK Uki 30 September 2013Sintong SianturiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TerryDokument1 SeiteTerrySintong SianturiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolisme Batu EmpeduDokument17 SeitenMetabolisme Batu EmpeduSintong SianturiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart Drugs Best Taken at Bed Time - MEDICAL TRIBUNE JULY 2011Dokument1 SeiteHeart Drugs Best Taken at Bed Time - MEDICAL TRIBUNE JULY 2011Sintong SianturiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE Scenario Editor ManualDokument34 SeitenEE Scenario Editor ManualViviane Maria Dos SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- TerryDokument1 SeiteTerrySintong SianturiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TerryDokument1 SeiteTerrySintong SianturiNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Hirschsprung DiseaseDokument19 SeitenWhat Is Hirschsprung DiseaseSintong SianturiNoch keine Bewertungen
- It Is Well With My Soul LyricDokument1 SeiteIt Is Well With My Soul LyricSintong SianturiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gout Diet Foods To Avoid and Low-Purine Foods To Eat InsteadDokument1 SeiteGout Diet Foods To Avoid and Low-Purine Foods To Eat InsteadDesiree Jolly Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- FLEBUXOSTATDokument12 SeitenFLEBUXOSTATdemrik13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ebook Effective Human Relations Interpersonal and Organizational Applications 12Th Edition Reece Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDokument28 SeitenEbook Effective Human Relations Interpersonal and Organizational Applications 12Th Edition Reece Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFgloriaazurah8ki100% (10)
- Foods ranked by purine contentDokument7 SeitenFoods ranked by purine contentShamim RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adult Medical SOAP NoteDokument4 SeitenAdult Medical SOAP NoteBhanu100% (6)
- Febuxostat lowers uric acid for goutDokument2 SeitenFebuxostat lowers uric acid for goutJoshua Pascasio100% (1)
- Gout DietDokument2 SeitenGout DietMarina Tomasenco - Danici100% (1)
- COAP Forum CollectionDokument6 SeitenCOAP Forum Collectionprashmanic100% (1)
- Fibromyalgia & Candida - Part 1Dokument66 SeitenFibromyalgia & Candida - Part 1Carol MarkusNoch keine Bewertungen
- VLD 411Dokument66 SeitenVLD 411बनकर परिवाराचा लाडका गोट्याNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enfoque Inicial en ReumatologíaDokument33 SeitenEnfoque Inicial en ReumatologíaLuis Alberto Romero JaimesNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSF & Body FluidDokument42 SeitenCSF & Body FluidlopaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Mnemonics Batch 2Dokument84 SeitenMedical Mnemonics Batch 2Laura L-RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Veramita Augusta Arisandy&Team - EDAWA - Full PaperDokument6 SeitenVeramita Augusta Arisandy&Team - EDAWA - Full PaperveramitaugustaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foods To Aid The Kidneys To Eliminate Uric AcidDokument25 SeitenFoods To Aid The Kidneys To Eliminate Uric AcidSabbra CadabraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 440 - Med Surg HESI 2Dokument8 Seiten440 - Med Surg HESI 2Chalcey Polson87% (15)
- Natural Ways to Reduce Uric Acid: Limit Purines, Add BroccoliDokument17 SeitenNatural Ways to Reduce Uric Acid: Limit Purines, Add Broccoliaj dancel marcosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacotherapy of Gout and HyperuricemiaDokument40 SeitenPharmacotherapy of Gout and HyperuricemiaJambo BuneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vikash Homeo Research Compile Book For Homeopath To Promote Homeopath For AllDokument1.384 SeitenVikash Homeo Research Compile Book For Homeopath To Promote Homeopath For AllvijaykakraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rheum PPT 2018Dokument58 SeitenRheum PPT 2018Verónica Duménez JofréNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acidul uric: producere, eliminare, hipo si hiperuricemiiDokument8 SeitenAcidul uric: producere, eliminare, hipo si hiperuricemiiStud2345Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case Report of Acute and Chronic Interstitial NephritisDokument10 SeitenCase Report of Acute and Chronic Interstitial NephritisDoncyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aratiles Chap 1 3Dokument34 SeitenAratiles Chap 1 3Gilbert75% (12)
- Journal Homepage: - : Manuscript HistoryDokument12 SeitenJournal Homepage: - : Manuscript HistoryIJAR JOURNALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mastering Medical Terminology Australia and New Zealand Walker 9780729541114Dokument39 SeitenMastering Medical Terminology Australia and New Zealand Walker 9780729541114joyturualloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Solving in LogyDokument293 SeitenProblem Solving in Logyveravero100% (2)
- Asam UratDokument43 SeitenAsam UratIhsan AndanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homeopathic ProjectDokument71 SeitenHomeopathic ProjectAtit Sheth100% (2)
- cp201007 Spotlight Febuxostat-261Dokument2 Seitencp201007 Spotlight Febuxostat-261Rafaeyza Al KarimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orthopedic Study Guide 2018Dokument9 SeitenOrthopedic Study Guide 2018Alif AllahNoch keine Bewertungen